VM 585 Diagnostic Imaging Midterm
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
44 Terms
How should the pelvic limbs be positioned for a VD abdominal radiograph when evaluating urinary structures?
Flexed and allowed to rest in a natural, relaxed position (frog leg)
What structures are best evaluated on a lateral caudal abdominal radiograph with pelvic limbs pulled cranially?
Urethral region and os penis
What additional radiographic technique can be used to differentiate cystic calculi from superimposed bowel contents on a lateral abdominal radiograph?
Compression shot
What radiographic changes are associated with retroperitoneal fluid or retroperitonitis?
A. Loss of normal retroperitoneal detail
B. Poor visualization of the kidneys
C. Heterogenous soft tissue opacity with a streaked appearance
D. All of the above
D.
What are differentials for retroperitoneal fluid?
Hemorrhage
Edema/transudation
Uroabdomen
Cellulitis
Neoplasia
Name three differential diagnoses for hemorrhagic retroperitoneal fluid in dogs or cats.
Coagulopathy (rodenticide vs envenomation vs ITP)
Trauma
Ruptured neoplasia (renal vs adrenal)
What radiograph projection is more accurate for assessment renal enlargement or reduced size?
VD — kidneys remain in a consistent position and there is less magnification
Normal renal length in dogs has been described in relationship to the length of the ________ vertebral body
L2
Which of the following is TRUE regarding normal feline abdominal radiographs?
A. The kidneys are never visible on lateral radiographs.
B. Fat opacity at the renal hilus is a normal finding in many cats.
C. The liver always obscures the right kidney on VD views.
D. The adrenal glands are visible on lateral radiographs.
B.
What does ‘big kidney, little kidney syndrome’ indicate?
One kidney fibrotic/atrophic, other kidney compensatory hypertrophic
How does acute renal disease differ radiographically from chronic renal disease?
AKI: normal to mildly enlarged, smooth outline
Chronic: small kidney, irregular outline
What is the most common ultrasound abnormality seen in both acute and chronic kidney disease?
Increased renal echogenicity
Which renal neoplasm typically causes bilateral renal enlargement?
Lymphoma
What infectious disease can cause either smooth or irregular margin renal enlargement?
A. Leptospirosis
B. Rocky Mountain Spotted Fever
C. FIP
D. Leishmaniasis
C.
Which of the following is NOT a differential for irregularly marginated kidneys?
A. Renal abscess
B. Renal hematoma
C. Polycystic kidney disease
D. Subcapsular hematoma
D.
What does distention of the renal pelvis and pelvic diverticula indicate on ultrasound?
Hydronephrosis
You perform an AFAST on a cat in-hospital receiving IV fluids and notices mild dilation of the renal pelvis with normal cortical thickness. This finding is most consistent with:
A. Hydronephrosis
B. Pyelonephritis
C. Pyelectasia
D. Renal lymphoma
C.
A dog comes in as a hit by a car and has been stabilized. Three-view abdominal radiographs are taken. You note:
Loss of serosal detail in the caudal abdomen
Urinary bladder cannot be visualized
What is the top differential?
Bladder rupture with uroabdomen
What other imaging modalities or procedures could help identify urinary bladder location when it is not radiographically visible?
Abdominal ultrasound
Contrast cystography (retrograde, rarely antegrade/normograde)
Urethrography
T/F: The normal uterus and ovaries are not seen radiographically in the bitch or queen
True
An intraabdominal retained testicle can be visualized on abdominal radiographs if:
neoplastic transformation has occurred.
Which of the following features helps differentiate an enlarged uterus from loops of small intestine or colon?
A. Presence of gas within the structure is common in both uterus and intestine.
B. The uterus often stays peripheral along the body wall, whereas intestinal loops are more central.
C. Mild distension makes differentiation easy.
D. End-on loops of intestine rarely appear as circular masses.
B. — gas rare in uterus
On lateral radiographs, the uterine body will show as a tubular soft tissue stricture dorsal to _________ and ventral to _________
urinary bladder
colon
What is the most common uterine neoplasia in dogs?
Leiomyoma
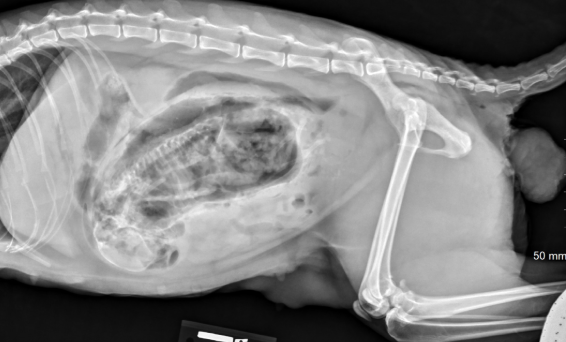
What fetal position is observed that would result in dystocia?
Breech
What organs would be displaced with marked prostatomegaly?
Bladder, colon and body wall
Which radiographic finding is most supportive of prostatic malignancy in a neutered male dog?
A. Symmetric prostatic enlargement
B. Irregular prostatic margins
C. Prostatic mineralization
D. Mild dorsal displacement of the urinary bladder
C.
What is the most common prostatic disorder is:
benign prostatic hypertrophy
Which of the following are differentials for asymmetric prostate enlargement? Select all that apply
A. BPH
B. Prostatitis
C. Neoplasia
D. Cysts
C and D
Prostatic size that exceeds _______% of the distance from the pubis to the sacral promontory is suggestive of a mass lesion
90%
Positive contrast that is ultrasound guided into renal pelvis in cases where IV contrast is contraindicated
Percutaneous pyelogram
IV positive contrast for renal and ureteral evaluation
Excretory urogram (IV pyelogram)
This type of tumor is associated with hyperestrogenism is male dogs
Sertoli cell
T/F: Cryptorchidism is usually unilateral, with the right testis affected 2x more than the left
True
When is a retained testicle most likely to be identified radiographically?
When it is neoplastic
Which secondary radiographic finding may support the presence of a retained testicle?
A. Cranial displacement of both kidneys
B. Caudal displacement of the ipsilateral kidney
C. Ventral displacement of the colon
D. Dorsal displacement of the bladder
B.
Which feature helps differentiate a retained testicle from other abdominal soft-tissue masses?
A. Fixed position regardless of patient movement
B. Presence of gas
C. Marked mobility with changes in body position
D. Bilateral kidney displacement cranially
C.
A perineal hernia in dogs is typically due to failure of which of the following structures?
A. Rectal mucosa
B. Muscular pelvic diaphragm
C. Urinary bladder wall
D. Sacroiliac ligament
B.
How does a Sertoli cell tumor cause feminization syndrome in male dogs?
By secreting aromatase, which converts androgens to estrogen
Obstruction at which of the following sites is most likely to cause hydronephrosis in a dog or cat?
A. Distal urethra only
B. Renal pelvis or ureter
C. Urinary bladder body only
D. Proximal urethra
B. — also urinary bladder trigone
A 10-year-old male neutered Labrador presents for lethargy and vomiting for 3 days. Chest radiographs reveal pleural fluid and a diffusely narrowed trachea. Which of the following should be high on your differential list?
A. Rodenticide toxicity or other coagulopathy
B. Congestive heart failure
C. Primary tracheal collapse
D. Pulmonary edema secondary to pneumonia
A.
The most common prostatic neoplasia in neutered dogs
Adenocarcinoma
The most common location for transitional cell carcinoma in dogs and cats is:
urinary bladder (trigone)
Which of the following imaging modalities would be best to confirm a suspected uroabdomen in a dog or cat?
A. IV pyelogram
B. Abdominal ultrasound
C. Urethrography
D. Cystography
A.