HISTO OF URINARY SYSTEM
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
45 Terms
What are the two main compositions of the kidney?
The kidney is composed of the outer renal cortex and the inner renal medulla.
What is the site of the kidney?
The kidney is retro-peritoneal.
What is the shape of the kidney and what feature is located on its medial side?
The kidney is bean-shaped with a concave medial hilum where the ureter, nerves, blood, and lymph vessels enter and exit.
What structures compose the renal medulla?
The renal medulla is composed of 10-18 medullary pyramids.
What structures separate the medullary pyramids?
The medullary pyramids are separated by extensions from the renal cortex called renal columns.
What is the apex of each renal pyramid called?
The apex of each pyramid is called the renal papilla.
What structures receive urine from the renal papillae?
7-10 minor calyces receive urine from the renal papillae.
What structures receive urine from the minor calyces?
2-3 major calyces receive urine from the minor calyces.
What dose renal lobe consist of?
A renal lobe consists of a medullary pyramid and the overlying cortical tissue.
What dose renal lobule consist of?
A renal lobule consists of a medullary ray and the overlying cortical tissue.
What are the two main components of the histological structure (parenchyma) of the kidney?
The parenchyma of each kidney contains around 1 million functional units called Nephrons and Collecting ducts.
What are the four main divisions of the nephron?
The divisions of the nephron are the Renal Corpuscle, Proximal Tubule, Loop of Henle, and Distal Tubule.
What is the Renal Corpuscle formed of?
The Renal Corpuscle is formed of Bowman's capsule and Glomerular capillaries.
What is the space between the two layers of Bowman's capsule called?
The space between the two layers of Bowman's capsule is the Capsular (Bowman’s) space.
What are the two poles of Bowman's capsule and what are their functions?
Bowman's capsule has two poles: Vascular pole (site of entry of the afferent arteriole and exit of the efferent arteriole) and Urinary pole (connected to the Proximal tubule).
Describe the two layers of Bowman's capsule.
Bowman's capsule has a Parietal layer (outer) made of simple squamous epithelium and a Visceral layer (inner) formed of podocytes.
What are podocytes?
Podocytes are stellate-shaped cells that rest on the glomerular capillaries.
Describe the processes of podocytes.
Podocytes have Primary processes that arise from the cell body and curve around the glomerular capillary, and Secondary processes (pedicels) that arise from the primary processes and are implanted on the basement membrane of glomerular capillaries.
What are filtration slit pores?
Filtration slit pores are pores located between the secondary processes (pedicels) of podocytes, covered by slit diaphragms.
What are the components of the filtration membrane?
The filtration membrane is composed of Fenestrations of capillary endothelium, Thick glomerular basement membrane (GBM), and Filtration slit pores.
Where are mesangial cells located and what are their functions?
Mesangial cells are located in the renal corpuscles between the glomerular capillaries. They secrete components of the mesangial matrix, modify the diameter of glomerular capillaries, and are involved in turnover of the GBM.
List the parts of the renal tubules.
The renal tubules consist of the Proximal convoluted tubule, Loop of Henle, Distal convoluted tubule, Connecting tubules, and Collecting ducts.
Where does the proximal convoluted tubule start and what does it become continuous with?
The proximal convoluted tubule starts at the urinary pole of the renal corpuscle and becomes continuous with the loop of Henle.
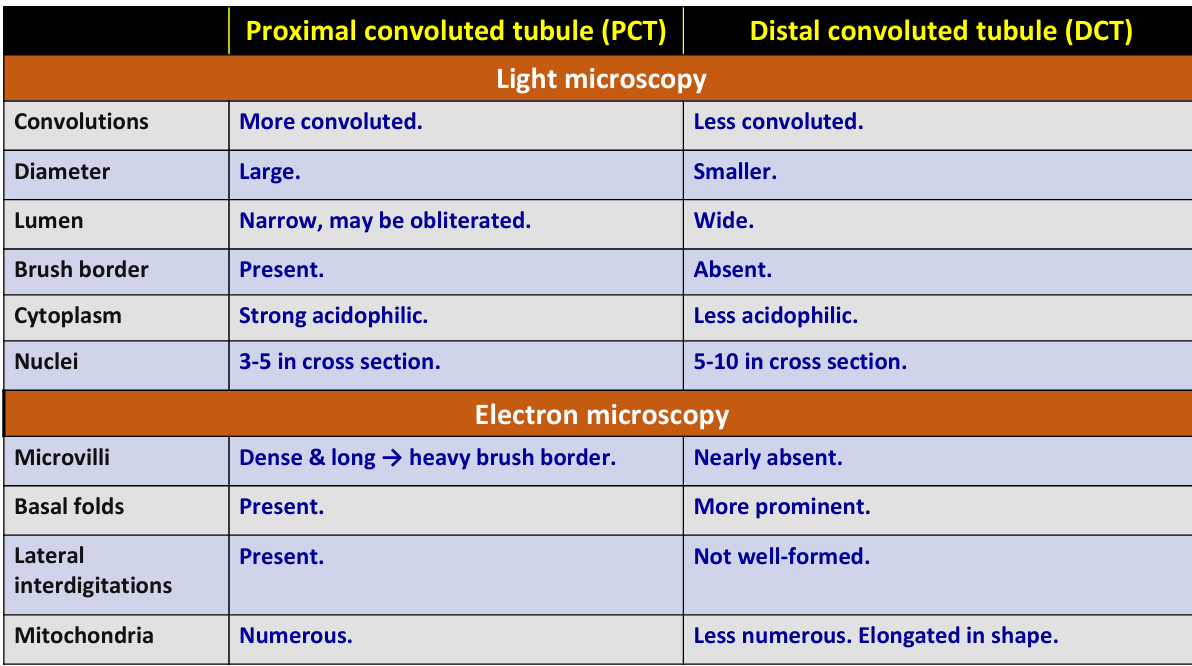
Describe the light microscopy features of the Proximal Convoluted Tubule (PCT).
PCT is long and highly convoluted with a large diameter and narrow lumen, cuboidal cells, apical brush border, strongly acidophilic cytoplasm, and round & central nuclei.
Describe the electron microscopy features of the cells of the Proximal Convoluted Tubule (PCT).
PCT cells have dense apical microvilli, numerous basal folds, present lateral interdigitations, numerous mitochondria, lysosomes, and pinocytotic vesicles.
What are the main functions of the proximal tubule?
The functions of the proximal tubule are Reabsorption and Secretion.
Describe the light microscopy features of the Distal Convoluted Tubule (DCT) and compare them to the PCT.
DCT is less convoluted with smaller diameter, wide lumen, cuboidal cells, no brush border, less acidophilic cytoplasm, and round nuclei compared to PCT.
Describe the electron microscopy features of the cells of the Distal Convoluted Tubule (DCT) and compare them to the PCT.
DCT cells have few apical microvilli, lateral interdigitations that are not well-formed, more prominent basal folds, elongated mitochondria and round euchromatic nucleus compared to PCT.
What is the main function of the distal tubule?
The distal tubule performs much less reabsorption than the proximal tubule and is involved in the reabsorption of sodium ions regulated by aldosterone.
Describe the structure of the Loop of Henle.
The Loop of Henle is a U-shaped structure with descending and ascending limbs, has an initial thick part and a thin descending limb.
What are the functions of the thin parts and the thick ascending limb of the Loop of Henle?
The thin parts are for passive reabsorption of sodium & chloride ions while the thick ascending limb is for active reabsorption.
Where are collecting ducts located and what do they merge to form?
Collecting ducts are located in the medullary ray and merge to form ducts of Bellini and then papillary ducts.
What are the types of cells found in the collecting ducts and their characteristics/functions?
The collecting ducts contain Principal cells (pale staining, respond to ADH) and Intercalated cells (dark staining, maintain acid-base balance).
What are the components of the Juxtaglomerular apparatus (JGA)?
The JGA is composed of Juxtaglomerular cells, Macula densa, and Lacis cells.
What are Juxtaglomerular cells (JG)?
JG cells are modified smooth muscle cells of the afferent arteriole that secrete renin.
What is the Macula densa (MD)?
The Macula densa is part of the distal tubule with crowded columnar cells located between arterioles.
What are Lacis cells?
Lacis cells, also known as Polar cushion, are supportive mesangial cells.
What is the main function of the Juxtaglomerular apparatus (JGA)?
The main function of the JGA is the regulation of blood pressure through the renin-angiotensinogen system.
What are the layers of the ureter wall?
The ureter wall has three layers: Mucosa, Muscularis, and Adventitia.
Describe the Mucosa layer of the ureter.
The mucosa of the ureter is folded and consists of Transitional epithelium with a thin basement membrane and Lamina propria.
Describe the Muscularis layer of the ureter.
The muscularis of the ureter consists of irregular bundles of smooth muscles separated by loose connective tissue.
What are the layers of the urinary bladder wall?
The urinary bladder wall has three layers: Mucosa, Muscularis, and Adventitia.
Describe the Mucosa layer of the urinary bladder.
The mucosa of the urinary bladder is folded and consists of Transitional epithelium with a thin basement membrane and Lamina propria.
Describe the Muscularis layer of the urinary bladder and its name.
The muscularis of the urinary bladder consists of three loosely arranged layers of smooth muscles called the detrusor muscle.
Compare between (PCT) & (DCT)
.