mod 11 - respiratory system
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
39 Terms
structure: upper respiratory tract
- Nares
- Nasal passages
- Pharynx
- Larynx
- Trachea
- All the air that enters the respiratory system must enter and exit the upper respiratory tract.
the nasal passages functions to:
warm air, humidify air, and filter (Cilia, mucus)
the sinuses:
they are the outpouching of the nasal passages that can be found within spaces in certain skull bones
Pharynx is also known as
throat
pharynx
common passageway for respiratory and digestive systems
larynx
- connects with the trachea
- supported by hyoid bone
- composed of cartilage segments
trachea
short, wide tube (fibrous tissue and smooth muscle held open by cartilage rings)
extends from larynx into thorax where it divides (bifurcation of the trachea)
the structure of the trachea
- C-shaped cartilage rings spaced along length of trachea prevent collapse during inhalation
- Ciliated lining
- Mucous layer
structures of the lower respiratory tract
the bronchial tree
- bronchi
- bronchioles
- alveolar ducts
- alveoli
the bronchial tree connects __________
the trachea to the lungs
autonomic nervous system: bronchial tree
controls diameter of tubes by adjusting muscle fibers in their walls
- bronchodilation
- bronchoconstriction
alveoli
tiny sacs around capillaries,
- oxygen and carbon dioxide exchange takes place in the alveoli
lungs structure
- cone-like shape
- light, spongy consistency
diaphragm
- Thin sheet of skeletal muscle
- Forms caudal boundary of thorax
- Acts as respiratory muscle
- bases of lungs lie directly on its cranial surface
function: respiratory system
respiration,
voice production,
body temperature regulation,
acid-base regulation,
sense of smell
respiration
the process of bringing oxygen to all body cells
and carrying carbon dioxide out of the body
voice production
pharynx
body temperature regulation:
- Panting can lower body temperature
- Nasal passages warms inhaled air. Thus, preventing hypothermia
acid-base regulation
by influencing the amount of CO2 in the blood
what does more CO2 run the blood mean?
acidic = pH is low
what does less CO2 run the blood mean?
basic or alkaline = pH is high
sense of smell
the nasal passage epithelial contain olfactory receptors
negative intrathoracic pressure
The pressure within the Thorax is less than the atmospheric pressure. (Negative Pressure).
if negative pressure is lost what would happen?
lungs would collapse
negative pressure pulls lungs _____
tightly against thoracic wall
where does gas exchange occur?
in the lungs (alveoli)
inhaled air:
high in oxygen and low in carbon dioxide
blood entering capillary:
low O2, high CO2
alveolar gas exchange occurs by
diffusion
explain gas exchange
- high level of O2 in air diffuses into blood where O2 level is lower
- high level of CO2 in blood diffuses into air where level is lower
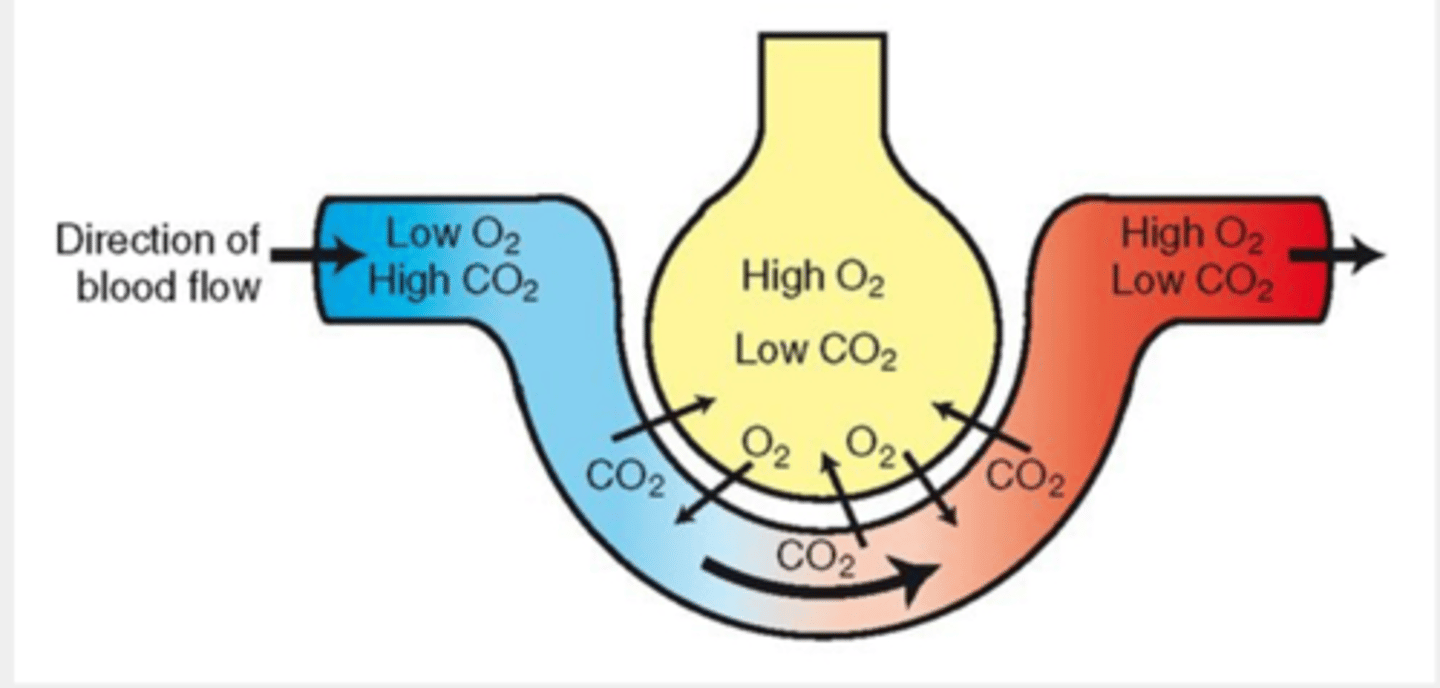
exhaled air
Higher CO2, lower O2
acid-base balance
- Important homeostatic mechanism of the body
- Necessary for normal chemical reactions in cells
- respiratory system influences amount of CO2 in blood by the rate breathing
the more CO2, the lower ______
the blood pH
what is the normal pH of blood?
7.4 (range 7.35-7.45)
what are the standardized terms for describing quantity of air involved in respiration?
- tidal volume
- minute volume
- residual volume
are respiratory volumes important?
yes! very important during surgery
tidal volume
The volume of air inspired and expired during one breath.
minute volume
The volume of air inspired and expired during on minute
residual volume
The volume of air remaining in the lungs after maximum expiration