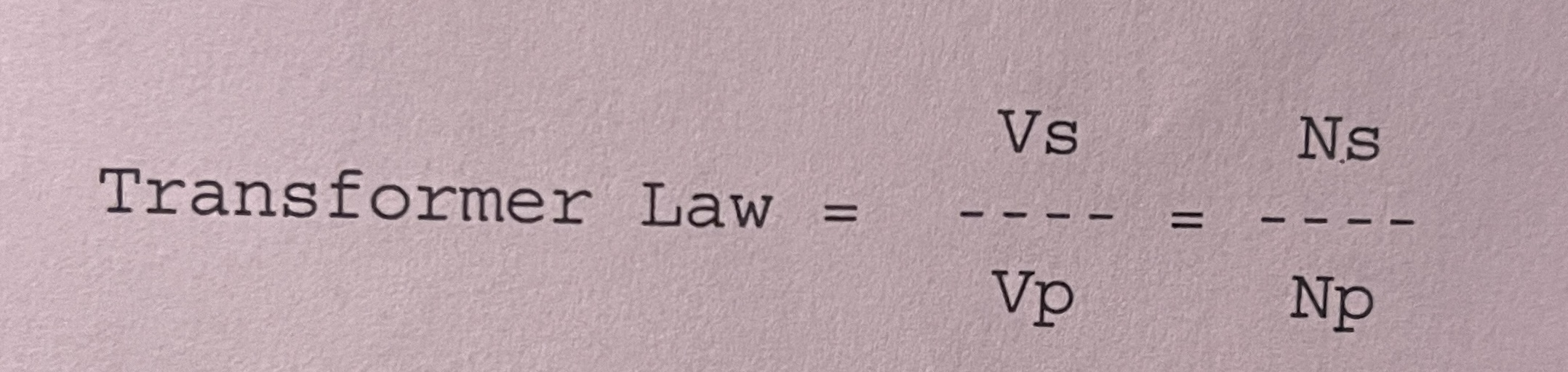transformers test 🤖
1/57
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
58 Terms
why is Iron used as a core in a transformer?
High permeability and low retentivity
when an electrical current flows through a wire, what is induced?
A magnetic field
What happens to the strength of that magnetic field if the wire is coiled?
It increases it
And what do we call just the coil of wire?
Helix
If you place an iron bar in that solenoid, what is gonna happen to the induced magnetic field?
It is going to increase
what part of the transformer intensifies the induced magnetic field?
The core
Which part of the Transformer carries electrical current and or voltage that induces a magnetic field? What part of that transformer is going to do that?
The primary side
Label closed core transformer
we know that, that the primary coil is what induces that magnetic field. Which part of the transformer carries electrical current or voltage that was induced by the magnetic field. That's gonna be your what?
The secondary coil
we know that with transformers, we know energy cannot be created nor destroyed, power input should equal power output 100%. But is that ever gonna happen all the time?
No because of power losses
So where does this power go? There's three types of power losses in transformers. What were the names of them?
hysteresis
Eddy current losses
Copper losses
Which type of transformer electrical power losses occur in the solenoids of the transformer due to the resistance placed on the electrical current because of the coiling of the wire?
Copper losses
Which type of transformer electrical power losses occur in the core of the transformer?
Eddy current losses
Hysteresis
Now, which type of transformer electrical power losses are those little small, swirling currents of electricity in the core due to the changing magnetic field, what do we call that one?
Eddy current losses
I want to know what type of Transformer consists of two solenoids placed side by side with a single iron core placed in the middle of each solenoid, meaning the iron bars are not connected in this type of transformer. What is that called?
Open core
I want to know what type of Transformer consists of a continuous steel core with the primary and the secondary solenoids both wound around the center strut
Shell transformer
I want to know what type of transformer consists of a continuous steel core with the primary coil wound around the left side and the secondary coil wound around the right side. What is that called?
Closed core
Of those, which type of transformer is the most efficient?
Shell
transformer efficiency
just refers to how little power is lost in the production of the secondary current or the secondary voltage
where is that power going?
it could be a copper loss, it could be an eddy current loss or a hysteresis loss
Let's say if you have 100 coils on the secondary side of a transformer to every one coil on the primary side, what kind of transformer is that? voltage output will be how many times greater than the voltage input? It'll be how much is it going to go down?
So if it is a one to 100, that means that's it’s a step up transformer, voltage goes up 100 times, Amperage is going to go down 100 times
what is a unit measurement of electrical power?
Watt
so what is the purpose of the high tension transformer?
to take that bolus of electrons and shoot it over to the anode
why do you have the filament circuit Transformer?
The necessary current or amperage to heat the filament
if you have a Transformer core that is highly permeable, that means it is going to have what kind of retentivity?
Low retentivity
Why do we want a high permeability and load retentivity?
once that exposure has ended, it is desirable for that iron core to become demagnetized immediately so that current in that secondary side stops
X ray tubes have to have what kind of current to operate?
direct current
Transformers require what kind of current to operate?
Alternating current
Transformers are used to either raise or lower what?
Voltage and amperage
auto transformer
has one iron bar and one coil that is used for both the primary and the secondary windings. it is a variable turn ratio. where when you select your KVP, the tap it moves up and down, you're telling it to either step up the voltage or you're telling it to step down the voltage if you lower your kVp
Describe the what the autotransformer looks like
the bottom part of the coil that is considered the primary side, the top part of the coil is considered the secondary side
in an auto transformer, the tapit or contact replacement can be manipulated by you changing the what?
kVp
In a transformer with 100% efficiency, power input will equal power output. Is that true?
Yes
Transformer efficiency formula

Watts formula
Which side of the X-ray circuit is generally considered low voltage and high amperage?
Primary side
What refers to the ease with which a material and the magnetized?
Permeability
what do we call the ability of a material to remain magnetized?
Retentivity
Transformers operate on the principle of what?
Mutual induction
Auto transformers operate on the principle of What?
Self induction
The production of an electric current in a conductor by changing the strength of the magnetic field is called what?
Induction
what type of core is used in Transformers to reduce magnetic power loss in the transformer?
Closed core
Transformer power losses result in the production of what?
Heat
So what can be done to reduce copper electrical losses in the transformer?
reduce the resistance by making the wire diameter larger
What can be done to reduce eddy current and hysteresis electrical losses in the transformer?
we can use laminated silicon steel cores and Using a material with high permeability and low retentivity
In an auto transformer, if the contactor or Tappet is set above the primary coils, the exiting voltage will be greater or less than the incoming voltage?
Greater
when we have a transformer that the exiting voltage is greater than the incoming voltage, what kind of transformer is that?
Step up transformer
You can change the auto transformer by changing the what? How do you make the auto transformer either a step up or a step down?
Change the kVp
auto transformers operate on a variable or a fixed turns ratio?
Variable
And how do you alter that variable turns ratio?
Increase or decrease the kVp
step up and you're step down transformers, also known as regular Transformers, those operate on what, with what kind of turns ratio?
Fixed
what are the two circuits within that big X ray wiring diagram?
High tension circuit or high voltage circuit and the filament circuit
what is the bridge between the High tension circuit or high voltage circuit and the filament circuit?
Xray tube
which X ray circuit does the auto transformer belong to?
High tension circuit
which X ray circuit has a step down transformer?
Filament circuit
Voltage turns formula

Current (amps) and voltage formula

Amperage turns formula