Infection Control: History, Terms, and Precautions in Healthcare
1/65
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
66 Terms
What is the definition of infection?
Invasion of an organism's body tissues by disease-causing agents, their multiplication, and the reaction of host tissues to the infectious agents and the toxins they produce.
What does infection control aim to prevent?
The spread of pathogenic microorganisms that have the potential to cause infectious disease.
What are the two types of infections based on their source?
Exogenous infection (from the environment) and endogenous infection (from the patient's own microflora).
What is an example of an exogenous infection?
A pathogen entering the patient's body from a contaminated device or healthcare worker.
What is an example of an endogenous infection?
A pathogen from the patient's own microflora that grows unchecked due to a compromised immune system.
What role does normal flora play in the body?
Normal flora prevents harmful bacteria from invading and causing infections.
What historical practices were used for infection control in ancient Egypt?
Egyptians used honey, lard, and other substances to dress wounds, and honey contains hydrogen peroxide which can kill bacteria.
What significant developments in infection control occurred in the late 1800s to early 1900s?
Quarantine regulations, the beginning of immunization, large-scale soap production, pasteurization, water treatment, and sewer systems.
What is the significance of body substance isolation?
It involves avoiding direct physical contact with all moist and potentially infectious body substances.
What is the body's reaction to being invaded by microorganisms?
Prostaglandins are released, which increases body temperature as part of the immune response.
What are some early practices of infection control?
Personal cleanliness, isolation practices, food hygiene, and diagnosis and treatment of infections.
What is the importance of barrier protection in infection control?
Barrier protection involves covering open wounds and wearing gloves when handling bodily fluids or contaminated materials.
What does the term 'normal flora' refer to?
A community of bacteria that normally live in specific parts of the body and prevent harmful bacteria from causing infections.
How did ancient civilizations use molds in infection treatment?
Molds in bread were believed to produce raw forms of antibiotics to treat infected wounds.
What is the definition of disease?
A disorder or abnormal condition that negatively affects the structure or function of body parts, producing specific signs and symptoms.
What is the role of antiseptics in ancient Egyptian medicine?
Antiseptics such as pitch, tar, resins, and aromatics were used in embalming and to prevent infection.
What is the impact of a compromised immune system on infections?
It allows endogenous pathogens to grow unchecked, increasing the risk of infections.
What is the significance of treating all bodily fluids as infectious?
It helps prevent the transmission of infections in healthcare settings.
What is the relationship between stress and infection?
Intense stress can compromise the immune system, making the body more susceptible to infections.
What are some signs that an infection may be present?
Symptoms such as increased body temperature, inflammation, and other reactions from the immune system.
What is the historical significance of honey in infection control?
Honey was used for wound treatment due to its antibacterial properties, particularly its hydrogen peroxide content.
What does the term 'aseptic techniques' refer to?
Methods used to prevent contamination by pathogens, including the use of antiseptics like hydrogen peroxide.
What significant public health measures were enacted in the late 1800s to early 1900s?
Quarantine regulations
beginning of the immunization era
large-scale soap production
improvements in pasteurization
water treatment
sewer systems
What is Body Substance Isolation?
It refers to the avoidance of direct physical contact with all moist and potentially infectious body substances.
What are some key practices for using barrier protection in infection control?
Cover open wounds, wear gloves when handling bodily fluids, use face masks/gowns, exercise caution with sharp objects, and discard contaminated materials following biohazard procedures.
What historical event prompted improvements in sewer systems?
A cholera outbreak.
Who invented the microscope and discovered cells in 1665?
Robert Hooke.
What important practice did Ignaz Semmelweis advocate in 1850?
Washing hands to save lives.
What antiseptic technique did Joseph Lister introduce in 1867?
The use of carbolic acid (phenol) to clean surgical tools.
What contributions did Louis Pasteur make to microbiology?
He created vaccines for anthrax and rabies and invented the process of pasteurization.
Who first described microorganisms using a microscope?
Antonie van Leeuwenhoek.
What was Robert Koch known for in public health?
discovered bacteria related to diseases
invented sterilization methods
changed attitudes about hygiene
What role did Florence Nightingale play in nursing?
She is regarded as the founder of modern nursing and organized care for wounded soldiers.
What are Universal Precautions?
A standard set of guidelines aimed at preventing bloodborne pathogen transmission through exposure to blood and other potentially infectious materials.
What are bloodborne pathogens?
Diseases spread when the blood of an infected person enters the bloodstream of another, including HIV, hepatitis B virus (HBV), and hepatitis C virus (HCV).
What types of body fluids are considered potentially infectious?
Cerebrospinal fluid
synovial fluid
pleural fluid
peritoneal fluid
pericardial fluid
amniotic fluid.
What did the CDC's 1996 guideline for Isolation Precautions combine?
It combined the major features of Universal Precautions and Body Substance Isolation into what is now referred to as Standard Precautions.
When should standard precautions be practiced?
They should be practiced regardless of whether the patient has an infection or not.
What is the significance of the term 'Standard Precautions'?
It refers to guidelines that aim to prevent the transmission of bloodborne pathogens.
What is the role of disinfectants in infection control?
They are used to clean areas thoroughly to eliminate infectious agents.
How long should hands be washed to ensure effective cleaning?
At least 20 seconds.
What should be done with contaminated clothing?
It should be washed in hot water.
What is the purpose of wearing gloves in infection control?
To protect against exposure to bodily fluids and contaminated materials.
What is the importance of using caution when handling sharp objects?
To prevent injuries and potential exposure to infectious materials.
What are Standard Precautions in healthcare?
Basic, minimum infection prevention practices that apply to all patient care regardless of the patient's infection status.
What are the three categories of Transmission-Based Precautions?
Contact transmission, Droplet transmission, Airborne transmission.
What size are droplets considered to be for droplet transmission?
Droplets are considered to be ≥ 5 micrometers in size.
What pathogens can be transmitted via airborne transmission?
Influenza, tuberculosis, measles, chicken pox, shingles, SARS, MERS, and COVID-19.
What practices are included under Standard Precautions?
Hand hygiene, use of personal protective equipment, respiratory hygiene, sharps safety, safe injection practices, sterile instruments, and cleaning/disinfecting environmental surfaces.
What is the purpose of Contact Precautions?
To prevent transmission of infectious agents requiring additional control measures for patients known or suspected to be infected.
What is the difference between direct and indirect contact transmission?
Direct contact requires physical contact between an infected person and a susceptible person, while indirect contact involves contact with contaminated surfaces.
What are aerosols in the context of airborne transmission?
Dissemination of airborne droplet nuclei or small particles in the respirable size range ≤ 5 micrometers.
What are some examples of frequently touched surfaces that should be disinfected?
Door knobs, tables, medical instruments, computer keyboards, and children's toys.
What are the requirements for an Airborne Infection Isolation Room (AIIR)?
6 air exchanges/hour
Negative air pressure
Exhaust via HEPA filter
Materials cleaned 2x daily
Proper signage
What should a patient wear when outside of their room under Droplet Precautions?
A mask.
What is the role of personal protective equipment (PPE) in infection control?
To protect healthcare workers from exposure to infectious agents.
What is the significance of respiratory hygiene/cough etiquette?
To minimize the spread of respiratory infections.
What is the recommended action for reusable items taken into an exam room?
They should be cleaned and disinfected before removal.
What is the importance of hand hygiene in infection control?
It reduces the risk of transmitting infectious agents.
What should be done with disposable items used in patient care?
They should be discarded at the point of use.
What is the purpose of observing 6 feet distancing in infection control?
To minimize the risk of droplet transmission.
What is the epidemiologic triad model of infection?
A model that describes the interaction between the agent, host, and environment in the context of disease transmission.
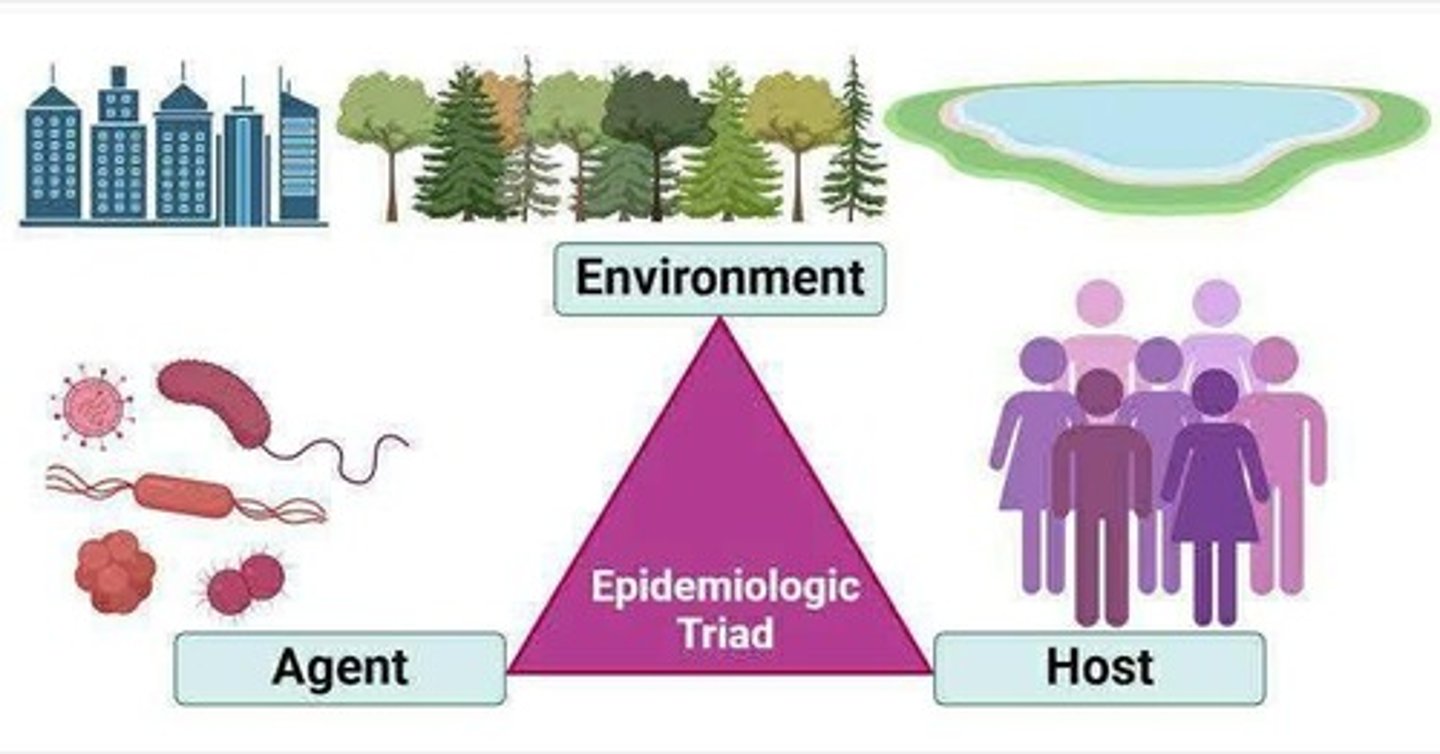
What is the role of administrative controls in infection control?
To implement policies and procedures that help prevent the spread of infections.
What is the significance of cleaning and disinfecting environmental surfaces?
To reduce the risk of indirect contact transmission.
What should be done if a patient is suspected to be infected with an airborne pathogen?
They should be placed in an AIIR and referred to an appropriate facility.
What is the purpose of special air handling ventilation in airborne precautions?
To ensure proper airflow and reduce the risk of airborne transmission.