AP Human Geography: Language
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/44
Last updated 2:00 AM on 11/13/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
45 Terms
1
New cards
Accent
A distinctive mode of pronunciation of a language, especially one associated with a particular nation, locality, or social class.
2
New cards
Developing language
A language spoken in daily use with a literary tradition that is not widely distributed.
3
New cards
Dialect
A regional variation of a language distinguished by vocabulary, spelling, and pronunciation, particular to a specific region or social group.
4
New cards
Extinct Language
A language that no longer has any speakers, or that is no longer in current use.
5
New cards
Institutional language
A language used in education, work, mass media, and government.
6
New cards
Isogloss
A geographic boundary line delimiting the area in which a given linguistic feature occurs.
7
New cards
Isolated Language
A natural language with no demonstrable genealogical (or "genetic") relationship with other languages or language families; that is, one that has not been demonstrated to descend from an ancestor common with any other language. i.e A language family with only one language. [Japanic, Mongolic, Hmongic, Gregorian (Basque)]
8
New cards
Language Branch
A Subsection of a Language Family. Differences are not as extensive or old as with language families.
9
New cards
Language
The method of human communication, either spoken or written, consisting of the use of words in a structured and conventional way.
10
New cards
Language Group
A collection of languages within a branch that share a common origin in the relatively recent past and display relatively few differences in grammar and vocabulary.
11
New cards
Language Family
A collection of languages related to each other through a common ancestor long before recorded history. The trunk of the language tree, from which language branches come from.
12
New cards
Language Tree
A representation of the relationships of languages to each other, showing language families, branches, and groups.
13
New cards
Linguist
a language specialist; someone who studies multiple languages
14
New cards
Indo-European Language Family
Largest language family that includes English and most other languages in the Western Hemisphere. Also used in South and Southwest Asia. Includes the Germanic, Baltic, Slavic, Romance, "Indic", Balto-Slavic, Armenian, Albanian, Indo-Iranian, Anatolian (dead)
15
New cards
Sino-Tibetan Language Family
2nd largest language family. Includes Chinese dialects (Madarin and Cantonese) Thai, and Burmese
16
New cards
Lingua Franca
A Language mutually understood and commonly used in trade by people who have different native languages (currently English worldwide).
17
New cards
Monolingual State
A country in which only one language is spoken (i.e. Japan, Korea)
18
New cards
Bilingual
The ability to speak two languages.
19
New cards
Multilingual State
A country in which more than one language is in use (India, Nigeria, Belgium, Switzerland)
20
New cards
Official Language
The language adopted for use by the government for the conduct of business and publication of documents, a language that is given ☆special legal status☆
21
New cards
Pidgin Language
A Form of speech that adopts a simplified grammar and limited vocabulary of a lingua franca, used for communications among speakers of two different languages.
22
New cards
Standard Language
The specific form of a language used for official government business, education, and mass communications.
23
New cards
Toponym
The name of a place, often reflecting that place's history and culture.
24
New cards
Vernacular
Using a language or dialect native to a region or country rather than a literary, cultured, or foreign language. It is usually the language of the common people.
25
New cards
Creole
A language that results from the mixing of a colonizer's language with the indigenous language of the people being dominated. Developed out of an earlier pidgin stage.
26
New cards
Romance Branch
A language branch of the Indo-European Language Family. This branch includes languages that evolved from Latin (the language of the Romans). Includes Spanish, French, Portuguese, Galicain, Canatolian, Italian, Romanian, Romansh
27
New cards
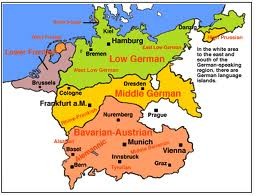
Germanic Branch
A language branch of the Indo-European Language Family.
North group inncludes Scandinavian languages (Swedish, Danish, Norwegian, Icelandic), which all came from Old Norse.
West group is further divided into High and Low subgroups. Includes the standard German language, English, Dutch, Flemish (Dialect of Dutch), Afrikaaans, and Frisian.
North group inncludes Scandinavian languages (Swedish, Danish, Norwegian, Icelandic), which all came from Old Norse.
West group is further divided into High and Low subgroups. Includes the standard German language, English, Dutch, Flemish (Dialect of Dutch), Afrikaaans, and Frisian.
28
New cards
Indo-Iranian Branch
Branch of the Indo-European language family; includes more than 100 individual languages divided into an eastern group (Indic), which includes the languages of Hinid and Urdu and a western group (Iranian), which includes Farsi and Kurdish.
29
New cards
Balto-Slavic Branch
Branch of the Indo-European language family; can be broken down into four groups: East Slavic (Russian, Ukrainian, Belarusian), Baltic (Latvian, Lithuanian), West Slavic (Polish, Czech, and Slovak), and South Slavic (Serbo-Croatian).
30
New cards
Celtic Branch
Branch of the Indo-European Language Family; divided into two language groups: Goidelic (Gaelic), which includes Irish Gaelic and Scottish Gaelic, and Brythonic, which includes Welsh, Breton, and Cornish.
31
New cards
Uralic Language Family
Language Family in Europe that includes the languages of Estonian, Finnish, and Hungarian.
32
New cards
Austronesian Language Family
Language Family spoken mostly in Indonesia. This family includes the languages of Javanese, Indonesian, Malay, and Malagasy.
33
New cards
Afro-Asiatic Language Family
Includes the languages of Arabic and Hebrew.
34
New cards
Niger-Congo Language Family
Includes Swahili, the lingua franca in Africa, and Zulu (the languages of the Bantu peoples)
35
New cards
Prehistoric Subgroup
A language that predates the current language family, before the written record. Ex: Proto-Indo-European
36
New cards
Altaic Language Family
A language family spoken across central Asia named after the Altai Mountains. Includes Turkish, the languages spoken in the Caucasus Region and across Central Asia, and is spoken in countries like Azerbaijan, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Turkmenistan, Uzbekistan, Mongolia and Georgia.
37
New cards
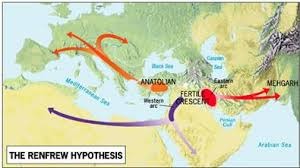
Renfrew (Anatolian) Theory
Argues the Proto-Indo-European language diffused by way of agricultural practices from Anatolia (Turkey) in 6300 BC.
38
New cards
Language Divergence
When a lack of spatial interaction (isolation) among speakers of a language breaks the language into dialects and then new languages.
39
New cards
Language Convergence
When peoples with different languages have consistent spatial interaction and their languages collapse into one (i.e. pidgin and creole).
40
New cards
Backward Reconstruction
When linguists track sound shifts and the hardening of consonants backward to reveal an "original" language.
41
New cards
vigorous language
a language that is spoken in daily use but that lacks a literary tradition (written evidence, etc)

42
New cards
Language Revival
an attempt to halt or reverse the decline of a language or to revive an extinct one
43
New cards
Tai Kadai or Kra Dai family
Tai, Lao
44
New cards
Austro Asiatic family
Vieatnamese, Khamer, Mon (Burma)
45
New cards
dravidian family
Southern India and Shri Lanka