CH 4 - Organisms, Cell Structure & Functions
1/49
Earn XP
Description and Tags
- characteristics of life, organism levels, cellular structure and organelles, cell growth & specialization
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
50 Terms
6 characteristics of life
organization
metabolism
material exchange
responsiveness
movement
reproduction, growth, development
organization (and example)
organisms’ cells, tissues, organs internal compartments
optimal functioning
ex/ organelles within cells, blood inside vessels, separation btwn extra and intra cellular fluids
metabolism (and example)
energy to fuel
includes catabolic and anabolic systems
catabolism (and example)
process of creating large substances from simple mlcs
ex/ amino acids to proteins
anabolism (and example)
process of breaking down large substances into smaller mlcs, releasing energy
ex/ digestion breaking down food
ex/ maltose breaking into glucose + glucose
____ is the sum of all ___ and ___ reactions within the body
[metabolism] [catabolic] [anabolic]
exchange of material (and example)
organisms interacting with environment
input and output
ex/ ingesting food, expelling waste
ex/ glucose crossing plasma membrane
ex/ ingesting oxygen, expelling co2
responsiveness (and example)
organism’s ability to respond to internal+external changes
ex/ internal: body temp raises → sweat is produced to cool it
external: threat/danger is perceived → brain sends signals to move away
movement (and example)
constantly occurring at all parts within organism
ex/ unicellular: movement of substances in and out of cell membrane
blood moving through vessels, muscle cells contracting,
_____ takes place within all levels of organization
movement
growth, development, and reproduction (and example)
growth - increase in size
ex/ cell size, number, or non-cellular material increase
development - cell differentiation, growth + repair
reproduction - formation of new organisms from parent organisms
_____ is the specialization of cells
cell differentiation
briefly name (in order) the levels of structural organization
chemical → cellular / organellar → tissue → organ → organ system → organismal level
chemical level (desc and example)
atoms
molecules - at least 2 atoms held via chemical bond
macromolecules - large mlcs formed by
combining small monomer units
ex/ DNA molecule (nucleic acid held via hydrogen bonds)
organisms’ chemical level involves ____, ____, and _____ particles
[atoms] [molecules] [macromolecules]
cellular/organellar level (desc and example)
organelles - structures within cell membrane providing specialized functions
cell - fundamental unit of living organisms
uni or multi cellular
an organism with just a single cell is _____, while an organism with many cells is ______
[unicellular]
[multicellular]
tissue / organ level (desc and examples)
tissues - groups of similar cells carrying out same function
organs - tissue sharing common functions that are grouped together, forming organs
list tissues and organs found in the following groups:
animals
plants
animals
tissues: muscle , connective , epithelial , nervous
organs: kidney, liver, brain, heart, lungs
plants
tissues: dermal, vascular, ground
organs: root, stem, leaves
organ system / organism levels (desc and example)
high level of organization of functionally related organ groups working to serve specific purpose
ex/ digestive system, respiratory system are organ systems
______ can be unicellular or multicellular
organisms
organisms (desc)
individual living entities (unicellular or multicellular)
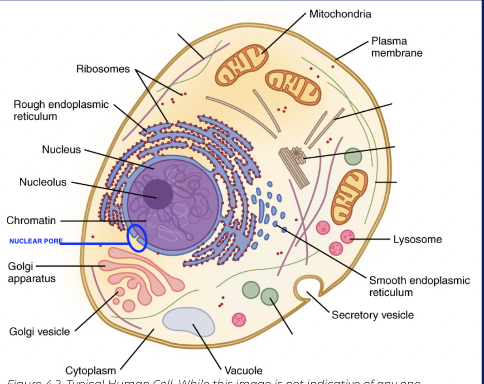
list components of the cell structure (10)
cell membrane
cytoplasm (internal cytoplasmic compartment)
cytosol
organelles
nucleus
nucleolus
chromatin
nuclear pore
nucleic fluid
endoplasmic reticulum
smooth ER
rough ER
golgi apparatus
mitochondria
vacuole
vesicles
golgi vesicle
secretory vesicle
transport vesicle
ribosomes
lysosome
label the following diagram
_______ separates inner contents of the cell from its external environment
[cell membrane]
_____ and _____ make up the _____, which all multi-cellular organisms contain within their cells
[cytoplasm] [organelles] = [internal cytoplasmic compartment]
internal cytoplasmic compartment
made up of cytoplasm and organelles
organelles
mostly membrane-enclosed bodies performing various functions within a cell
cell membrane: structure + function
structure
phospholipid bi-layer with proteins, glycolipids, glycoproteins, cholesterol embedded
function
structure surrounding cell
A) regulating passage/gateway: separates interior of cell from external environment
B) regulates material movement in and out of cell
the phospholipid _____ is a ______ barrier; some materials can pass through evenly while others cannot
[bilayer] [selectively permeable]
cytoplasm: structure & function
contents of cell between plasma membrane + nucleus
structure:
organelles: structures within the cell that have unique operational functions
cytosol: jelly-like fluid suspending organelles
what % of the cytoplasm is water?
70-80%
endomembrane system (definition + list)
organelle/membrane group that modifies, packages, and transports proteins and lipids
cell membrane
endoplasmic reticulum (SER and RER)
golgi apparatus
vesicles
lysosome
endoplasmic reticulum (ER): structure and function
ER - interconnected tubules
Rough ER
structure
connects to nucleus, studded with ribosomes, flat membranes
function
makes phospholipids and proteins
ribosomes on RER synthesize/make the proteins
chemically modifies those proteins and phospholipids
transports them to the golgi apparatus in structures called transport vesicles
smooth ER
structure
connects to rough er, no ribosomes on it, tubular membrane
function
synthesis of carbs and lipids, detoxes medications and poisons, alcohol metabolism, stores calcium ions
golgi apparatus: structure and function
structure
stacks of flat membranes
2 sides: cis face (facing ER), trans face (facing cell membrane)
function
transport vesicles fuse onto apparatus (cis face) and empty out contents
contents (lipids and proteins) from RER undergo further modification
contents get modified, tagged with mlcs so they are enabled to be routed to proper destination
modified and tagged proteins, lipids exit through the _______ of the golgi apparatus.
they can leave in ____, which deposit them in other parts of the cell, or in _____, which fuse with plasma membrane and release them outside of cell
[trans face], [transport vesicles], [secretory vesicles]
lysosomes: function and structure
structure
specialized vesicles produced by golgi apparatus
function
contain digestive enzymes that breakdown organic macromolecules
recycles organelles
destroys pathogenic organisms
vesicles: structure and function
structure
produced by RER, golgi apparatus, cell membrane
membrane surrounded sacs that carry materials (ex/ proteins, phospholipids)
function
transport sacs, move materials around the cell
can fuse to other membranes (ex/ if coming from RER, it fuses to cisface of golgi apparatus)
ribosomes: structure and function
structure
1 small subunit and 1 large subunit join together
free ribosomes float in the cytoplasm
ribosomes can be bound to cytoplasmic side of cell membrane or ER
function
synthesizes proteins
ribosomes are assembled by fusing a large and a small _____ in the _____, then transporting it to the _____ where the final ribosome is assembled
[subunit], [nucleus], [cytoplasm]
in the process of _____, a section of plasma membrane ____ large particles like debris, dead cells to be digested. this section then pinches off from the plasma membrane and becomes a ______. It then fuses with a lysosome, whose ____ ____ destroy the pathogen.
[phagocytosis] [invaginates/engulfs] [vesicle] [digestive enzymes]
mitochondria: structure and function
structure:
double membrane: inner membrane (cristae folds) + outer membrane
contains semi-fluid called matrix
contains its own ribosomes and DNA
function:
make ATP from glucose breakdown during cellular respiration
nucleus: structure and function
structure
is continuous with ER
nuclear envelope: double membrane enclosing nucleus structure
nuclear pores: passageways in/out of nucleus on the nuclear envelope
nucleoplasm: semi-fluid inside nucleus holding chromatin, nucleolus
nucleolus: ribosome factory
chromatin: DNA chromosomes (linear pieces of proteins) + protein
function
houses DNA in form of chromatin
directs synthesis of ribosomes and proteins
____ is part of the cell cycle, which _____
[cell division], [generates 2 new cells]
somatic cell
general term for body cell (except for cells producing sperm/eggs)
germ cells
cells producing eggs and sperm
after cell division, cells _____ and _____
ex/ muscle cell
[grow], [increase in size]
ex/ muscle cells elongate, becoming extremely long as muscle forms
cell differentiation
process of cells achieving final physiology and morphology
cells become specialized to carry out specific funtions
unspecialized cells are ____
[stem cells]
name the following and explain why they take the described shape after cell differentiation:
muscle fibers: long and slender
_____ / nerve cells: long and thin
_____ / red blood cells: tiny, lack of nucleus and mitochondria
____ / white blood cells: larger than _____
so fibers can contract and produce movements
[neurons]: so they can transmit information
[erythrocytes]: no nucleus = squeeze through capillaries. no mitochondria = oxygen they carry doesn’t get used up
[leukocytes]: larger than erythrocytes so they can engulf particles/cells