cell adhesion and junctional complexes
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
what are the two types of extracellular membrane (ECM)
basement membrane/basal lamina
fibrillar matrix
basement membrane
thin 2D sheet on which the epithelial cells adhere
fibrillar matrix
3D matrix composed of various fibres
cells are loosely packed
contains proteins and fibroblasts
basal membrane location
underlies epithelia and surrounds some non-epithelial cells
basal membrane contains which proteins
Collagen IV
Laminin
Nidogen
Perlecan
fibrillar matrix contains
collagen I
fibronectin
elastin
proteoglycans
types of junctional complexes
occluding junction (tight)
cell-cell anchoring junction (adherens and desmosomes)
channel forming junctions (gap)
cell matrix anchoring junction (focal adhesions and hemidesmosomes)
which basal adhesions hold cells to the basement membrane
focal adhesions
hemidesmosomes
desmosomes and hemidesmosomes are connected to
intermediate filaments
desmosomes located at
cell-cell contacts
hemidesmosomes located at
cell-ECM interface
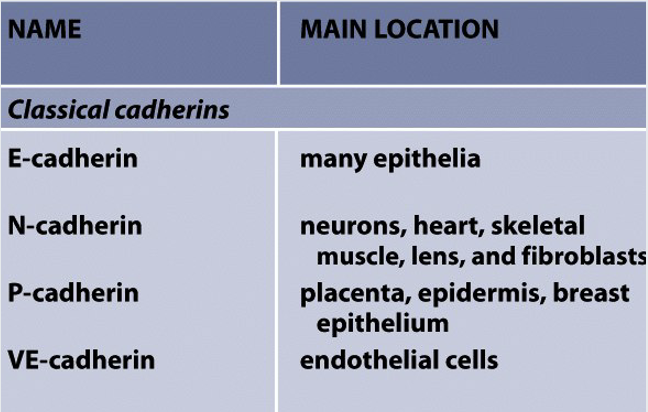
cadherins form
homophilic interactions meaning they can only attach to same type of cell
epidermolysis bullosa
caused by mutation in intermediate filaments or desmosomal factors
tight junctions are found
close to the apical surface
tight junction function
prevents passage of molecules in both apical and basal directions
form a ring around the cell
fully sealed and always found close to apical surface
acts as a physical barrier
tight junctions are formed by
claudin and occludin
pemphigus
when autoantibodies are produced against desmosomes
gap junctions function
create a pore which can open to allow the passage of molecules and ions (which maintain the membrane potential of neurons) between cells
important for chemical and electrical signalling
adheren junctions are linked to
actin
When actin myosin filaments interact and generate contractile forces
apical surface constricts causing cell to change shape
sheet of cells become more rounded
Focal adhesions link the actin cytoskeleton to the ECM
via integrins
Focal adhesions form transiently during cell movement
cell movement is a dynamic process
filopodia contains
actin fibres
what do the actin fibres in filopodia enable
navigation of space
movement
what would happen if cells did not have junctions
cancer
cells can lose attachment to each other and squeeze through endothelium cells, leave circulation and become malignant through metastasis
which junctions have homophilic interactions
desmosomes
gap junctions
tight junctions
adheren junctions