108 exam 3
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/86
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 3:54 PM on 4/10/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
87 Terms
1
New cards
carbohydrate ending
\-ose
2
New cards
chirality
describing how molecules are connected
3
New cards
A chiral
requires four groups (different) around the carbon
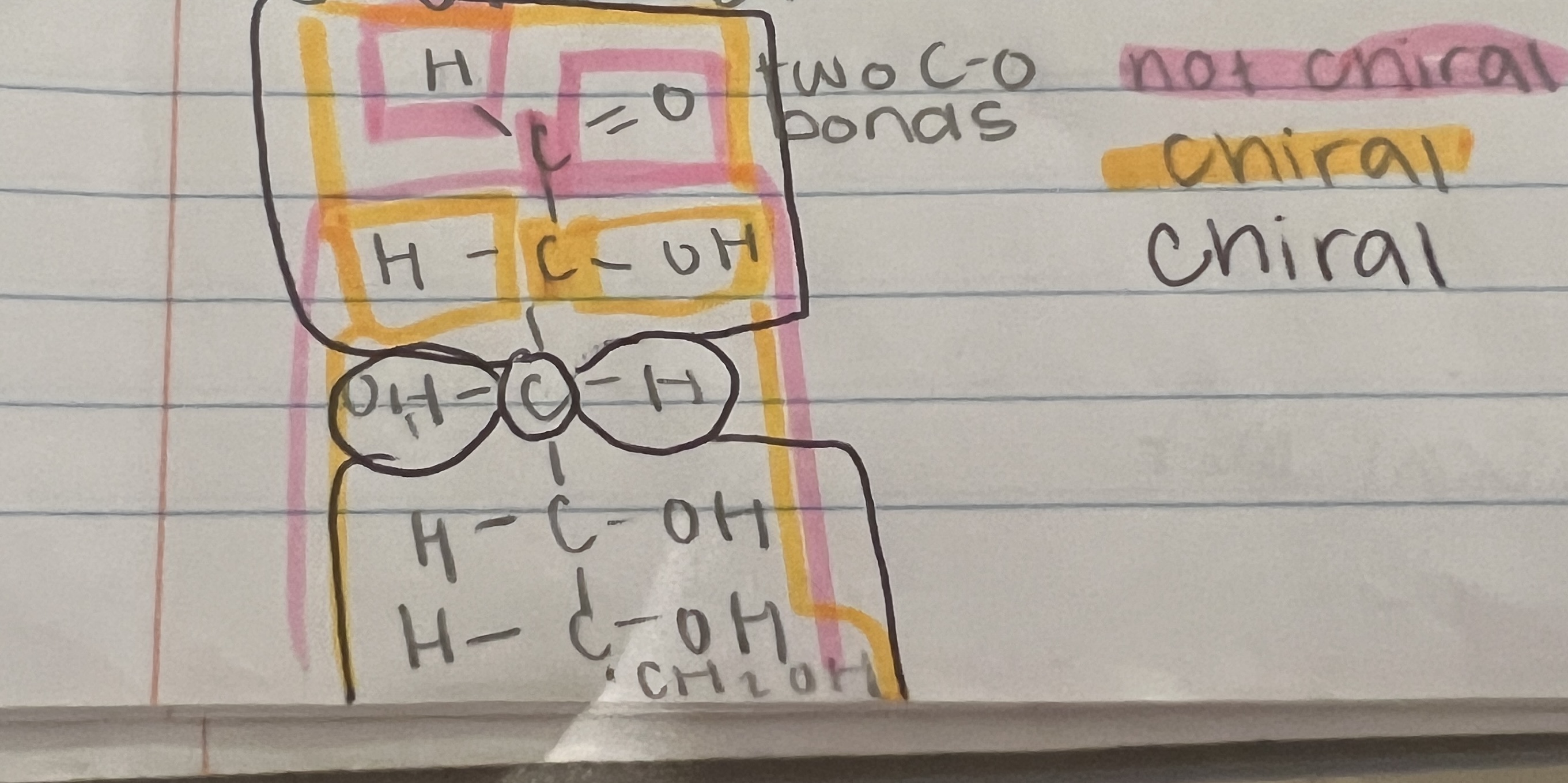
4
New cards
L sugar
alcohol group on left side
5
New cards
D sugar
alcohol group on right side
6
New cards
aldehyde + alcohol=
hemiacetal
7
New cards
five common monosaccharides
1. fructose
2. galactose
3. glucose
4. ribose
5. deoxyribose
8
New cards
Negative Delta G=
exergonic (energy is released)
9
New cards
Positive Delta G=
endergonic (energy is made)
10
New cards
catabolism
breaking down molecules into smaller parts
ex. digestion
ex. digestion
11
New cards
anabolism
build up of molecules
12
New cards
oxidation
gain of C-O bond and loss of C-H bond
13
New cards
Reduction
Gain of C-H bond loss of O-H bond
14
New cards
Co-enzyme chart
…
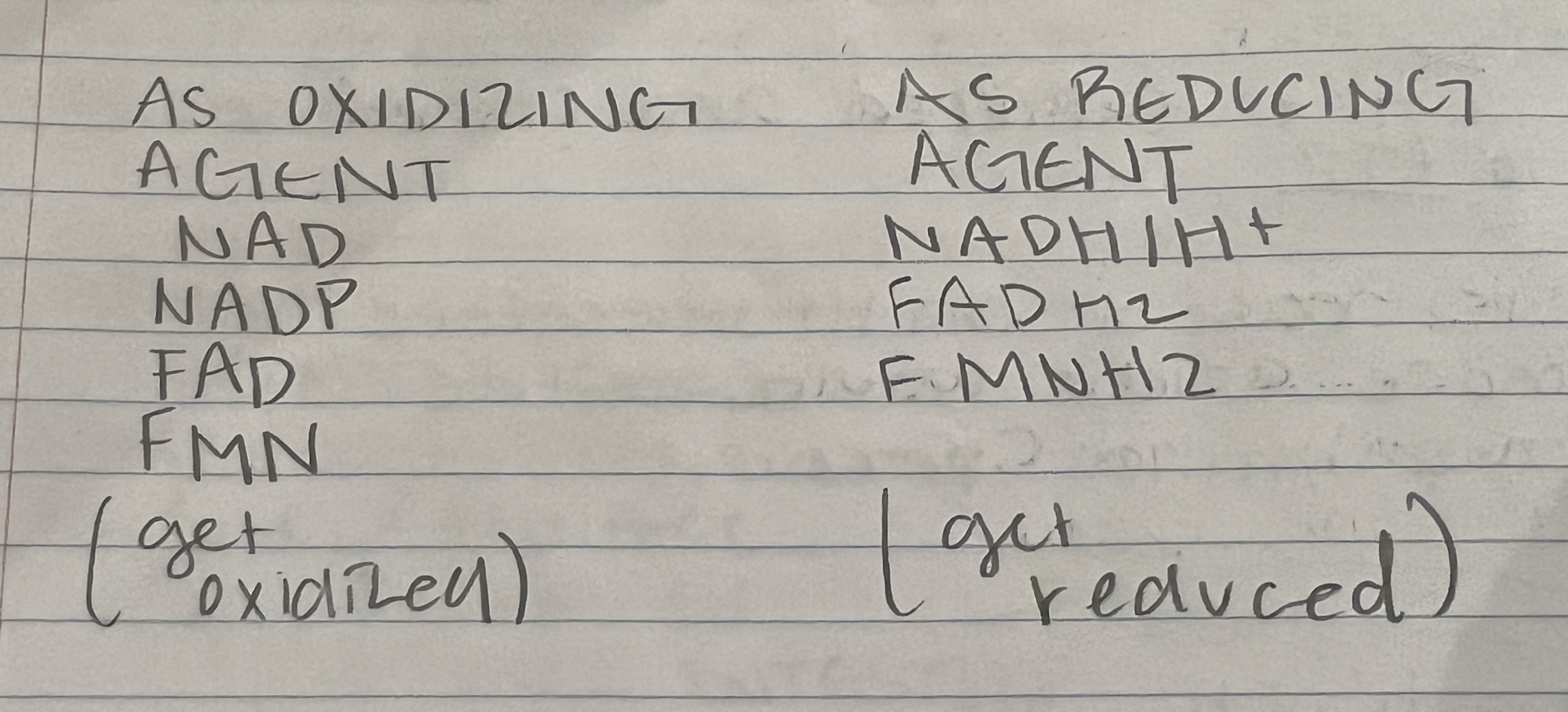
15
New cards
what three monosaccharides are naturally absorbed by the body
1. fructose
2. glucose
3. galactose
16
New cards
where does fructose originate
plants
17
New cards
where does glucose originate
plants
18
New cards
where does galactose originate
lactose
19
New cards
where does ribose originate
backbone of RNA
20
New cards
where does deoxyribose originate
backbone of DNA
21
New cards
hemiacetal + alcohol =
acetal
22
New cards
Hemiacetal
OH
|
C-OR
|
C-OR
23
New cards
disaccharides
two monosaccharides combined
24
New cards
Maltose consists of
Glucose + glucose
25
New cards
lactose consists of
galactose + glucose
26
New cards
sucrose consist of
fructose + glucose
27
New cards
cellulose structure
horizontal lines
28
New cards
starch (amylose) structure
squiggly horizontal
29
New cards
starch (amylopectin)
branches
30
New cards
glycogen structure
branched in circular formation
31
New cards
metabolism
process of energy created from breakdown of food
32
New cards
coenzymes are responsible for
making a reaction occur
33
New cards
products of citric acid cycle
* reduced coenzymes
* GTP
* GDP
* GTP
* GDP
34
New cards
Why is the intermembrane space acidic
abundance of H+
35
New cards
Mitochondrial matrix (dummy terms)
1. reduced coenzymes enter electron transport chain (mitochondrial matrix)
2. H+ is removed and passed into intermembrane
3. remaining electrons post removal become water
4. H+ is captured (step 2) and stored in ADP/ATP
36
New cards
coenzymes are made from
oxidation and reduction
37
New cards
GTP/GDP is made from
phosiphication or isomerfication
38
New cards
what is the function of H+ in ATP synthesis?
H+ becomes ATP
39
New cards
glycolysis
conversion of glucose to pyruvate
40
New cards
gluconeogenesis
synthesis of glucose from amino acids, pyruvate, and other noncarbohydrates
41
New cards
glycogenesis
synthesis of glycogen from glucose
42
New cards
glycogenolysis
breakdown of glycogen to glucose
43
New cards
pentose phosphate pathway
conversion of glucose to five carbon sugar phosphate
44
New cards
what happens when there is more glucose in the body than needed?
body will create glycogen
45
New cards
Carbohydrate digestion
\*carbohydrates are eaten- Mouth/saliva
\*polysaccharides, sucrose, lactose, and maltose
\-stomach
\-small intestine
\*monosaccharides created
\*monosaccharides enter blood stream- absorbed through lining
\*polysaccharides, sucrose, lactose, and maltose
\-stomach
\-small intestine
\*monosaccharides created
\*monosaccharides enter blood stream- absorbed through lining
46
New cards
1 molecule of NADH= ____ ATP
3
47
New cards
1 molecule of FADH2= ____ ATP
2
48
New cards
Body’s reaction to starvation
1. breaks down glycogen (stored glucose) to glucose through glucagon
1. if starvation continues…
2. amino acids from proteins
1. if starvation continues…
1. switches to lipids
49
New cards
glucagon
hormone to make glycogen to glucose
50
New cards
Step 1
ATP-ADP (-2 ATP)
51
New cards
step 5
two glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate’s are made
52
New cards
step 6
reduced coenzymes are formed from glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate (+2NADH)
53
New cards
step 7
ADP-ATP (+2ATP)
54
New cards
step 9
H2O is removed
55
New cards
step 10
ADP-ATP (+2ATP) resulting in +2 pyruvate
56
New cards
importance of steps 6-10
two molecules of glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate therefore two products are made in each step
\
Ending with- 2 NADH, 2 ATP, 2 Pyruvate
\*\*\*\* all for one molecule of glucose broken down!!!
\
Ending with- 2 NADH, 2 ATP, 2 Pyruvate
\*\*\*\* all for one molecule of glucose broken down!!!
57
New cards
glucagon in diabetes
Raises blood sugar
makes glycogenolysis happen: break down glycogen
makes glycogenolysis happen: break down glycogen
58
New cards
insulin in diabetes
lowers blood sugar
helps glucose enter cells, also helps with glycolysis
helps glucose enter cells, also helps with glycolysis
59
New cards
hypoglycemia
low blood sugar due to too much insulin
60
New cards
hyperglucemia
high blood sugar due to low insulin
(important symptoms to be aware of: frequent urination, weight loss, and thirst)
(important symptoms to be aware of: frequent urination, weight loss, and thirst)
61
New cards
type 1 diabetes
no insulin produced
62
New cards
type 2 diabetes
insulin resistant
63
New cards
classification of lipids: Wazes
ester- eaten by humans
64
New cards
classification of lipids: triacylglycerols
3 chain carbon with 3 fatty acids attached- eaten by humans
65
New cards
classification of lipids: glycerophospholipids
fatty acid is replaced with phosphate group- eaten by humans
66
New cards
three main functions of lipids
1. storage of energy
2. cell structure
3. chemical messanger
67
New cards
saturated solid or liquid
solid
68
New cards
unsaturated solid or liquid
liquid
69
New cards
saturated lipid
no double bond, as many H as possible
Shape: horizontal line
Shape: horizontal line
70
New cards
unsaturated lipid
double bond
shape: horizontal Curve
shape: horizontal Curve
71
New cards
why do saturated lipids have a higher melting point
their structure (horizontal line) is able to compact molecules together created a higher intermolecular force
72
New cards
hydrogenation of lipids
process of converting oil to saturated lipid
Structurally- double bond is removed
\*Not possible to perform cis/trans
Structurally- double bond is removed
\*Not possible to perform cis/trans
73
New cards
lipid
fat
74
New cards
saponidication
\*\*outside of body
base catalyzed + fatty acid= soap
base catalyzed + fatty acid= soap
75
New cards
three types of steroids
1. cholesterol (structure to cell)
2. bile acids (digest lipid)
3. hormones
76
New cards
lipid bilayer explained
Water loving (polar) \*hydrolyzed
\--------------------------------
water disliking (non-polar) \*hydrophobic
\--------------------------------
Water loving (polar) \*hydrolyzed
\--------------------------------
water disliking (non-polar) \*hydrophobic
\--------------------------------
Water loving (polar) \*hydrolyzed
77
New cards
why are lipids good for pharmaceuticals
water soluble drugs make it easy to transport within body
78
New cards
Eicosanoids
short lived chemical messengers
79
New cards
Eicosanoids- leukotriene shape
fish hook
80
New cards
Eicosanoids- prostaglandin shape
Half ovulated circle with ring structure
81
New cards
lipoprotein is labeled by
density
ex.
serum albumin= low (stored in liver)
very low density VLD (liver)
low density LDL(cholesterol in liver)
high density HDL (cholesterol in dead cells)
* excludes chylomicrons (lipids in diet)
ex.
serum albumin= low (stored in liver)
very low density VLD (liver)
low density LDL(cholesterol in liver)
high density HDL (cholesterol in dead cells)
* excludes chylomicrons (lipids in diet)
82
New cards
LDL good or bad
bad
83
New cards
HDL good or bad
good
84
New cards
three processes when fatty acids enter cell
1. activate
2. transport
3. oxidize
85
New cards
bioxidation
break down of carbon chain by 2 carbons at a time
86
New cards
2 carbons= 1 ____
Acetyl-COA
87
New cards
Beta oxidation (dummy version)
1. double bond added
2. water added to double bond to yield alcohol
3. alcohol is oxidized into a ketone
4. c-c is broken down to shorten fatty acid chain