Topic 5 - Forces (Without pressure or momentum)
1/53
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
54 Terms
What are vectors?
Vector quantities have a magnitude and direction
Examples of vector quantities?
Force
Velocity
Displacement
Acceleration
Momentum
What are scalar quantities?
Have a magnitude but no direction
Examples of scalat quatities?
Speed
Distance
Mass
Temperature
Time
What is a force?
Is a push or pull on an object that is caused by it interacting with something
What is a contact force?
When 2 objects have to be touching for a force to act
Examples of contact forces?
friction
tension in ropes
normal contact force
air resistance
What are non contact forces?
When the objects do not need to be touching for a force to act
Examples of non-contact forces?
Magnetic force
Gravitational force
Electrostatic force
What is mass?
Amount of “stuff” in an object - this will have the same value anywhere on the universe?
What is weight?
Weight is the force acting on an object due to gravity
What does the weight of an object depend on?
Depends on the strength of the gravitational field.
What is the unit for weight? How can weight be measured?
Newtons. Newtonmeter
What is the resultant force?
The overall force on a point or object
What does 1NM = ?
1 Joule of work
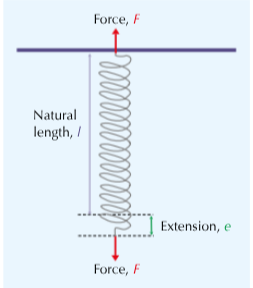
3 types of elasticity?
Stretch
Compress
Bend
What do you need to do these types of elasticity?
You need more than one force acting on the object
What is elastic deformation?
An object that can go back to its original shape and length after the force has been removed. Objects that can be elastically deformed are called elastic objects.
What is inelastic deformation?
Doesn’t return to its original shape and length after the force has been removed
What is the limit of proportionality on a graph?
When the line stopes being linear becomes a curve
Typical speed for a person walking?
1.5 m/s
Typical speed for a person running?
3 m/s
Typical speed for a person cycling?
6 m/s
Typical speed of a car?
25 m/s
Typical speed of a train?
55 m/s
Typical speeds for a plane?
250 m/s
Difference between distance and displacement?
Displacement is a vector - has a direction
Distance is a scalar - doesn’t have a direction
Difference between speed and velocity?
Speed is just how fast you’re going
Velocity is speed in a given direction
You can still have a constant speed, but a changing velocity
Speed of sound in the air?
330 m/s
How can speed of sound be affected?
What medium the sound waves are travelling through
How can wind speed be affected by?
Temperature
Atmospheric pressure
Large buildings or structures nearby
How can acceleration be defined as?
The change in velocity in a certain amount of time
What does the gradient of a distance-time graph signify?
Speed
What do flat sections of the distance-time graph?
The object is stationary
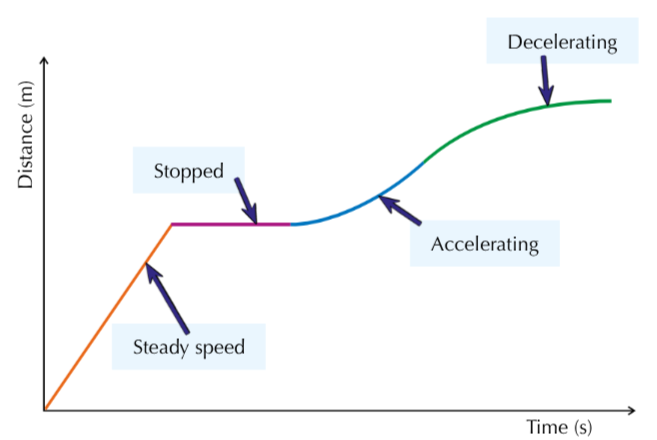
What do straight uphill sections mean on a distance-time graph?
Object is travelling at a steady speed
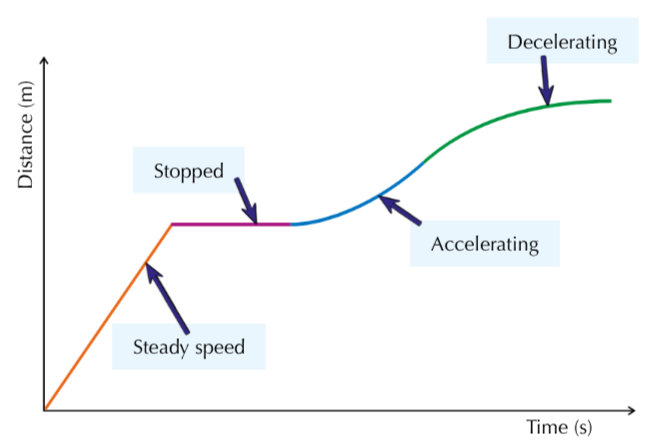
What do curves on a distance-time graph signify?
Acceleration or deceleration
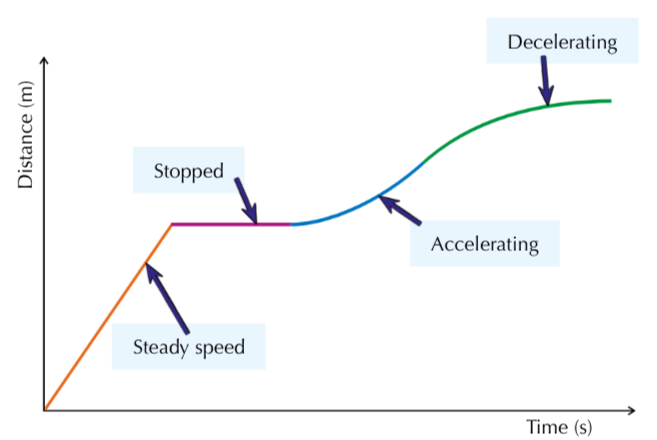
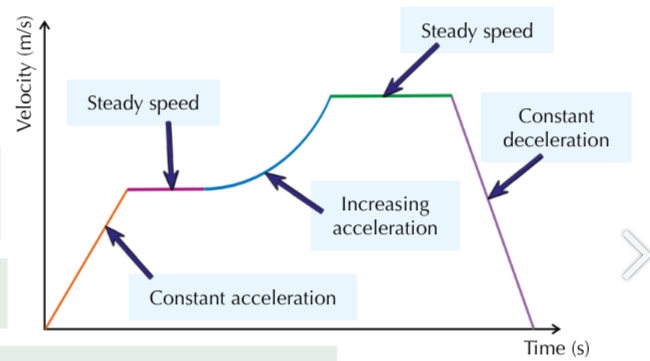
What does the gradient of a velocity-time graph signify?
Acceleration
What do flat sections signify on a velocity-time graph?
Steady speed
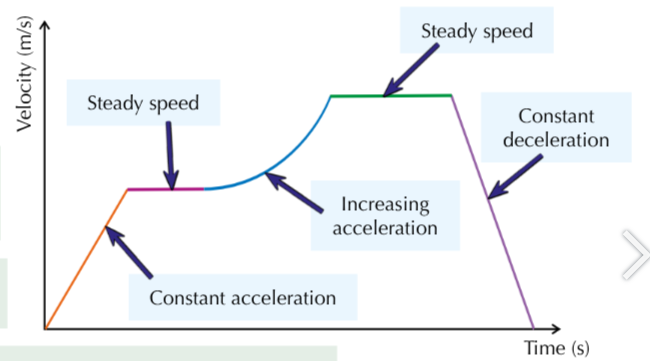
What does a curve mean on a velocity-time graph?
Changing acceleration
What is the area under the velocity - time graphs equal to?
Distance travelled in that time interval
When does friction occur?
When two surfaces are in contact, or when an object passes through a fluid
How to reduce drag?
Make it more streamlined
What is terminal velocity?
When the resultant force = 0 - when the acceleration force is equal to the frictional force
What does newtons 1st law state?
If the resultant force on a stationary object is 0, the object will remain stationary. If the resultant force on a moving object is zero, it’ll just carry on moving at the same velocity.
What does Newton’s Second law state?
Acceleration is directly proportional to the resultant force (F = ma)
What is an object’s inertia mass?
Measures how difficult it is to change the velocity of an object
What does newton’s third law state?
When two objects interact, the forces they exert on each other are equal and opposite
What are stopping distances?
Stopping distance = thinking distance + braking distance
What is the thinking distance?
How far the car travels during the driver’s reaction time
What is the braking distance?
The distance taken to stop under the braking force
What are the factors of tihnking distance?
Speed - the faster your going, the further you’ll travel
Reaction time
Tiredness
Drugs/alcohol
Distractions
What is braking distance affected by?
Your speed
Weather or road surface
Condition of tyres
How bood your brakes are
What is Hooke’s law?
Force is directly proportional to stretch
Different components of spring (think of diagram)