RBT exam study guide / RBT Task List - 2nd edition
1/164
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
165 Terms
What is Continuous Measurement?
Observing behaviors and collecting data on several instances across time
*Records all instances of behavior shown within an observation period.
What is Frequency?
Counting and recording the number of times a behavior happens within a specific time frame
*the number of times a behavior occurs in a session (tallying everytime a client bites)
What is Duration?
How long a client engages in a specific behavior.
*how long a behavior lasts (ex. Tantrum duration)
What data collection is appropriate for behaviors that have a distinct beginning and ending, or for those that occur at extremely high rates?
Duration
What is Latency?
The elapsed time from the onset of a stimulus to the time that the response started
Measuring how long it takes for the behavior to begin after a verbal demand or event has occurred
*the time between the SD and the response (ex. How long does it take the client to put his/her hands in her lap after given the SD "calm hands")
What is Interresponse time (IRT)?
Elapsed time between two successive responses
The amount of time between consecutive occurrences of a response
What is typically recorded as the time between the termination of one response and the initiation of the next?
Interresponse time (IRT)
When tracking specific behaviors, what type of measurement would you use?
Continuous
What are the subgroups of continuous measurement?
Frequency
Duration
Latency
Interresponse time (IRT)
What is Discontinuous Measurement?
Tracking/recording behavior during a particular sample of time
*Observation period is broken into smaller intervals
What is a Partial Interval?
Observing whether a behavior occurs or does not occur during specified time periods
*Data taken in intervals (ex. Measuring a client's falling. The BCBA may have 15 minute intervals set up for a 2 hour session and the RBT will only put a tally if the client falls during that 15 minute interval. The RBT may put a + or a - in that interval slot indication whether or not the behavior occurred.)
What is a Whole Interval?
Observing whether a behavior occurs or does not occur throughout the entire specified interval of time
*A behavior is recorded if it occurred within the ENTIRE interval of time (If they behavior occurs at all within the entire 2 hour session)
What is a Momentary Time Sampling?
Observing and recording whether client engaged or did not engage in the behavior at the very end of the specified interval of time
*Data is taken on a behavior at the end of the interval (ex. A RBT may only take data at the end of a 5 minute interval. If the behavior is occurring then they will mark a +, if a behavior is not occurring at that instance they will mark a -.
When you are looking to estimate the amount of behavior that occurred, what type of measurement would you use?
Discontinuous
What are the subgroups of discontinuous measurement?
Partial Interval
Whole Interval
Momentary Time Sampling
What type of graph is this?
Line Graph
With phase change lines
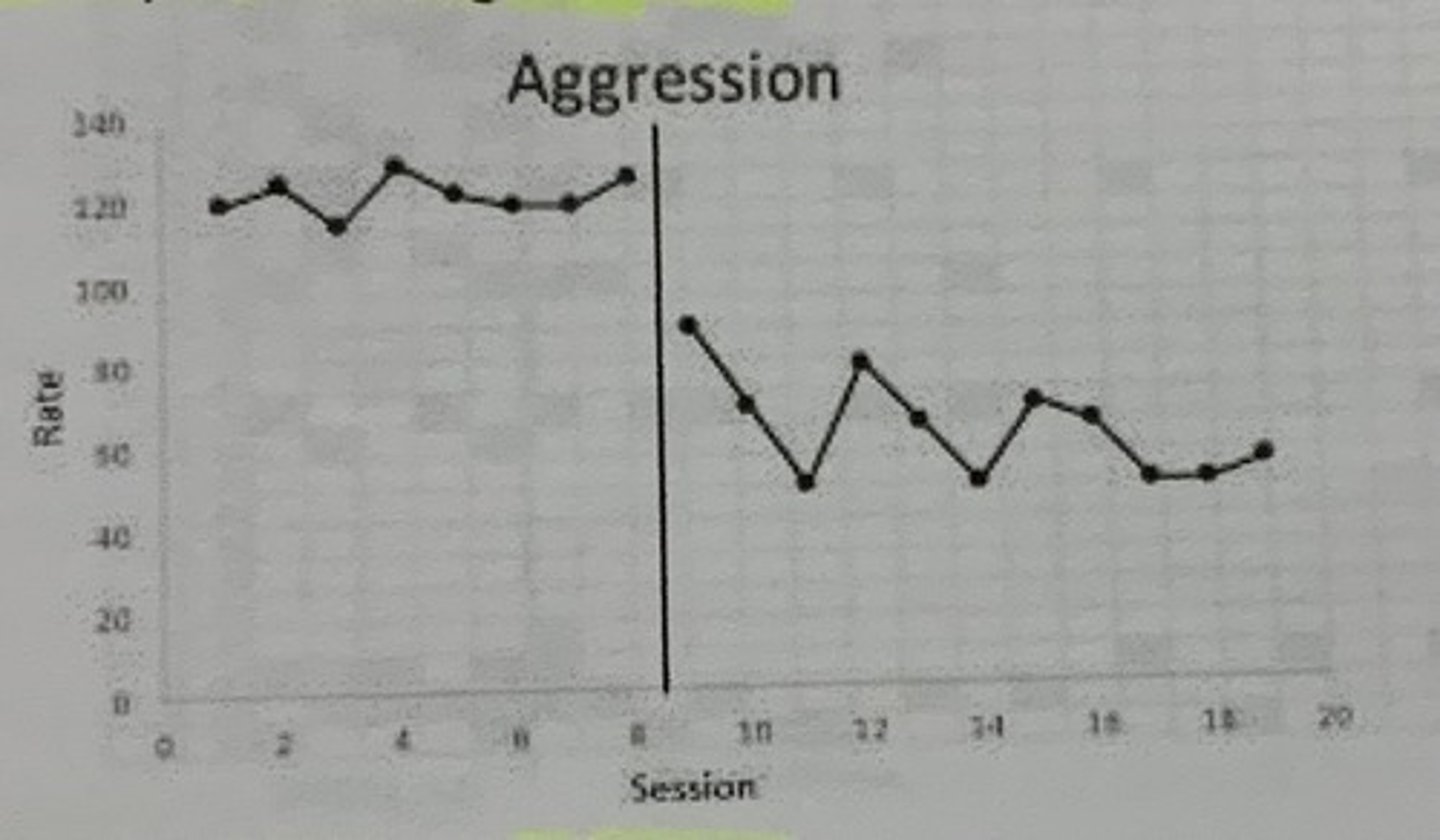
What type of graph is this?
Line Graph
Without phase change lines
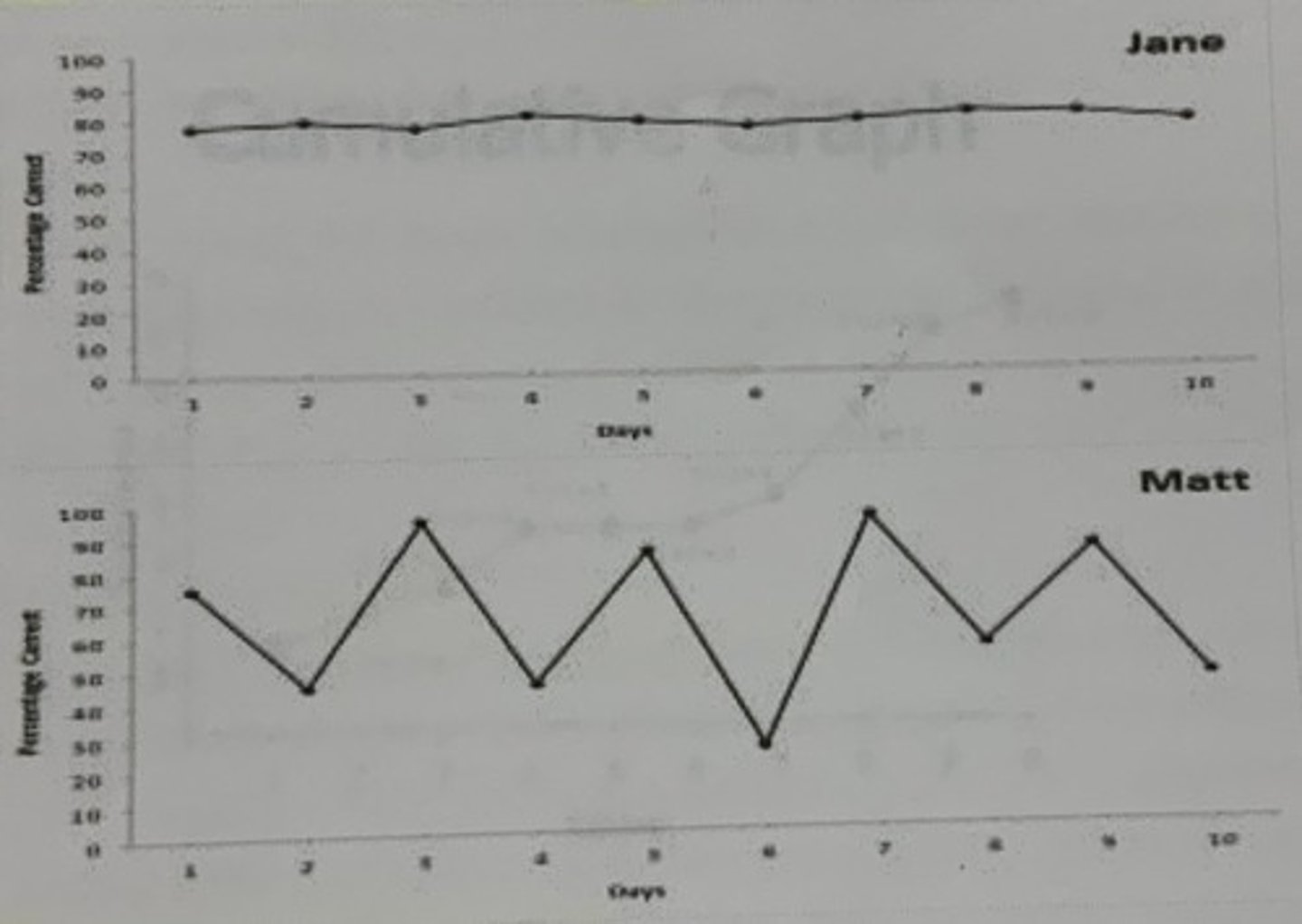
What type of graph is this?
Bar graph
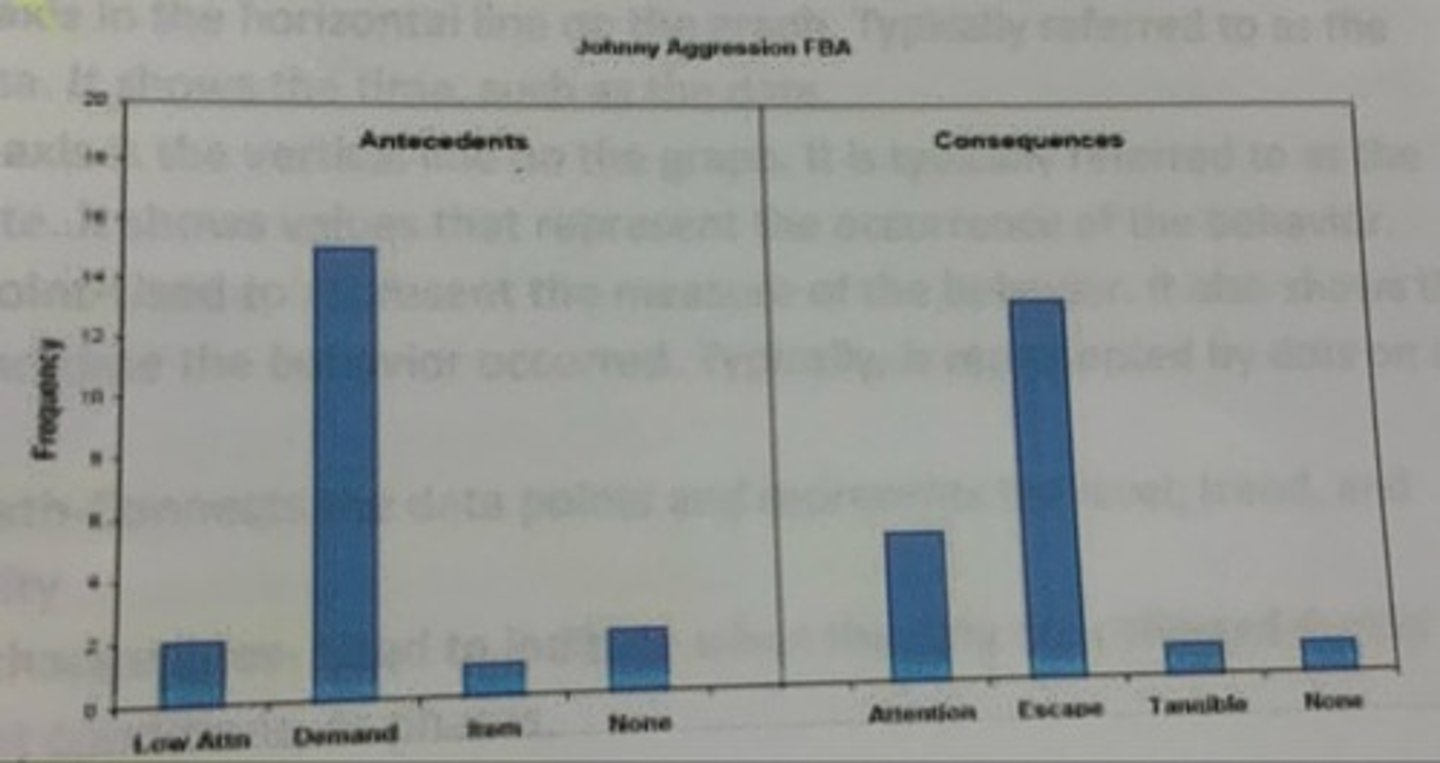
What type of graph is this?
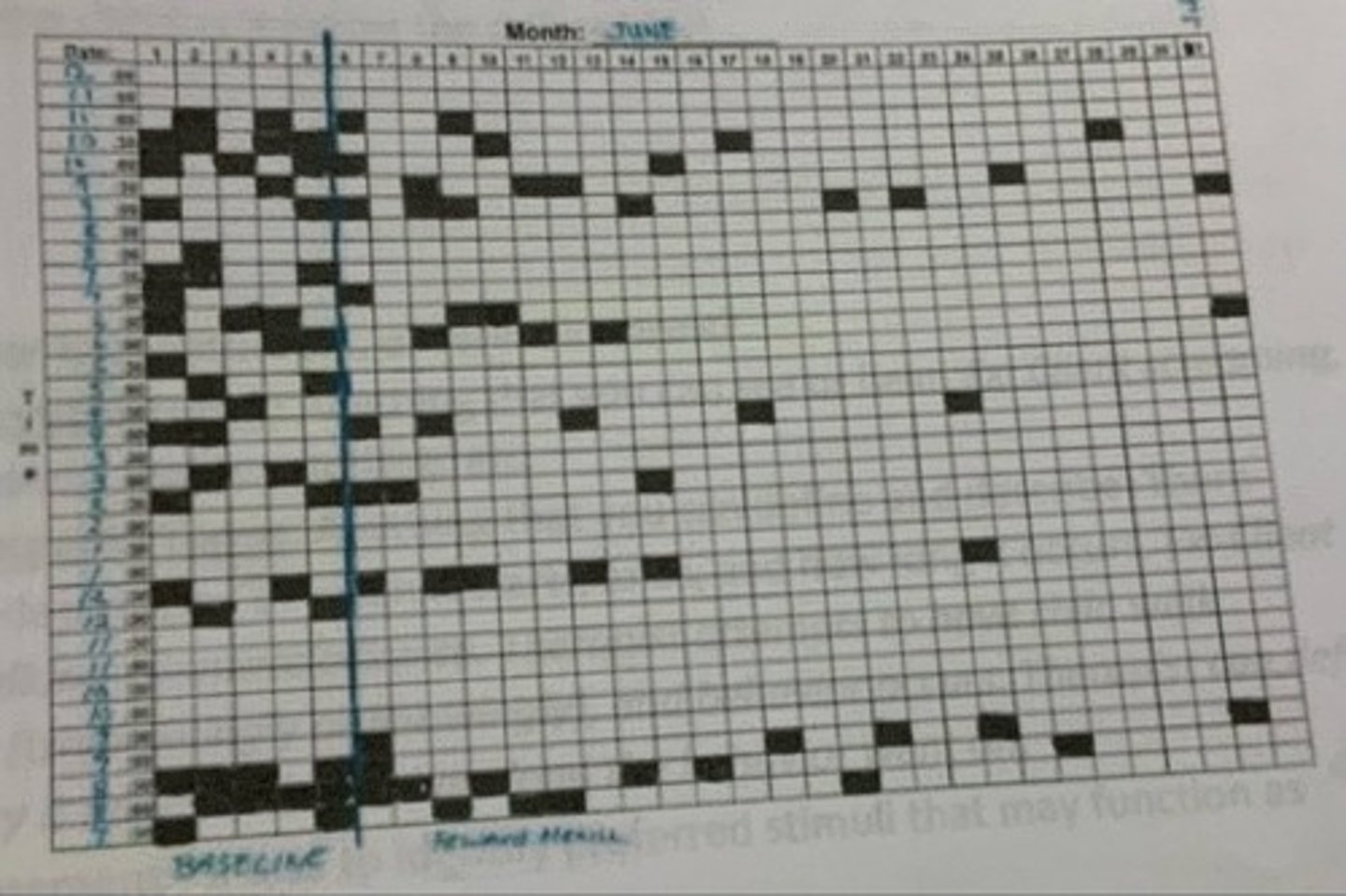
Scatter plot graph
What are the different parts of a graph?
X-axis
Y-axis
Data point
Data path
Phase change lines
What type of graph is this?
Cumulative graph

What is the horizontal line on a graph called?
X-axis
What is referred to as the Abscissa and shows time, such as date?
X-axis
What is the vertical line on a graph called?
Y-axis
What is referred to as the Ordinate and shows values that represent the occurrence of the behavior
Y-axis
What is used to represent the measure of the behavior, and shows the dated and time the behavior occurred?
Data point
What is represented by dots on a graph?
Data point
What connects the data points and represents the level, trend, and variability?
Data path
What is used to indicate when the data is collected during different conditions or phases?
Phase change lines
What does a steep upward slope mean?
High rate of responding
The steeper the slope of the data path, the ___ the rate of ___
Greater, response
-the client is learning the skill quickly
How do you describe a behavior in Observable Terms?
Anything that you can see or hear
How do you describe a behavior in Measurable Terms?
Anything that you can define and describe
-clear description of when it starts, ends, and how long it occurs
What is a Preference Assessment?
A tool to identify preferred stimuli that may function as reinforcers for your client
*Used to find preferred reinforcements (ex. offering the client choices and taking data on which reinforcements are most preferred)
What are the 3 ways to assess client preferences using Conduct Preference Assessments?
Interview
Direct Observation
Systematic Assessment
What are the subgroups of the Interview way assessing client preferences?
Client = straightforward method for determining stimulus preference
Significant Others = parents & caregivers can be useful as you determine what groups of items may function as reinforcers
Pre-tasks Choice = ask the client to choose what they want to earn for doing a task
What are the subgroups of the Direct Observation way assessing client preferences?
Contrived Free Operant Observation = prearranged for a particular purpose
Naturalistic Free Operant Observation = allowing clients to freely engage in a typical everyday environment for a predetermined time, with no interference
What are the subgroups of the Systematic Assessment way assessing client preferences?
Single Stimulus (successive choice) = may be well suited for individuals who have difficulty selecting among two or more stimuli. Consists of presenting one stimulus at a time and noting the client's reaction
Paired Stimuli (forced choice) = only two items are presented at any given time, repeat until all pairs have been presented
Multiples Stimuli =
——Multiple Stimulus w/o Replacement —> use if you are trying to move quickly, items do not return to the array after chosen by client
——Multiple Stimulus with Replacement —> client picks a preferred item which then gets placed back in the array of items as they choose the next preferred item
What is a Single Stimulus?
*a stimulus is presented and the person's reaction to it is noted
What is a Paired Stimulus?
*(forced-choice method) - Each trial consists of presenting two items and recording the person's choice of the two.
What is a Multiple Stimulus With Replacement?
*the item chosen remains in the array and all other items that were not selected are replaced by other items.
What is a Multiple Stimulus Without Replacement?
*the item chosen is taken out of the array and the array diminishes in size on each selection
Which method is most accurate?
Direct Observation
Giving a Systematic Preference assessment
Which method takes longest?
Giving a Systematic Preference Assessment
What is ABC data?
(A) Antecedent, (B) Behavior, (C) Consequence
What is the (A) Antecedent?
The action, event, or circumstance that occurs immediately before the bahveior
What is the (B) Behavior?
An observable measure / something that can be seen and counted
What is the (C) Consequence?
What happens after a behavior / can be positive or negative and increase or decrease the behavior
When should ABC data be collected?
When a behavior is new or highly challenging
How long do you want to take ABC data for?
Until the pattern is identifiable
What is an important step in carrying out a Functional Behavior Assessment to determine why a client is engaging in a problem behavior?
ABC data
An RBT collects ABC data by doing what?
Writing down what is said or done
On the ABC data, the RBT can abbreviate but should avoid ___?
Interpretations
Can a RBT give behavioral assessments on their own?
No
A BCBA can ask a RBT to help assist with a behavioral assessment
What occurs when a BCBA (or RBT) is teaching a new, functionally related alternative behavior, to replace an inappropriate problem behavior; or to teach academic, self-care, motor, social skills, etc.
Skill Acquisition
What are the essential components of a Skill Acquisition Program?
Target skill being taught
SD
Materials
Prompting Procedures
Consequences for incorrect responses (error correction/errorless teaching)
Mastery criteria
Reinforcement strategies
Plan for Generalization/Maintenance
What is the method of teaching in simple and structures steps, instead of teaching all at once, where the skill is broken down and built up, and where each step is taught one at a time called?
Discrete Trial Teaching (DTT)
(Therapist-led teaching)
What is Discrete-Trial Teaching (DTT)?
*Structured teaching; The RBT is manipulating the environment (ex. Pulling a child from play and using a token board while having the child sit at a table or on the floor working on matching similar pictures.)
What is Naturalistic Teaching?
*Learning in a natural environment; learning through play, eating, scenery, etc. (ex: a child reaches for a toy car. The RBT holds out the car and says "car" and the client repeats "car" to gain access to the item.)
What is Chaining?
*Sequences linked together (ex. Hand washing, tying a shoe)
What is Shaping?
*Reinforcing gradual steps towards a desired response (ex. Reinforcing a client for each gradual step in saying his name. If his name is James you can break it up by teaching him to say single syllables of "Jay" and "mes" and then move towards bringing them together.)
What is Discrimination Training?
*Teaching the client to recognize the difference between the discrimitive stimulus (reinforcement is provided) and the stimulus delta (reinforcement is not provided).
What is Stimulus Control Transfer?
*Changing the cue (ex. Moving from a partial physical prompt to a gestural prompt).
What is Prompting?
*Full physical - partial physical - modeling - verbal - gestural - independent
What is Token Systems?
*A token is given as reinforcement, when a certain number of tokens are received they may be turned in for a preferred reinforcement (ex. Token board)
What is Crisis/Emergency?
*Understand Fire drill & tornado drill procedures. Know when to call the nurse vs calling 911. (Ex. If a child's bone is sticking out call 911 then get someone's attention to get the nurse)
What is Antecedent Intervention?
*Alter the environment before the behavior occurs (ex. Knowing a child falls to the floor when passing a specific room so you place your hands under his arms when passing that room to prevent him from falling)
What is Differential Reinforcement?
*Reinforcing the appropriate behavior
skittles for peeing in potty (A.K.A desired behavior) but you may verbally praise a kid for sitting for a certain amount of time still is an example of what?
Differential Reinforcement
What is Extinction?
*Target challenging behavior identified, reinforcement withheld, teach and reinforce appropriate behavior. (ex. Planned ignoring a tantrum, but reinforcing when the client protests appropriately or follows through with a demand.)
*Who will review the session notes?
The BCBA
What does considering your attitude in the way you talk to or about a client pertain to?
*Client Dignity
What does Not babysitting a client you treat for therapy; not performing or accepting additional favors from clients outside of what is expected at work refer to?
*Professional Boundaries
What is the supervision requirement?
*5% each month
*What is the Clinical Direction?
Work in accordance to Peds Plus policies
What are the steps for discrete trial teaching?
1) An initial SD (demand/instruction)
2) A prompt or cue given by the therapist to help the child respond correctly
3) A response given by the child
4) An appropriate consequence, such as correct responses receiving a reinforcement designed to motivate the child to respond correctly again in the future
5) A pause between trials
What is the method of teaching using a very personalized approach, which allows the client's daily activities and routines to dictate how and where the therapist works with the child called?
Naturalistic Environmental Training (NET)
How do you implement Naturalistic Environmental Training (NET)?
-Incidental teaching
-Pivotal Response Training
-Instructional control gained through pairing yourself with child
-Child-led (follows child's MO)
-Easier to program for generalization
-Play-based programming
What is another name for Naturalistic Environmental Training (NET)?
Incidental Training
What is it referred to as when you are breaking the skill down into very specific steps to create manageable steps?
Task Analysis
What is it referred to as when you use a set of teaching procedures used to teach a task analysis, where it is important to use when trying to teach a very specific skill or set of skills?
Chaining
What are the different types of Chaining?
Forward Chaining
Backwards Chaining
What type of Chaining involves teaching the steps in order, using the very first step first?
Forward Chaining
What type of Chaining involves teaching the last step first?
Backwards Chaining
What is it called when you are reinforcing a behavior in the presence of one stimulus but not others?
Discrimination Training
What are the techniques in which prompts are discontinued once the target behavior is being displayed in the presence of the SD called?
Stimulus Control Transfer
What is term used to define something that is arranged or done to increase the likelihood that a client will give the correct response?
Prompt
What is the term used to define gradually reducing the prompts? (something that is arranged or done to increase the likelihood that a client will give the correct response)
Prompt Fading
What are the types of Prompt Fading?
-Full Physical
-Partial Physical
-Modeling
-Full Verbal
-Partial Verbal
-Gesture
-Independently
What is it referring to when a client applies something learned in a specific situation to situations that might be similar?
Generalization
What is it referring to when there is a continued use of a trained behavior over time, after the direct intervention period has ended?
Maintenance
What is it when a behavior or skill that is gradually taught by differentially reinforcing successive approximations to the behavior that the person teaching wants to create?
Shaping
What is it when one emphasizes the use of positive reinforcement to target behavior change?
Token Economy
What helps the client visualize their progress, accept and work for a delayed reinforcement, learn to regulate behaviors, and self-monitor?
Token Economy
Who will decide if the client is an appropriate candidate to benefit from the token system?
The client's BCBA
What does everything that people do/an organism's interaction with its environment refer to?
Behavior
What describes what the behavior of interest looks like in a way that is observable, measurable, and repeatable?
Operational Definition of Behavior
What do you provide when listing behaviors that Should be tracked with the BIP?
Examples
What do you provide when listing behaviors that would not be tracked with the BIP?
Non-examples
What is data collection on various skills or behaviors?
Measurement Type