econ 1 topic 11
1/13
Earn XP
Description and Tags
output and spending
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
14 Terms
Aggregate demand
total demand for an ouput in a year
AD = C + I + G + (X-M)
c- consumption
i- investment
g- government
x- exports
m -imports
c - consumption
disposable income - Yd = Y + TR -TA
(income + transfers - taxes)
marginal propesnity to consume (MPC)
ex if mpc = .6 stim check = 1200, .6×1200 = 720 (spent); 1200 - 720 = 480 saved
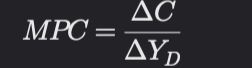
output and aggregate demand
gdp > AD - inventory accumulation, more produced than sold → decrease production, gdp falls
gpd < Ad, inventory depletion → increase production gdp rise
gdp=ad = macroeconomic equalibruium
marginal propensity to consume (mpc) margian propesnity to save (mps)
mpc -how much consumption changes when disposable income changes
mps - how much saving changes when disposable income changes
ex; mpc =.6 is 60% of the check
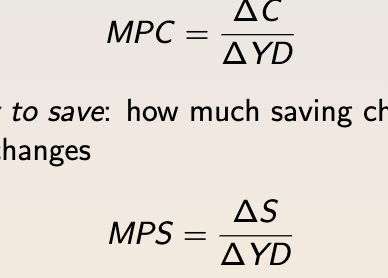
average propesnity to consume apc and save
apc = c/yd
aps = s/yd
saving rate
consumption function
c = f(D)
→ ignore tax - YD = Y
c= c old + c new Y

investment
intrest rate → hugher - less investment spending
expceted rate of return on captial, higher if = more expected revenue, lower price of capital and to use
consumption smoothing
insure agaisnt shocks, keep consumtion constant
ex; saving for retirement, borrowing money for college
keynesian cross
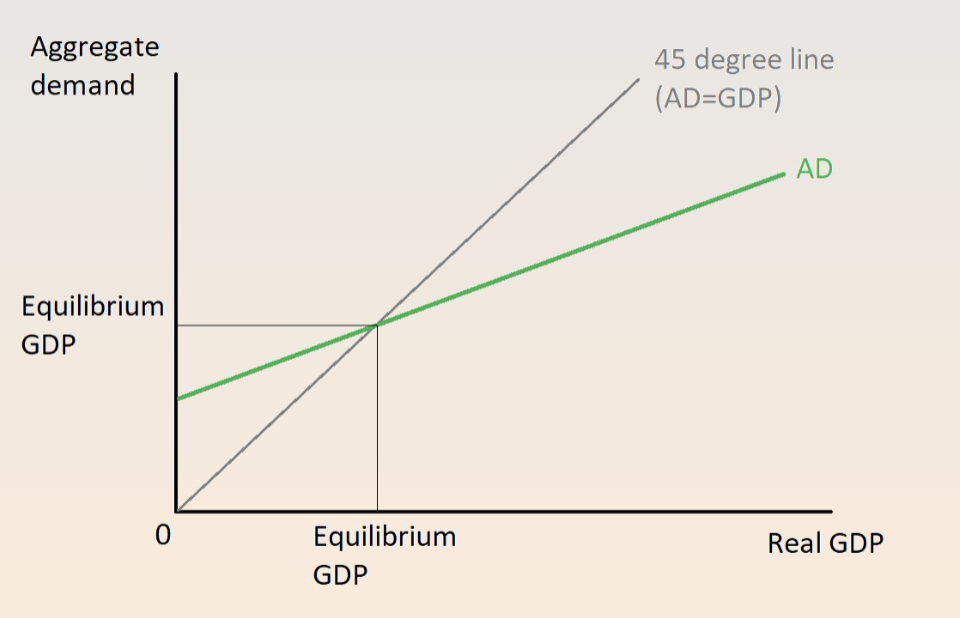
spending multiplyier
taxes change when income changes, consumption spending and imports change when income changes
taxes - reduces the extend to which change in income leads to change in disposable income
imports - reduces the extend to which change in disposable income leads to change in home econ spending
higher tax rate = lower multiplier
more income spend on imports = lower multiplier
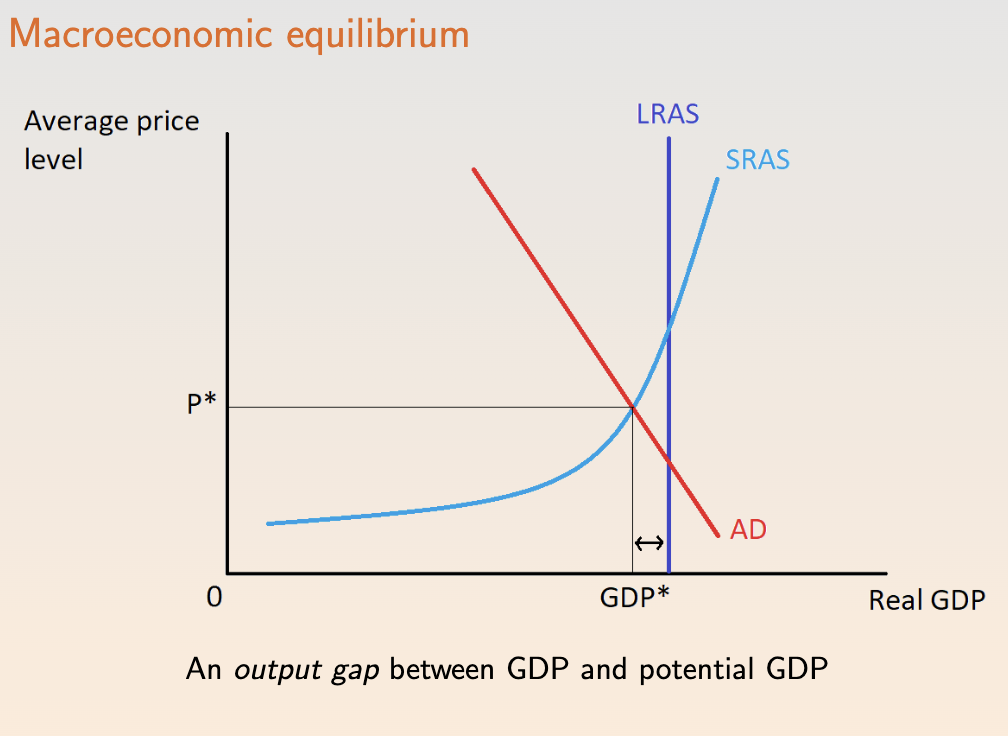
AS/AD, aggreae supply and demande
ad - same wiht regural S&D cruve
increaseing Gov or TR(total revenue) or decreasing TA (tax) shif ad to right, decreasing = left
increase money supply = sift ad right
increase prefrenece in saving will shift ad left, consumption will shift right
more wealth - ad right
long run AS curve (LRAS) - is gpd line
vertical line, econ growth push it to right
short run AS curve
upward sloping, both directions bc sticky wages/input costs
more output = more input depend
can extend lras but not forever bc costs and not sustainable
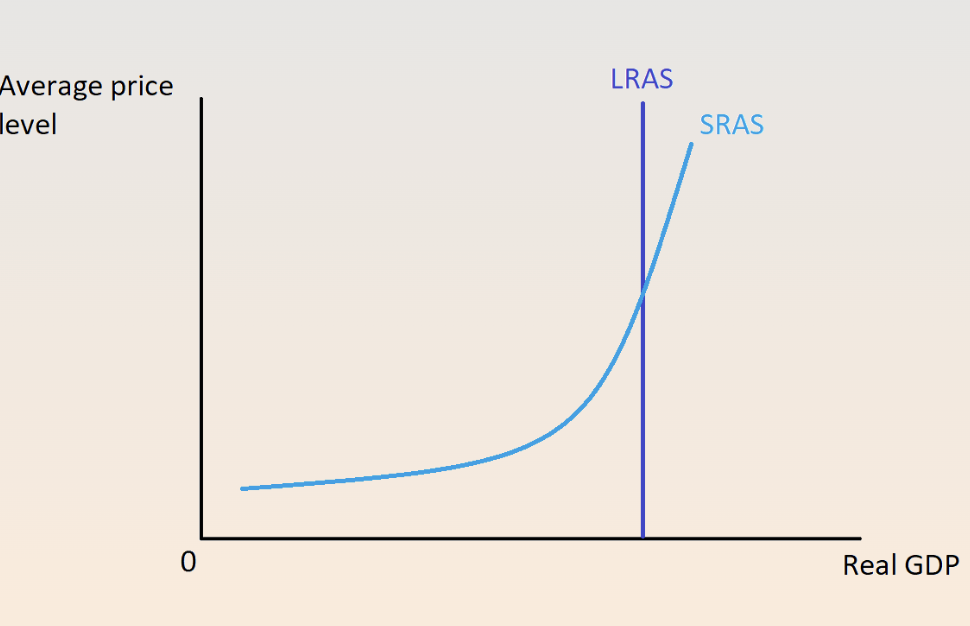
macroecon equilirium