Labour Market
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
Marginal Productivity Theory
Firms only demand labour if another worker increases profit, meaning that demand for labour is derived demand from the demand for the product the labour produces.
Marginal Revenue Product of Labour
The monetary value of the added output of one additional worker (The Demand Curve in a Labour Market)
Supply of Labour
The sum of all individual supply curves in the labour market.
Net Advantage
The sum of monetary and non monetary benefits gained by those who work.
Wage elasticity of the supply of labour
The responsiveness of the supply of labour to a change in the wage rate offered.
Wage
The monetary compensation paid by an employer to an employee in exchange for labour.
Wage Differentials
Differences in the wage paid to workers doing the same work.
Perfectly Competitive Labour Market
Where there are lots of firms and workers, with all labour being homogenous and everyone having perfect information. Firms are wage takers and there are no barriers to entry or exit.
Monopsony
A labour market containing one employer of labour who have significant power over workers.
Average Cost of Labour
A curve which shows the quantity of workers willing to work at different wage levels, it is equal to the supply curve.
Marginal Cost of Labour
The cost of employing 1 additional unit of labour, it is upward sloping and steeper than the ACL because of the cost incurred raising the wage of every worker to the new value required to attract more labour.
Trade Unions
Organisations formed to represent the interests of a group of workers, aimed at maintaining and improving workers conditions and providing job security.
Collective Bargaining
Where a union uses the threat of collective member strikes to influence firms to change something, either wage or working conditions.
Productivity Bargaining
Where unions agree to certain changes leading to increased productivity in return for increased wages or another benefit.
Trade Unions in a Perfectly Competitive Labour Market
When there is a closed shop union the trade union can control the supply of labour, but by raising the wage rate above equilibrium, they reduce the amount of labour demanded by firms, causing an excess of supply which leads to increased unemployment rates.
Closed Shop Union
Where all workers in a given profession all workers are part of only 1 trade union.
Trade Unions in a Monopsony Market
Within a monopsony, the level of employment is below equilibrium, so the action of trade unions leads to both increased wages for workers and an increase in the quantity of workers employed.
Union Density
The % of workers in a labour market who are in the trade union.
Union Legislation
Unions lost power in the 70s, banning closed shop trade unions.
Unions can only strike if 75% of the members agree.
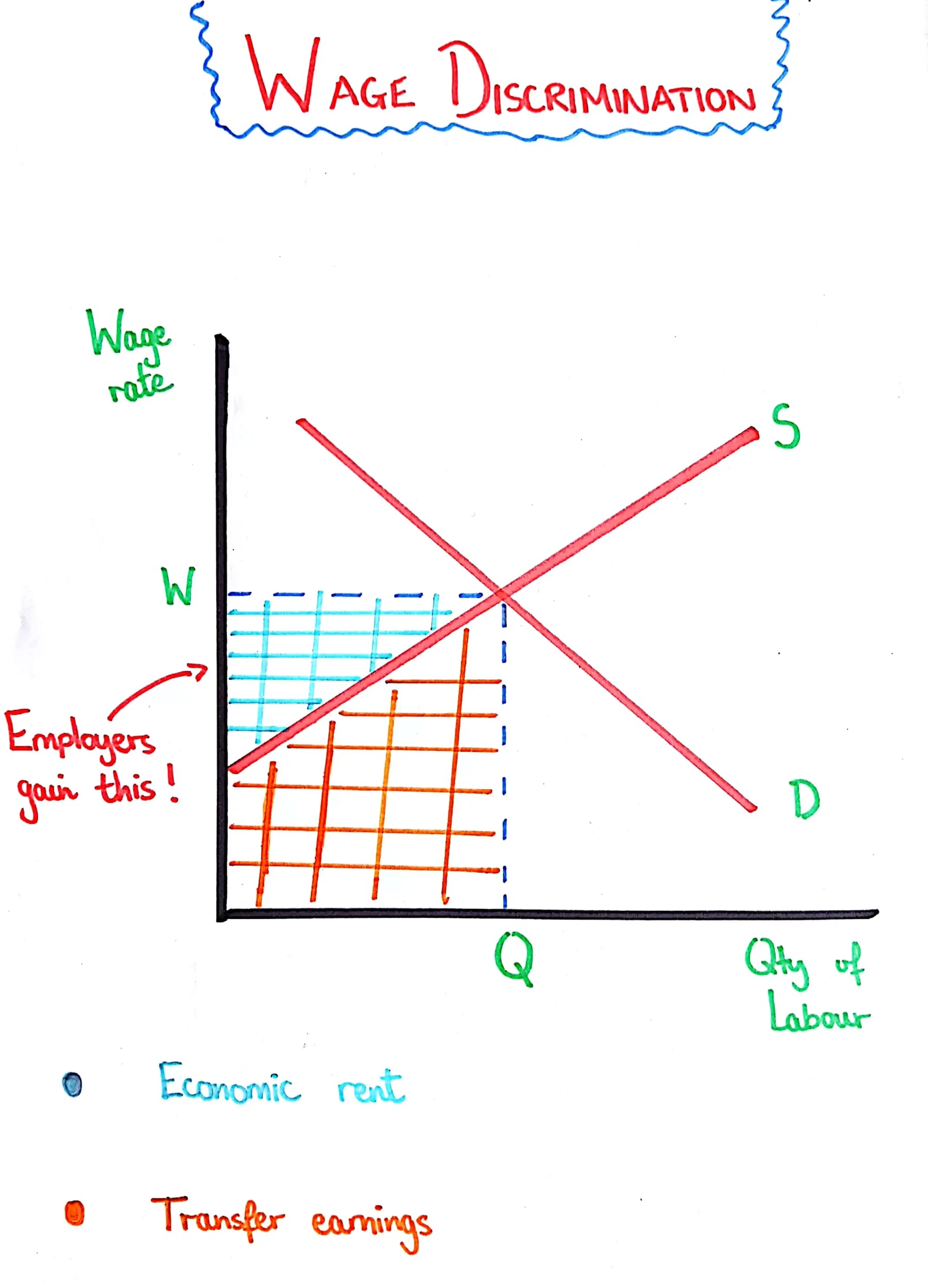
Wage Discrimination
Where different workers are paid different wage rates for performing the same job.
Emploters gain at the expense of their workers, causing trade unions to act.
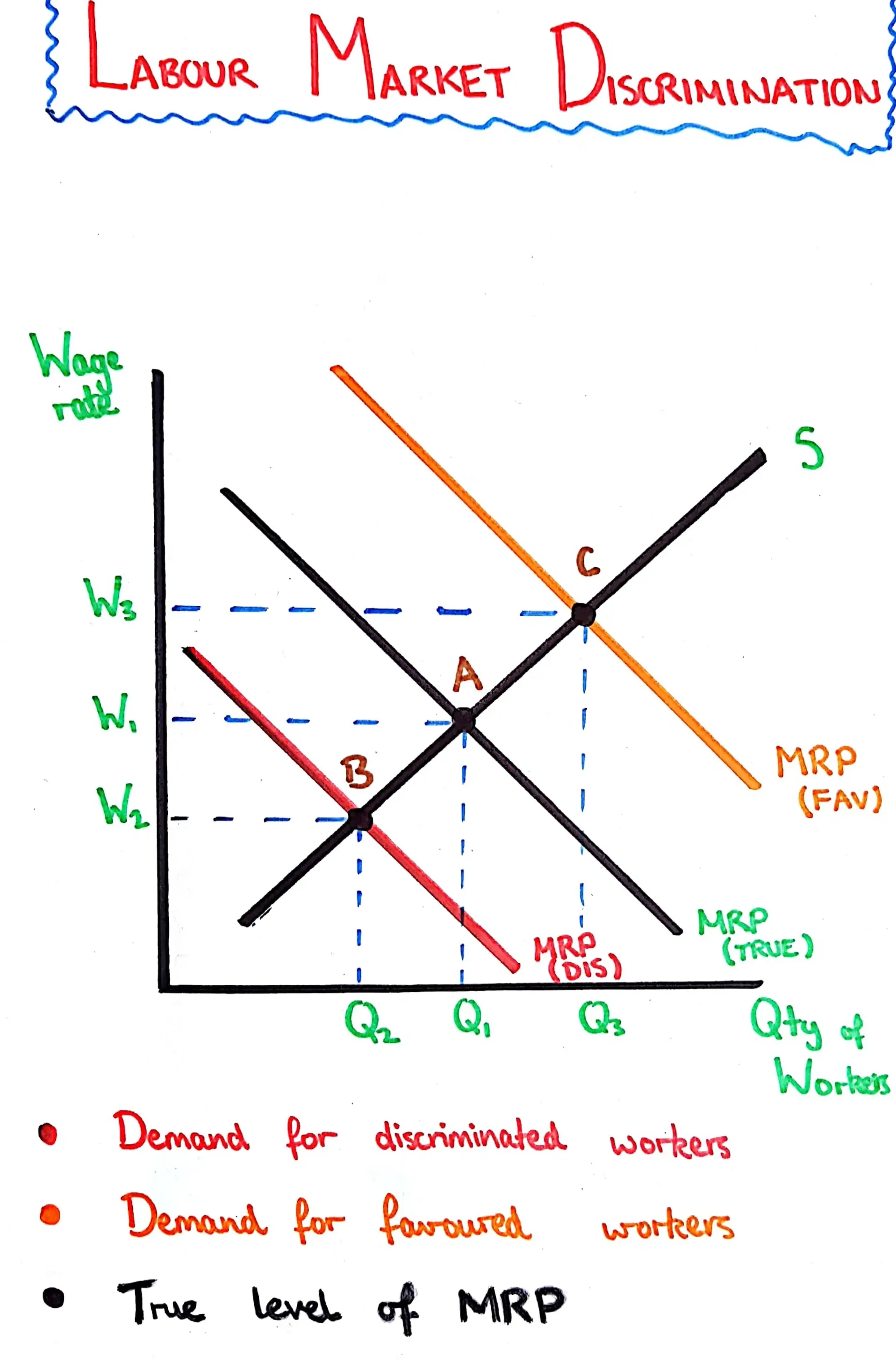
Labour Market Discrimination
When groups of workers are given different treatment because of a protected characteristic, such as Race, Gender, Sexuality, Religion, Disability or Age.
Equality Act of 2010
A law which outlaws labour market discrimination.
Gender Discrimination
The gap in pay between male and female workers, economically justified because of the movement in and out of the labour market women go through due to maternity leave.
Government Costs of Discimination
Disciminated workers require higher welfare payments and get payed less, generating less tax revenue for the government.
Discriminated workers may end up in positions they are overqualified for, a form of resource misallocation which causes a loss of efficiency.
Geographical Immobility
Where workers cannot move to a different location to get the best job for them, due to connections in the area or because of expenses and existing assets.
Occupational Immobility
Some people may find it difficult to switch between jobs and occupations, due to notice periods, retraining or age.
Labour Force Flexibility
The government may have to intervene in a labour market to overcome labour market immobility and improve flexiblity.
Contract Flexibility
A worker’s contract affects their flexibility as employers can hire or reduce the size of their firm quickly in response to a change in the market if their workers are under short term or zero hour contracts.
Zero Hour Contracts
Where an employer hires a worker without any set guarantee of hours, allowing them to only use the worker’s labour when they need it and do not have to worry about things like sick pay.
Wage Flexibility
Some employees receive performance related pay based on what they achieve.
Regional pay awards are dependent on living costs in different regions, wages in more expensive regions are higher to cover additional costs.
Wages in a Recession
During a recession some people may accept lower levels of pay as it is preferable to being unemployed.