AP Bio - Ch.15: Regulation of Gene Expression
1/9
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
10 Terms
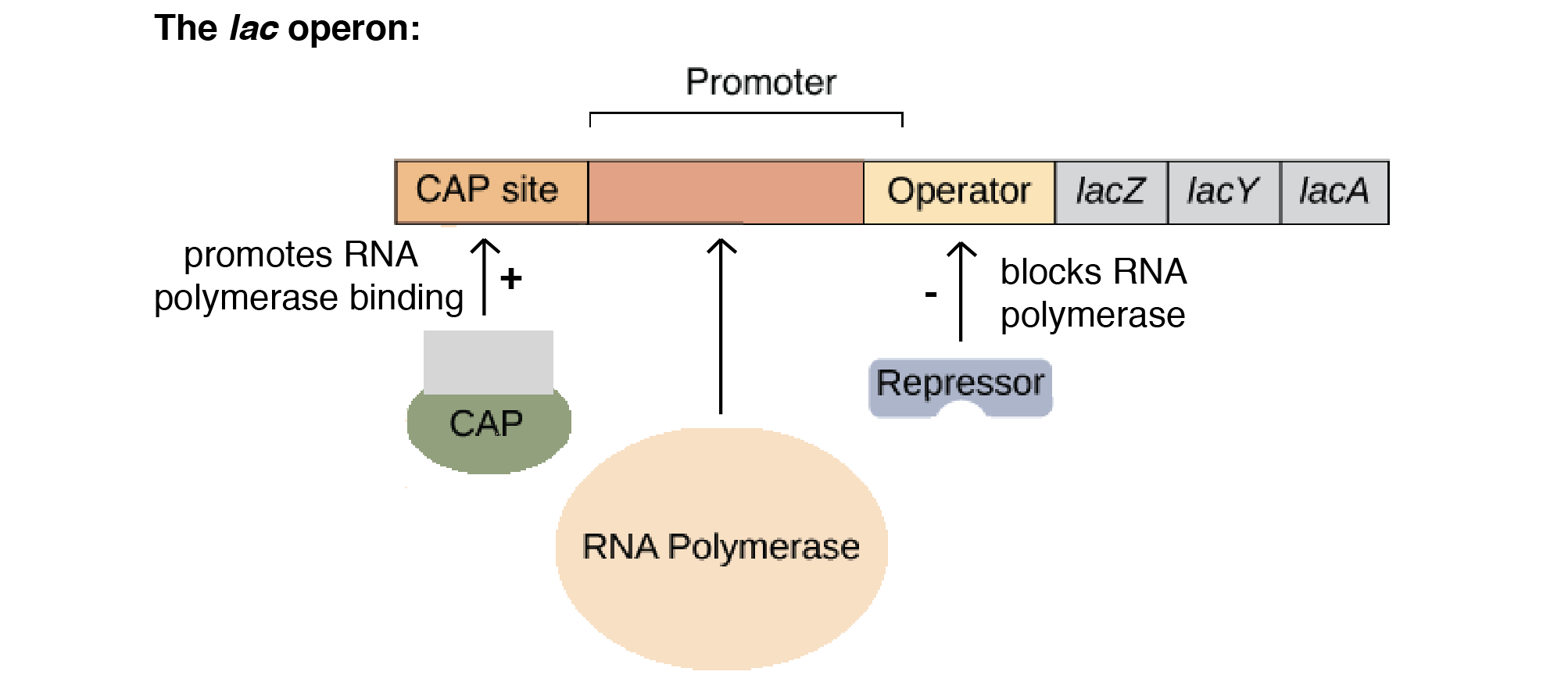
Operon Model
how Prokaryotes undergo gene regulation.
promoter — where RNA polymerase binds
operator — on/off switch for transcription
related-transcription genes
feedback inhibition
Inhibiting the transcription of a product when there is enough product already → seen in repressible operons in prokaryotes
Repressible
_____ operons are turned ON produces end-product→ anabolic → turned off
eg. trp operons
co-repressor
what the product acts as in repressible operons → activates the repressor
Inducible
____ operons are turned OFF → catabolic → can be turned on to reduce accumulated end-product
eg. lac operons
inducer
what the product acts as in inducible operons → inactivates the repressor
Control elements
also known as enhancers, they’re non-coding segments of DNA where transcription factors attach.
How Eukaryotes undergo gene regulation alongside its chromatin structure
Acetylation
the loosening of the chromatin structure → promotes transcription in Eukaryotes
Methylation
the tightening of the chromatin structure → reduces transcription in Eukaryotes
can be passed on to offspring → irreversible → epigenetic inheritance
ncRNAs
non-protein coding RNAs. Still play a crucial role in regulation gene expression (though not producing any proteins) via direct interference in the transcription process