Slipped Capital Femoral Epiphysis
1/5
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
6 Terms
Limping in 10-15 years: A slipped capital femoral epiphysis occurs when what plate of what structure is weak? then becomes what?
When the growth plate of the proximal femoral epiphysis is weak and becomes displaced (slips down) from its normal position
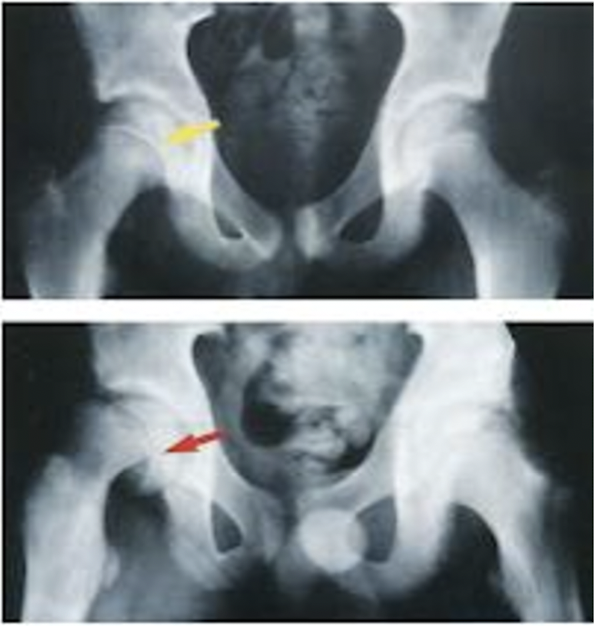
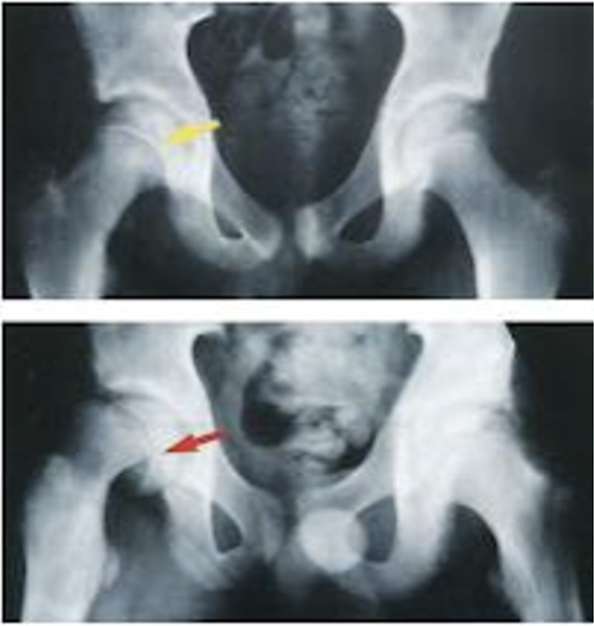
what is the exact cause of slipped capital femoral epiphysis?
what 2 factors are likely?
exact cause is unknown
endocrine and mechanical factors are likely
what is the incidence rate of slipped capital femoral epiphysis?
in which gender?
10.8 per 10,000
M>F with 2-3:1 ratio
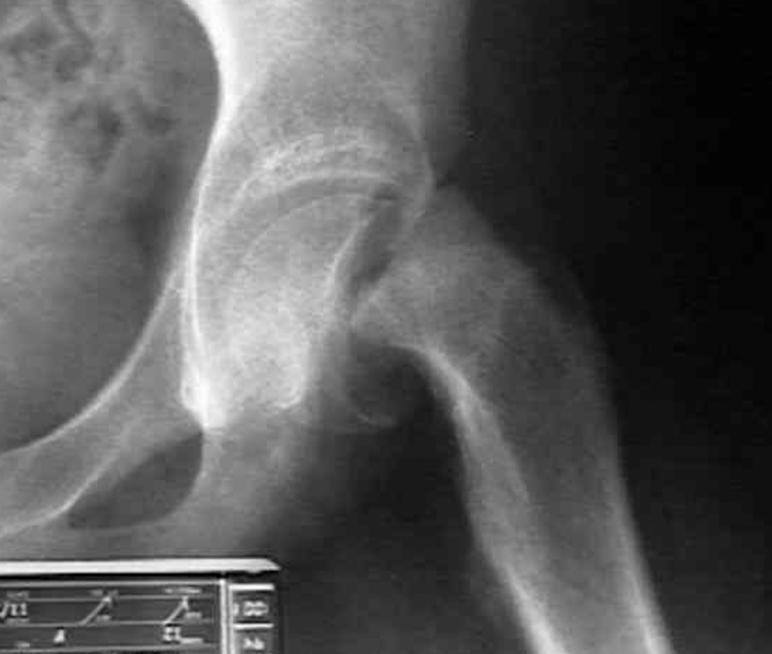
Clinical manifestations for slipped capital femoral epiphysis:
onset in who and when?
what side involvement in how many cases?
early presentation is what associated with what pain?
referred to what side and of what 2 body parts?
what is the motion limitation? (3)
Onset in boys usually at puberty (10-16 in males, 9-15 in females)
B/L involvement occurs in 1/4 to 1/3 of cases
early presentation = limp w/ groin pain, referred to anteromedial side of thigh and knee
Motion limitation in hip flexion, abd, and IR
Clinical Manifestations: Radiographs demonstrate what displacement? in what direction?
what is the limitation of anterior view?
Initial displacement in a posterior and inferior direction
may be missed on an anterior view x-ray
Treatment for SCFE:
goals to maintain ___, keep ___ to a minimum if not a severe case, prevent early ___
_____ using screw or pins in severe, ___, or progressing cases
be aware of what?
Maintain ROM, keep displacement to a minimum if not a severe case, prevent early degenerative arthritis
Surgical fixation using screw or pins in severe, unstable, or progressing cases
be aware of avascular necrosis