Chapter 17 The Respiratory System Anatomy ll
1/93
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
94 Terms
Respiratory System
supplies oxygen, gets rid of carbon dioxide; Maintains homeostasis
Gas exchanger
need constant removal of carbon dioxide
Respiratory Organs
nose, pharynx (throat), larynx (voice box), trachea (windpipe), bronchi, lungs
Upper Respiratory system
located outside of thoracic (chest); nose pharynx, larynx (head cold)
Lower Respiratory System
located almost entirely in the thoracic cavity; trachea, bronchial tree, lungs (chest cold)
Respiratory Mucosa
lines the tubes of the respiratory tree, secretes mucus (goblet cells)
nose
air enters through the nostrils (external nares) into the nasal cavities lined by respiratory mucus
sinuses
lighten the skull; serve as resonant chambers to enhance the production of sound
conchae
shelf-like bones that protrude into nasal cavity on each side
Parynx
the throat; air and food pass through here on its way to the lungs and stomach
Nasopharynx (1)
uppermost part behind the nasal cavities
uvula
closes off nasopharynx during swallowing
Oropharynx (2)
behind the mouth
Laryngopharynx (3)
lowest segment; air and food passes though here on the way to the lungs and stomach
Larynx
"voice box" just below; made of cartilage; largest carilage-thyroid cartilage in the front (Adam's Apple)
Eustachian tube
connects the middle ear; equalization of air pressure
Glottis
space between vocal cords
Vocal Cords
stretch across the interior of the larynx; muscles can pull on cords to make them tense or relax
Tense vocal cords
high pitch
Relaxed vocal cords
low pitch as air passes over them
Epiglottis
cartilage that off the larynx during swallowing (does not work when unconscious); prevents food from entering trachea
Trachea
"windpipe"; only pathway for the air from the larynx; can feel it by feeling the throat about one inch above the sternum; mad of C-Shaped cartilage rings
Bronchi
branch off the trachea, one to each lung
Bronchus
Branches into secondary bronchi leading to bronchioles
Bronchioles
branch off the bronchi; end in clusters of microscopic alveolar sacs, the walls which make up the alveoli
Alveolar Ducts
Branches off the bronchioles into the alvolar sacs (like the main stem of a bunch of grapes)
Alveolar Sacs
group of air sacs that resemble a cluster of grapes
Alveoli
Air sacs (comes in contact with capillary)
surfactant
covers inside of alveoli; reduces surface tension to keep alveoli from collapsing and permit easy air movement in and out of sacs
Lungs
function is breathing; each lobe acts separately and doctors will remove lobes as necessary
Right Lung
3 lobes
Left Lung
2 lobes
Pleura
covers the outer surface of the lung and lines the inner surface of the rib cage
Inspiration
inhalation; moving air into the lungs
Expiration
exhalation
Quite Expiration
ordinarily a passive process; passive as inspiratory muscles just relax
Forced expiration
expiratory muscles contract
gas exchange
The function of the respiratory system is to serve as a:
Larynx, pharynx, and bronchi
Which of the following is an organ of the respiratory system?
nasopharynx, oropharynx, and laryngopharynx
The pharynx has a portion known as the:
Larynx (voice box)
The "adam's apple" is part of the:
oropharynx
The palatine tonosils are located in the:
During inspiration:
the instpiratory muscles (diaphragm and external intercostals) are active
residual volume
The air that remains in the lungs after the most forceful expiration is:
medulla and pons
Respiratory control centers are located in the:
laryngitis
A disorder of the upper respiratory tract is:
chronic bronchitis, emphysema, and asthma
Which of the following is a common disorder in chronic obstrucitve pulmonary disorders?
eupnea
normal breathing

apnea
breathing stops for a brief period; this happens to many in their sleep
hyperventilation
rapid and deep respirations

hypoventilation
slow and shallow respiration

Dyspnea
labored or difficult respirations (associated with hypoventilation)
Orthopnea
Dyspnea relieved by moving into an upright or sitting position
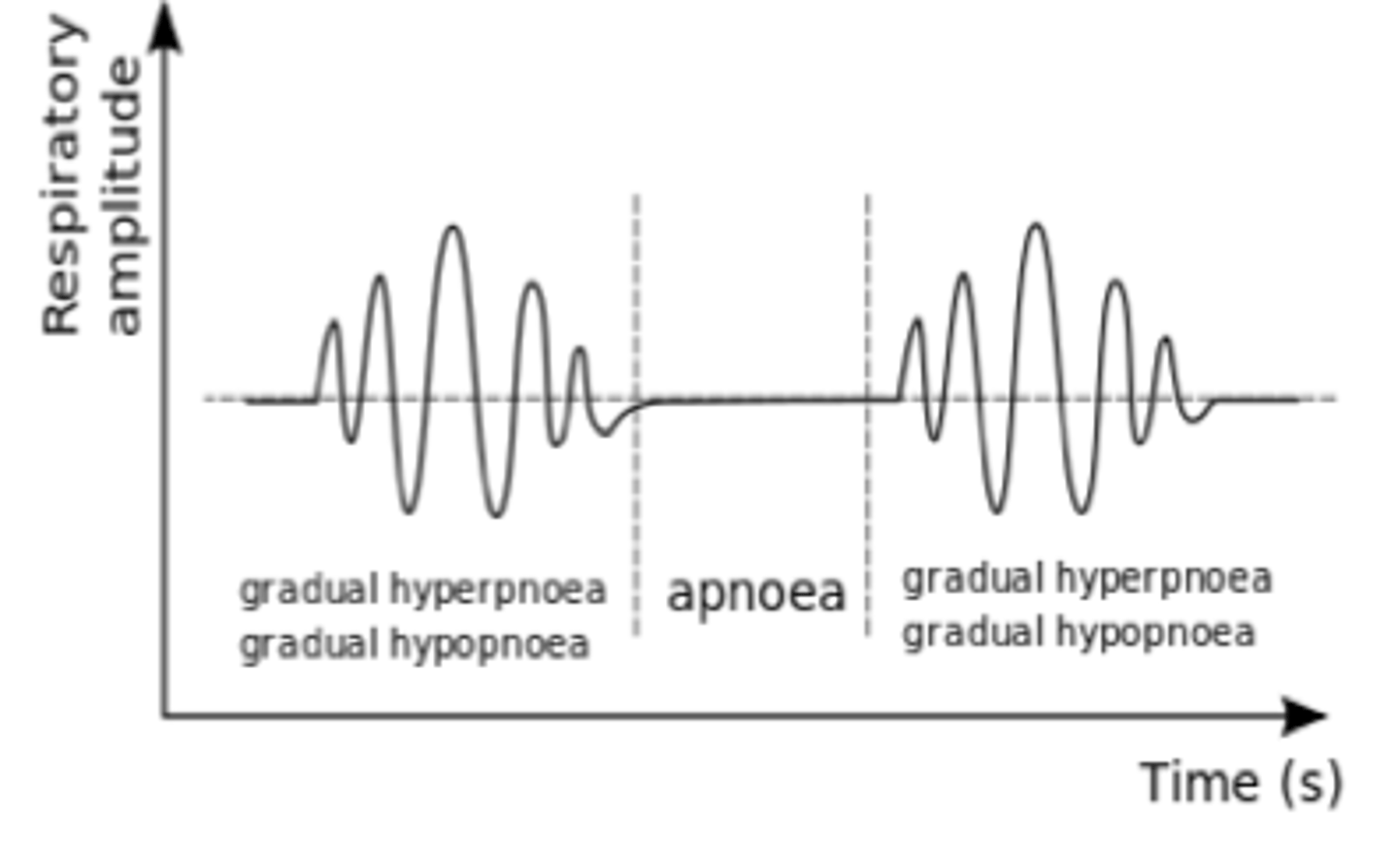
Cheyne-Strokes
person alternating between apnea and hyperventilation associated with critical conditions
hiccup
sudden spasm of diaphragm; at the beginning of the inspiration the glottis suddenly closes causing the sound; could be caused by irritation of phrenic nerve, the stomach, or by pressure on parts of the brain
Cough reflex
protection of lower tract; you inhale, then the epiglottis and vocal cords trap the air in the lungs until you forcefully expel it with the source of irritation; Productive (cough up mucus)
sneeze
air trapped then expelled mainly through the nasal passages
SIDS
Sudden Infant Death Syndrome;
Upper Respiratory Infection
so easy to get because we breathe in pathogens; may lead to sinusitis or middle ear infections
Rhinitis
Inflammation and swelling of the nasal mucosa; red, itchy, "runny nose"; can be caused by common cold virus or influenza, nasal irritants, and allergic reactions; can only treat the symptoms
Infectious Rhinitis
common cold
Allergic Rhinitis
Hay fever (not contageous)
Nasal Sprays
Should only be used for a few days because of the "rebound effect", in which the congestion comes back worse (people can get addicted to this)
Pharyngitis
Inflammation or infection of the pharynx (sore throat); can be caused by a virus or bacteria
Laryngitis
Inflammation of mucous lining of the larynx; swelling of vocal cords causes los of voice or "horseness"
Epiglottitis
Life-threatening; caused by Haemophilus influenza type B (Hib) infection; now have a vaccine for this; rare today
Croup
Non-life-threatening; seen in children under 3; caused by pharainfluenza viruses; barklike cough and labored inspirations
Deviated Septum
nasal septum strays from the midline and will block the nasal cavity; surgery can correct; anatomical disorder
Epistaxis
nosebleed; caused by a bump to the nose, rhinitis, or in the winter when the air is dry and the nasal cavity becomes so dry that it cracks easily, brain injury, or other causes; can be cauterized or have the vessels burnt shut
respiratory distress
relative inability to inflate the alveoli
infant respiratory distress syndrome (IRDS)
leading cause of death in premature infants resulting from lack of surfactant production in alveoli; treatment involvs delivering air under pressure and applying surfactant into the baby's airway by a tube
adult respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS)
Impairment or removal of surfactant; Inhalation of foreign substances like water, vomit, smoke, or chemical fumes (getting your stomach pumped)
Pleurisy
Inflammation of the parietal pleura; stabbing pain and difficulty in breathing; lining rubs together; can be caused by infections or tumor
Pneumothorax
puncture to the chest wall or rupture makes a hole in the pleura; air rushes into the space and the pressure causes the lung to collapse; fixed by sucking air back out the pluera
Hemothorax
blood in pleural space
Bronchitis
inflammation of the bronchi; most often caused by an infection but can be caused by smoke or chemicals; acute or chronic
pneumonia
inflammation of the lungs inwhich the alveoli and bronchi get plugged with thick fluid; High fever, chills, headache, cough, chest pain; can be caused by a virus or bacteria; virus, have to let it run its course; Bacteria-some forms are fatal; antibiotics can be given
Tuberculosis (TB)
bacterial infection in which protective capsules grow around the bacteria; get it by inhaling or swallowing; can be treated but can cause death; symptoms may include fatigue, chest pain, weight loss, fever, lung hemmorrhage, dyspnea
Influenza
highly contagious respiratory infection; can be severe and fatal
Obstructive pulmonary disorders
obstructs airways, obstructing inspiration and expiration; acute obstructing can be immediately life-threatening
chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD)
can develop from pre-existing obstructive condition; chronic difficulties empting the lungs and pyperventilated chest; productive cough and intolerance of activity
Emphysema
walls of alveoli break down and form large spaces; surface area is reduced; breathing is very difficult; no cure, can cause death
asthma
bronchial air passages narrow due to an allergic, exercise, stress, or other irritants; recurring spasms of the airways accompanied by edema and mucous production
cystic fibrosis
mucus clogs air passages; inherited, mostly in caucasians 1/1600 people; no cure, usually fatal
Transport of gases by blood
concentration of carbon dioxide is higher in the blood capillaries so carbon dioxide diffuses from the blood into the alveoli
tidal volume
volume of air that enters and leaves the lungs during normal breathing
expiratory reserve volume
maximun volume that can be exhaled after exhaling the tidal volume
inspiratory reserve volume
maximum volume of air that can be forcibly inhaled over and obe a normal inspiration
vital capacity
the largest amount of air we can exhale out after deepest possible inhalation
total lung capacity
all of the air in the lungs
hypothalamus
Emotional factors acting through the __ can affect rate of breathing
What to do if someone has hyperventilated
1) calm them down and tell them to just concentrate on breathing very slowly (this allows carbon dioxide levels to build back up)
2) Have them breathe into a paper bag (they breathe carbon dioxide back in which will build the level back up)
stratified squamous epithelium
lines nostrils, vocal folds, pharynx; protective function
Simple squamous epithelium
line alveoli; facilitates gas exchange