Category 1: Late Nineteenth and Early Twentieth Century
1/57
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
58 Terms
Long-term Causes of the Civil War
- Sectionalism
-Slavery: Differing economic needs/reliance on slavery in the South
- Extension of Slavery
-States' Rights

Compromise of 1850
California admitted as a free state; sale of slaves banned in D.C.; Fugitive Slave Act of 1850 enacted; rest of Mexican Cession territory open to slavery based on popular sovereignty (will of the people)

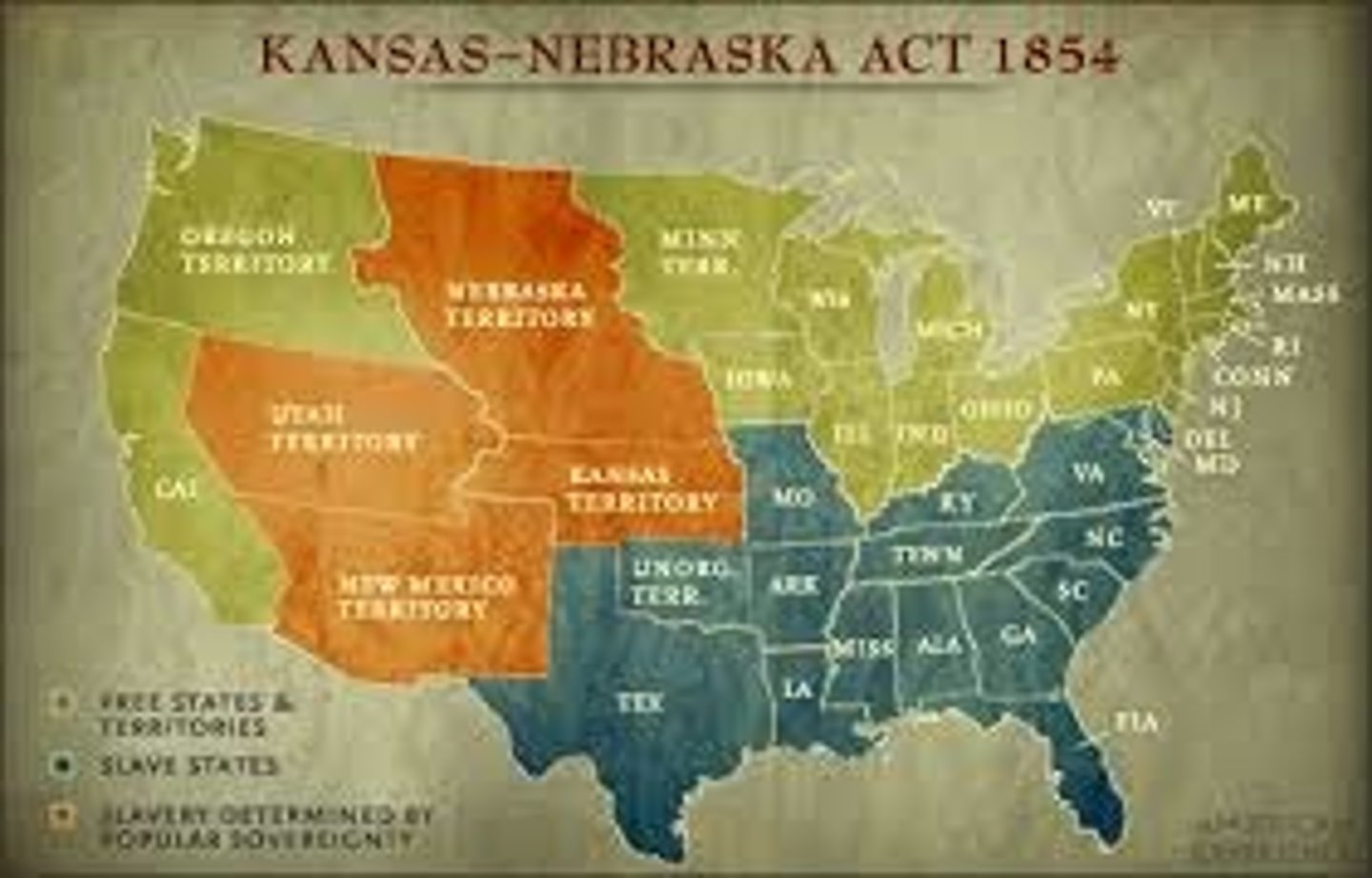
Kansas-Nebraska Act
Divisive act introduced by Stephen Douglas, which repealed the Missouri Compromise by applying popular sovereignty to both the Kansas and Nebraska territories. The Republican Party (opposing the extension of slavery) was formed in 1854 due to this Act
Dred Scott Decision
Supreme Court decision (1857) stating that Scott did not have the right to sue for his freedom since he was not a U.S. citizen, but property of another person. Decision went further to claim that the Missouri Compromise prohibiting slavery in territories was unconstitutional. Congress had no right to take away another person's property.

Freeport Doctrine
Idea put forth by Stephen Douglas, during a debate with Lincoln, that the residents of a territory could still ban slavery despite what the Supreme Court decided with Dred Scott.

Ostend Manifesto
An attempt to expand U.S. territory; pushed for Spain to sell Cuba to the United States for $120 million dollars in 1854. The document caused uproar because Cuba was already an established slavery territory. It was declared unconstitutional due to the Fugitive Slave Law that was passed as part of the Compromise of 1850; therefore Cuba did not become a U.S. territory.

Emancipation Proclamation
Lincoln's announcement that all slaves in those states still rebelling would be freed. Did not free slaves in border states that were loyal to the Union.

Gettysburg
July 1863 battle that was the turning point in the war. The South never advanced into the North again

Gettysburg Address
Short speech given by Lincoln to honor Union losses at Gettysburg.

13th Amendment
Outlaws slavery in all states and all lands governed by the United States.
14th Amendment
Granted full citizenship to African Americans. States citizens cannot be deprived of rights without due process of the law. Guarantees equal protection under the law

15th Amendment
States that no one can be denied suffrage (right to vote) based on race or color.

Black Codes
Laws written by Southern states (each state's was slightly different) that were based on slave codes from the past. Prevented freedmen (persons of color) from voting, holding office, serving on juries, etc. Helped spur the creation of the 14th Amendment.

Radical Republicans
Group of Republicans who believed the South should face punishment for the Civil War and that African Americans should be given full political and civil equality. Gained power in Congress - was able to push through "Congressional Reconstruction".

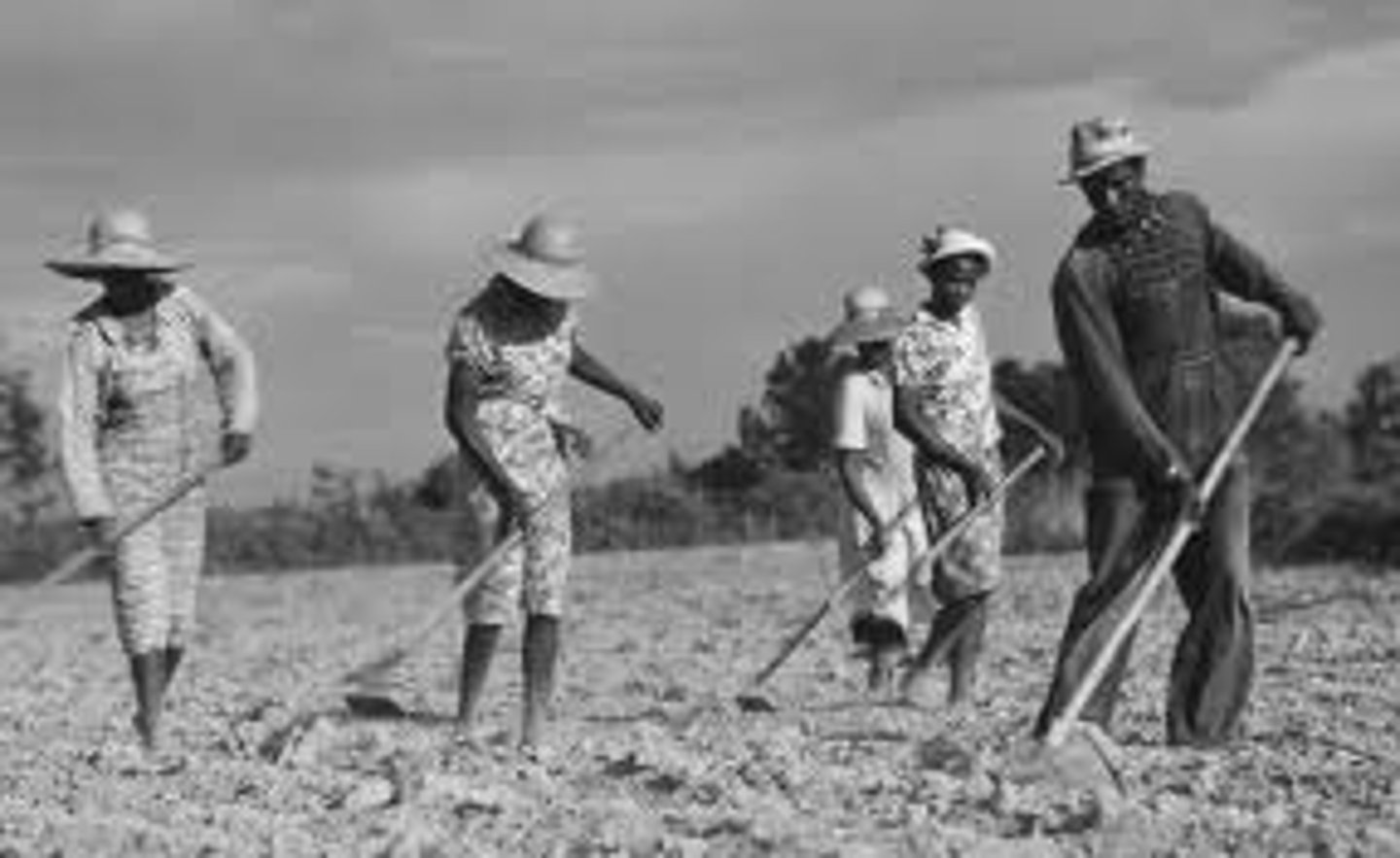
Sharecropping
System of agriculture used in the South with former slaves. Farmers would give a portion of their crops to the landowner in exchange for use of the land.

Debt Peonage
Also called debt slavery. Land or business owner forces a worker to pay off a debt with work - think sharecroppers and tenant farmers. Workers are often unable to re-pay the debt, and find themselves in a continuous work-without-pay cycle

Carpetbagger
Northerners who moved to the South after the Civil War to take advantage of the unstable social, financial, and political climate

Ku Klux Klan (KKK)
Groups that believe in white supremacy. Were formed in the South to terrorize African Americans. Helped to enforce the Jim Crow laws and keep African Americans "in their place."

Granger Laws
Series of laws passed in several Midwestern states that shared the same intent: to make pricing of railroad rates more favorable to farmers, small rural farmers in particular. It was a topic of much debate at the time and ended up leading to several important court cases, such as Munn v. Illinois and Wabash v. Illinois
Populism
Political movement created out of the farmers alliances. Supported: graduated income tax, regulated banks, increase in the money supply, government ownership of railroad and telegraph lines, eight-hour work day, restrictions on immigration, and voting reforms.

Cross of Gold
Impassioned speech given by William Jennings Bryan (Democratic nominee for President in the 1896 election). Criticized the monetary policy of the government for being too hard on the farmer; said in the speech that farmers were being crucified on a cross of gold - helped gain him the support of the Populists.

Business Monopoly
When a company has total control over an industry. Many were formed in the late 1800s because of the government's laissez-faire (hands-off) attitude. Companies used the theory of Social Darwinism to justify their unfair business practices.

AFL - American Federation of Labor
Labor union of skilled workers created by Samuel Gompers in 1886. Focused on collective bargaining. Used strikes as a major tactic.

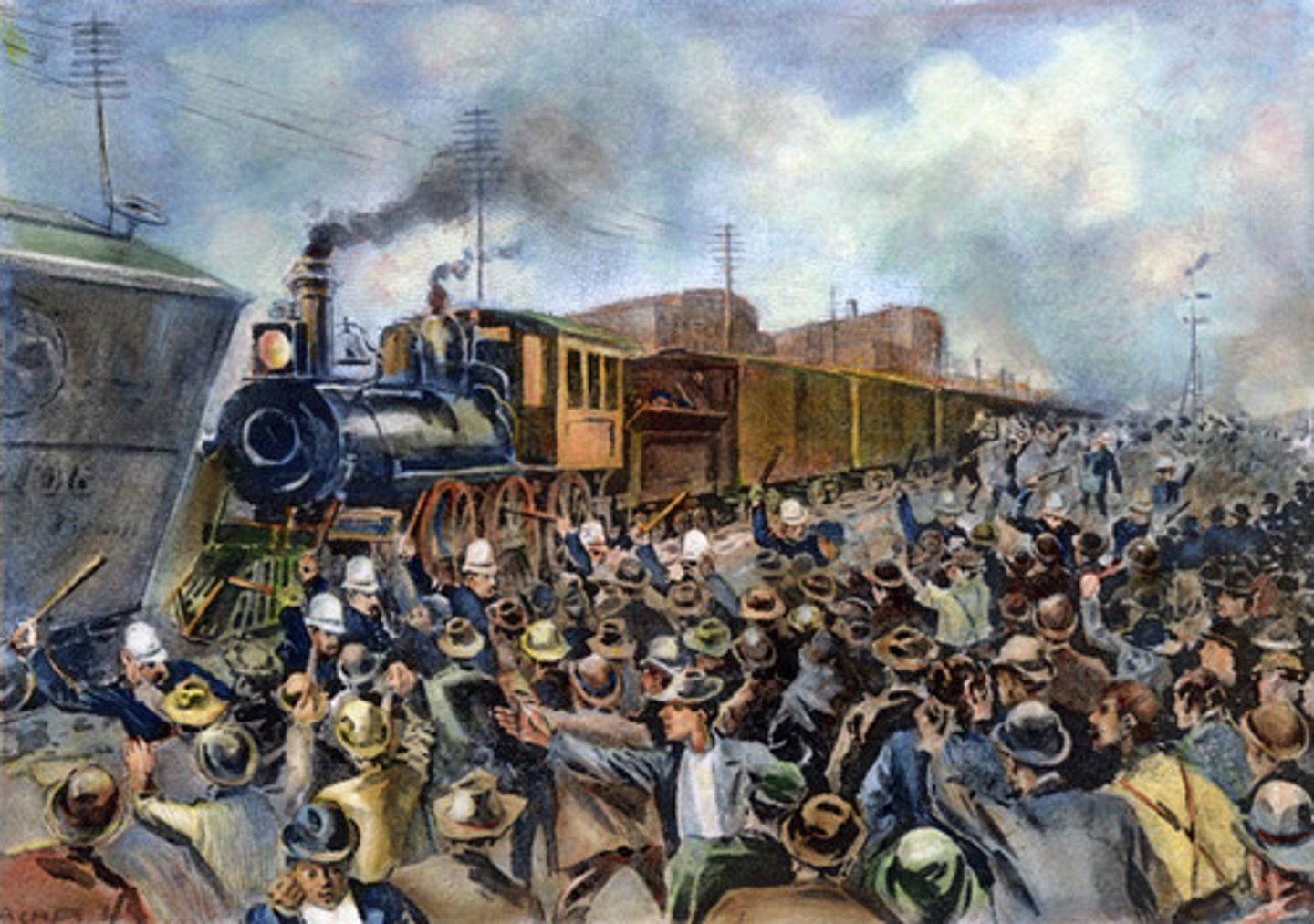
Pullman Strike 1894
Strike by railroad workers in and around Chicago refusing to operate passenger trains that used Pullman sleeping cars. Shut down much of the nation's freight and passenger traffic in the West. Army had to break up the strike and violence broke out in many cities. Strike began when nearly 4,000 Pullman factory employees began to strike in response to recent reductions in wages.

Social Gospel Movement
An early reform program that preached salvation through service to the poor. Called on governments, churches, and private charities to work together to help people in need.

Regulation of Food & Drugs
After Upton Sinclair's The Jungle, the public demanded action. Meat Inspection Act in 1906 regulated the meatpacking industry (until the 1990s). Pure Food and Drug Act in 1906 halted sale of contaminated food and medicines and called for truth in labeling.

Great Migration
The movement of 6 million African Americans out of the rural Southern United States to the urban Northeast, Midwest, and West that lasted up until the 1960s. The first Great Migration (1910-1930), numbered about 1.6 million who left mostly rural areas to migrate to northern industrial cities.

Hiram Rhodes Revels
First African American in Congress. He was appointed by the Mississippi state legislature to fill an empty Senate seat.

The Nadir
Time in the South (end of Reconstruction in 1877 through the early 20th century), when racism in the country was at an all-time high. African Americans lost many of the civil rights gains made during Reconstruction. Antiblack violence, lynching, segregation, legal racial discrimination, and expressions of white supremacy increased.
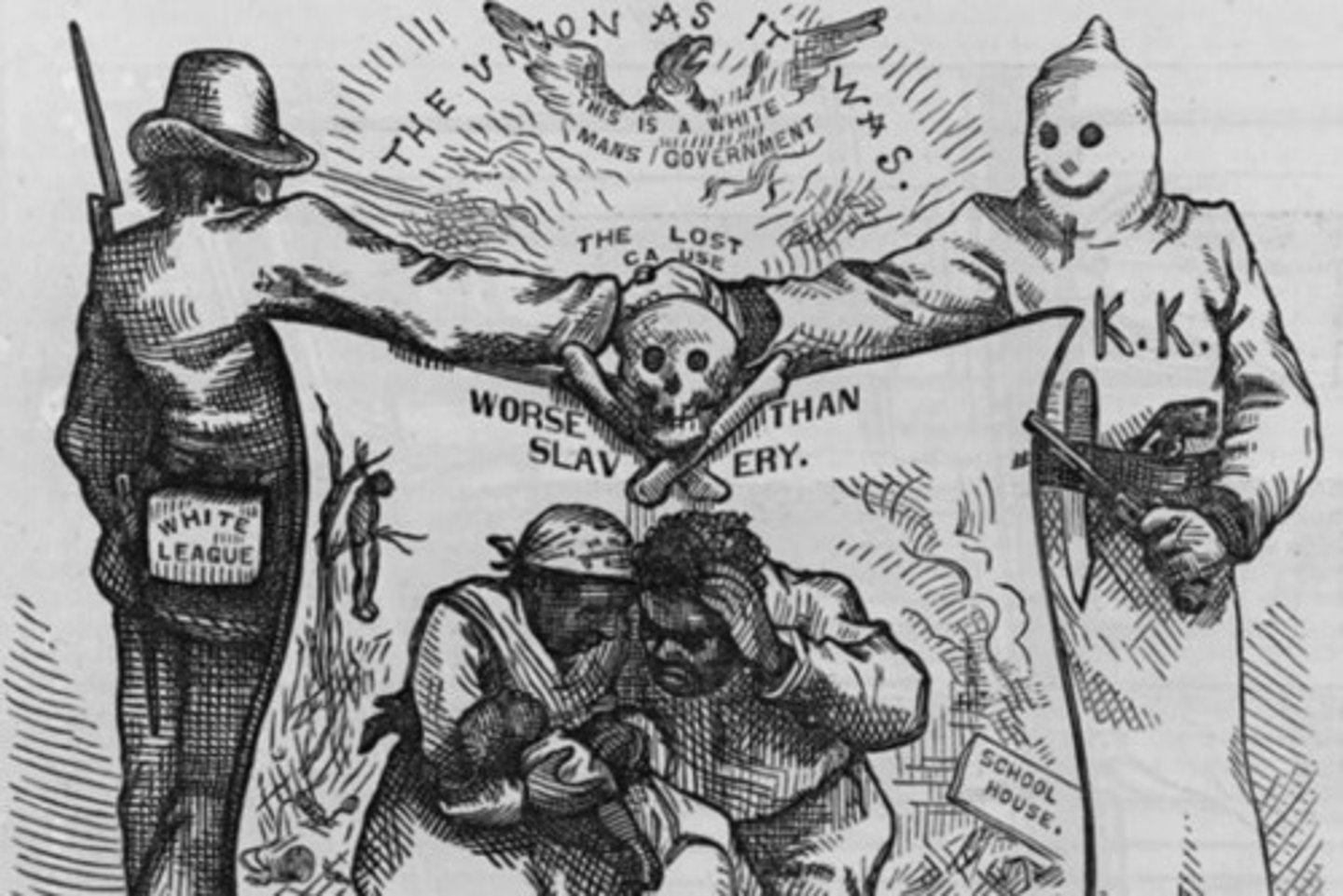

Jim Crow Laws
Laws passed in the South after Reconstruction that required racial segregation. African Americans were relegated to the status of second class citizens as these laws denied them their rights, including suffrage. Created to get around the 13th, 14th, and 15th amendments. Many of these laws lasted into the 1960s

Homestead Act 1862
Encouraged western migration by promising settlers 160 acres of land for $1.25 an acre after improving it for six months or for free if they farmed it for five years. Ten percent of the U.S. was claimed and settled under this act.

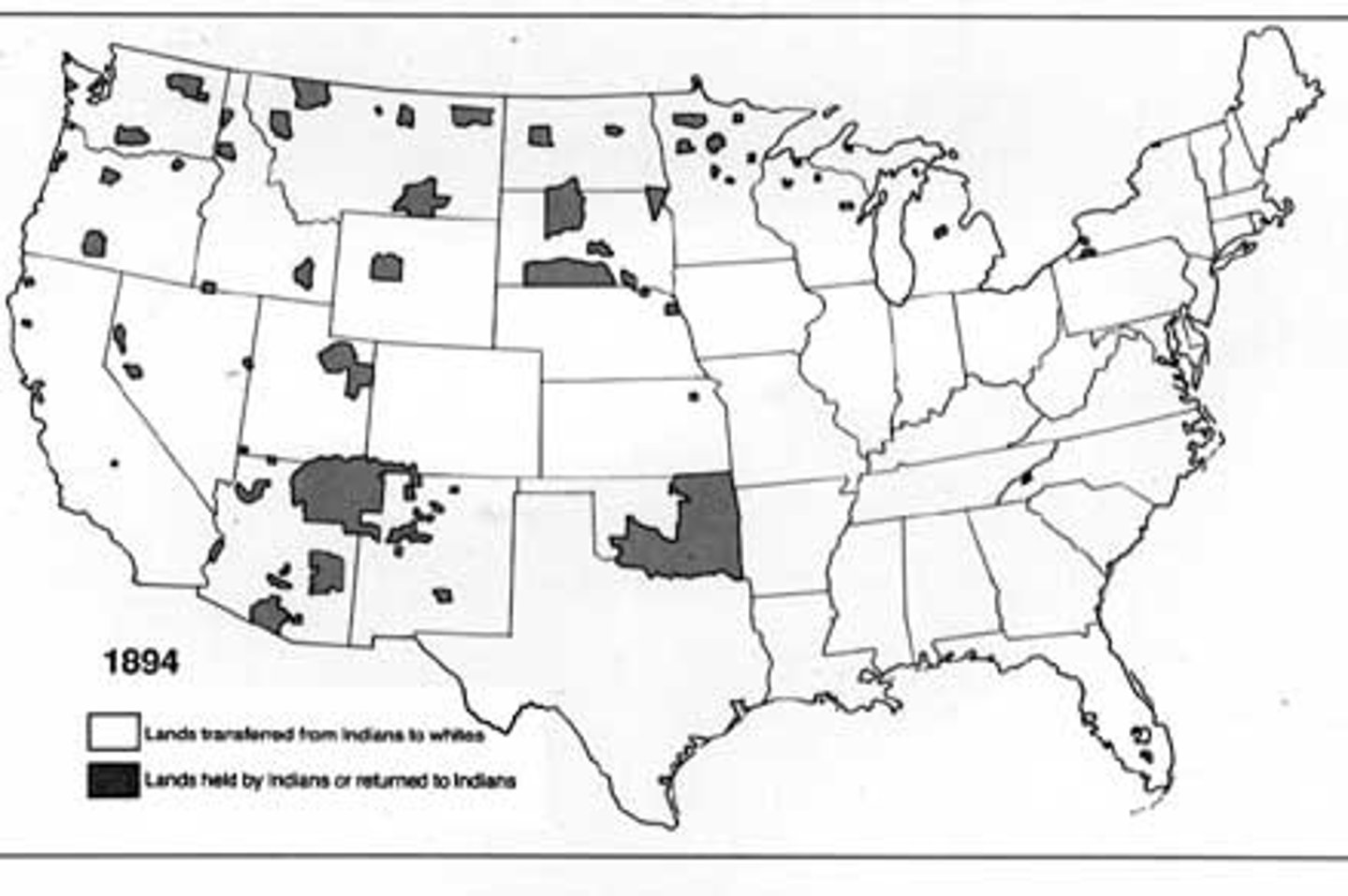
Dawes Act 1887
Passed by Congress to "Americanize" the Native Americans. Each adult male was allowed to claim 160 acres of reservation land as his own private property - led to mass sell-off of reservation land. Threatened the survival of Native American culture.

Reservation System
Land set aside for Native American tribes by the government. Native Americans were required to stay on their land. Usually the land was undesirable and unlike the land the tribe was used to living on.
Grange
Group formed to provide social and educational gatherings for isolated farm families. By 1870s, most of their time was spent fighting the railroads (misuse of government land grants, fixing prices, charging different customers different rates).

Farmers Alliance
Groups formed to educate farmers about topics such as interest rates on loans and government control of banks and railroads. Membership grew to more than 4 million - leads to the rise of the Populist Party.

Sherman Silver Purchase Act 1894
Passed in response to the growing complaints of farmers. It required the government to purchase almost twice as much silver as before, and added substantially to the amount of money already in circulation. It threatened to undermine the U.S. Treasury's gold reserves. After the panic of 1893 President Cleveland called a special session of Congress and secured (1893) the repeal of the act.

Interstate Commerce Act 1887
Reestablished the right of the federal government to supervise railroad activities and established an Interstate Commerce Commission (ICC) to carry out the act. Created over public pressure - railroads were perceived to have abused their power as a result of too little competition. The ICC was not effective since it lacked little power.

Railway Innovators
George Pullman - Inventor of the sleeping car. George Westinghouse - Inventor of the railway air brake, which stops all the cars of a train at the same time.

Thomas Edison
Inventor of many things including the phonograph, light bulb, and motion pictures. Had a winter home in Fort Myers.

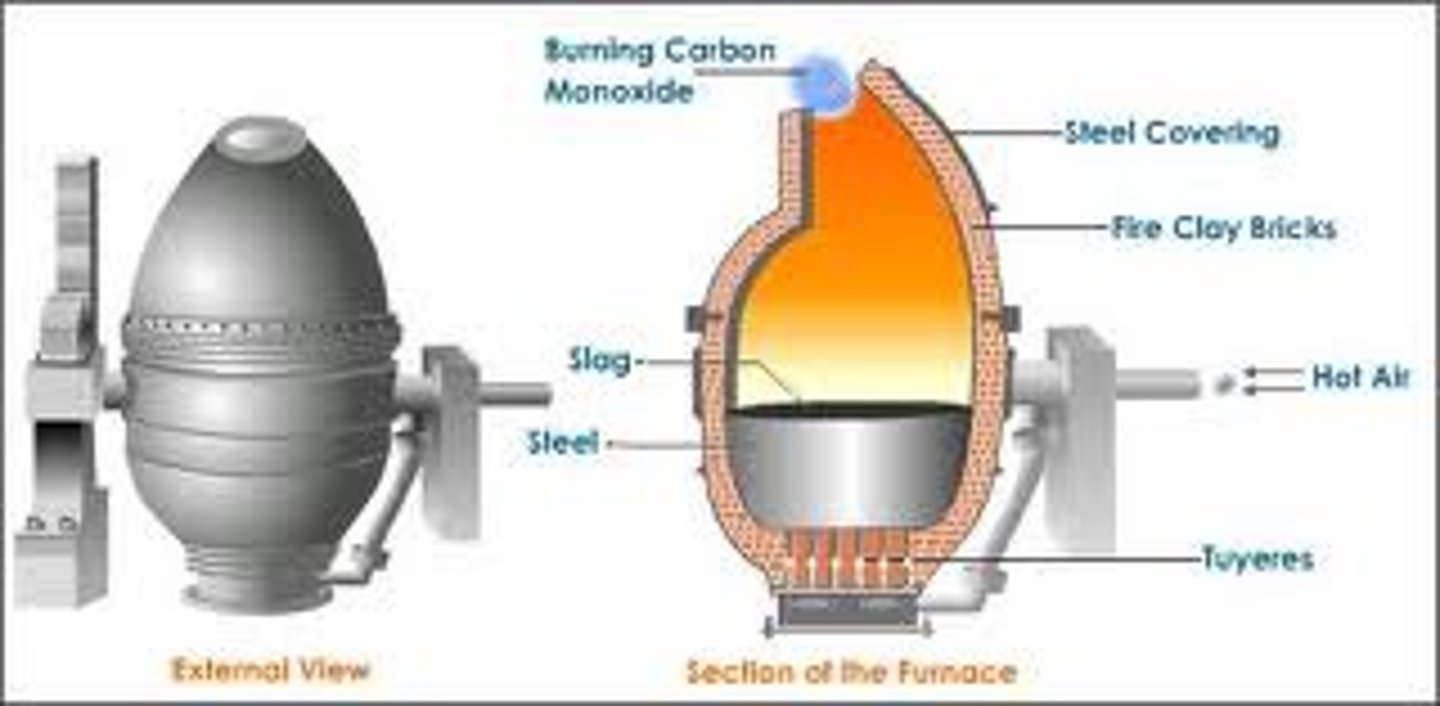
Bessemer Process
Cheap and efficient way to produce steel. Developed independently by Henry Bessemer (in Britain) and William Kelly (in America) around 1850. Cheaper steel makes it possible for more railroad tracks, suspension bridges, massive engines, and skyscrapers
Communication Inventors
Samuel Morse - Inventor of the telegraph.
Alexander Graham Bell - Inventor of the telephone in 1875.
Made instant communications possible even over long distances.

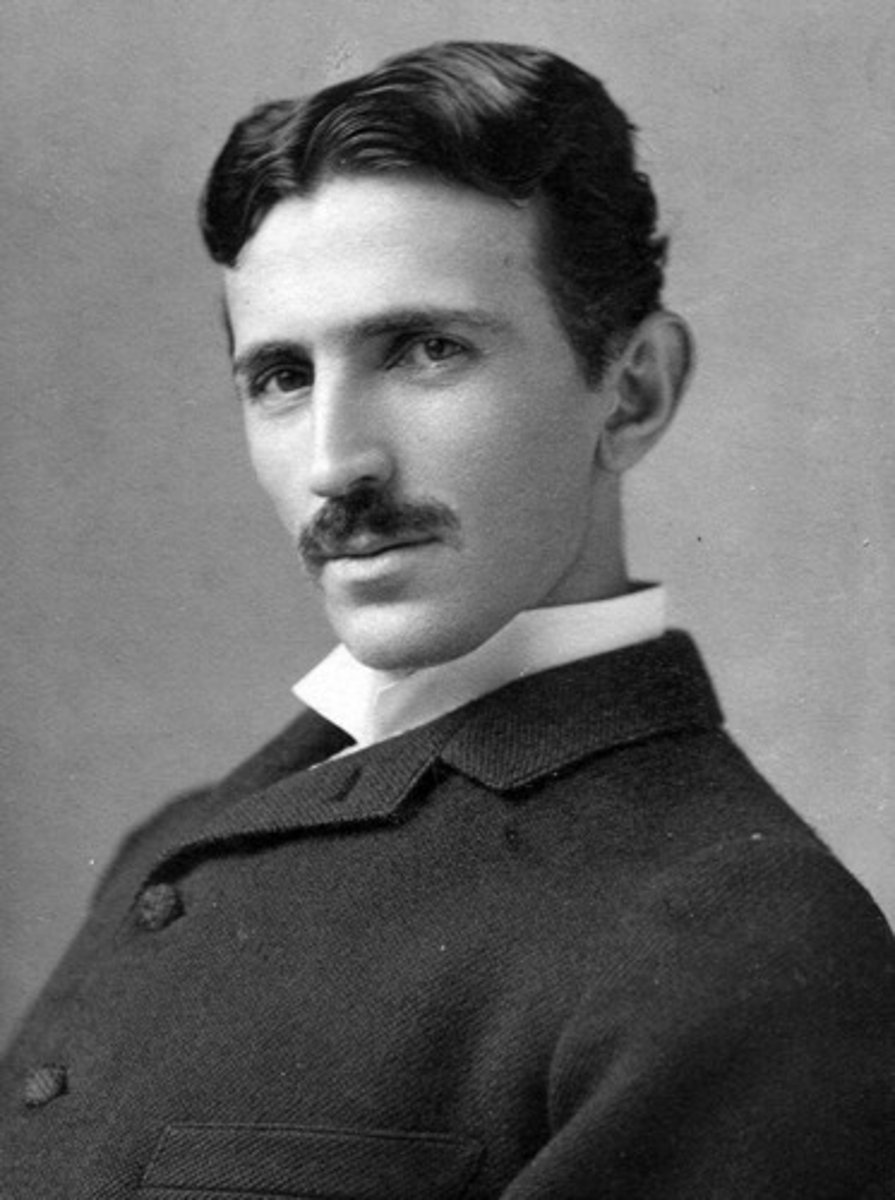
Nikola Tesla
Developed an alternating current (AC) motor which could travel further than a direct current (DC) model.

African American Inventors
John Albert Burr - rotary-blade lawnmower.
Jan Ernst Matzeliger - machine that attaches the upper and lower parts of a shoe.
Lewis Howard Latimer - improved method for producing carbon filaments used in light bulbs.
Madam CJ Walker - cosmetic products.

Social Darwinism
Belief that the successful had superior talents that allowed them to thrive. Used to justify the need for free competition and little government regulation in the economy

Sherman Antitrust Act 1890
Law passed by Congress making it illegal to form a trust that interfered with free trade between states or other countries. Language was vague, limiting its effectiveness.

Knights of Labor
Nationwide labor union created in 1869 that was open to all workers. Supported an 8 hour workday and equal pay for equal work. Saw strikes as a last resort. Fell apart after the failure of a series of strikes.

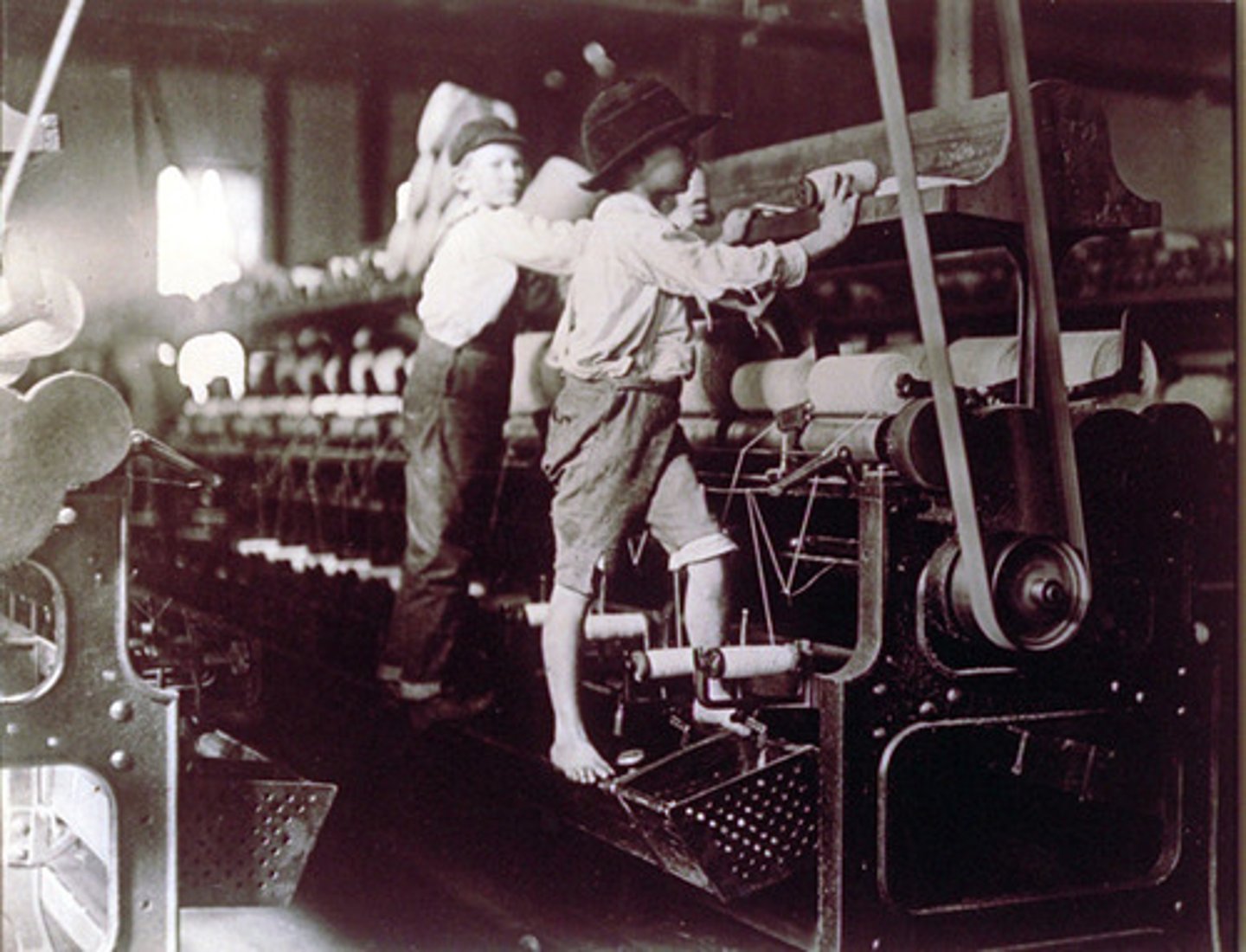
Child Labor
Used in textile mills and coal mines especially. Paid less than adults. By 1910, as many as 1 out of every 5 children under 15 years old was working outside the home.
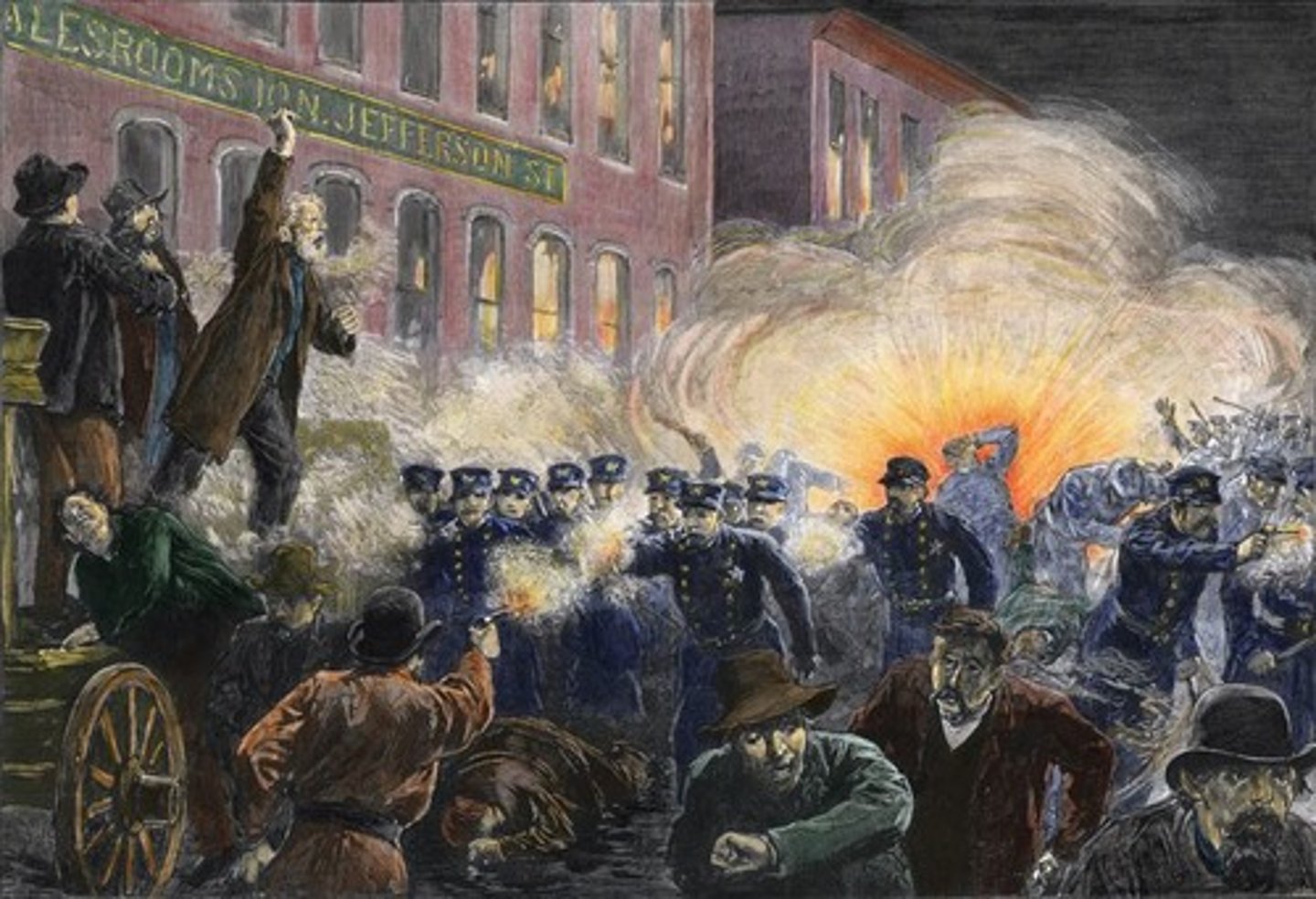
Haymarket Riot 1886
3000 people gathered to protest police brutality against striking workers. As the crowd was leaving, someone threw a bomb into the police line. Police fired on the protesters. Starts to turn the public against labor unions (the Knights of Labor specifically).

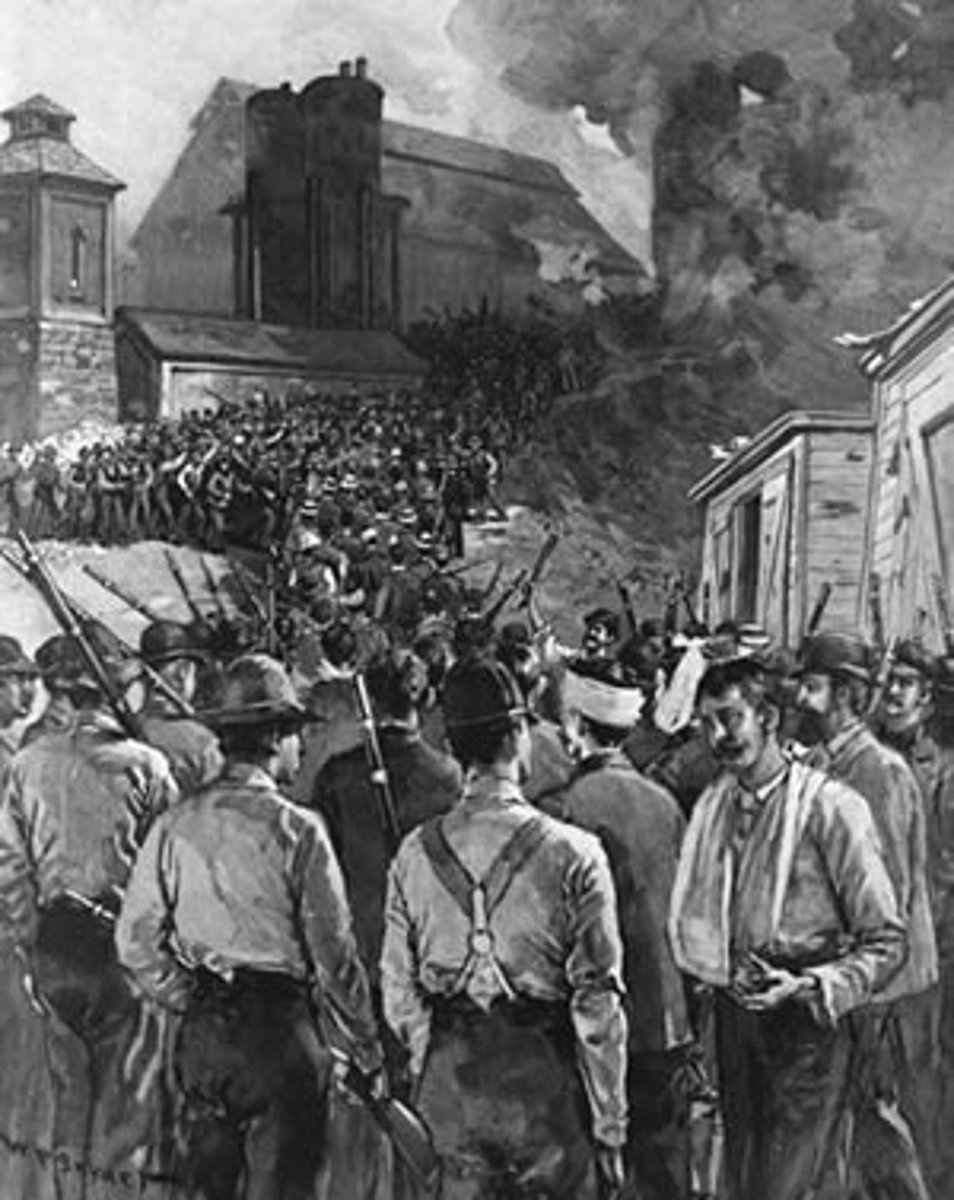
Homestead Strike 1892
Strike by steelworkers after the company's president announced plans to cut wages. Turned violent when the company tried to hire strikebreakers - state militia is called in to restore order. Continues to turn the public against labor unions.

Chinese Exclusion Act
1882 law banning Chinese immigration of skilled and unskilled laborers for a period of ten years. The act was periodically renewed and not repealed until 1943

Gentleman's Agreement
Japanese government's (1907-08) agreement to limit emigration of unskilled workers to the U.S. in exchange for the repeal of San Francisco's segregation order that had separated Japanese children and put them in a separate school.

Settlement Houses
Community centers established in "slum" neighborhoods to provide services for immigrants and the urban poor. Services included health care, child care, education, and help with obtaining naturalization. By 1910, about 400 existed. Helped cultivate social responsibility toward the urban poor

Political Machine
Powerful groups that controlled the activities of a political party in a city. Gained votes and financial support by offering help to voters and businesses. Helped solve urban problems, but were susceptible to corruption.

Muckrakers
Writers who exposed the abuses and corruption of society. Usually caused public outcry for reform.
Examples:
Upton Sinclair - meatpacking industry
Ida Tarbell - Rockefeller's (Standard Oil) ruthless business practices.

National Women's Suffrage Association
Group founded in 1869 by Susan B. Anthony and Elizabeth Cady Stanton. Pushed for voting rights for women

Henry Flagler
Industrialist who built many hotels along Florida's Gold Coast and built a railroad from Jacksonville, FL all the way to Key West (Florida East Coast Railroad). Railroad helped transport agriculture, supplies, laborers, tourists, and settlers in Florida

Vertical Integration
- Business strategy where a company controls the raw materials, manufacturing, and distribution of the finished product

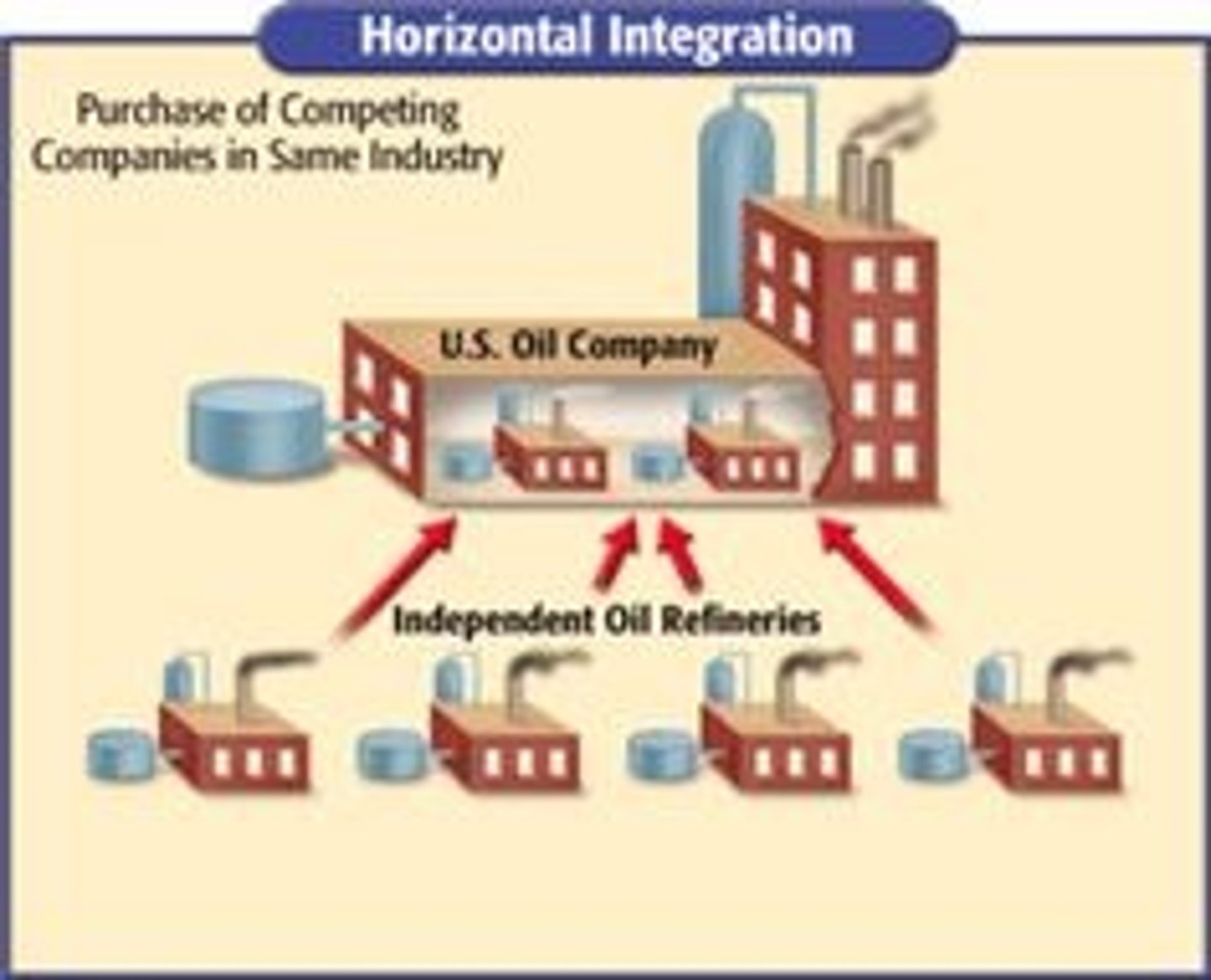
Horizontal Integration
Business strategy where companies producing similar products merge.