Week 2 Complete
5.0(1)
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/43
Earn XP
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
44 Terms
1
New cards
crime
a socially constructed concept defining certain behaviours as requiring ==formal== control and social intervention
\
latin: accusation
\
defined socially, culturally, and/or legally as wrong or anti-social
\
normative concept
\
Canada: federal legislation codified in the criminal code
\
latin: accusation
\
defined socially, culturally, and/or legally as wrong or anti-social
\
normative concept
\
Canada: federal legislation codified in the criminal code
2
New cards
Misdemeanor
==less serious OFFENCES== (public drunkness)
* often constitutes house arrest, community service, provincial prison (less than two years), and/or suspension
* you will have a criminal record
\
==summary offences==
* often constitutes house arrest, community service, provincial prison (less than two years), and/or suspension
* you will have a criminal record
\
==summary offences==
3
New cards
Felony
a ==serious CRIME== (such as murder or arson)
* means the charge you go to the trial (may be a jury or judge); if you are convicted you go to federal prison (the sentence is more than two years)
* fairly rare occurrence as most crimes are not this serious
\
==indictable offences==
* means the charge you go to the trial (may be a jury or judge); if you are convicted you go to federal prison (the sentence is more than two years)
* fairly rare occurrence as most crimes are not this serious
\
==indictable offences==
4
New cards
Offence
specific infraction of the law
5
New cards
indictable offence
a serious offence such as assault, theft over $5,000, robbery (with or without a firearm), or murder
6
New cards
summary offence
a less serious offence such as theft under $5,000, impersonating a police officer, or taking a motor vehicle without consent
7
New cards
conventional crimes
illegal activity committed by individuals or small groups, involving some degree of direct or indirect contact (e.g., robbery, motor vehicle theft, and break and enter)
8
New cards
non-conventional crime
explains that crime cannot be readily explained by customary references to the personality of the offender, it may be more difficult for the criminal justice system to pursue
9
New cards
deviance
behaviour that violates a social or moral norm but is not necessarily prohibited by law (e.g., butting in line at a supermarket or certain sexual practices)
10
New cards
decriminalization
the reduction or removal of criminal penalties attached to an act without legalizing it
11
New cards
relative
when applied to crime, the idea that what is defined as crime can vary with time and location
12
New cards
evolutive
when applied to crime, the idea that what comprises crime can change, taking different forms and meaning over time
13
New cards
Hagan's Pyramid: Consensus versus Conflict
How definitions change over time and forces behind such changes
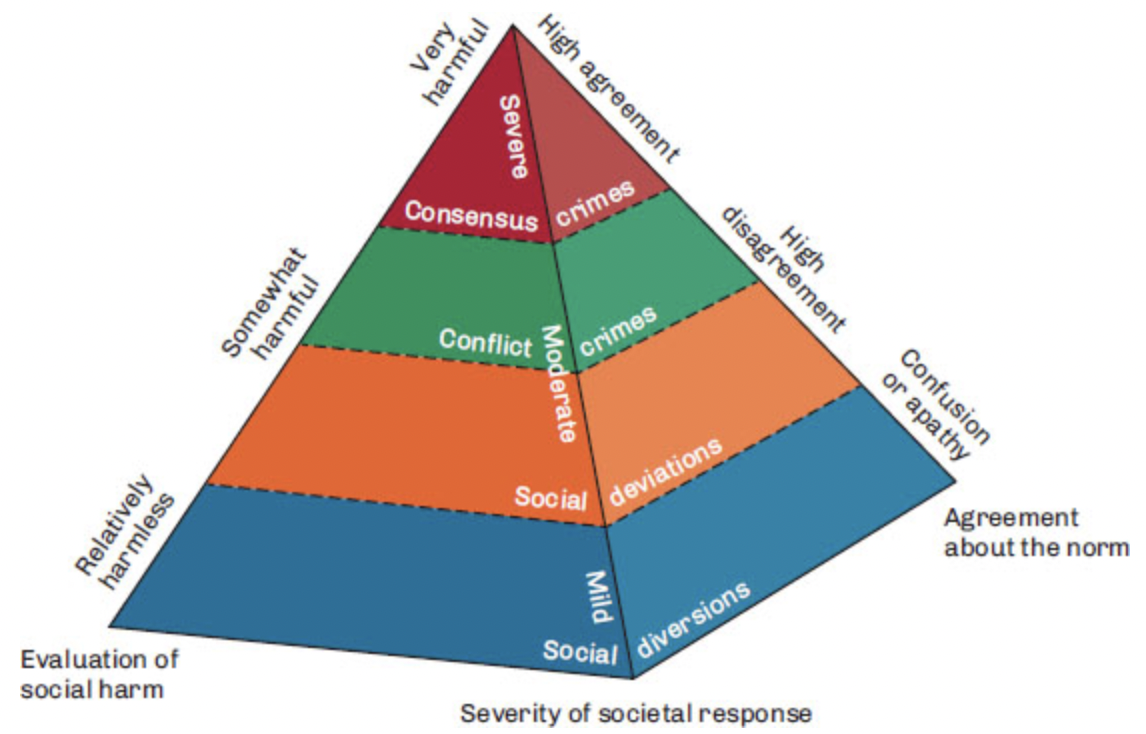
14
New cards
social diversions
minor forms of deviance such as unconventional dress or use of offensive language
15
New cards
social deviations
consists of behaviours considered disreputable in certain social settings and thus regulated: for example, swearing at a police officer or in court
16
New cards
conflict crimes
activities that are not universally considered crimes, although they are legally defined as such (e.g., procuring the services of a sex worker)
17
New cards
consensus crimes
activities generally considered very harmful therefore, there is strong support for sanctioning and controlling them
18
New cards
criminology
an interdisciplinary science that studies criminal behaviour, crime causation, crime prevention, and the punishment and rehabilitation of offenders
19
New cards
criminologist
a behavioural scientist who specializes in the identification, classification, and description of criminal behaviour
20
New cards
interdisciplinary approach
in criminology, the integration of knowledge from a variety of disciplines to formulate explanations or theories of criminal behaviour
21
New cards
Conceptualizing Criminological Thinking
bottom green portion of this is dismissive as sociology is looking at the root cause of crime (considering race, age, gender, and social class)
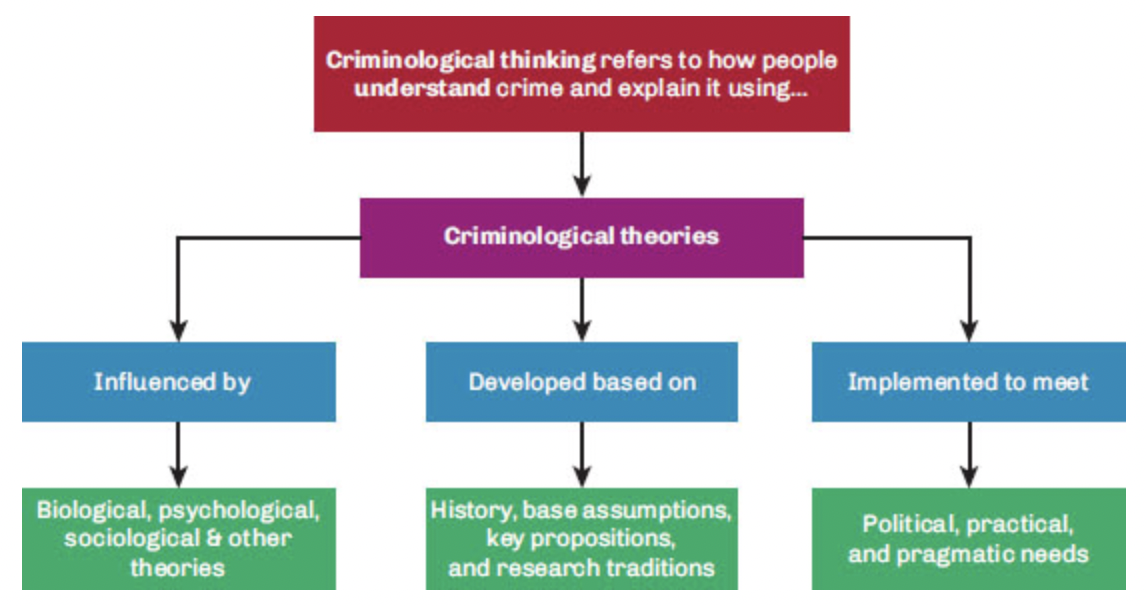
22
New cards
Sir Leon Radzinowicz
early advocate of an interdisciplinary approach to the study of criminology
23
New cards
The Canadian Criminal Justice Process: A Simplified Flow Chart
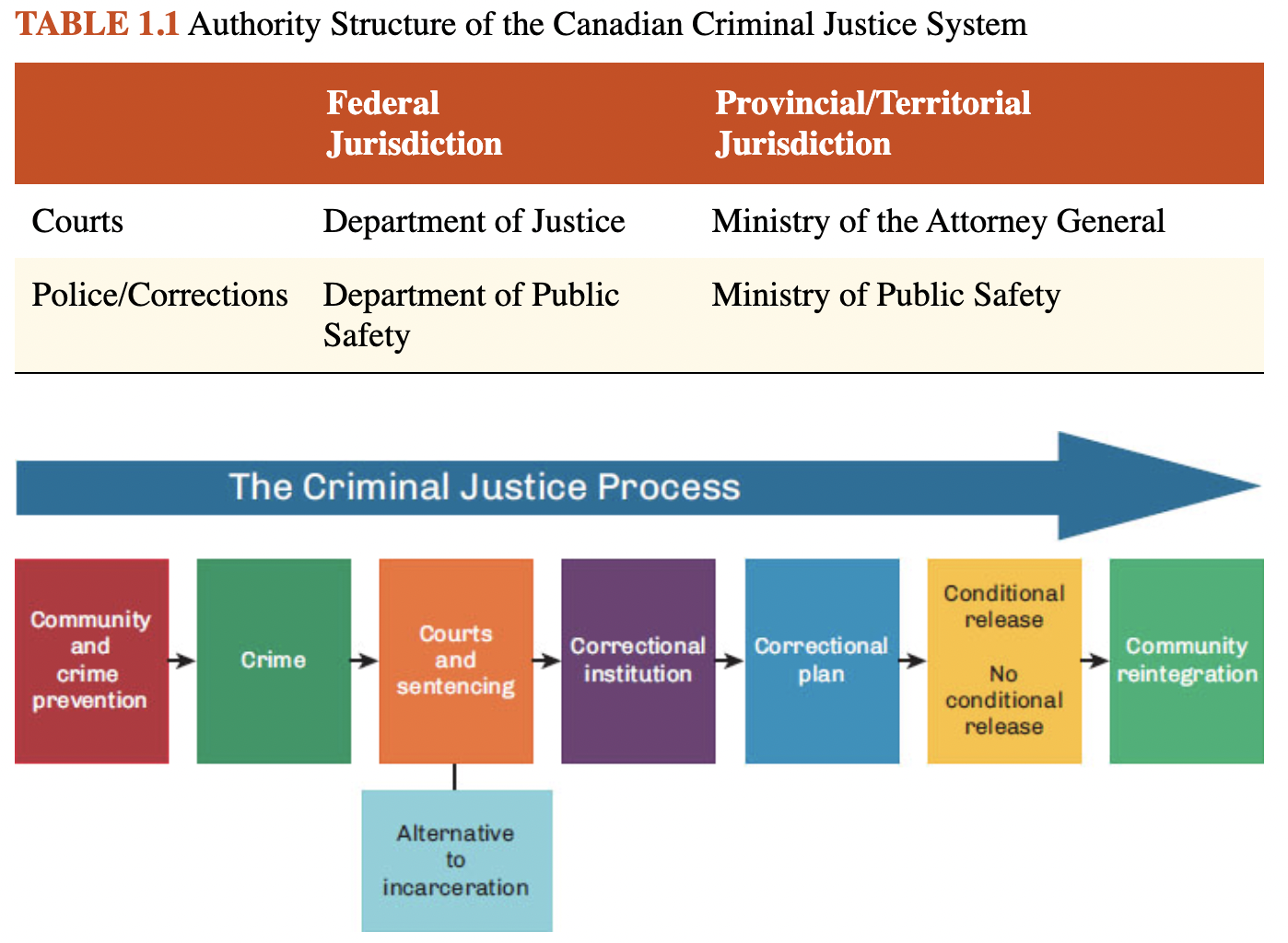
24
New cards
Paul Topinard and Raffaele Garofalo
1879, used term criminology to refer to the study of punishment and treatment of criminals
25
New cards
Cesare Beccaria and Jeremy Bentham
18th century
founders of classical school
argued for penal reform on humanitarian and philosophical principles.
founders of classical school
argued for penal reform on humanitarian and philosophical principles.
26
New cards
Maurice Parmelee
published the first criminology textbook.
27
New cards
The Core Sub-Areas of Criminology
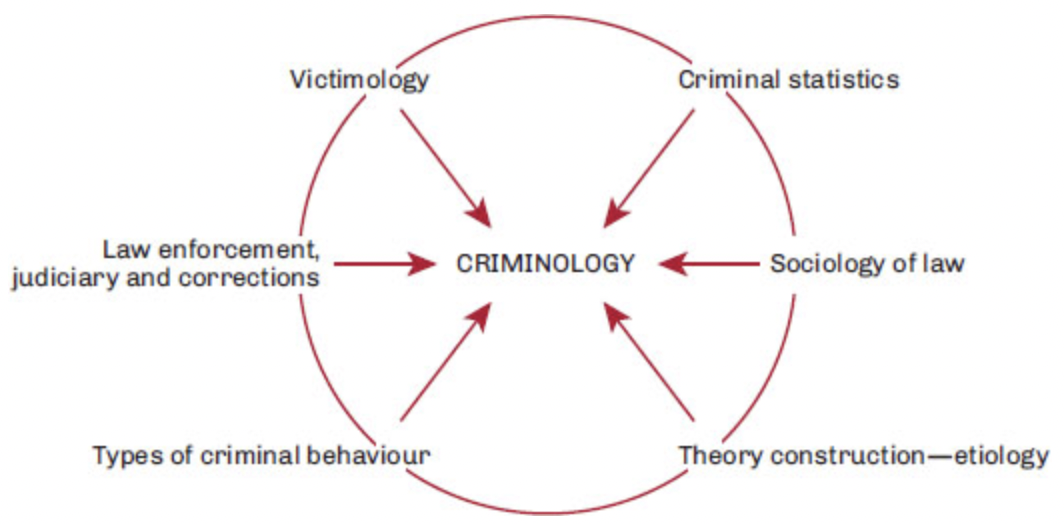
28
New cards
Etiology
The study of the origins or causes of a phenomenon.
29
New cards
penology
the study of how crime is punished
30
New cards
Cesare Lombroso
father of criminology
identified criminal typologies as "the born criminal," "criminals by passion," "criminaloids," and others
identified criminal typologies as "the born criminal," "criminals by passion," "criminaloids," and others
31
New cards
crime rate
the number of criminal offences in a category, recorded in a fixed ratio, such as per 100,000 people
32
New cards
victimless crime
no one is harmed by the activity, typically because the activity is consensual
33
New cards
public-order crimes
Activities deemed illegal because they are viewed as immoral or harmful, even though the parties who engage in them do so by choice.
34
New cards
==protect society== from behaviours that society considers immoral and/or harmful
Primary Purpose of Law
35
New cards
consensus perspective
A criminological perspective that sees laws as representing the ==interests of society==. Function to express and uphold a popular notion of public morality.
\
One of two general theoretical orientations that are not mutually exclusive
\
One of two general theoretical orientations that are not mutually exclusive
36
New cards
conflict perspective
A criminological approach that sees laws as representing the ==interests of specific groups== in society.
\
One of two general theoretical orientations that are not mutually exclusive
\
One of two general theoretical orientations that are not mutually exclusive
37
New cards
criminalistics
the science of crime detection and investigation, including such areas of specialization as weapons and DNA analysis. Alphonse bertillon was the first to apply this technique to law and criminology
38
New cards
Alphonse Bertillon
Father of criminal identification
39
New cards
Hans Gross
observed that police were good at maintaining order, but bad at solving crimes as they would rely on evidences from informers engaged in criminal activity
40
New cards
forensic science
The application of scientific knowledge to questions of civil and criminal law.
41
New cards
Crime Prevention through Environmental Design
A scientific approach that seeks to change environmental conditions to make them more crime resistant
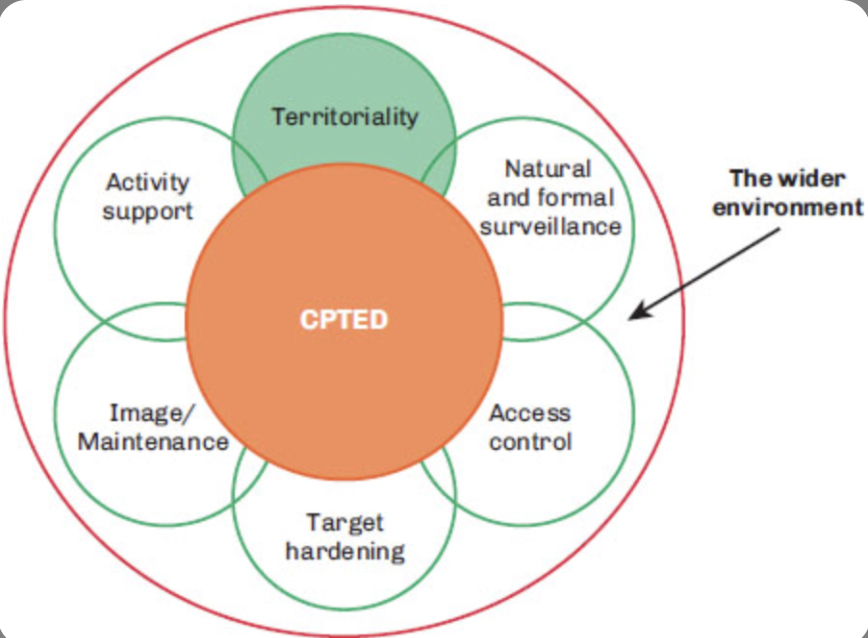
42
New cards
Tadeusz Grygier
==champion of the social protection code==
\
established university undergraduate program in criminology
\
academic interests in social justice, fair sentencing, and correctional practices
\
established university undergraduate program in criminology
\
academic interests in social justice, fair sentencing, and correctional practices
43
New cards
Denis Szabo
Father of Canadian Criminology
\
established Canada’s first criminology program and research centre for comparative criminology
\
believes criminology is inseparable from criminal policy: one cannot be studies without the proper consideration of the other
\
established Canada’s first criminology program and research centre for comparative criminology
\
believes criminology is inseparable from criminal policy: one cannot be studies without the proper consideration of the other
44
New cards
Patricia Brantingham and Paul Brantingham
leading ==Environmental Criminologists== in Canada