Chapter 4-6 study guide
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
45 Terms
Mesenchyme
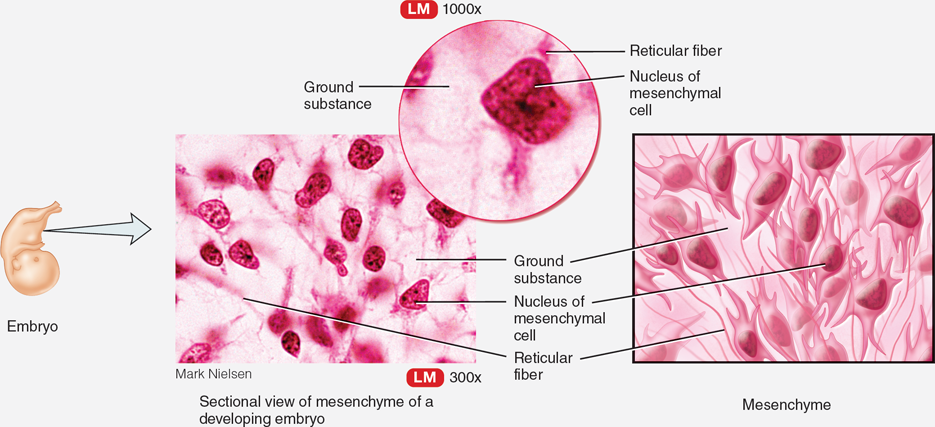
Found under the skin in embryos, forms almost all other types of connective tissue
Mucoid (mucous) connective tissue
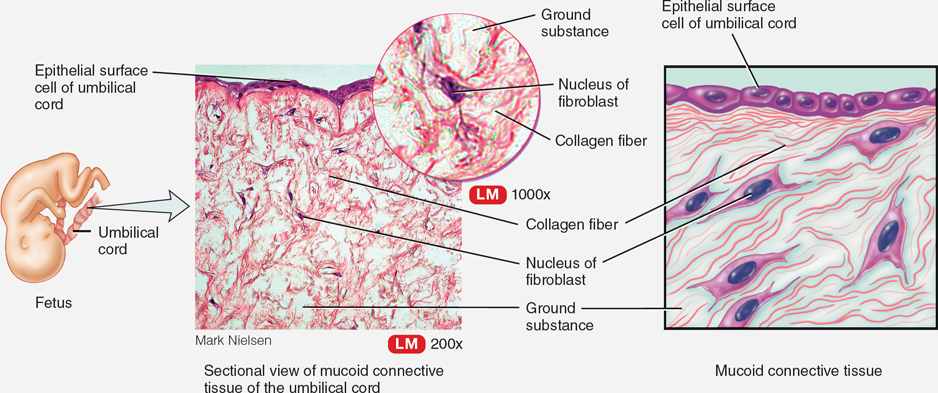
Found in the umbilical cord in a fetus, offers support.
Areolar Tissue
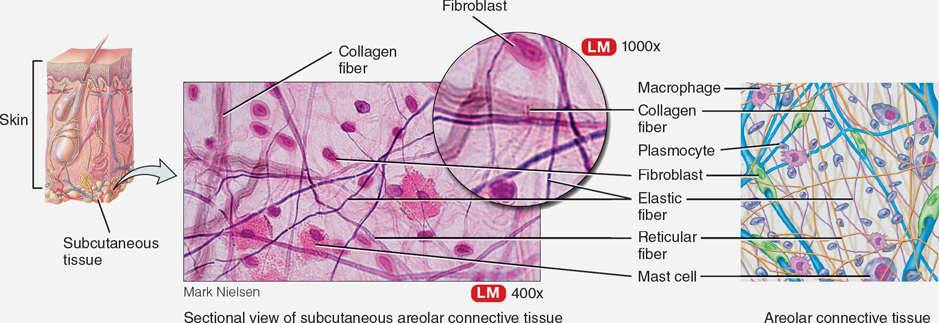
Loose connective tissue located in the hypodermis that provides support and elasticity, containing collagen and elastin fibers.
Adipose tissue
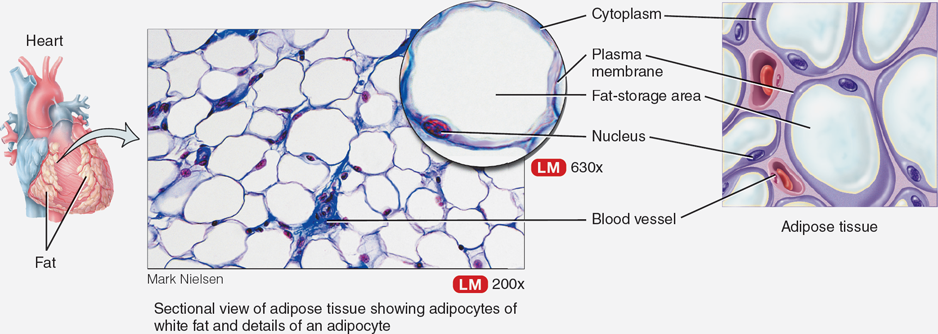
Loose connective tissue that stores fat, located in the hypodermis and around the heart.
Reticular Tissue
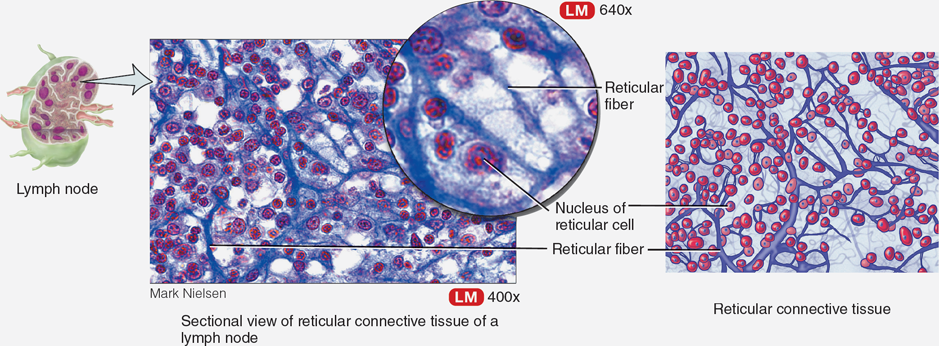
Loose connective tissue that provides framework for organs, located in spleen and lymph nodes
Dense Regular Tissue
Connective tissue that attaches to muscles and bones and forms tendons and ligaments, providing strength and stability.
Dense Irregular Tissue
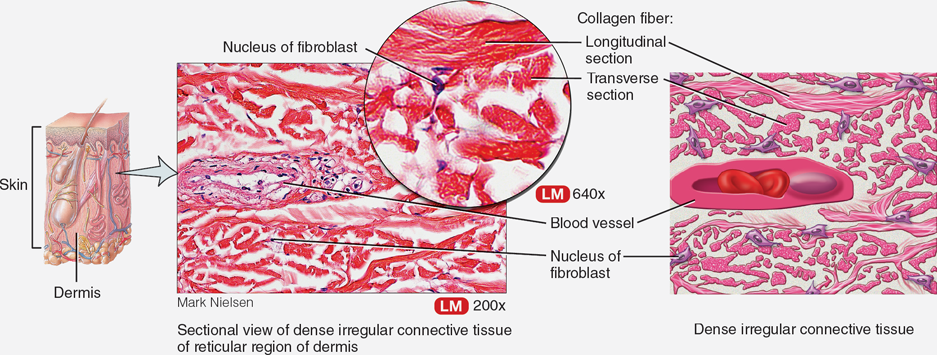
Connective tissue that is arranged irregularly, located in dermis of the skin.
Elastic tissue
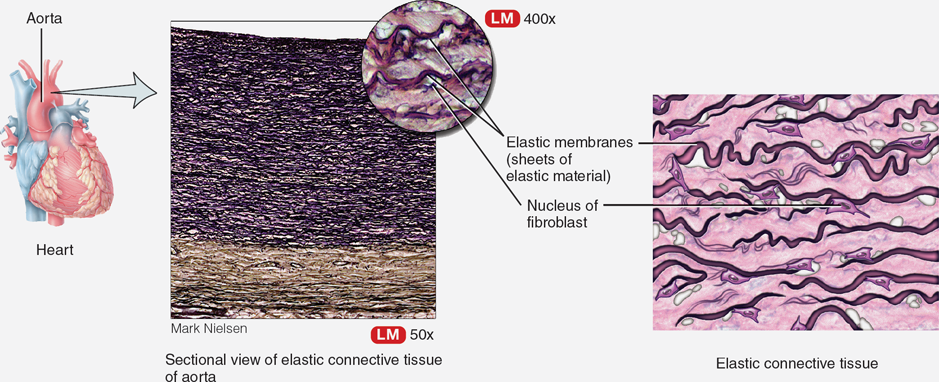
Connective tissue that allows stretching, found in arteries and lungs.
Hyaline Cartilage
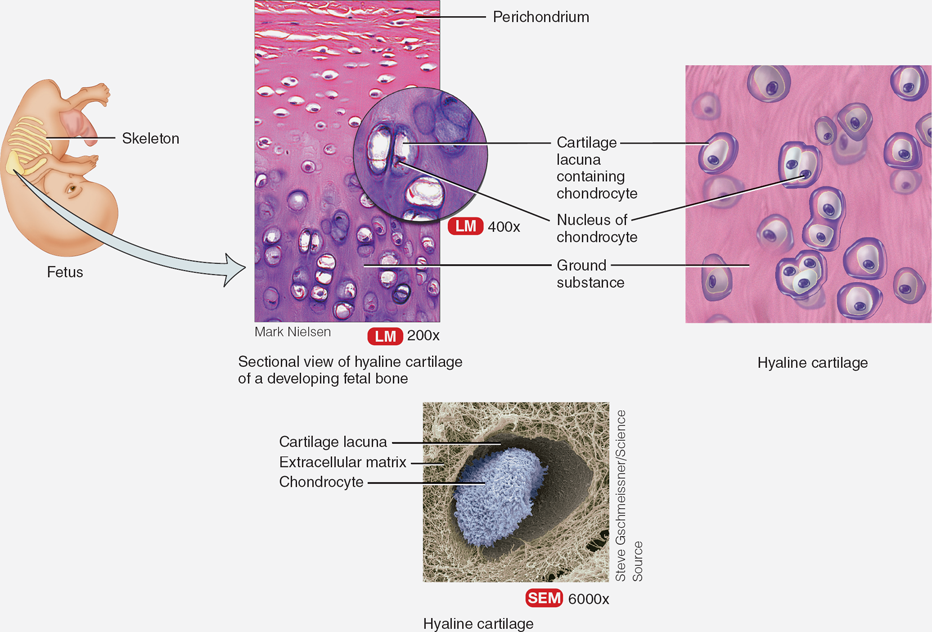
Most common cartilage type, providing support. Found at ends of long bones and in the nose.
Fibrous Cartilage
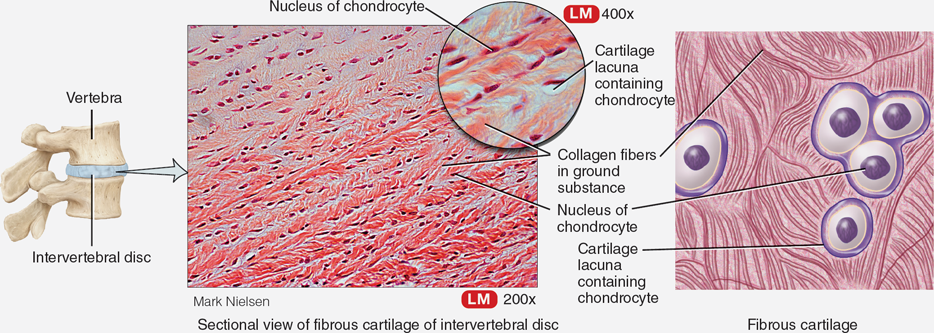
Cartilage that supports and joins structures, found between vertebral discs
Elastic Cartilage
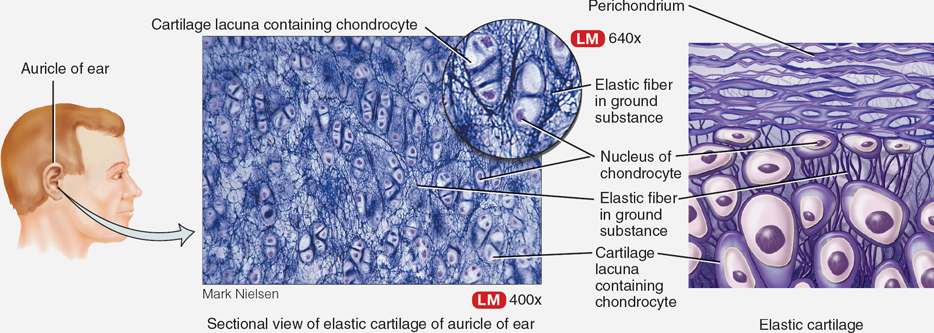
Cartilage that provides elasticity, found in the external ear.
Blood
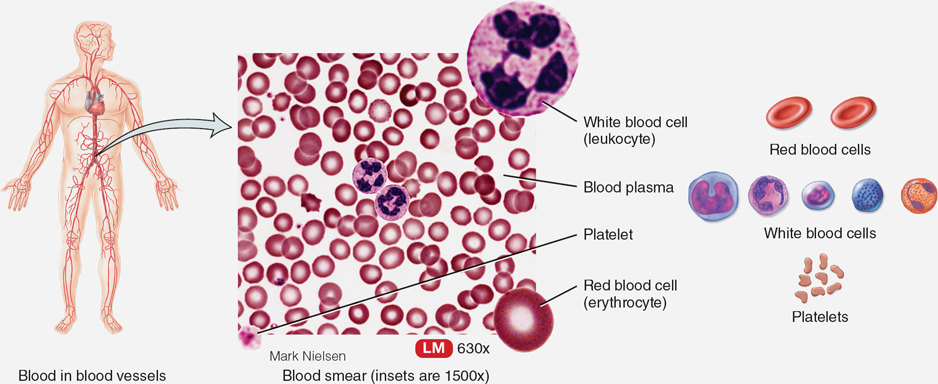
Connective tissue that transports oxygen and carbon dioxide, located in blood vessels.