Vcert Health and Fitness - Skeletal System
1/51
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
52 Terms
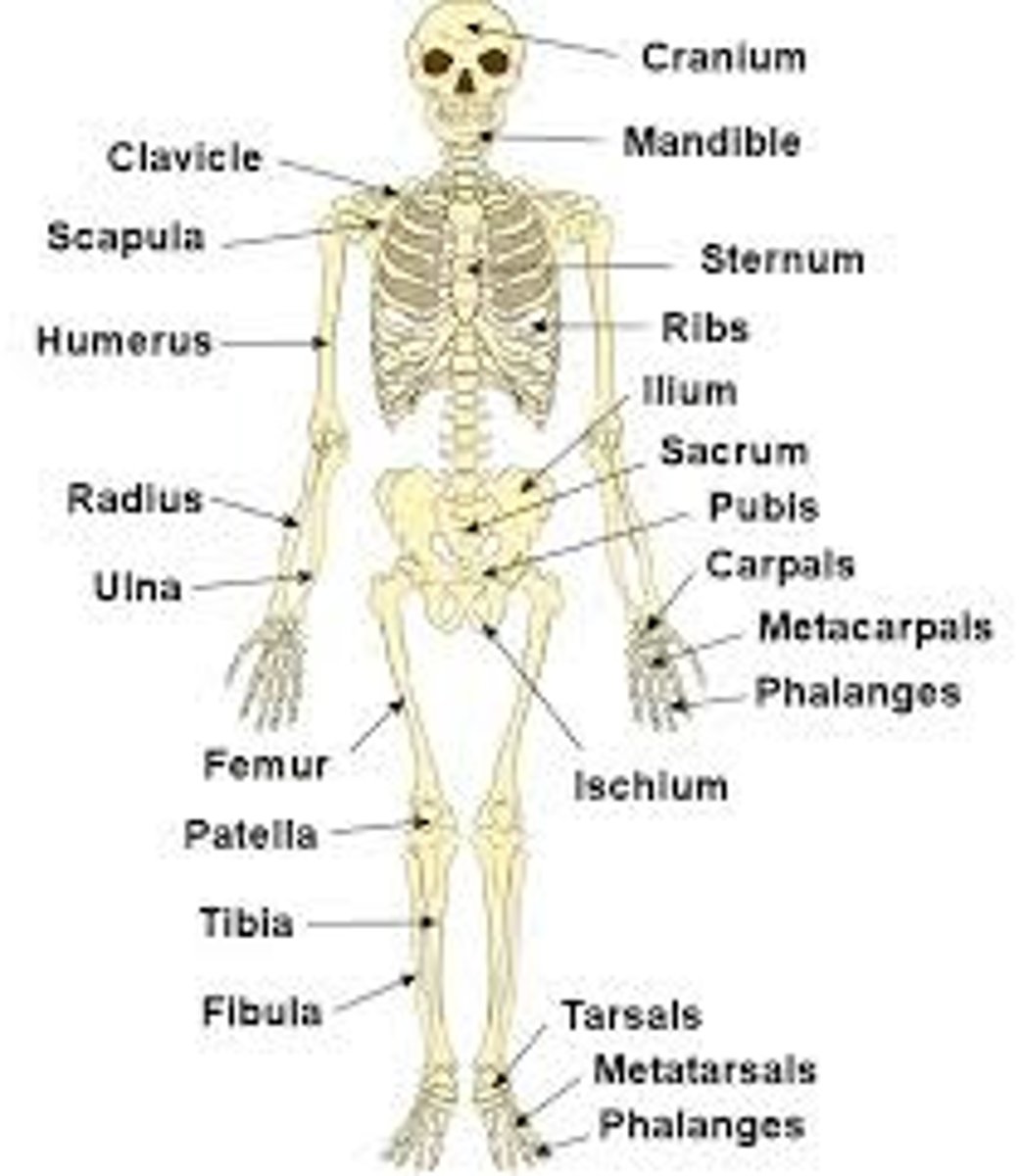
How many bones on axial skeleton ?
80 bones
Where are the bones in the axial skeleton ?
Bones of the head,neck,chest and back(on the inside part of skeleton)
How many bones in the appendicular skeleton ?
126 bones
Where are the bones in the appendicular skeleton ?
Made up of the upper and lower limbs(on the outside part of skeleton)
What are the five types of bones ?
long, short, flat, irregular, sesamoid
What is a long bone ?
a bone that is longer than it is wide for gross movement
Name one long bone in the body
humerus, radius, ulna, femur, tibia, fibula
What is a short bone ?
a bone that is as wide as they are long for fine movement
Name one short bone in the body
carpals or tarsals
What is a flat bone ?
a bone that has a flat broad surface for protection
Name one flat bone in the body
scapula or cranium
What is a irregular bone ?
a bone that has a specific shape and its functions are all unique
Name an irregular bone in the body
Vertebrate - allows various degrees of movement and flexibility
What is a sesamoid bone?
a bone that is embedded in a tendon or muscle for relieving stress on muscles
Name a sesamoid bone in the body
patella
Functions of the skeleton
Shape
Blood cell production
Movement
Mineral storage
Support
Protection
Shape
gives our body shape (e.g how wide or tall we are)
Blood Cell Production
produce RBC & WBC in marrow
Movement
skeleton is jointed so we move with our muscles(muscle contraction)
Mineral Storage
minerals stored in bones (e.g calcium,minerals help to repair)
Support
holds internal organs in place when playing sport
Protection
protects vital organs from damage
Just memorise where they are:
What is a joint ?
where 2 or more bones meet
What is flexion ?
decreasing the angle of a joint
What is extension ?
Increasing the angle of a joint
What is adduction ?
moving limbs toward the midline
What is abduction ?
moving limbs away from the midline
What is rotation ?
a circular movement around a joint or movement around an axis/fixed point
What is plantar flexion?
pointing toes down/away from body
What is dorsi flexion ?
pointing toes towards body
What is circumduction ?
limb moves in a circular direction
What are the types of joints ?
Fixed,slightly movable and synovial
What is a synovial joint ?
freely movable joints(due to the synovial fluid which lubricates allowing them to move freely)
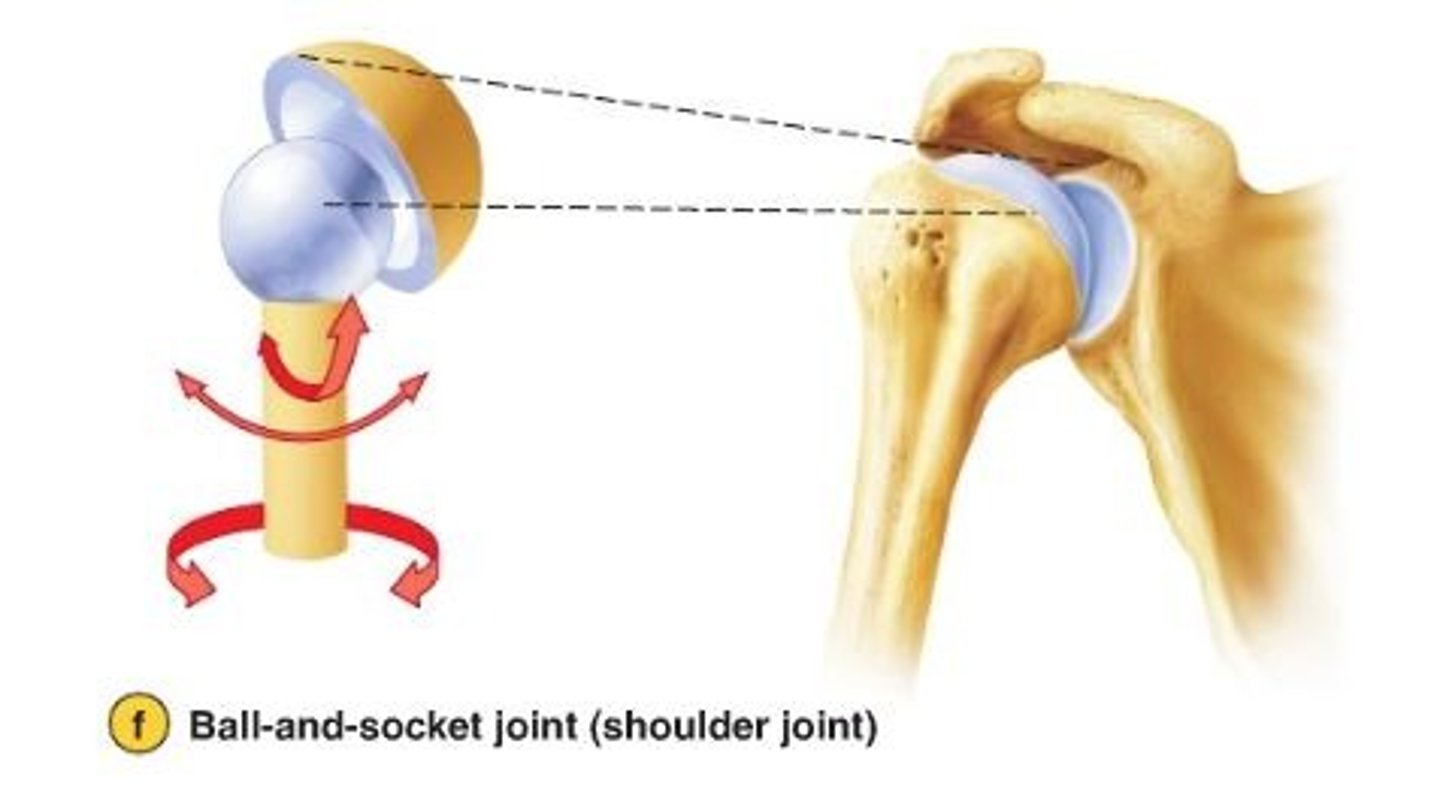
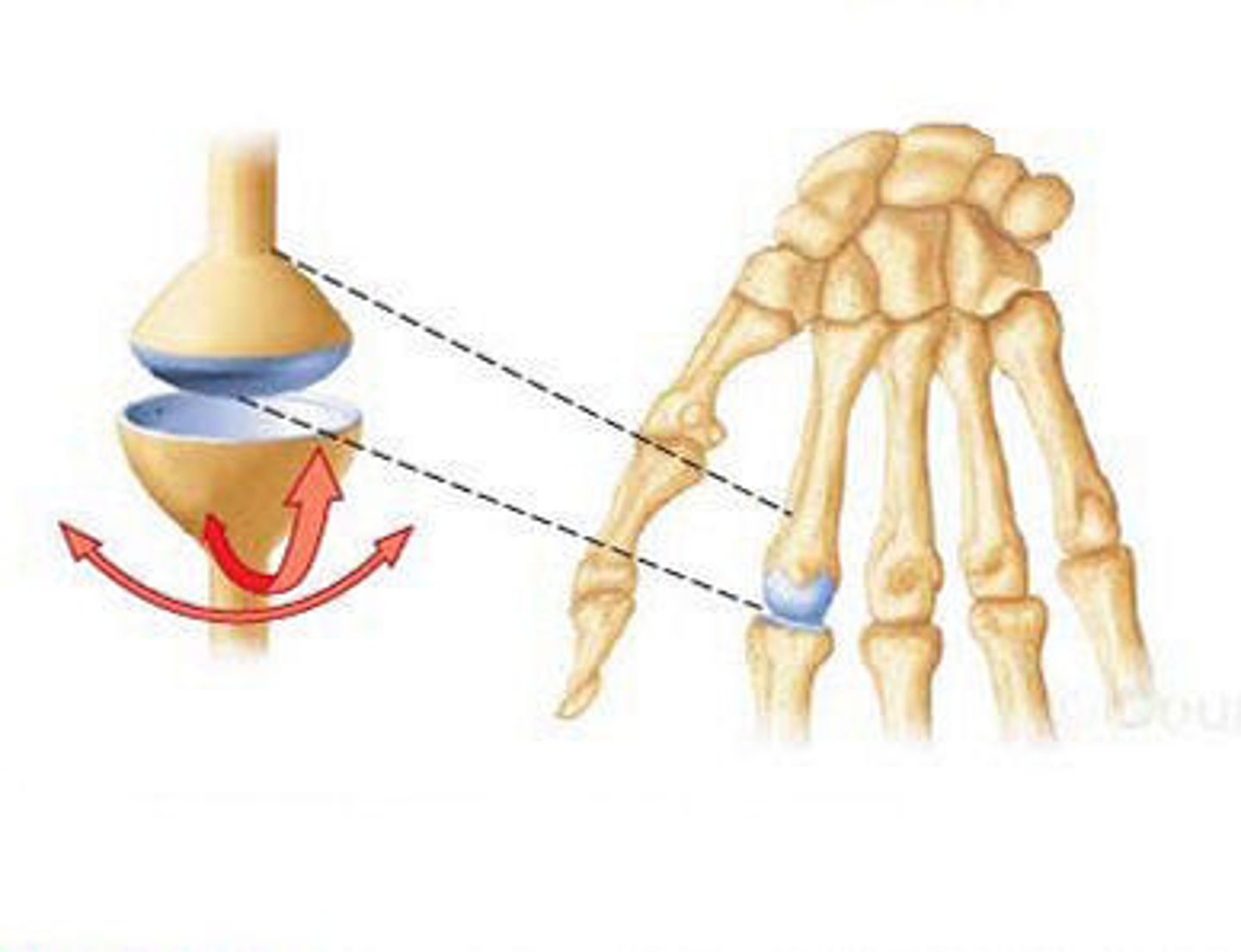
What is a ball and socket joint ?
one is ball-shaped and socket shaped and provides the widest range of movement in body.e.g shoulder and hip
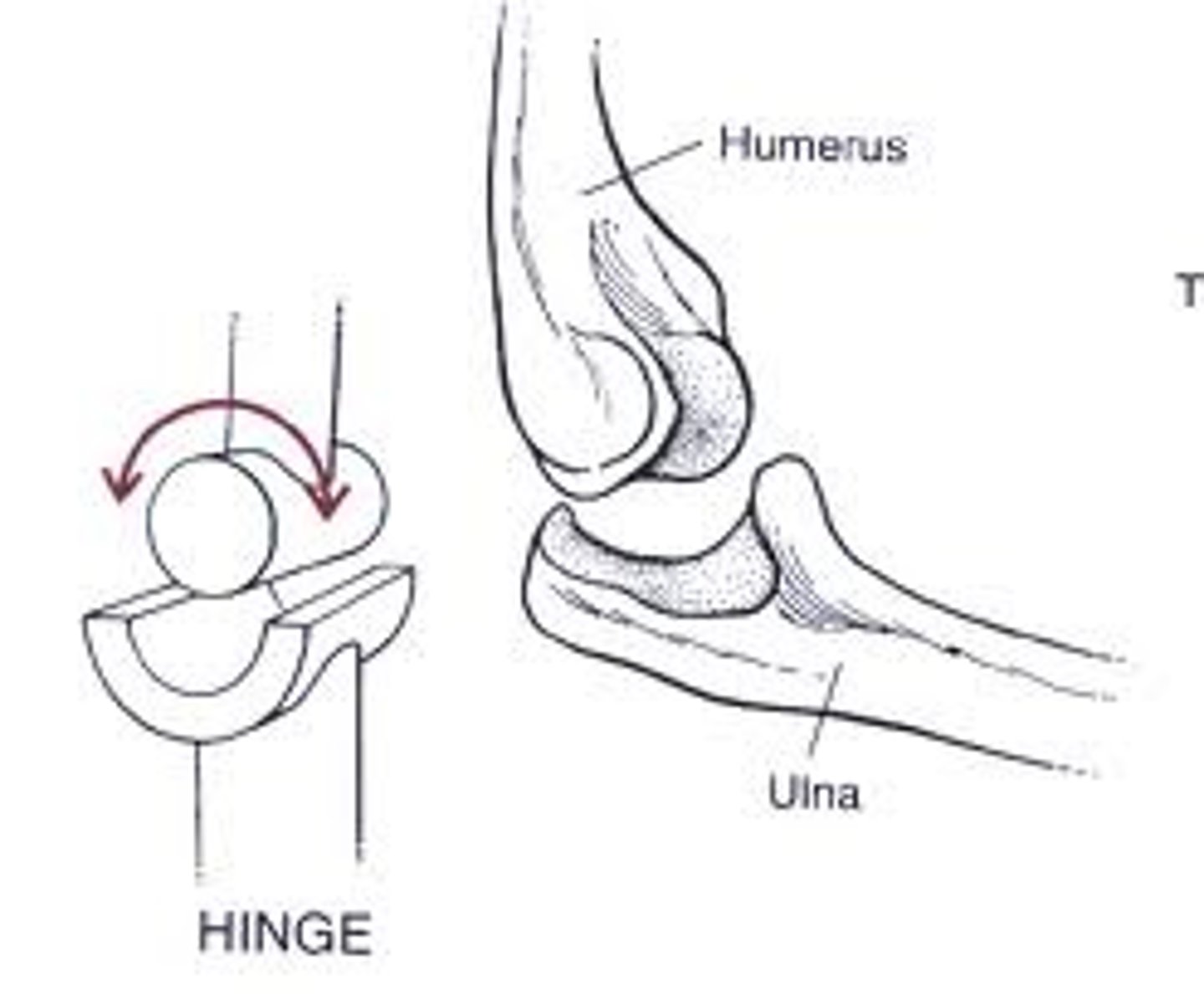
What is a hinge joint ?
allows extension and flexion.e.g elbow and knee
What is a pivot joint ?
one bone juts out and fits into other bone,only rotation.e.g pelvis or neck joint
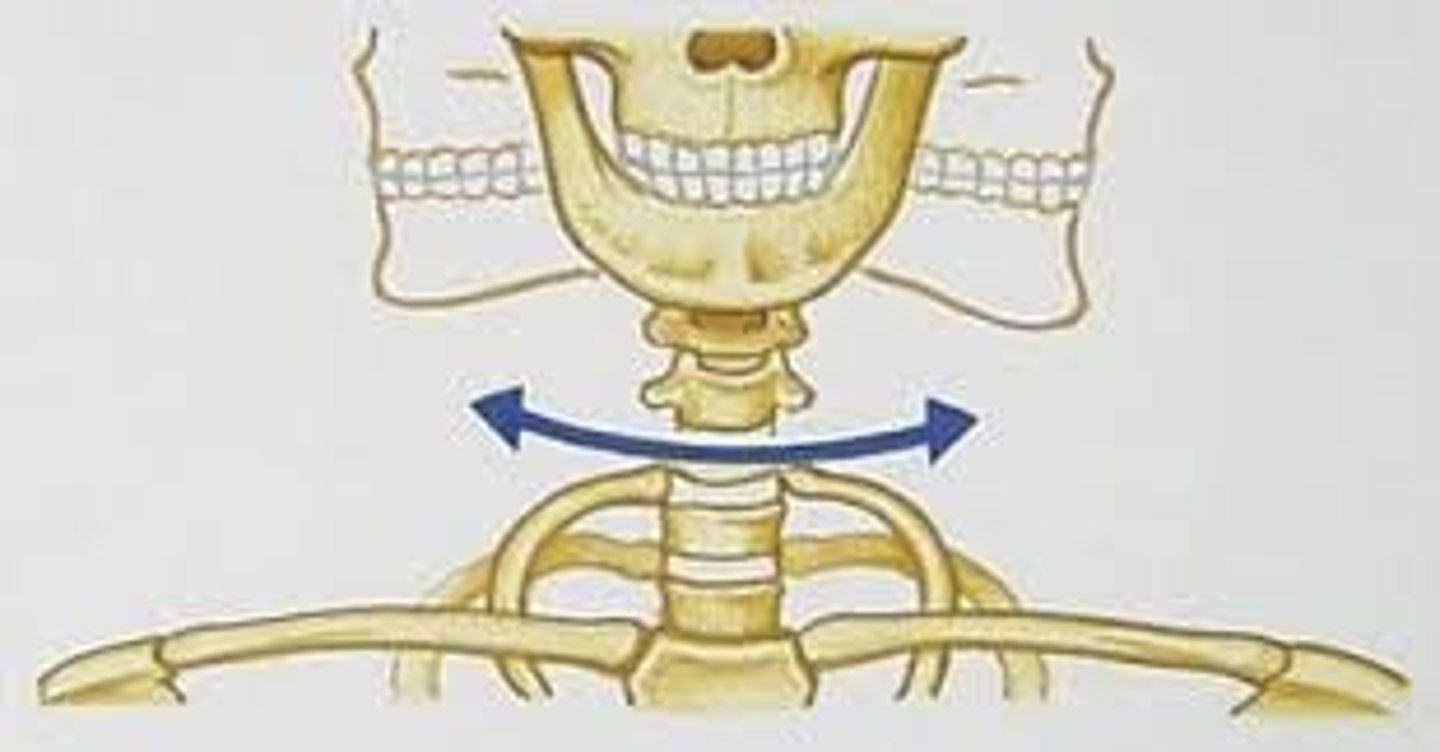
What is a gliding joint ?
Allows one bone to slide over another.e.g wrist and ankle
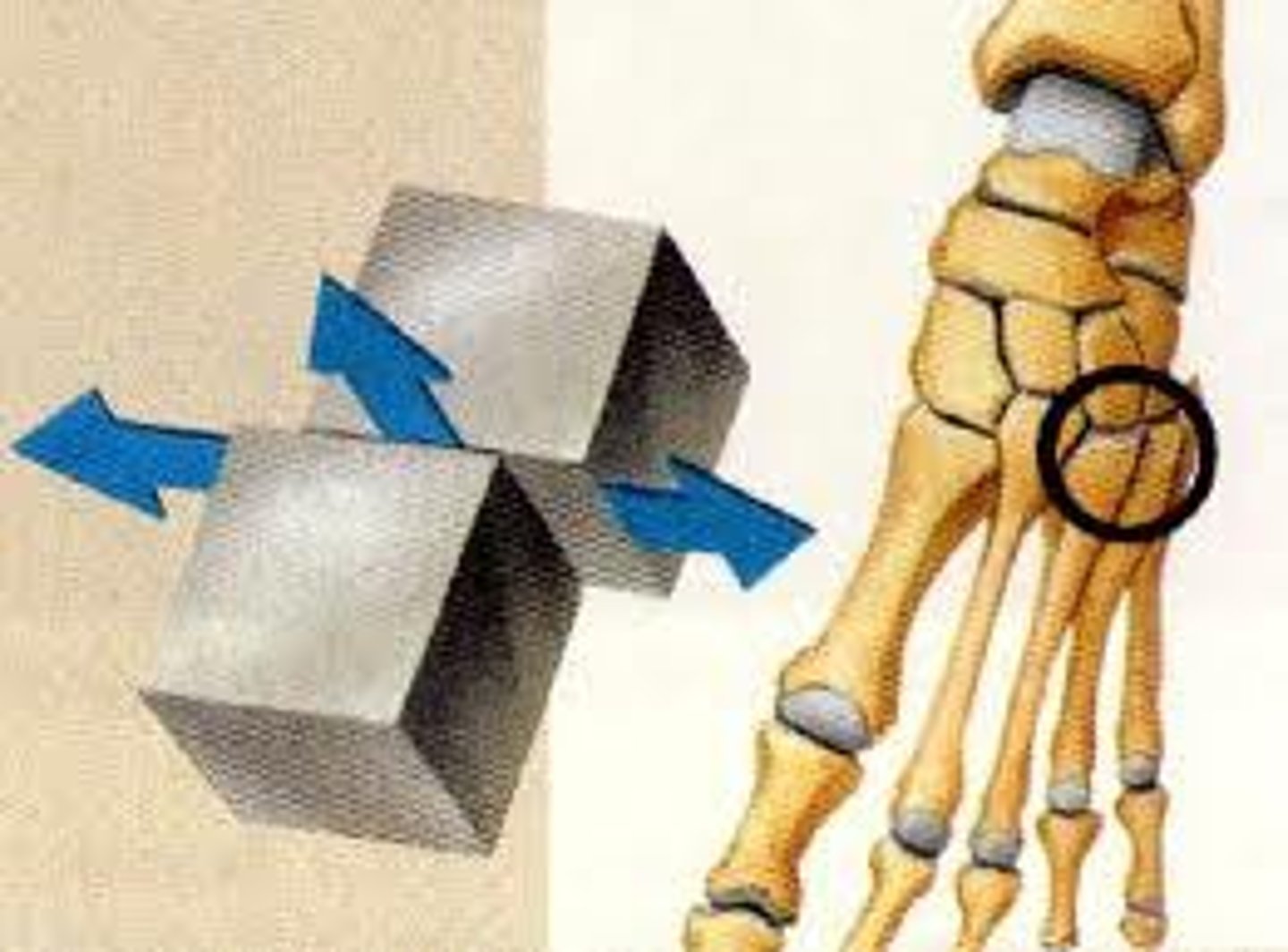
What is a saddle joint ?
2 bones that fit together like a rider in a saddle (allows for many movements)e.g thumb
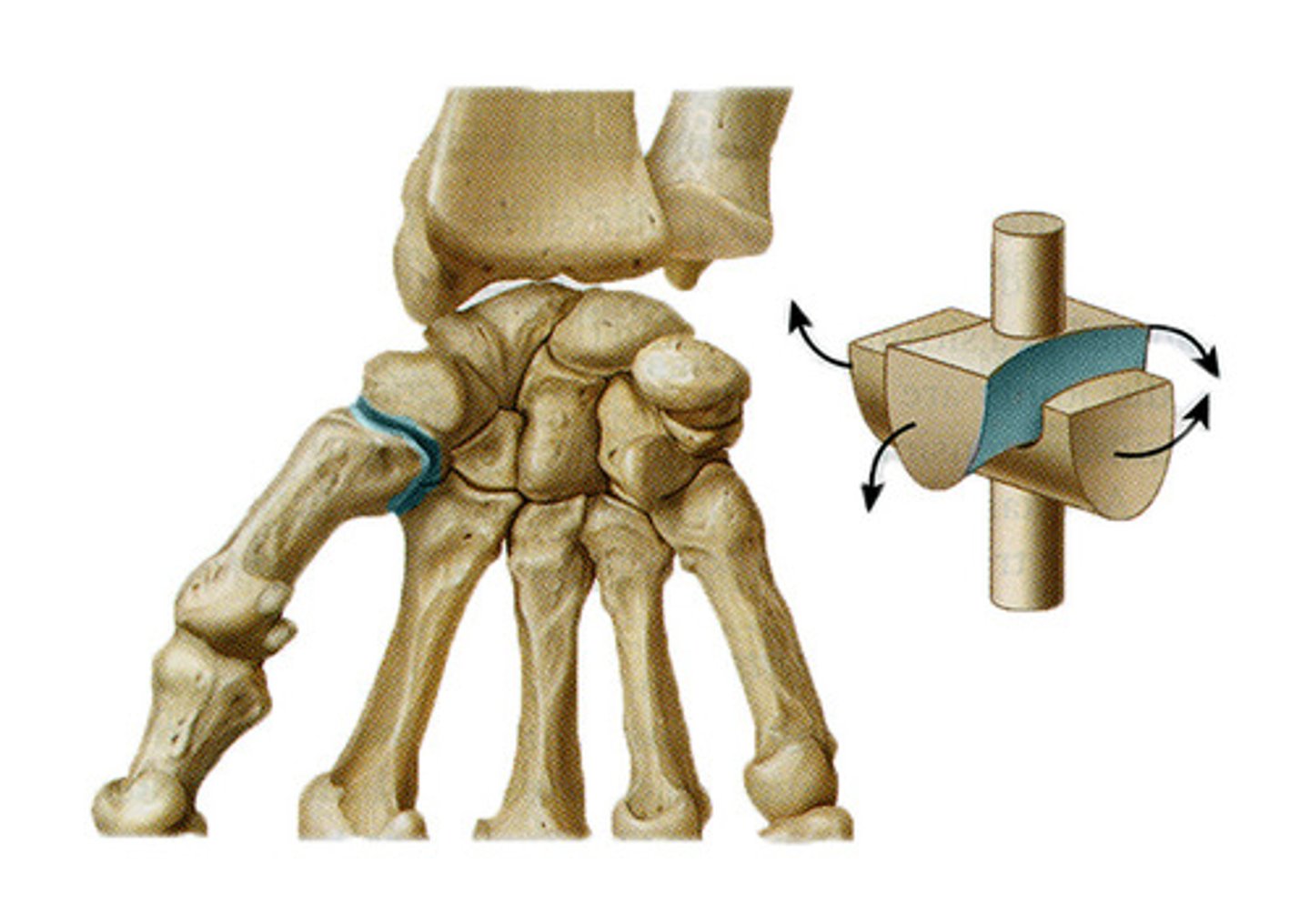
What is a condyloid joint ?
have an oval shaped bone fitting into another bone,allows flexion,extension,left & right movement.e.g between metacarpals and phalanges
What are the parts of the synovial joint ?
cartilage, joint capsule, synovial membrane & fluid, ligaments,tendon
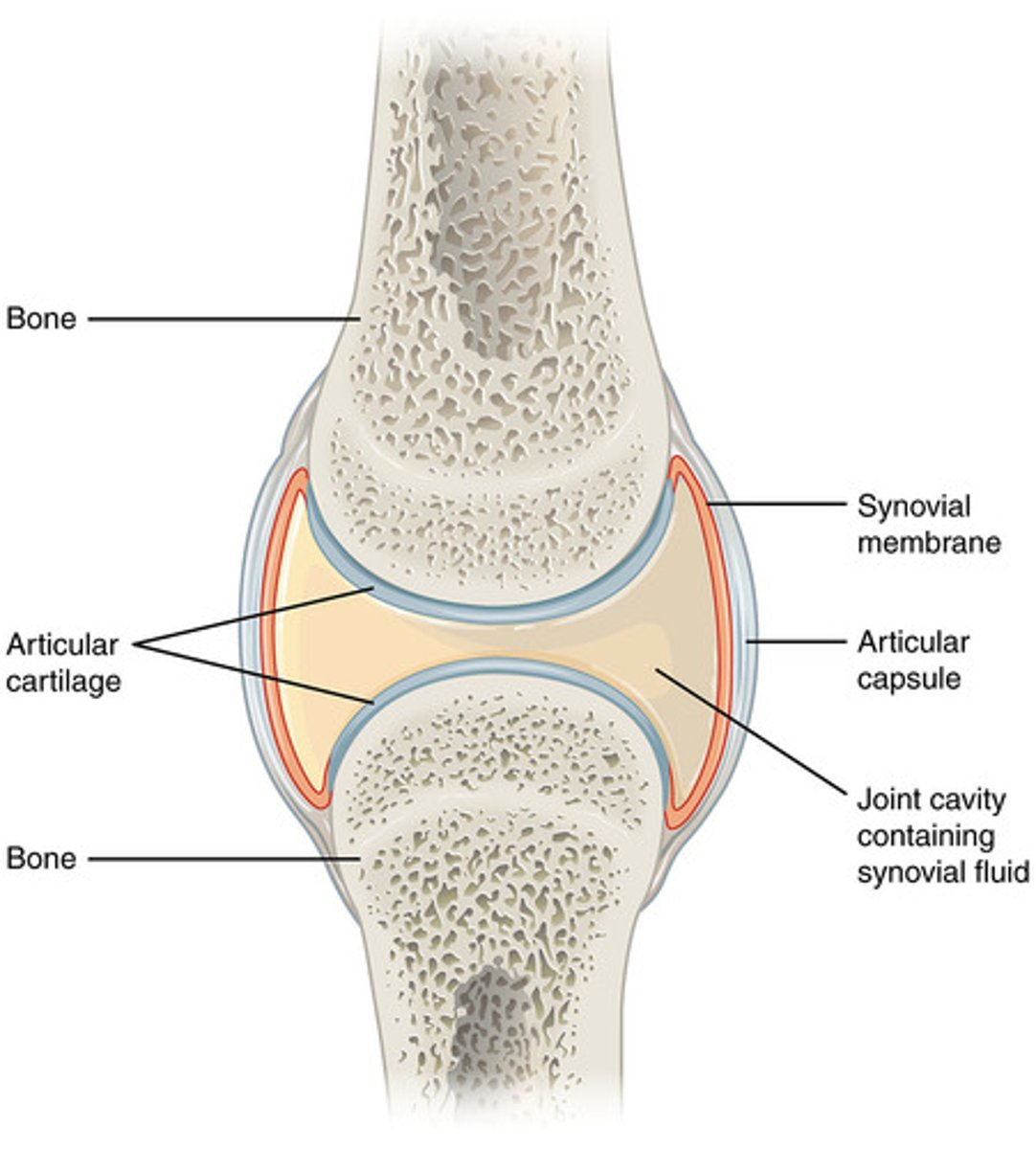
What does the synovial membrane do ?
secretes synovial fluid into joint capsule
What does the synovial fluid do ?
Lubricates the joint and reduces friction
What does the cartilage do ?
covers the edges of the bones to prevent friction
What does the joint capsule do ?
encloses the joint
What does a ligament do?
attaches bone to bone
What does a tendon do?
attach muscle to bone
What are the types of ligaments ?
posterior cruricate ligament,anterior cruciate ligament,medial collateral ligament,lateral collateral ligament,
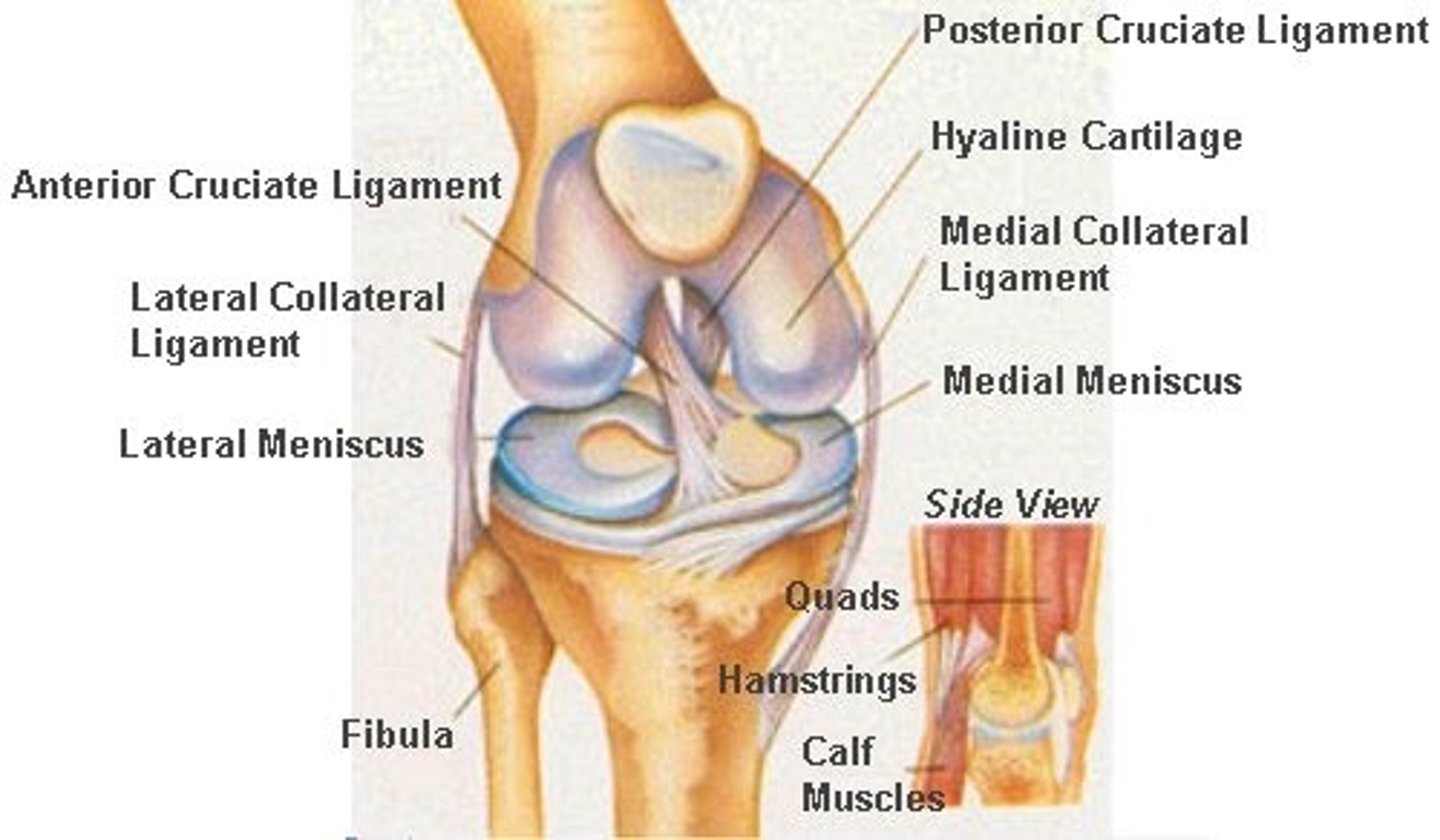
Just memorise vertebrae - remember made of 33 bones
Cervical(c3-c7),Thoracic(t1-t12),Lumbar(l1-l5),Sacrum(s1-s5),Coccyx - in order from top to bottom
What does posture mean ?
describe the position of the body
Why is posture important in health and fitness ?
Good posture helps prevent back ache and fatigue and a healthy spine absorbs stress from body
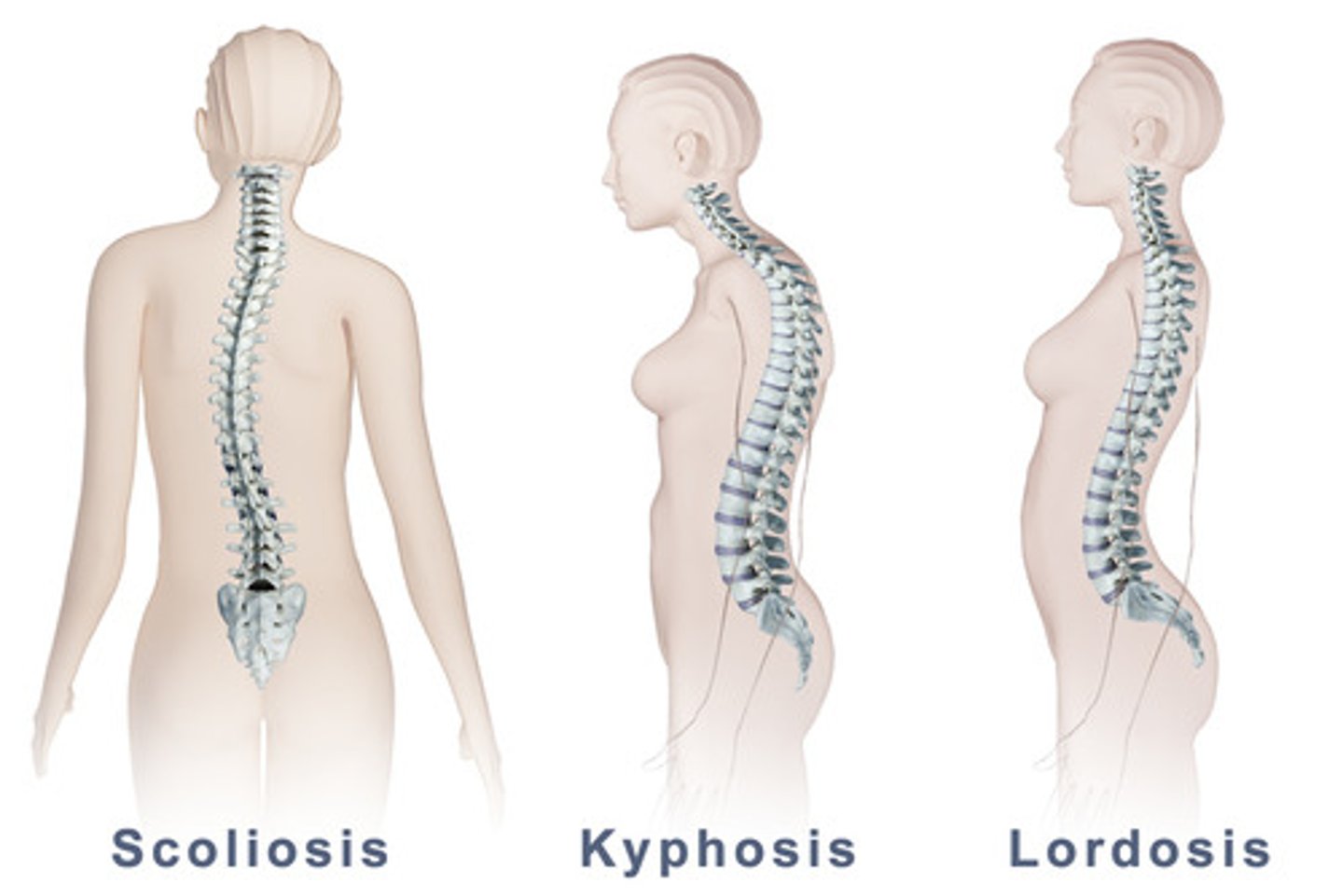
What are the spine curvature disorders?
Kyphosis - rounded upper back,hunch
Lordosis - spine curves inward
Scoliosis - S or C shaped curve(sideway curve)