Common Digestive Problems
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
46 Terms
Each year more than 5000 people in the United States die from
Choking on food
Almost all of the victims of choking are how old?
younger than 3 years or older than 74 years
What causes choking?
Food slipped into the trachea and blocked the air passageway
Without oxygen, the person may suffer permanent brain damage within
5 minutes
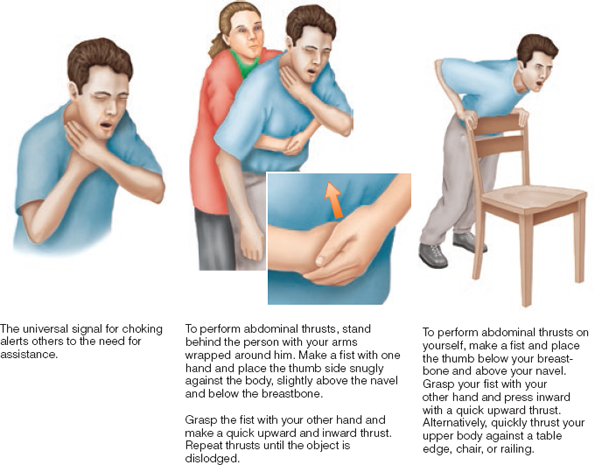
First Aid for Choking
As soon as possible, shout for help and call 9-1-1. If possible, get consent to begin first aid. First aid for choking relies on abdominal thrusts, repeated until the object is forced out, the person can cough or breathe, or the person becomes unconscious. In the case of someone losing consciousness, carefully lower the person to the floor.
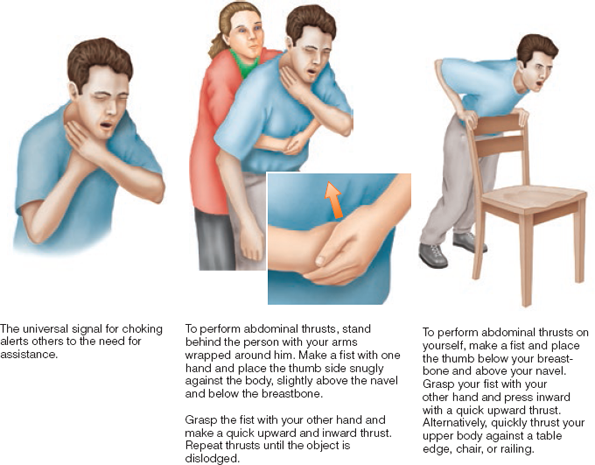
Abdominal thrusts
a technique for dislodging an object from the trachea of a choking person.
Acid controllers
medications used to prevent or relieve indigestion by suppressing production of acid in the stomach; also called H2 blockers.
Antacids
medications used to relieve indigestion by neutralizing acid in the stomach.
Belching
the release of air or gas from the stomach through the mouth
Bloating
uncomfortable abdominal fullness or distention.
celiac (SEE-lee-ak) disease
an intestinal disorder in which the inability to absorb gluten results in an immune response that damages intestinal cells; also called celiac sprue, nontropical sprue, or gluten-sensitive enteropathy
Colitis
inflammation of the colon.
Colonic irrigation
the popular, but potentially harmful practice of “washing” the large intestine with a powerful enema machine; also called colonic hydrotherapy
Constipation
the condition of having infrequent or difficult bowel movements.
Defecate
to move the bowels and eliminate waste.
Diarrhea
the frequent passage of watery bowel movements.
diverticula (dye-ver-TIC-you-la)
sacs or pouches that develop in weakened areas of the intestinal wall (like bulges in an inner tube where the tire wall is weak).
diverticulitis (DYE-ver-tic-you-LYE-tis)
infected or inflamed diverticula. • itis = infection or inflammation
diverticulosis (DYE-ver-tic-you-LOH-sis)
the condition of having diverticula. • osis = condition
Enema
solution inserted into the rectum and colon to stimulate a bowel movement and empty the lower large intestine.
Flatulence
passage of excessive amounts of intestinal gas.
FODMAP
a collective term used to describe fermentable oligosaccharides, disaccharides, monosaccharides, and polyols that are commonly found in such foods as wheat, onions, some fruits and vegetables, sorbitol, and some dairy.
gastroesophageal reflux
the backflow of stomach acid into the esophagus, causing pain and damage to its lining; commonly known as heartburn or acid indigestion.
Gluten
proteins in grains that give dough its elastic texture; in people with celiac disease, gluten damages the small intestine.
hemorrhoids (HEM-oh-royds)
Painful swelling of the veins surrounding the rectum
Indigestion
incomplete or uncomfortable digestion, usually accompanied by pain, nausea, vomiting, heartburn, intestinal gas, or belching.
IBS
an intestinal disorder of unknown cause. Symptoms include abdominal discomfort and cramping, diarrhea, constipation, or alternating diarrhea and constipation.
larynx (LAIR-inks)
the entryway to the trachea that contains the vocal cords; also called the voice box
Mineral oil
a purified liquid derived from petroleum and used to treat constipation.
nonceliac gluten sensitivity
a poorly defined cluster of digestive symptoms that seem to improve with the elimination of gluten from the diet
Peptic ulcer
a lesion in the mucous membrane of either the stomach (a gastric ulcer) or the duodenum (a duodenal ulcer). • peptic = concerning digestion
Stool softeners
substances that increase the amount of water the stool absorbs in the GI tract, making the stool softer and easier to pass.
trachea (TRAKE-ee-uh)
the air passageway from the larynx to the lungs; also called the windpipe
Ulcer
a lesion of the skin or mucous membranes characterized by inflammation and damaged tissues. See also peptic ulcer
Vomiting
expulsion of the contents of the stomach up through the esophagus to the mouth.
First aid for vomiting
The best advice is to rest and drink small amounts of liquids as tolerated until the nausea subsides
What are two things to do to prevent diarrhea?
Good hygiene by washing hands regularly and proper food preparation
Colitis first aid
may also suffer from severe diarrhea, abdominal pain, and bloating. Depending on the cause, treatment generally focuses on rehydration and medication to control diarrhea, abdominal pain, and inflammation. Some people find some relief by avoiding certain foods that tend to worsen symptoms—notably greasy foods, milk products, and high-fiber foods (such as popcorn, seeds, and nuts).
IBS first aid
FODMAP and gluten free diet
Other treatments that may be effective include exercise; antispasmodic and antidiarrheal drugs for diarrhea and fiber supplements and laxatives for constipation; and psychological and behavioral therapies to reduce stress.
Strategies to Prevent or Alleviate Choking
Take small bites of food.
Chew thoroughly before swallowing.
Don’t talk or laugh with food in your mouth.
Don’t eat when breathing hard
Strategies to Prevent or Alleviate diarrhea
Avoid strenuous activity.
Rest.
Drink fluids to replace losses.
Call for medical help if diarrhea persists.
Strategies to Prevent or Alleviate constipation
Eat a high-fiber diet
Drink plenty of fluids
Exercise regularly
Respond promptly to the urge to defecate
Strategies to Prevent or Alleviate belching
Eat slowly
Chew thoroughly
Relax while eating
Strategies to Prevent or Alleviate intestinal gas
Eat bothersome foods in moderation
Strategies to Prevent or Alleviate heart burn
Eat small meals.
Drink liquids between meals.
Sit up while eating; elevate your head when lying down.
Wait 3 hours after eating before lying down.
Wait 2 hours after eating before exercising.
Refrain from wearing tight-fitting clothing.
Avoid foods, beverages, and medications that aggravate your heartburn. Common irritants include foods that are fried or high in fat; chocolate and peppermint; coffee, alcoholic beverages, and carbonated beverages; mustard, ketchup, and tomato sauces; acidic substances such as vinegar, citrus juices, and citrus fruits.
Refrain from smoking cigarettes or using tobacco products.
Lose weight if overweight.
Take medicine as prescribed by your physician
Strategies to Prevent or Alleviate ulcers
Avoid coffee and caffeine- and alcohol-containing beverages.
Avoid foods that aggravate your ulcer.
Minimize aspirin, ibuprofen, and naproxen use.
Refrain from smoking cigarettes.