VLP 2: Cytology Evaluation
1/35
Earn XP
Description and Tags
A set of vocabulary flashcards based on key concepts from the lecture notes on veterinary laboratory procedures and cytology evaluation.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
36 Terms
Cytology
The study of cells, particularly for diagnosing diseases.
Microscopic Slide Evaluation
The analysis of prepared slides under a microscope to assess specimen quality.
Neutrophils
White blood cells that respond first to inflammation and typically phagocytize dead tissue and organisms.
Hypersegmentation
A morphologic change in neutrophils characterized by elongated, thin filaments connecting nuclear lobes.
Macrophages
Large immune cells derived from monocytes, involved in chronic inflammation and capable of phagocytizing other cells.
Eosinophilic Inflammation
Inflammation characterized by the presence of more than 10% eosinophils, often associated with parasitic infections.
Karyolysis (Degenerative)
Rapid cell death results in a swollen, ragged nucleus with reduced staining intensity.
Anisokaryosis
An unusual variation in the overall size of the nucleus, indicating potential malignancy.
Pleomorphism
Variability in size and shape of the same cell type, often associated with malignant tumors.
Benign Neoplasia
A non-cancerous growth with no criteria for malignancy, typically uniform in cell type and morphology.
Malignant Tumors
Cancerous growths characterized by multiple abnormal cellular features and behaviors.
Pyknosis (Degenerative)
Slow cell death (aging); Small, condensed, dark nucleus
Karyorrheis (Degenerative)
Nuclear Fragmentation, Often follows pyknosis.
Anisokaryosis
any unusual variation in overall of the nucleus
Pleomorphism (anisocytosis)
Variability in size and shape of the same cell type
Nuclear criteria of Malignancy
Anisokaryosis
Pleomorphism
High or variable nucleus/cytoplasm ratio
Increase mitotic activity
Coarse chromatin pattern
Nuclear molding
Multinucleation
Nucleoli
Nuclear Molding
Deformation of nuclei by other nuclei
Nucleoli
vary in size (anisonucleoliosis), shape, and number
Epithelial Cells
Highly cellular and often exfoliate in clumps or sheets
Malignant Carcinoma
Histiocytoma (discrete round cell tumors)
not usually highly cellular (bengin)
Lymphoma (discrete round cell tumor)
lymph cells (malignant)
Mast cell tumors (discrete round cell tumor)
prominent purple/black granules (malignant)
Plasma Cells tumors (discrete round cell tumor)
large number of cells of eccentrically located nucleus and prominent perinuclear zone (benign plasmacytomas or malignant multiple myeloma)
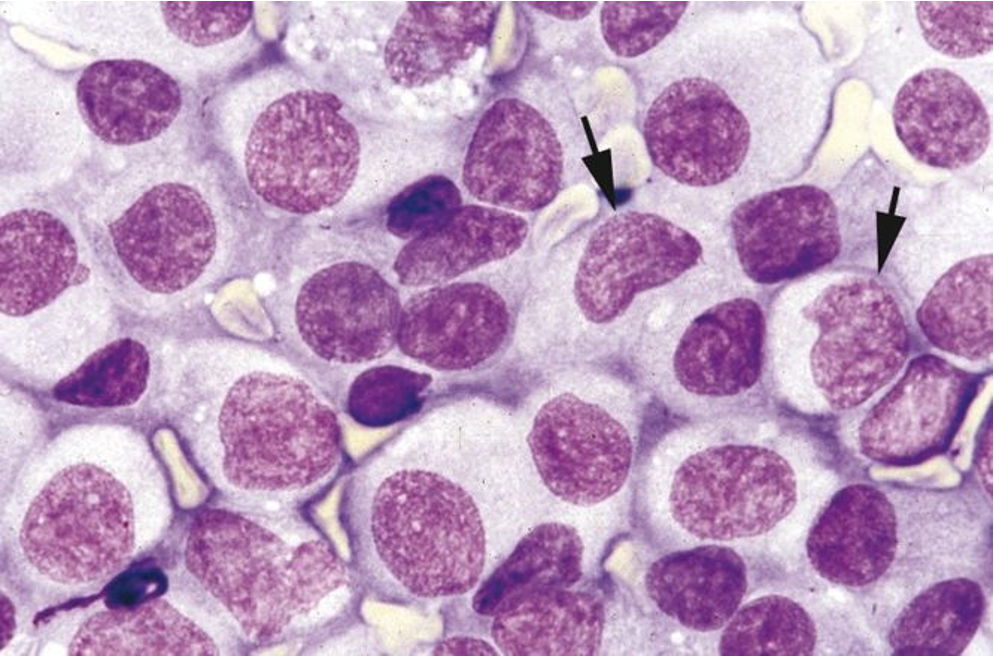
Transmissible venereal tumors (discrete round cell tumors)
similar to histiocytoma but with increased cellularity (malignant)
Melanoma (discrete round cell tumor)
cells with prominent dark black granules (benign or malignant)
Transmissible Venereal Tumor (image)
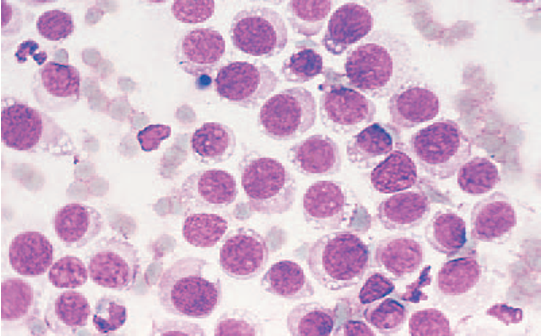
Mast Cell Tumor (image)
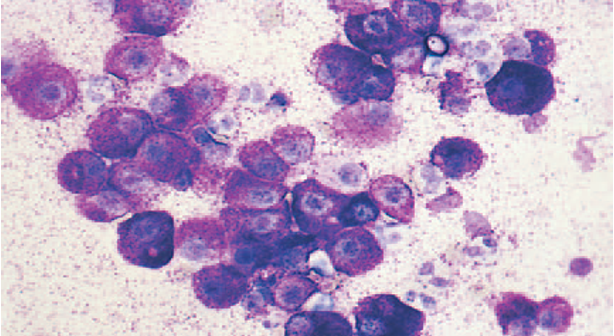
Plasma Cell Tumor (image)
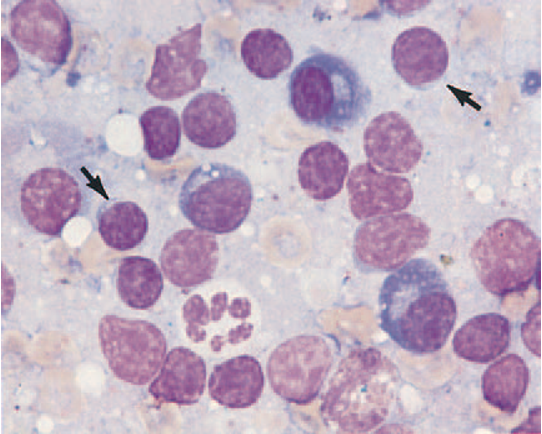
Melanoma (image)
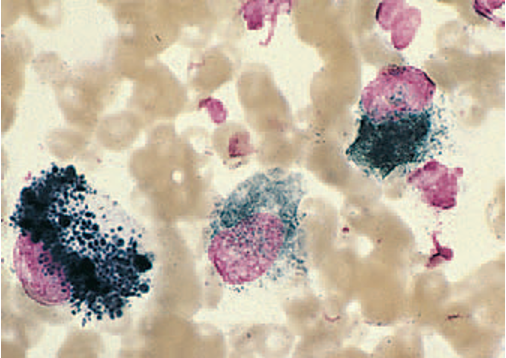
Histiocytoma
Cutaneous histocytoma is often called a “button lesion.”