Ancient Egypt Midterm
1/101
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
102 Terms
Rosetta Stone, Ptolemy V, made out of grandiorite, 196 BCE, found in the Egyptian Delta.

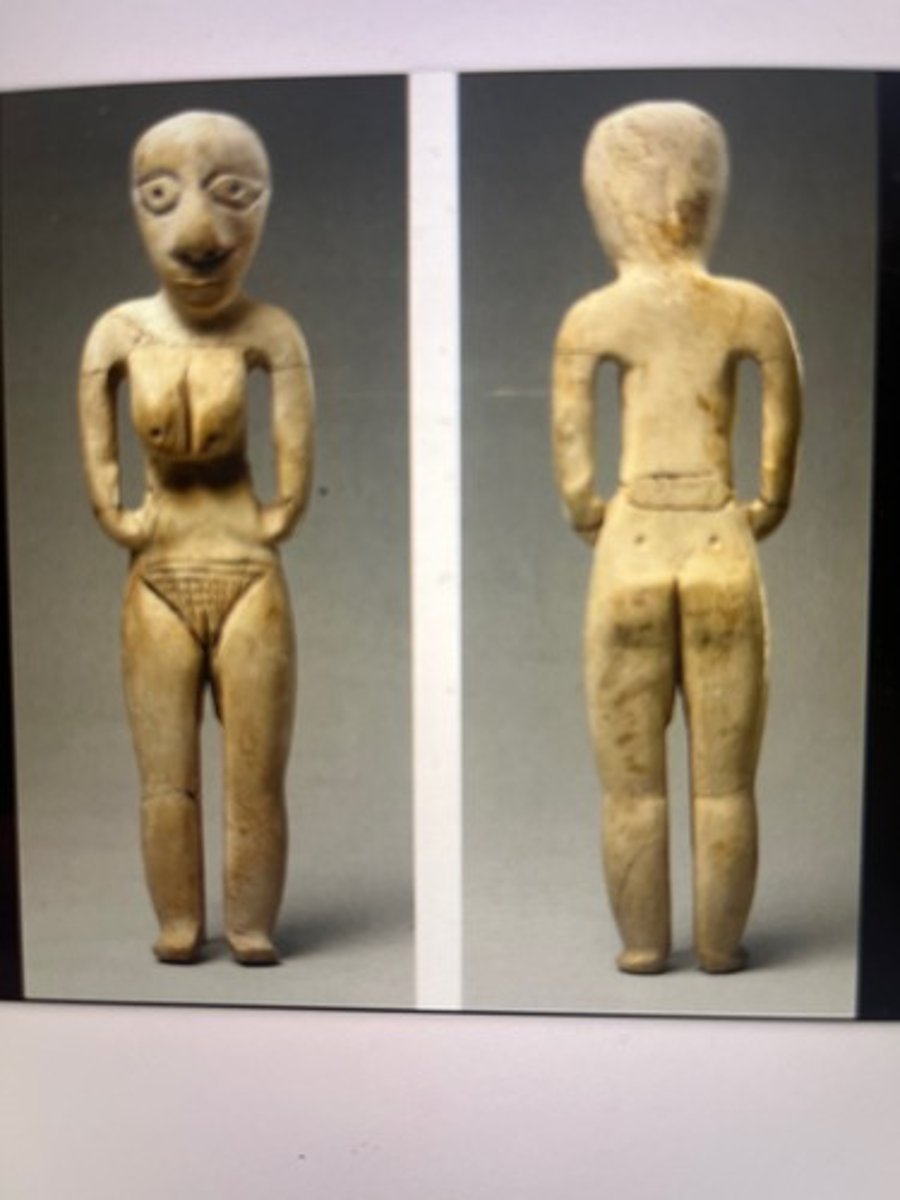
Statuette of a woman, Badarian Culture, made of ivory, ca. 4400-3800 BCE

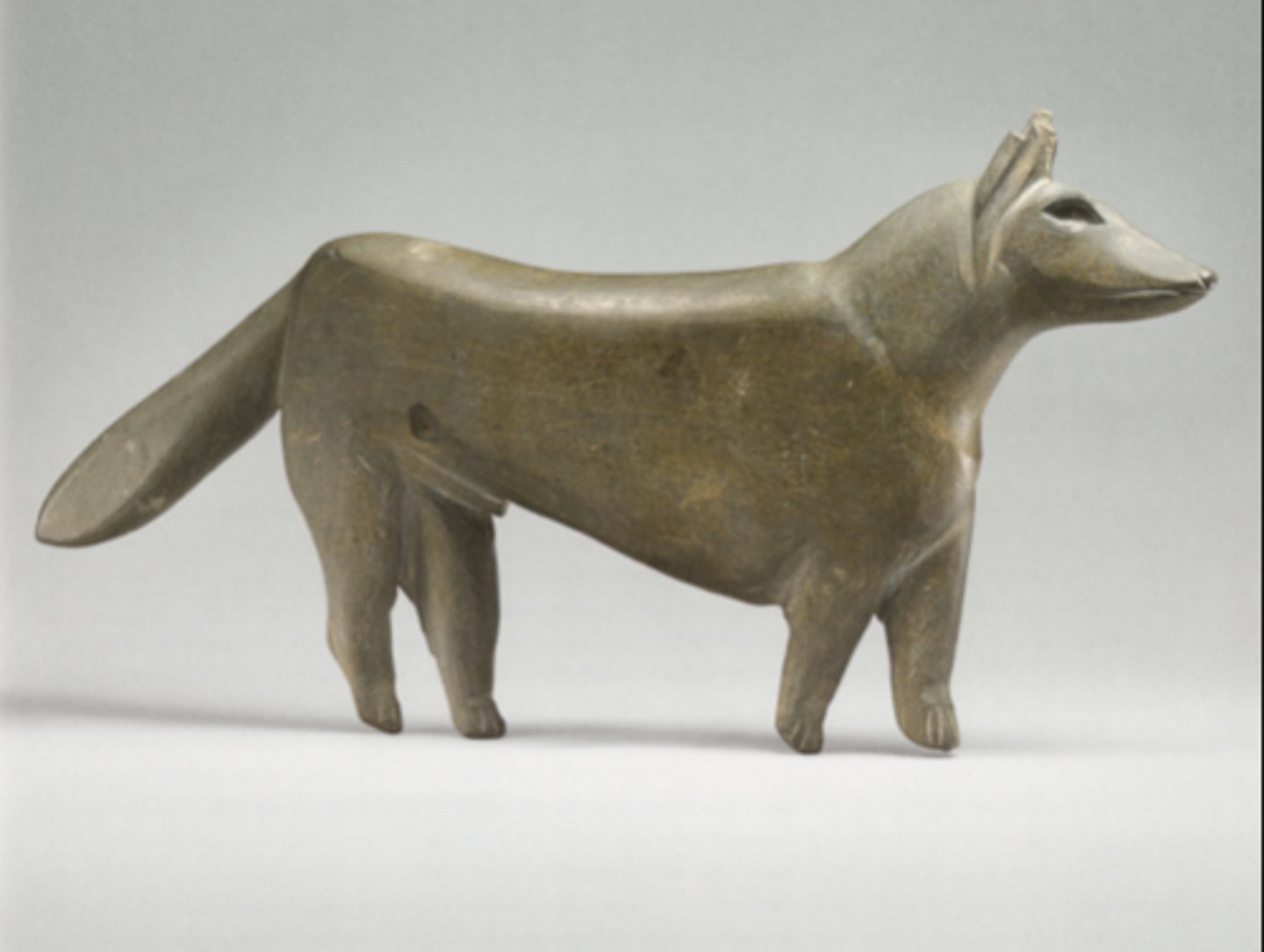
Jackal statue excavated in a woman's tomb, made of schist, ca. 3300-3100 BCE

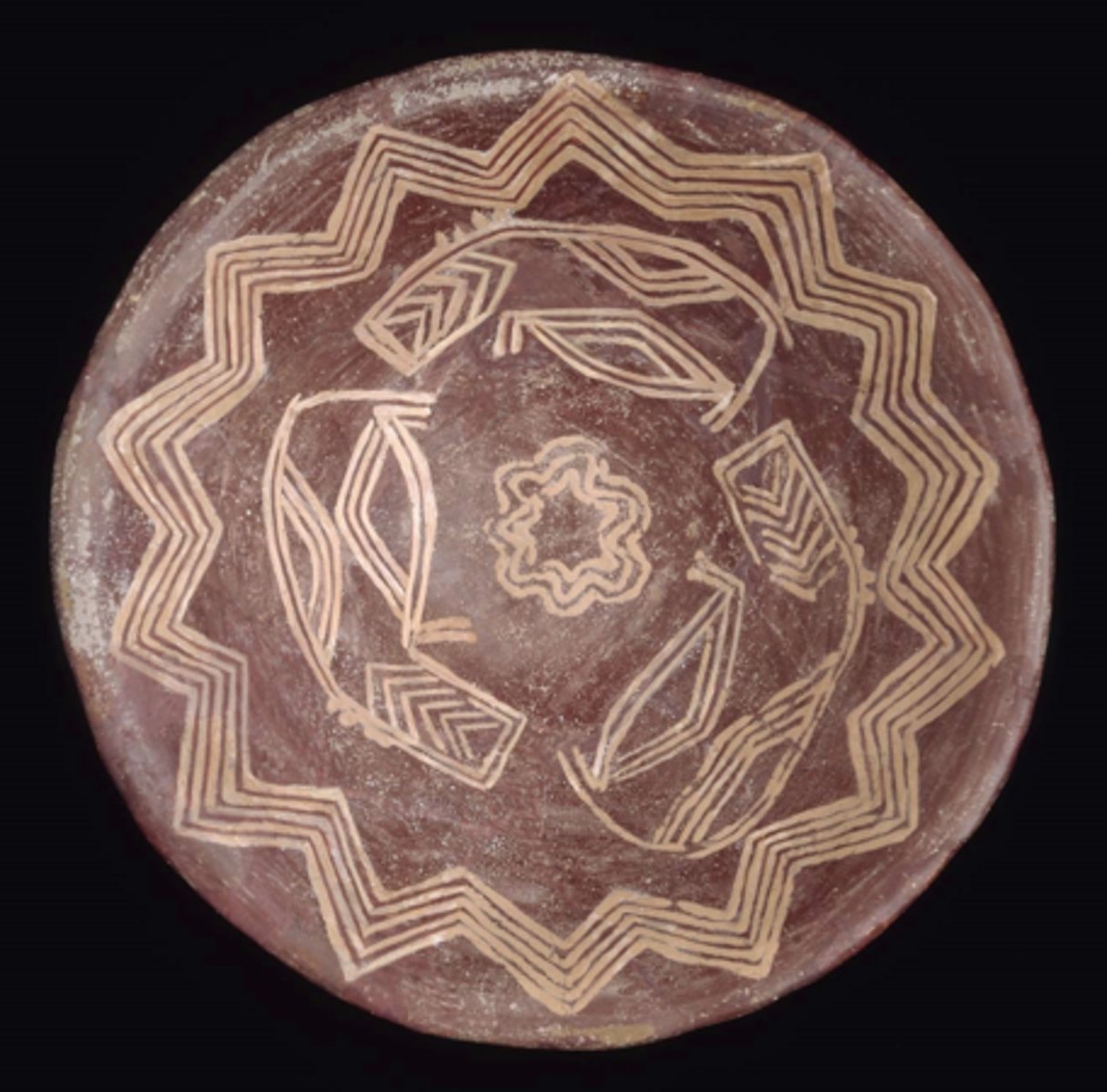
Bowl with hippopotami, Excavated in a tomb at el-Mesaid, ca. 3700-3450 BCE, h. 6.8cm, dia. 19.4cm

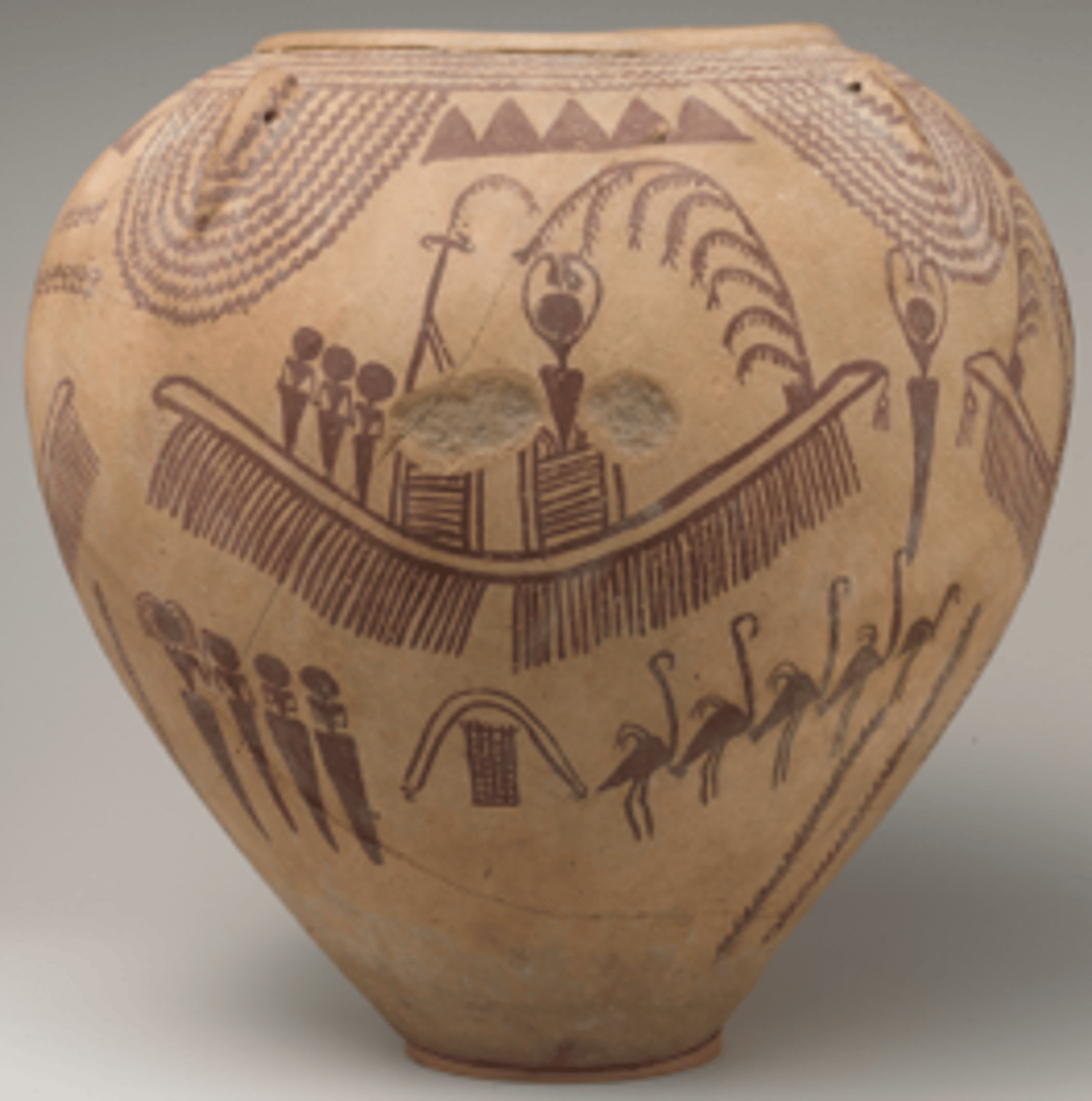
Decorated Ware Jar Depicting Ungulates and Boats with Human Figures, clay, excavated in a tomb, ca. 3500-3300 BCE

Wall painting from an elite tomb from Hierakonpolis,
Painting on plaster, ca. 3450 BCE
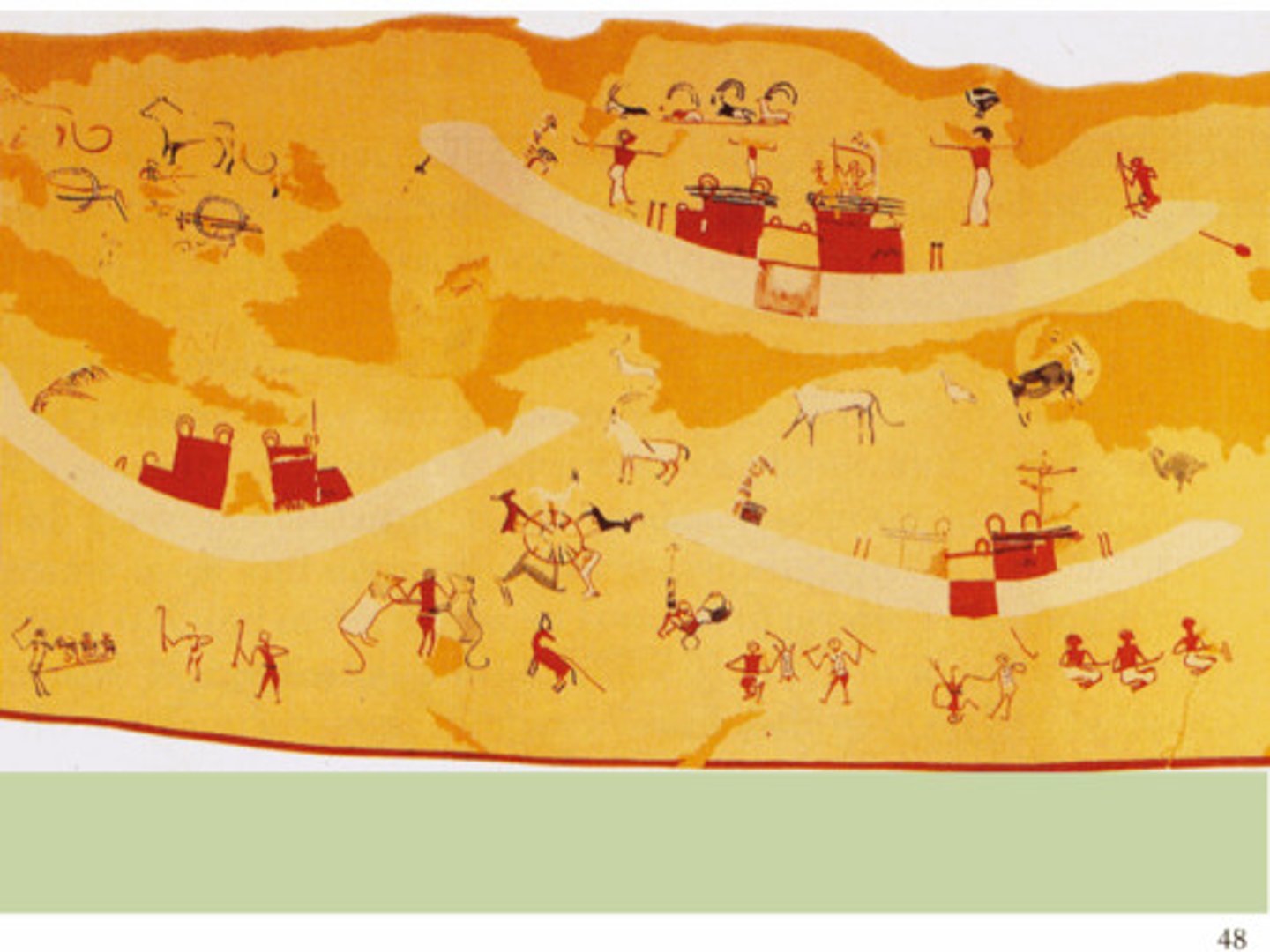
Ceremonial Palette, the so-called Two-Dog Palette, from a temple at Hierakonpolis, made out of greywacke, ca. 3300-3100 BCE
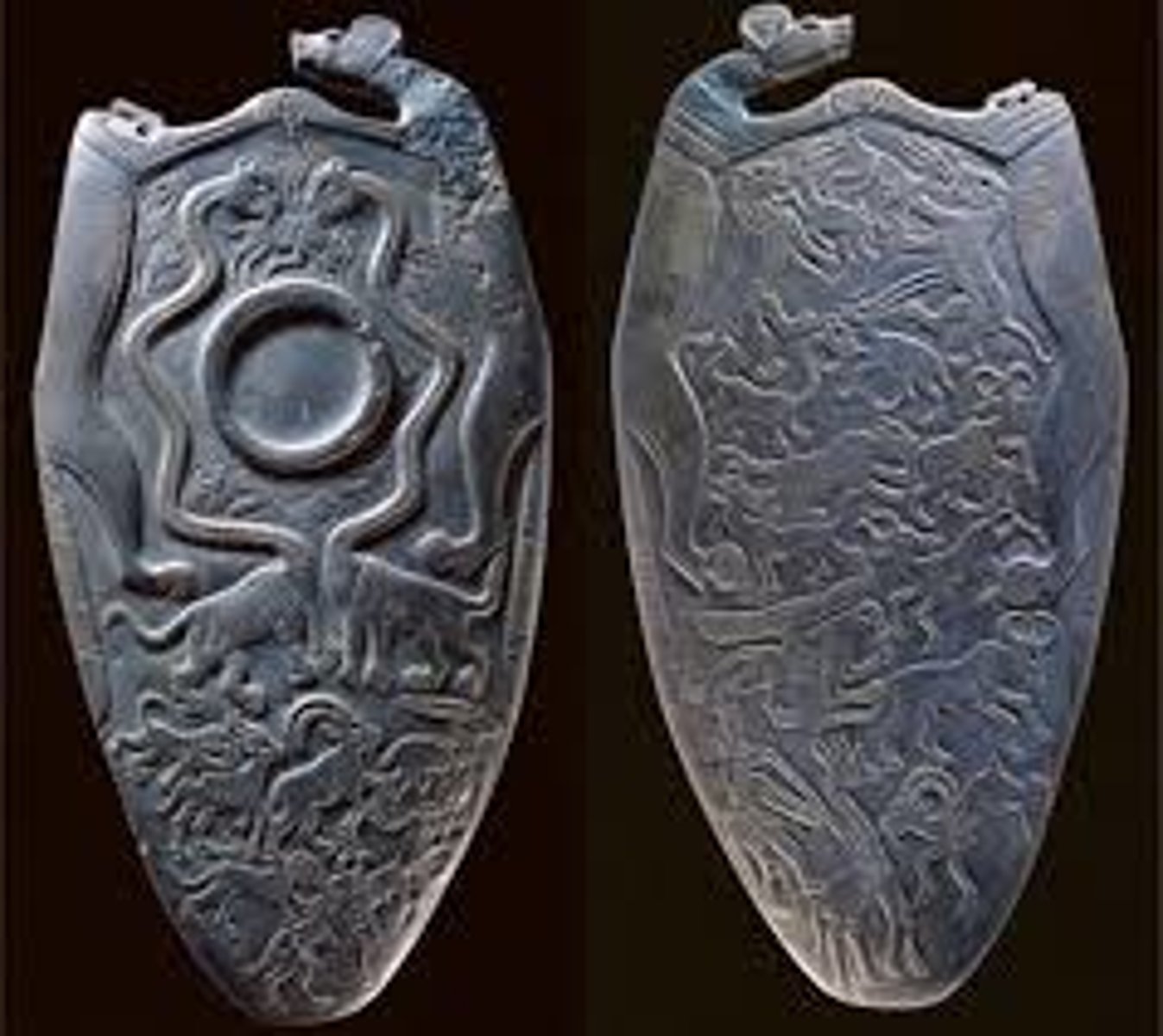

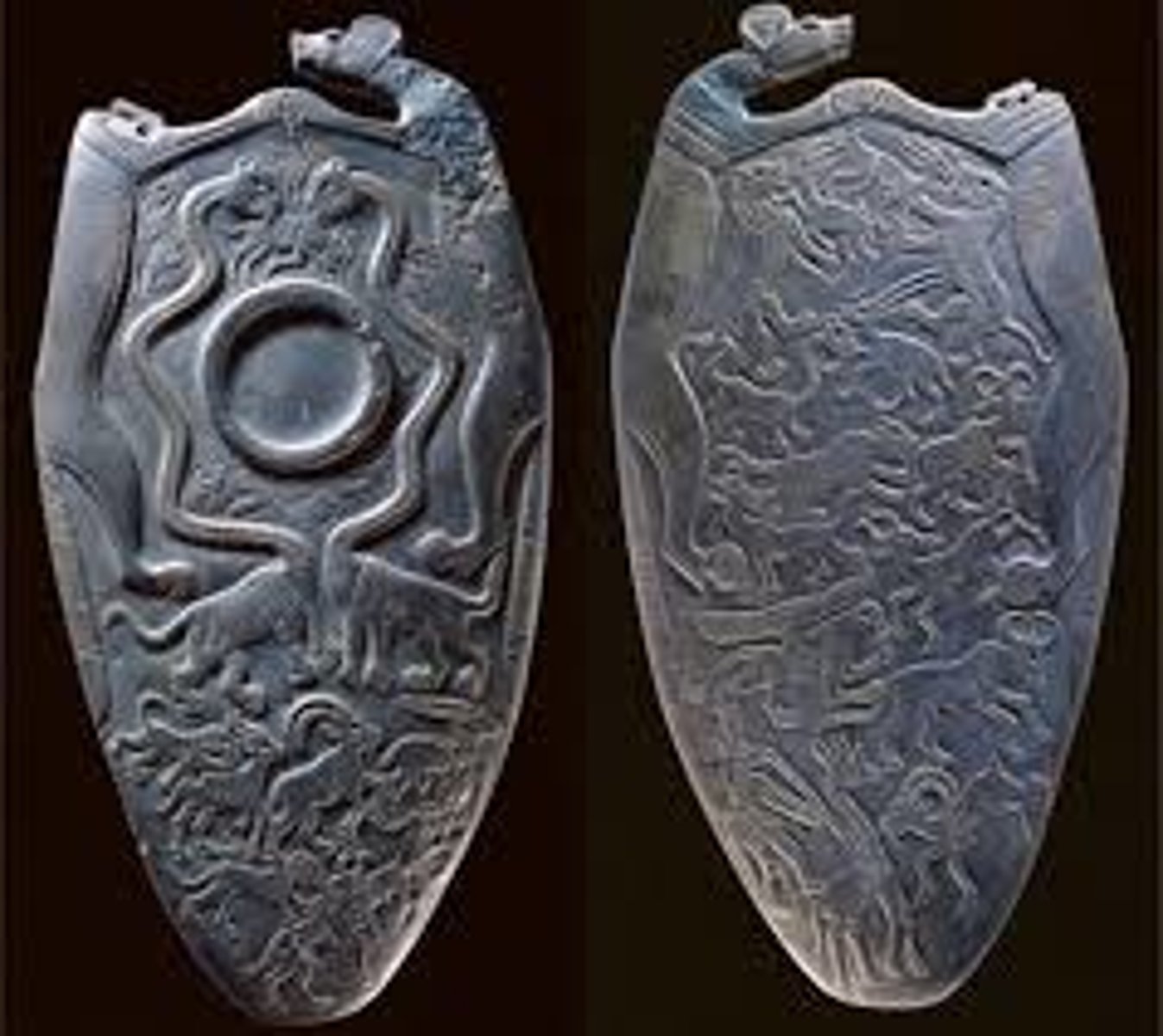
The Four-Dog Palette, made of greywacke, ca. 3300-3100 BCE

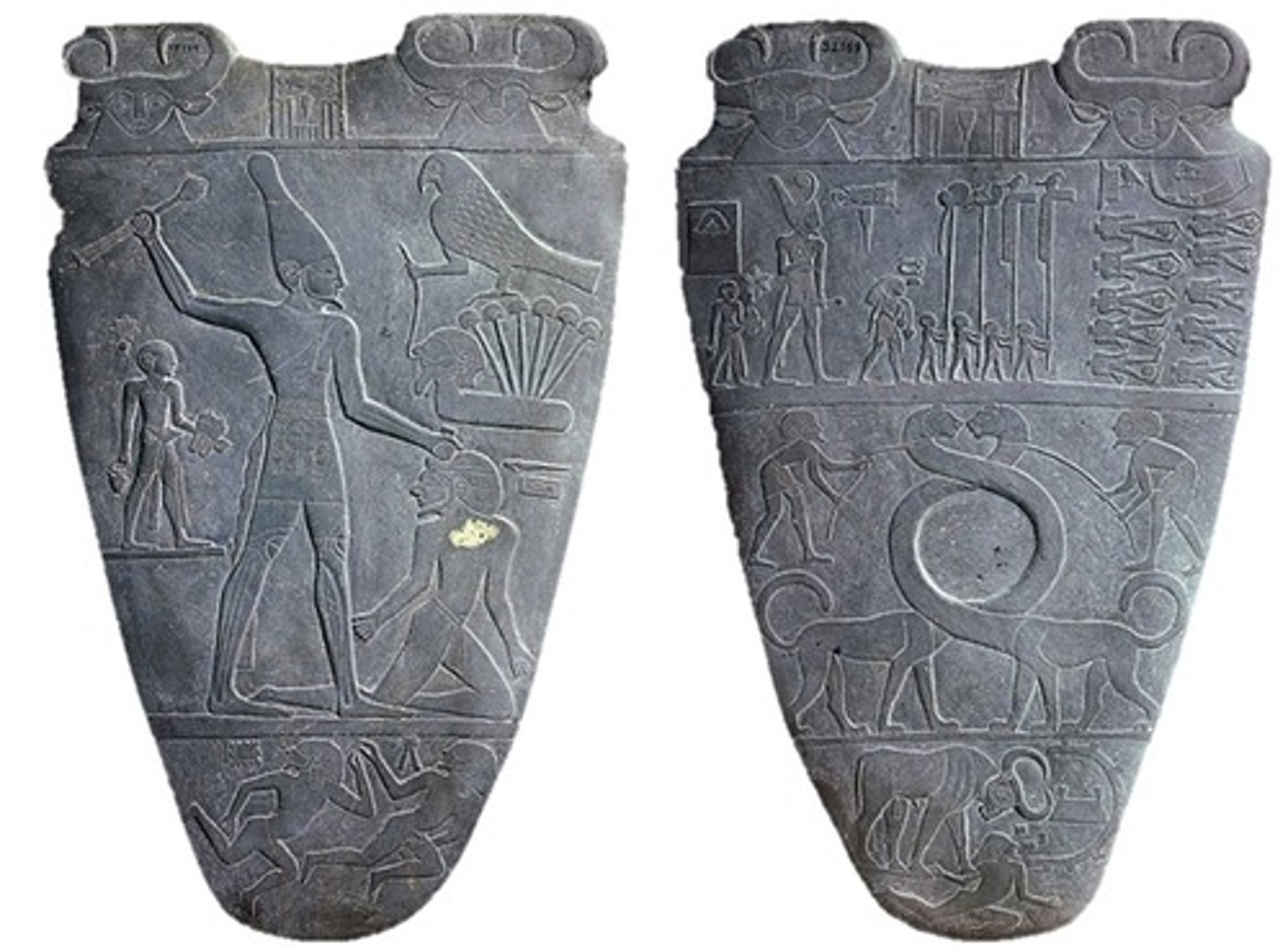
The Narmer Palette, excavated in a temple located at Hierakonpolis,
made out of schist ca. 3000 BCE

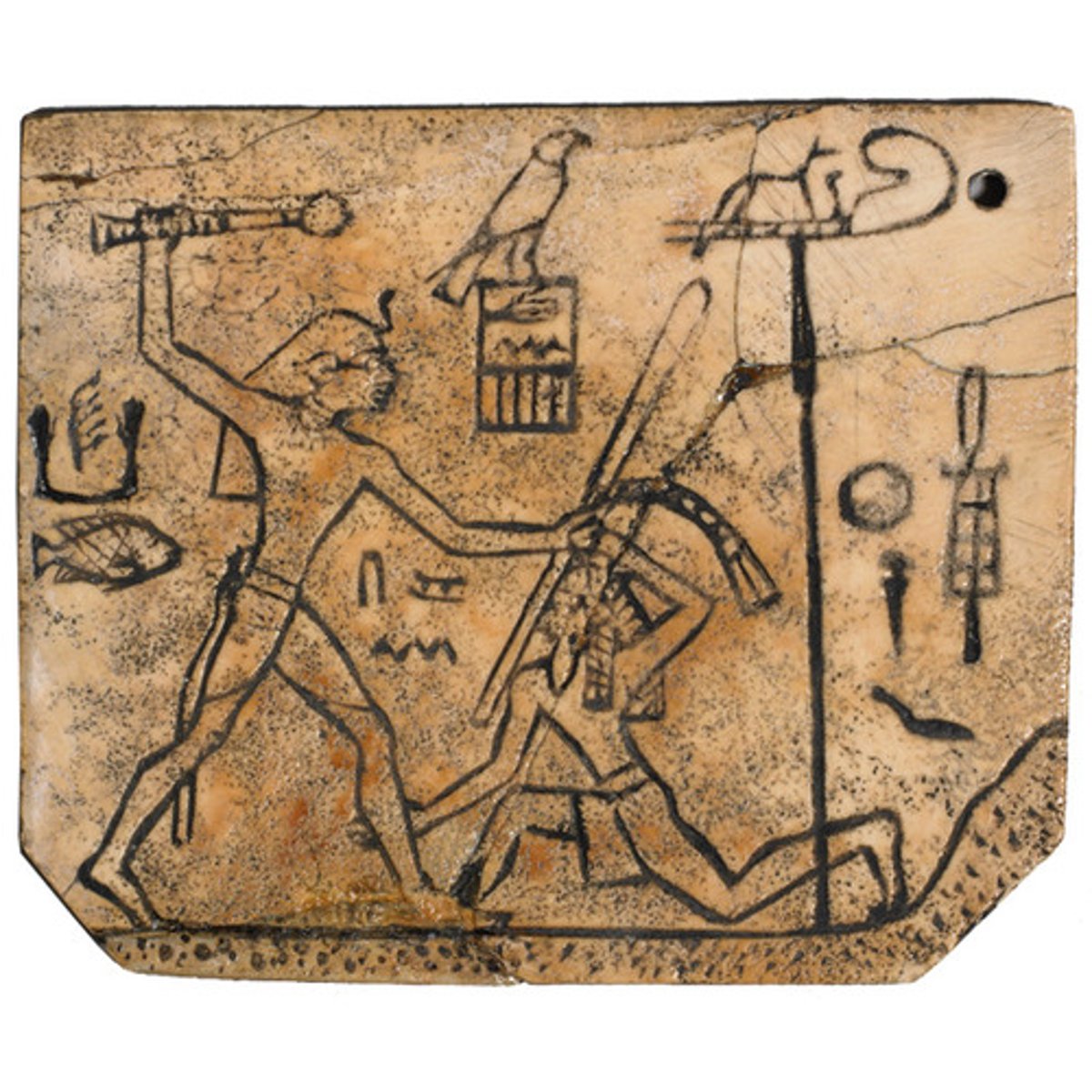
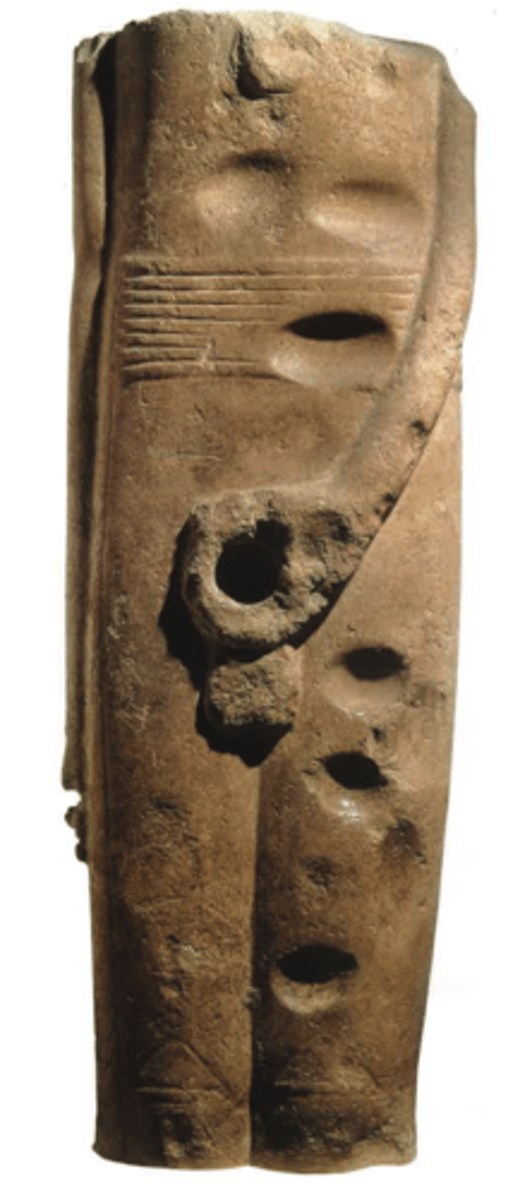
King Den's Label, Dynasty 1, made out of ivory, ca. 3000 BCE

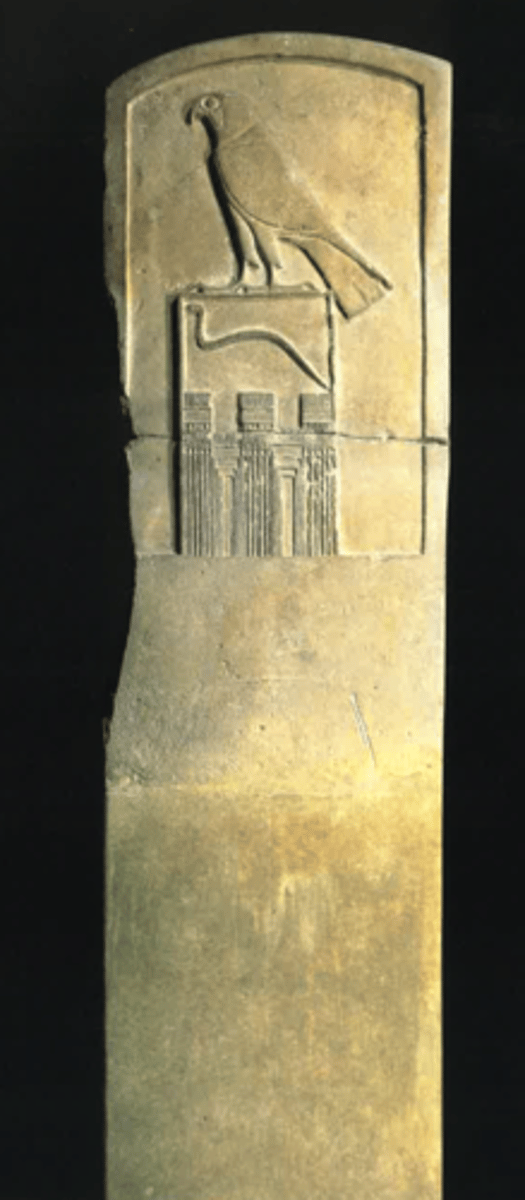
Stela of Wadji, from his tomb in Abydos, 143 cm in height,
Made out of limestone, ca. 2879 BCE

Ceremonial mace head in the form of a coiling snake, Dynasty 1,
Made of travertine, ca. 3100-2900 BCE
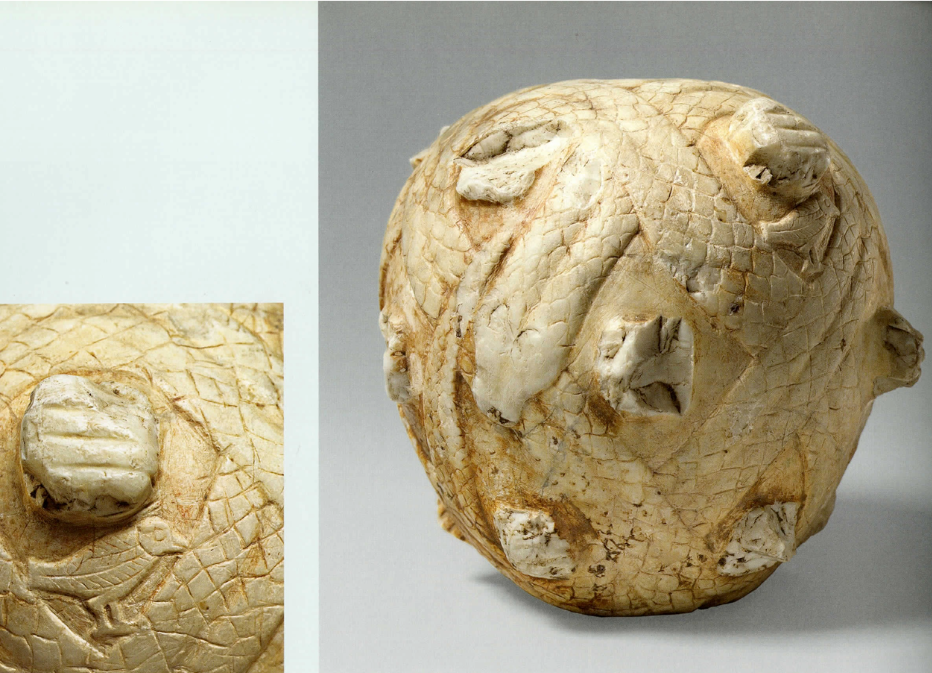

Mace head of the king Scorpion, made of limestone, L. 25cm, ca. 3100 BCE (Drawing by Richard Parkinson)
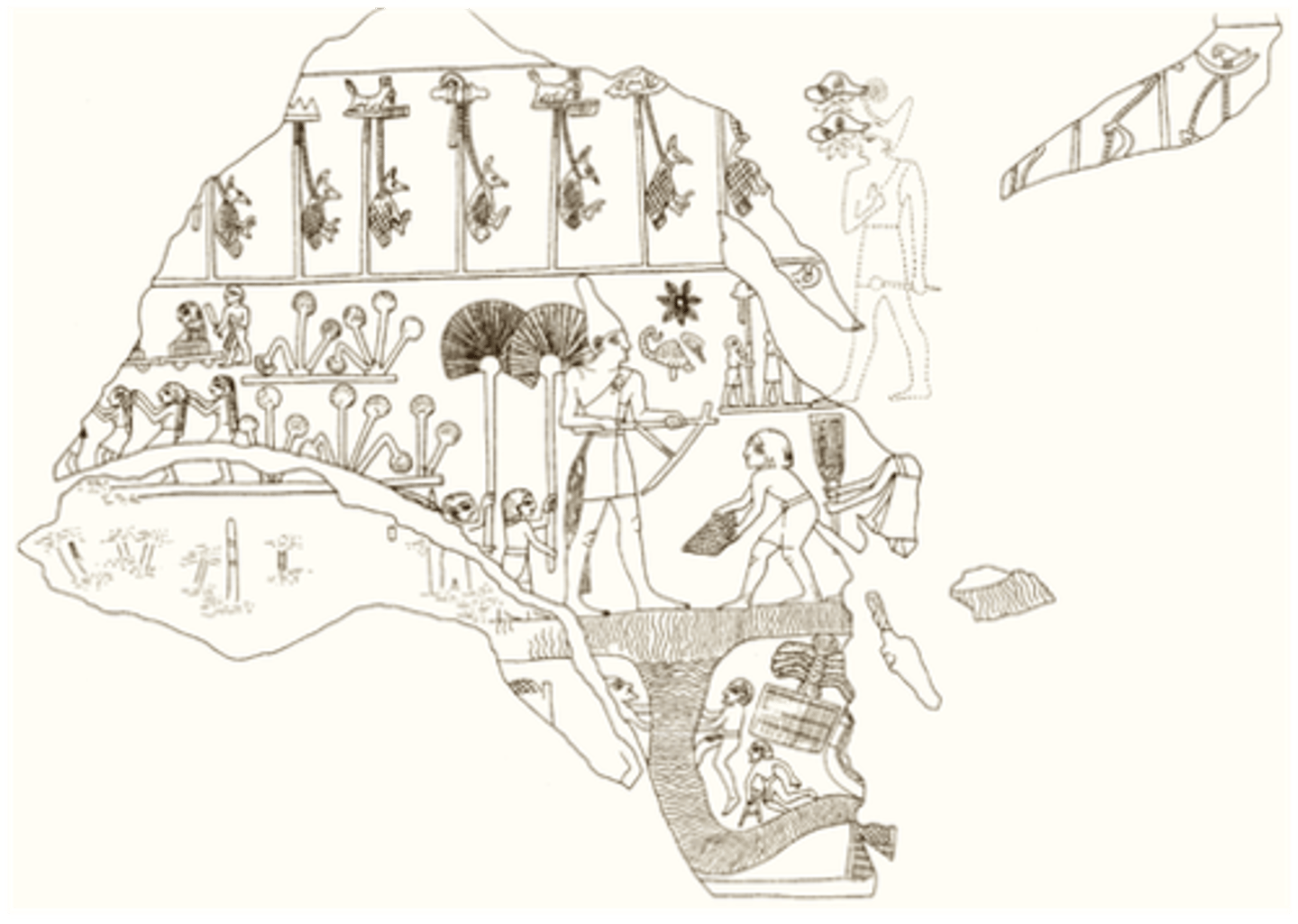
Temple doorpost, in the form of a bound prisoner, Dynasty 1,
from Hierakonpolis, made out of dolerite, ca. 3100-2900 BCE
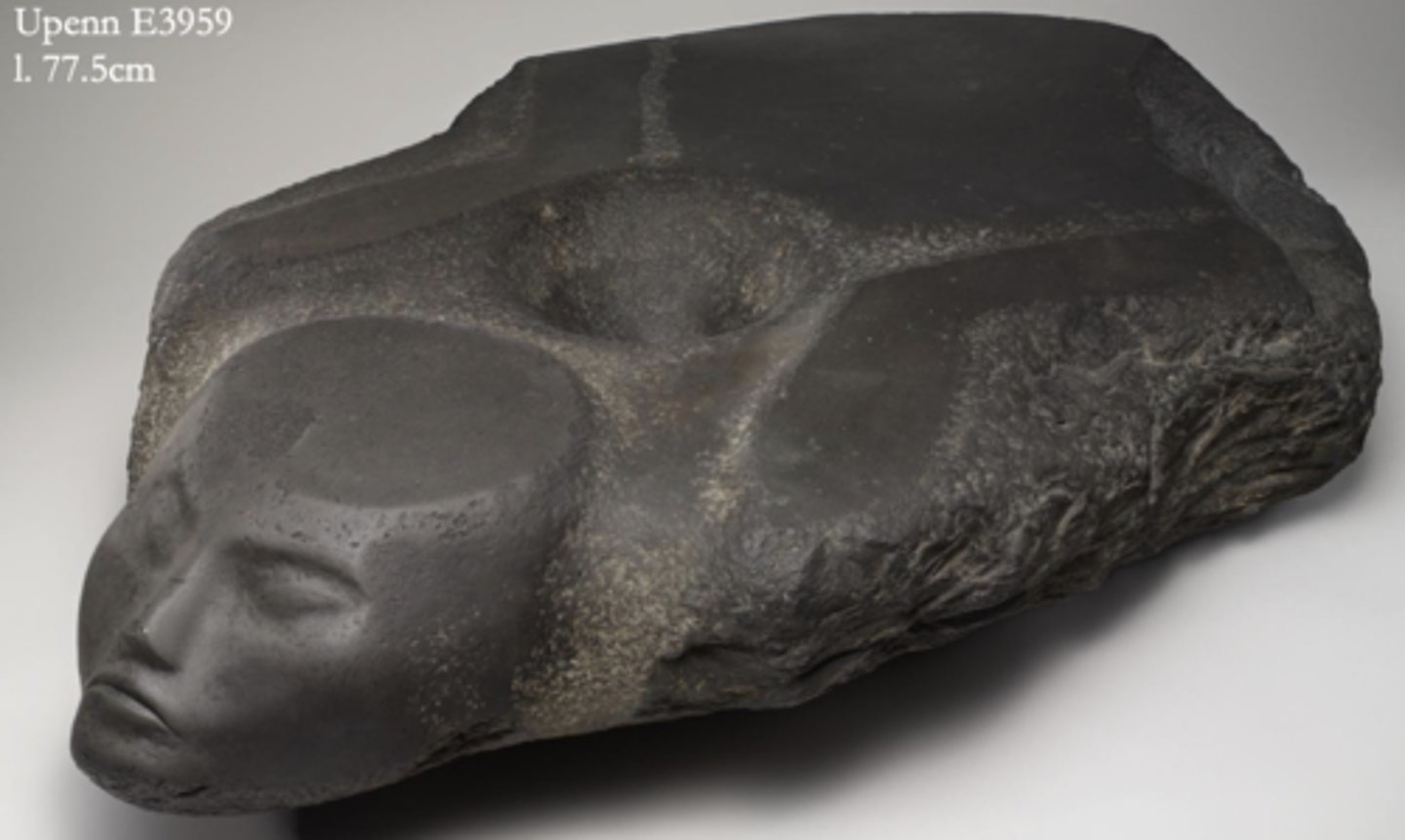

Colossal statue of Min from Coptos, limestone, Late 4th millennium BCE

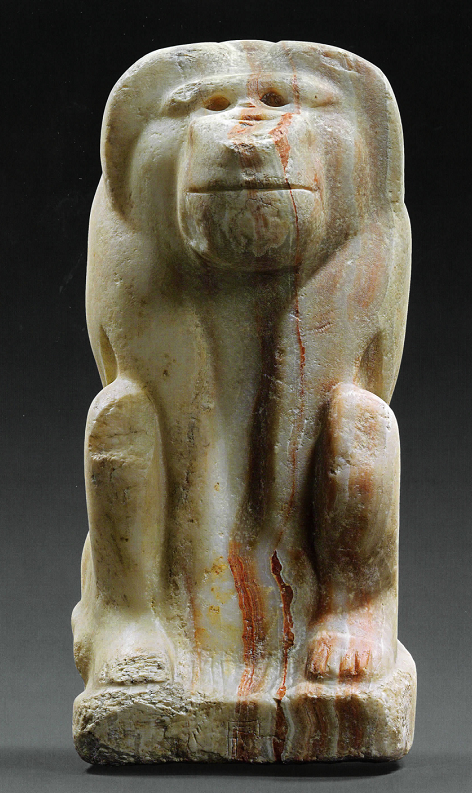
Statue of a baboon, Dynasty 0, Reign of Narmer, made of travertine, Ca. 3100 BCE

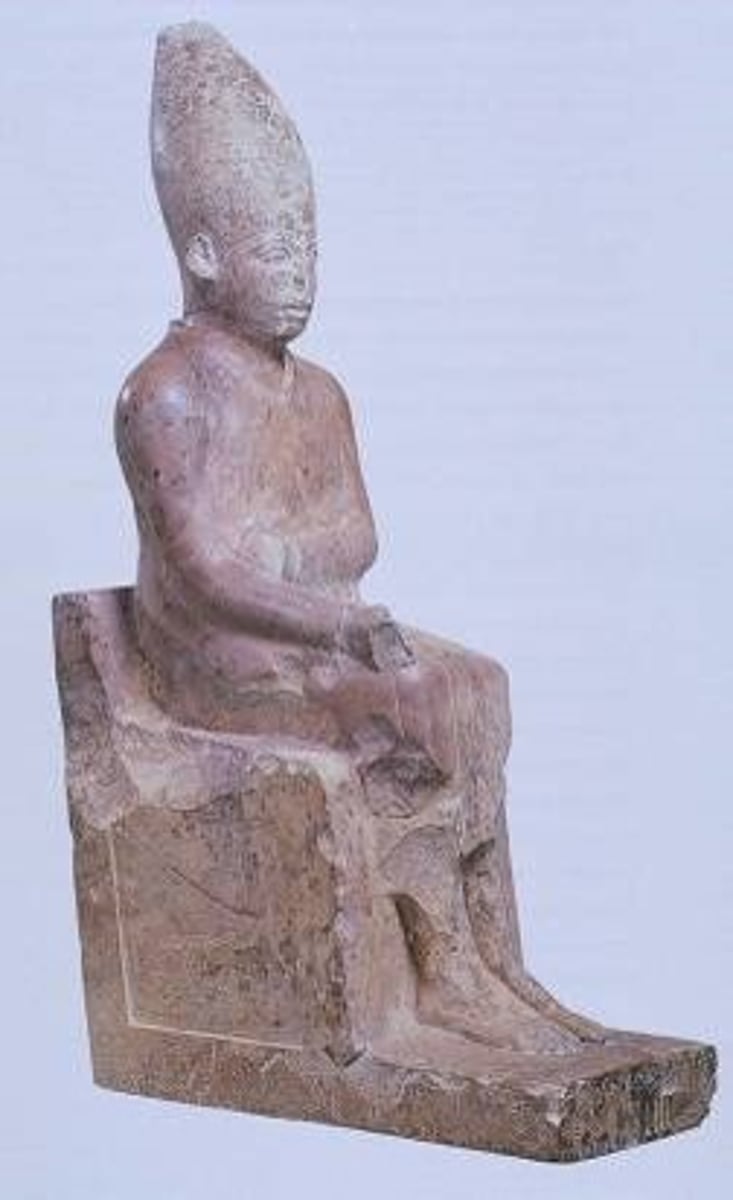
Limestone statue of Khasekhemwy, Dynasty 2, ca. 2690 BCE

Tomb of Khasekhemwy, mudbrick architecture
Dynasty 2, ca. 2890 - 2686 BCE

'Enclosure' of Khasekhemwy, mudbrick architecture, ca. 2890 - 2686 BCE

Pyramid Complex of Djoser in Saqqara, limestone, ca. 2686-2648 BCE
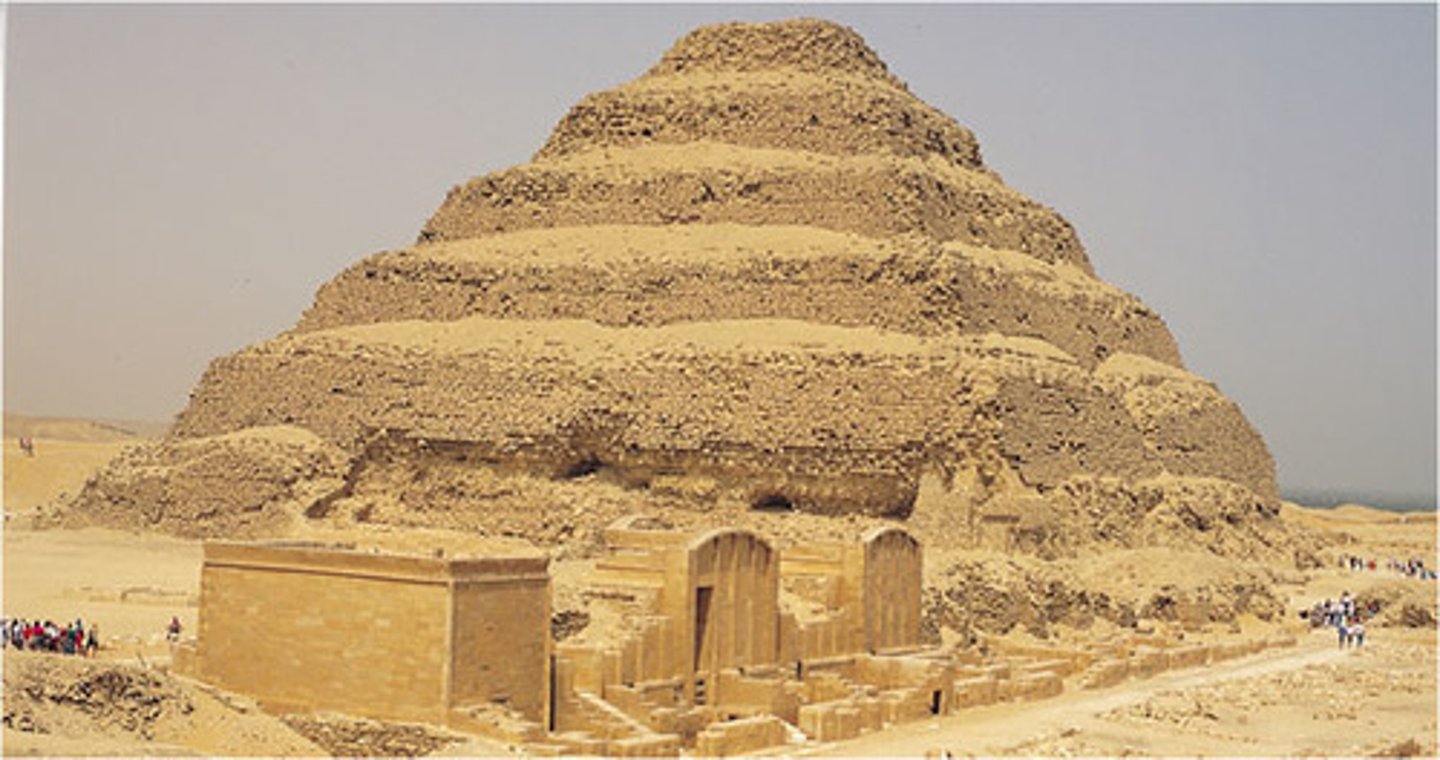

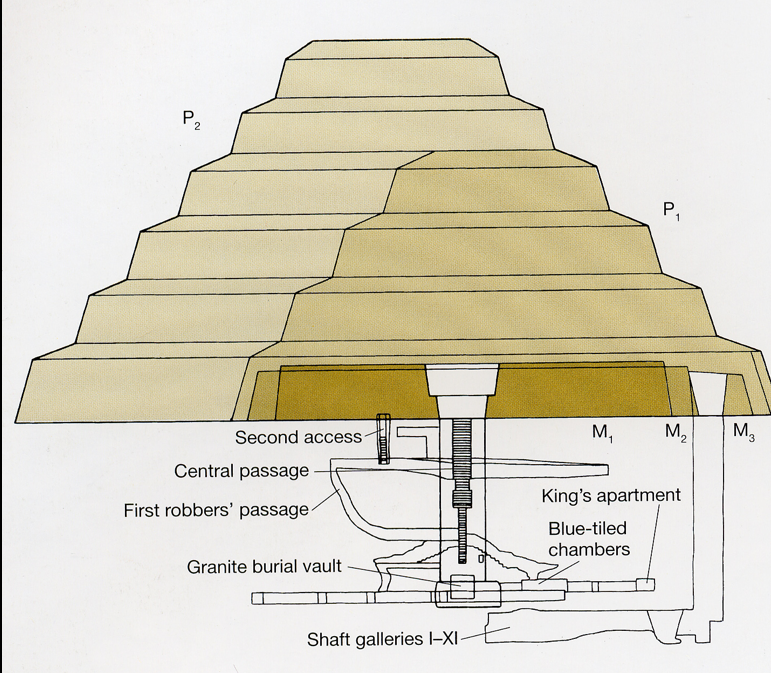
Cross section of the step pyramid of Djoser, Height of the pyramid: 62.5m, Base: 121 by 109m
Funerary Statue of Djoser, made out of limestone, found in the serdab of his tomb, ca. 2686-2648 BCE
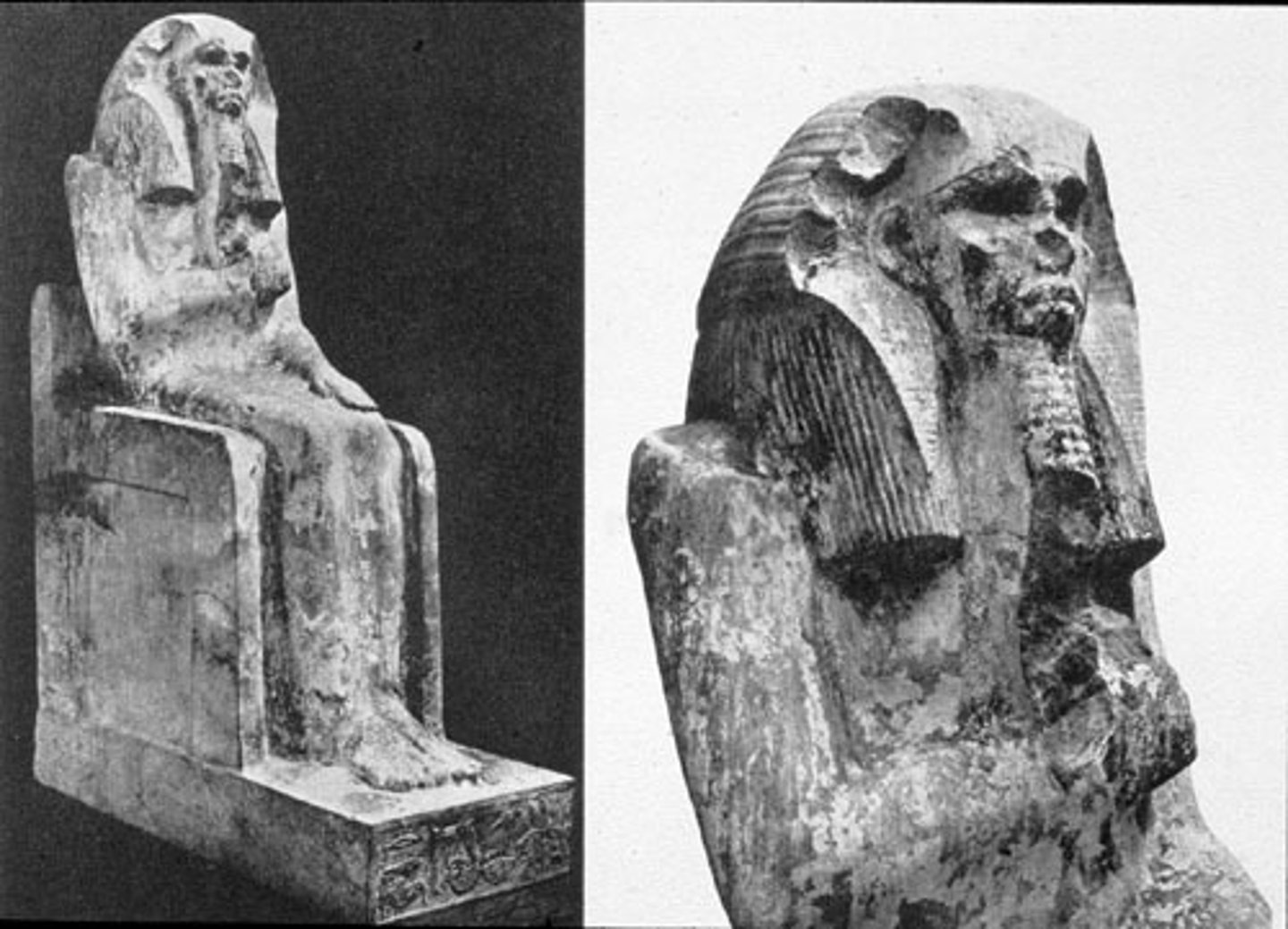

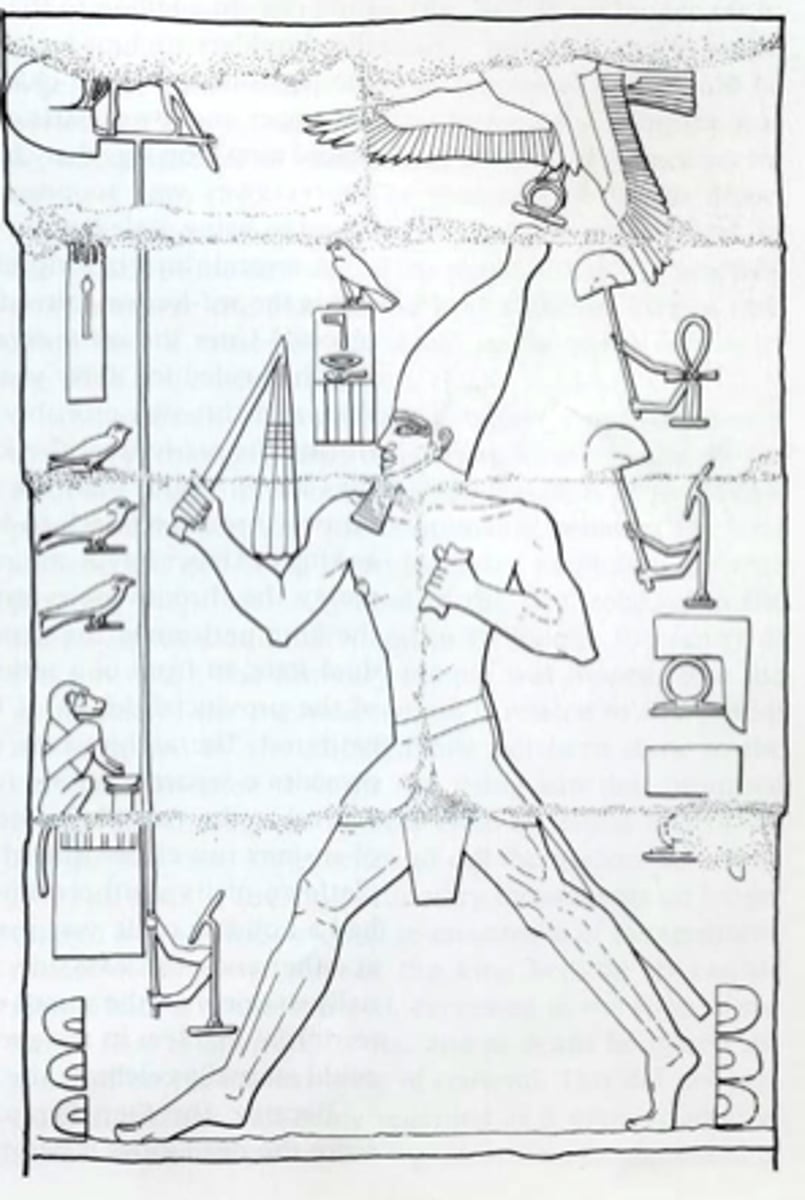
Relief depicting Djoser running between benben stone, Made of limestone, h. 87 cm, From Saqqara.
Bent pyramid of Sneferu at Dashur, made of limestone, ca. 2613-2589 BCE
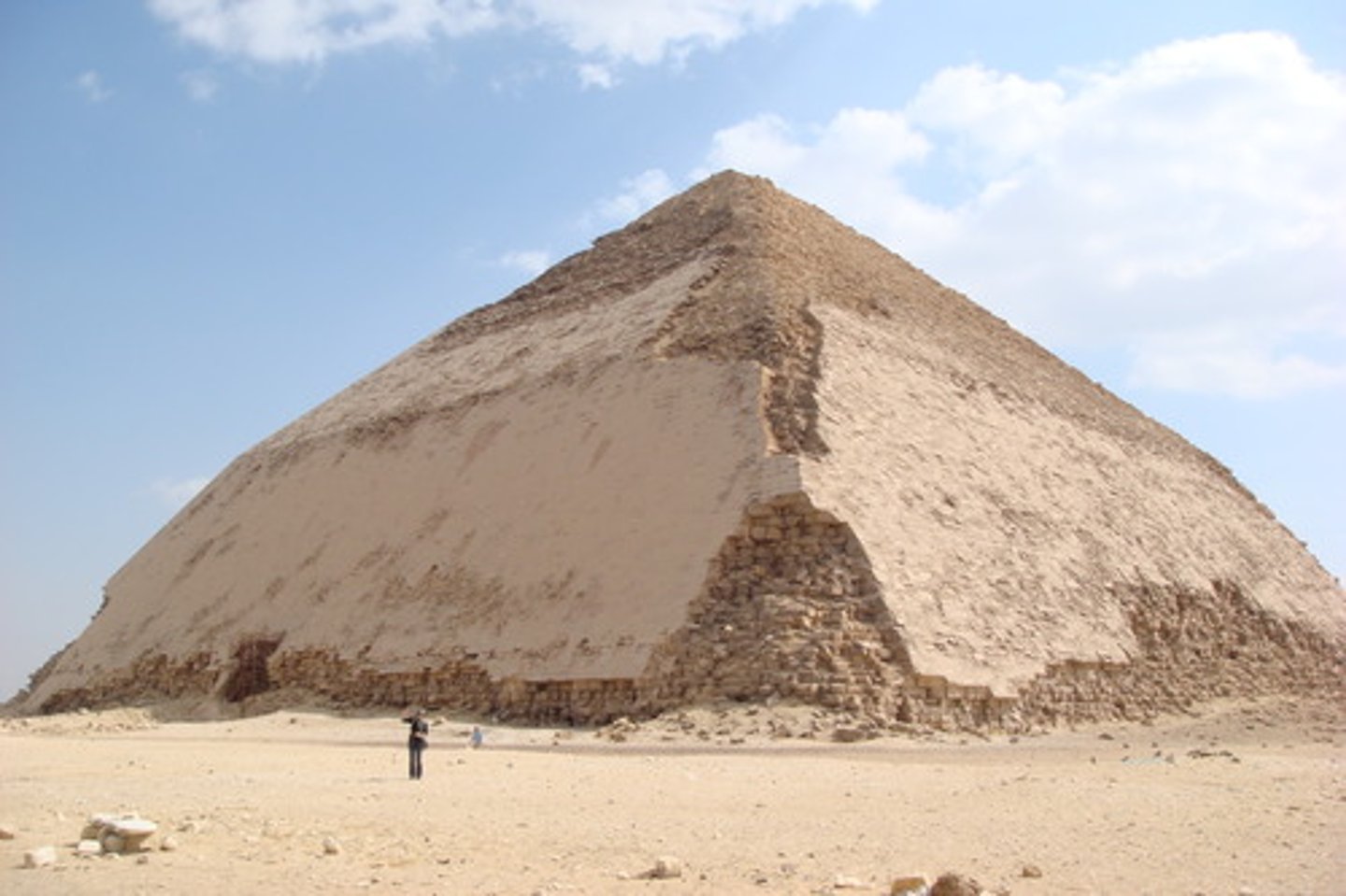

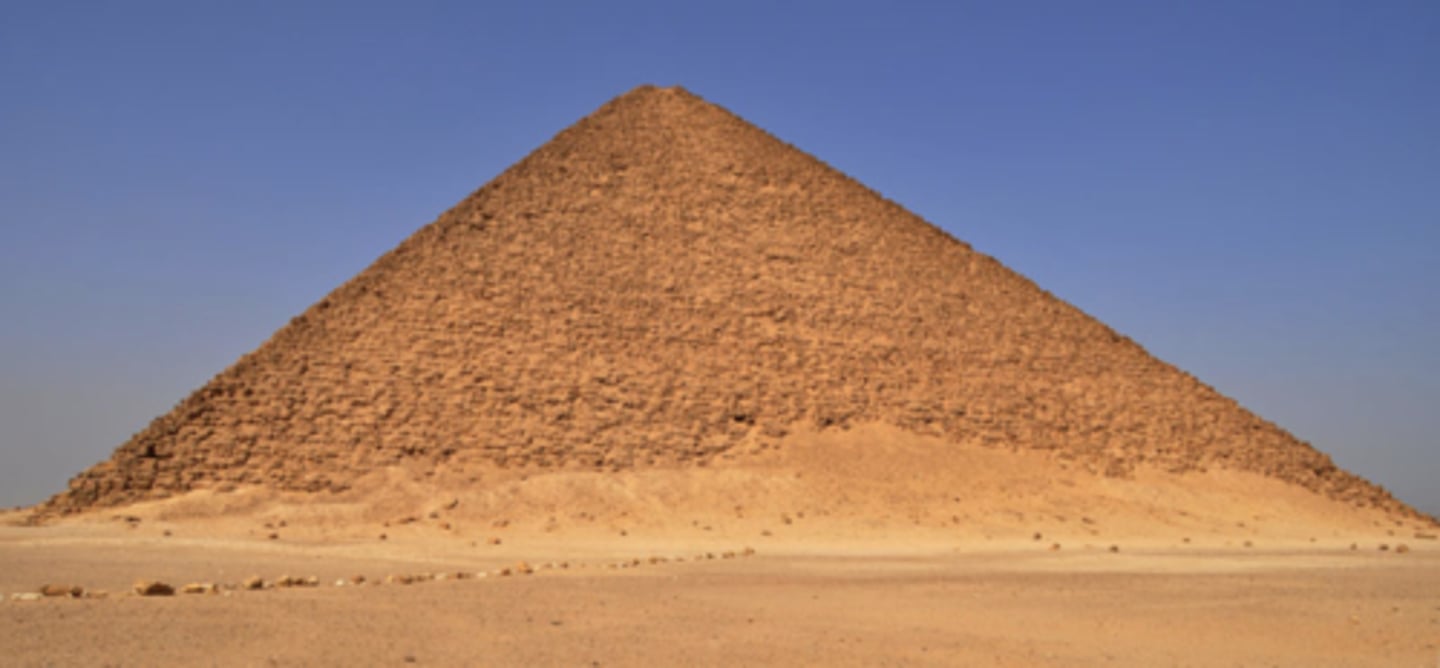
The red pyramid of Sneferu at Dashur, building material: limestone, Height: 105m, width at base 220m, ca. 2613-2589 BCE

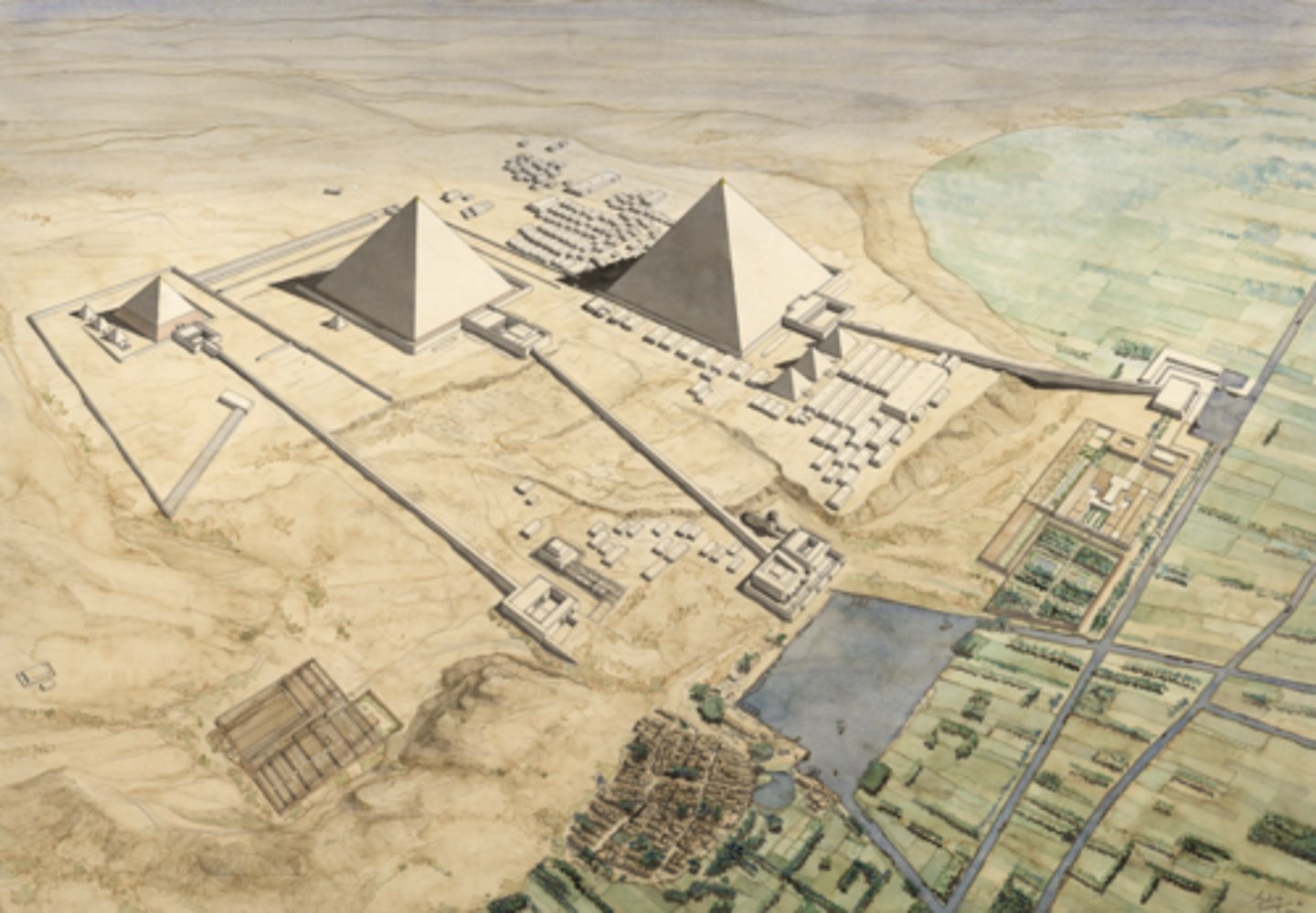
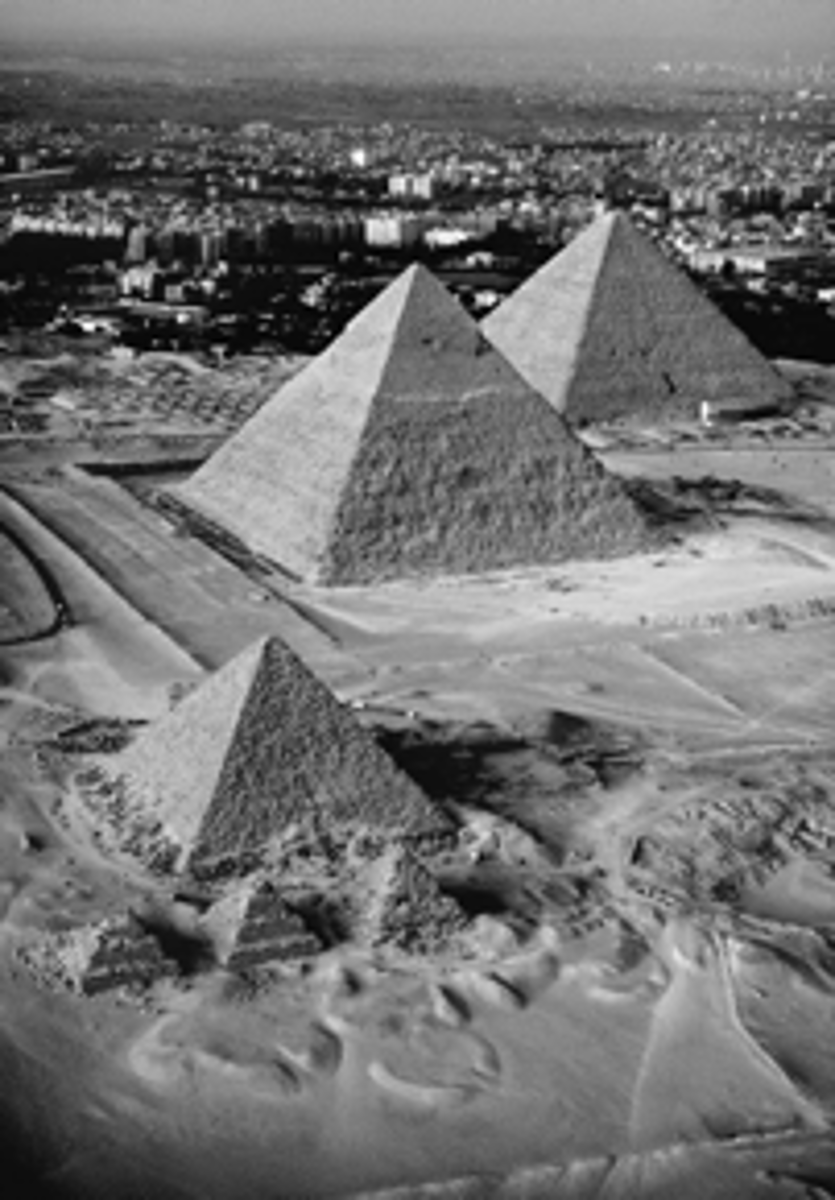
The Giza Pyramids, 4th Dynasty, 26th century BCE
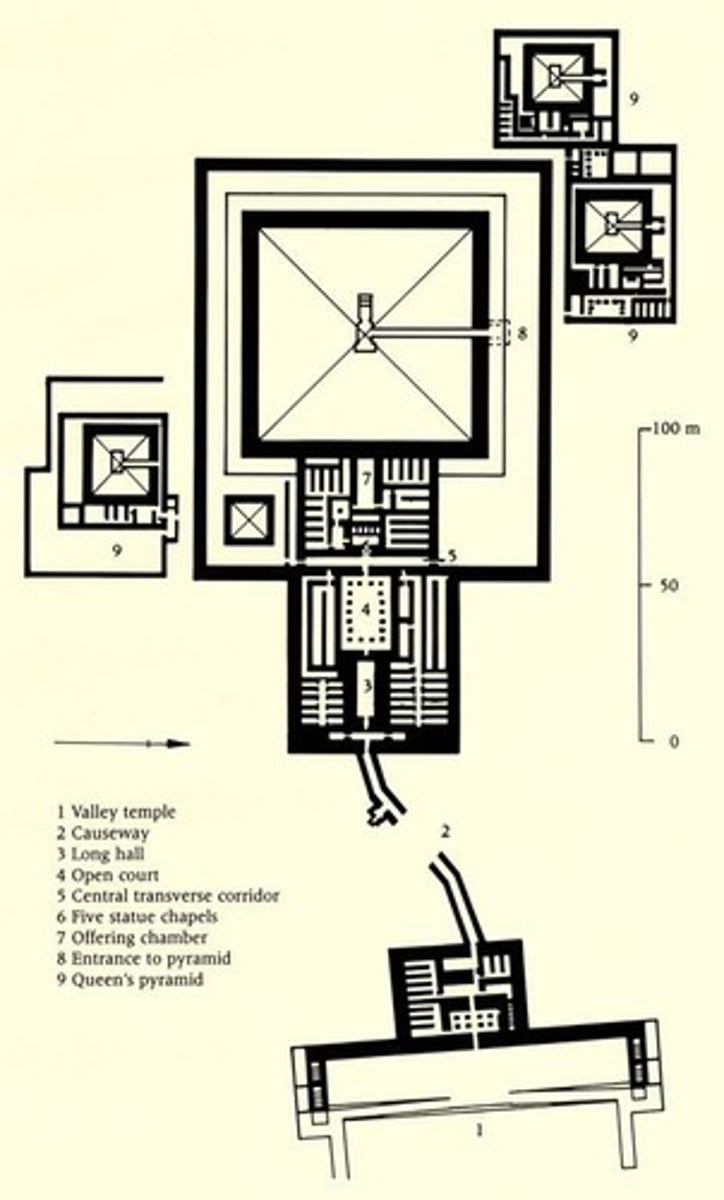
The plan of the pyramid complex of Pepy II, 6th dynasty, ca. 2278-2184 BCE
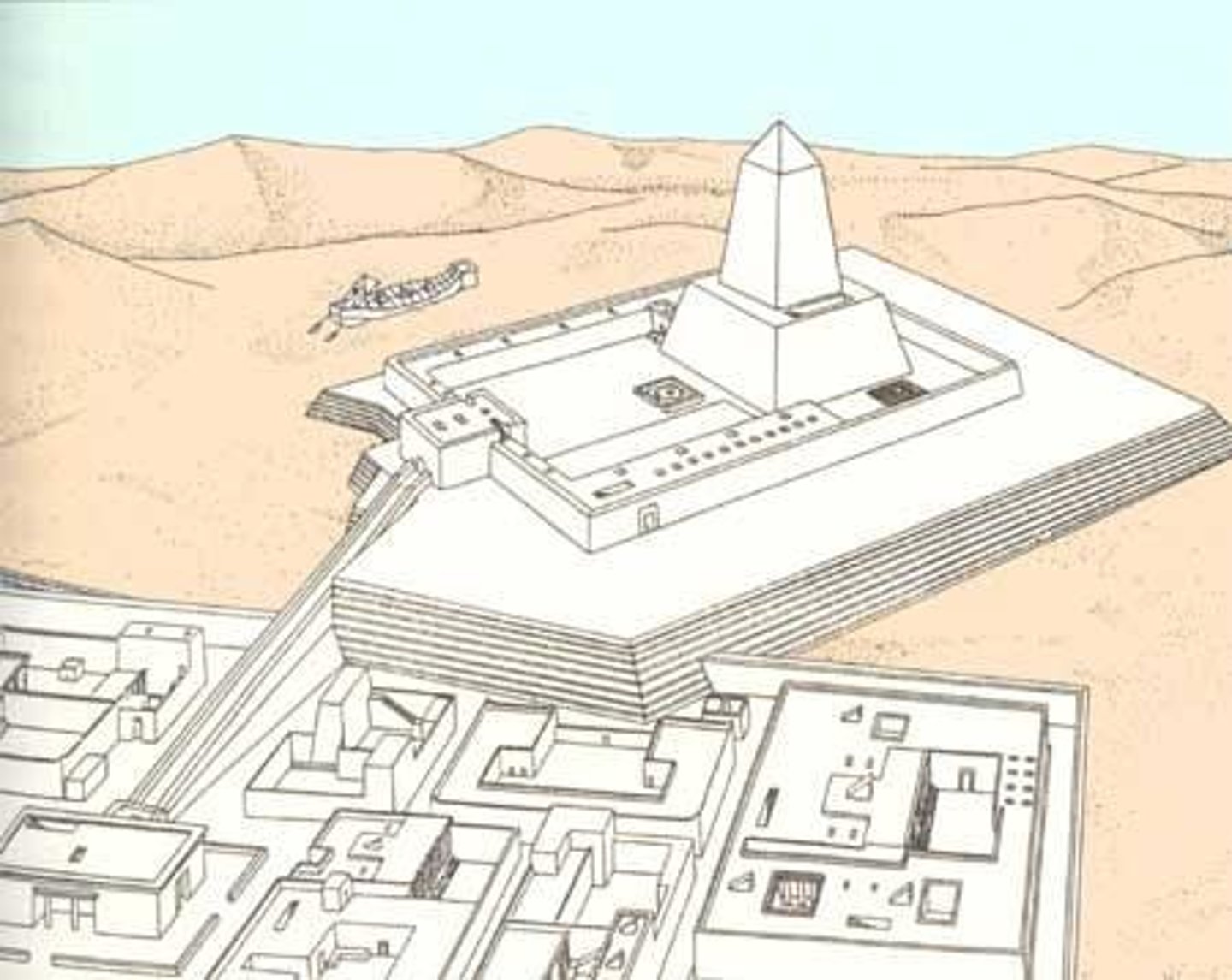
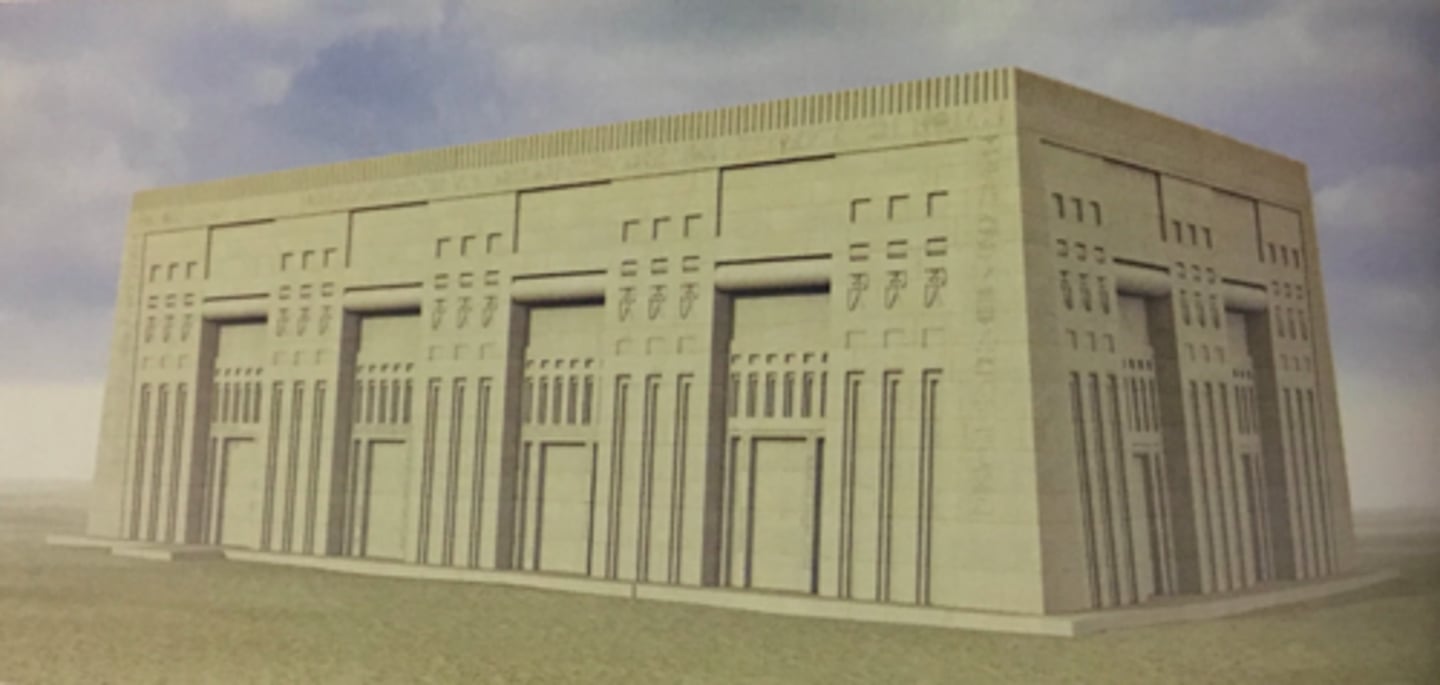
Plan and reconstruction of the sun temple of the king Neuserre at Abu Ghurob, ca. 2445-2421 BCE, Construction material: mostly limestone
(1)
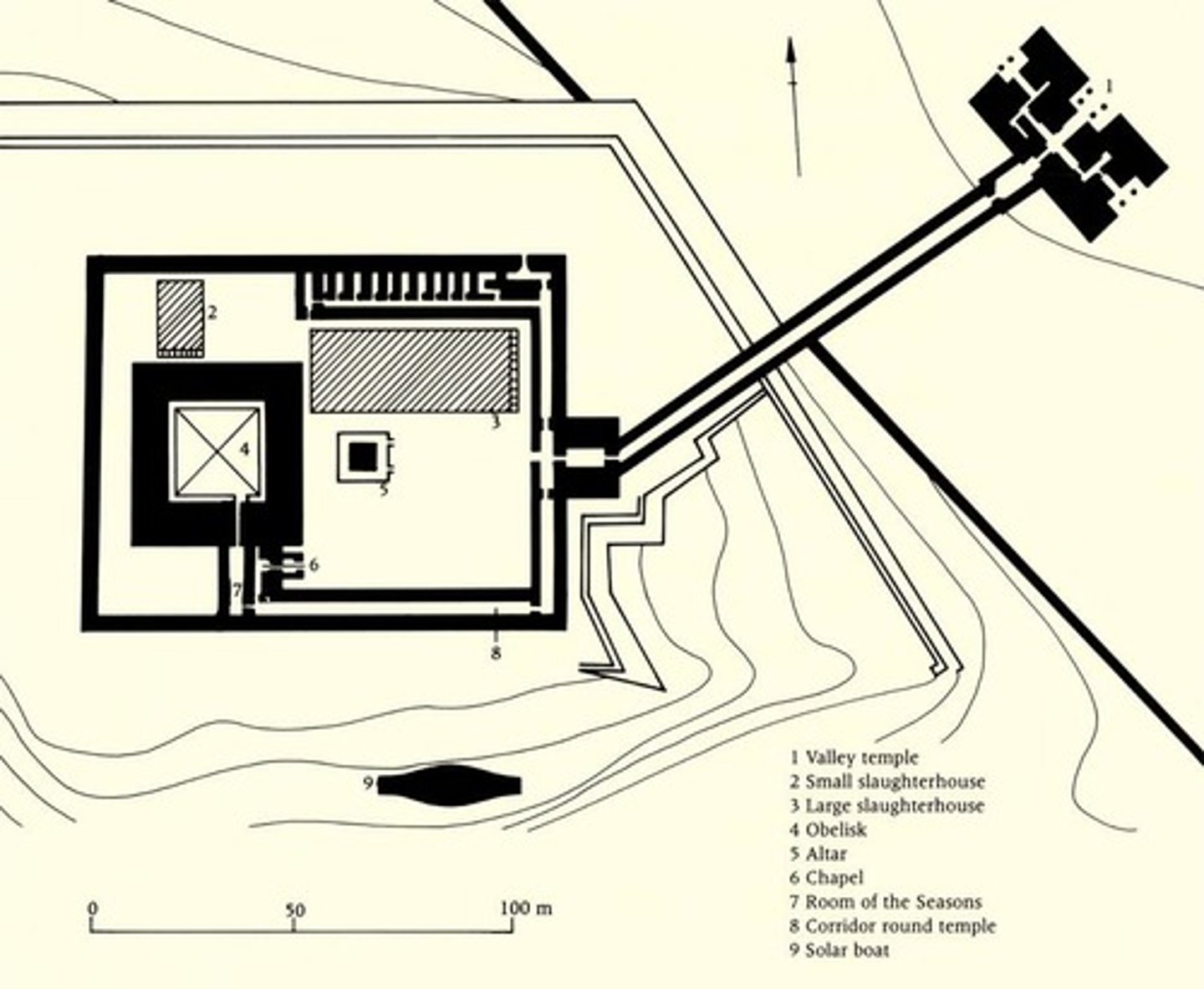
Plan and reconstruction of the sun temple of the king Neuserre at Abu Ghurob, ca. 2445-2421 BCE, Construction material: mostly limestone
(2)
Statue of Khafre, found in the mortuary temple of Khafre in Giza,
made of diorite, ca. 2558 - 2532 BCE
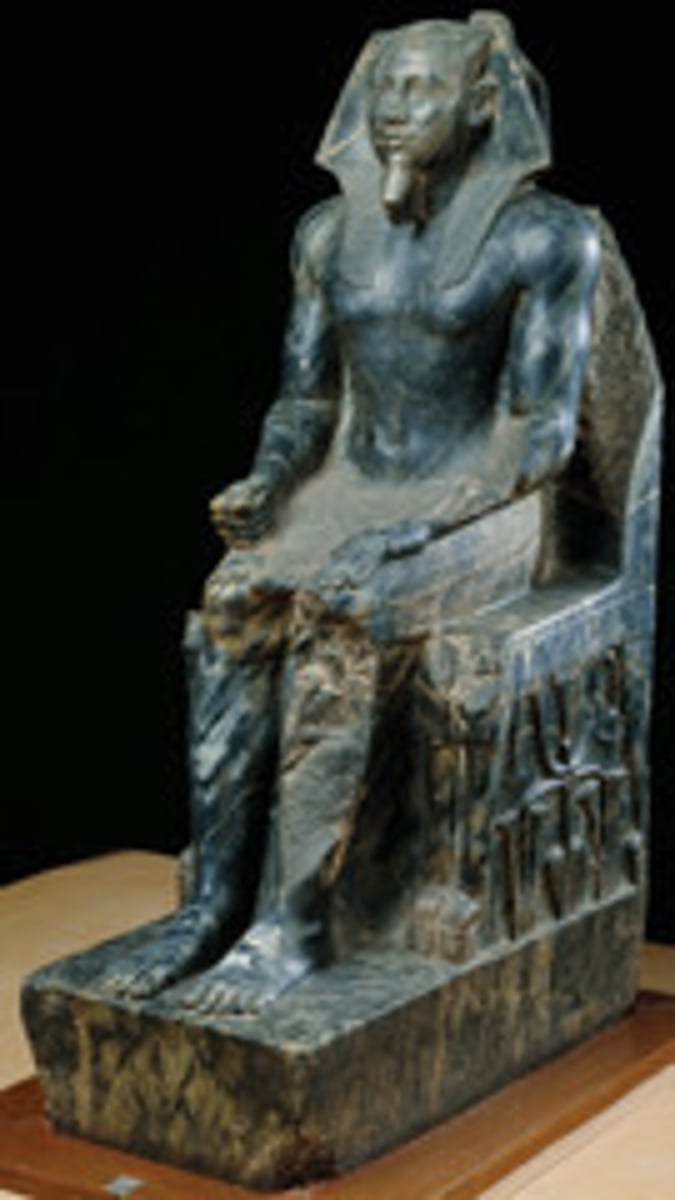

Triad of Menkaure, found in the valley temple
made of schist, ca. 2532-2503 BCE
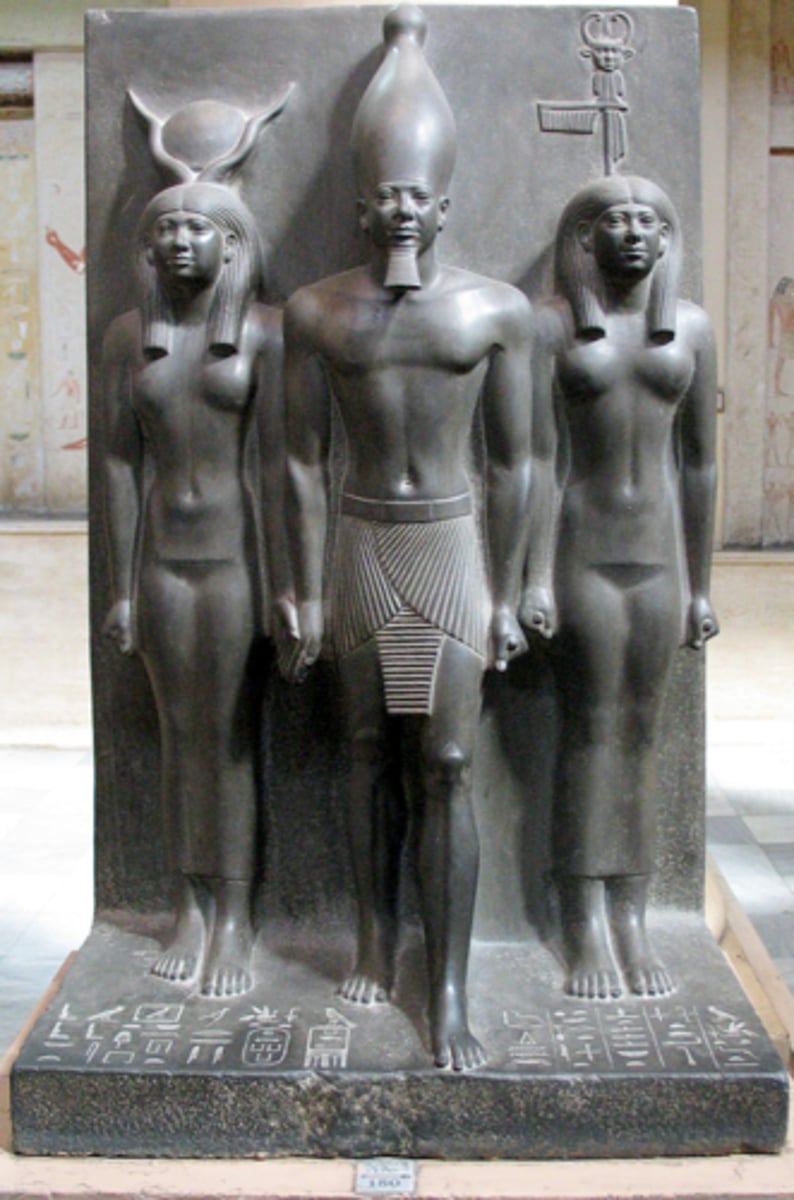

Statue of Menkaure with a queen, Valley temple of the mortuary complex., made of schist, ca. 2532-2503 BCE
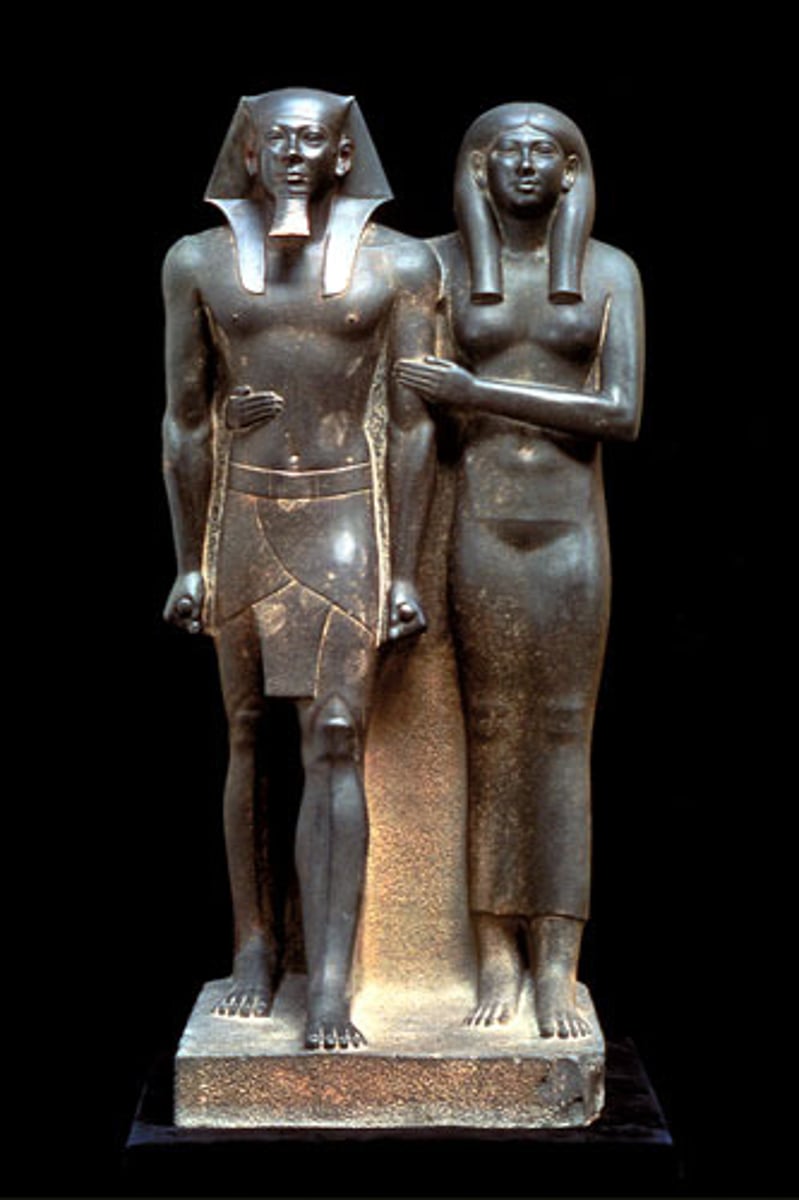

Statue of King Sahure and a Nome God, made of gneiss, ca. 2458-2446 BCE
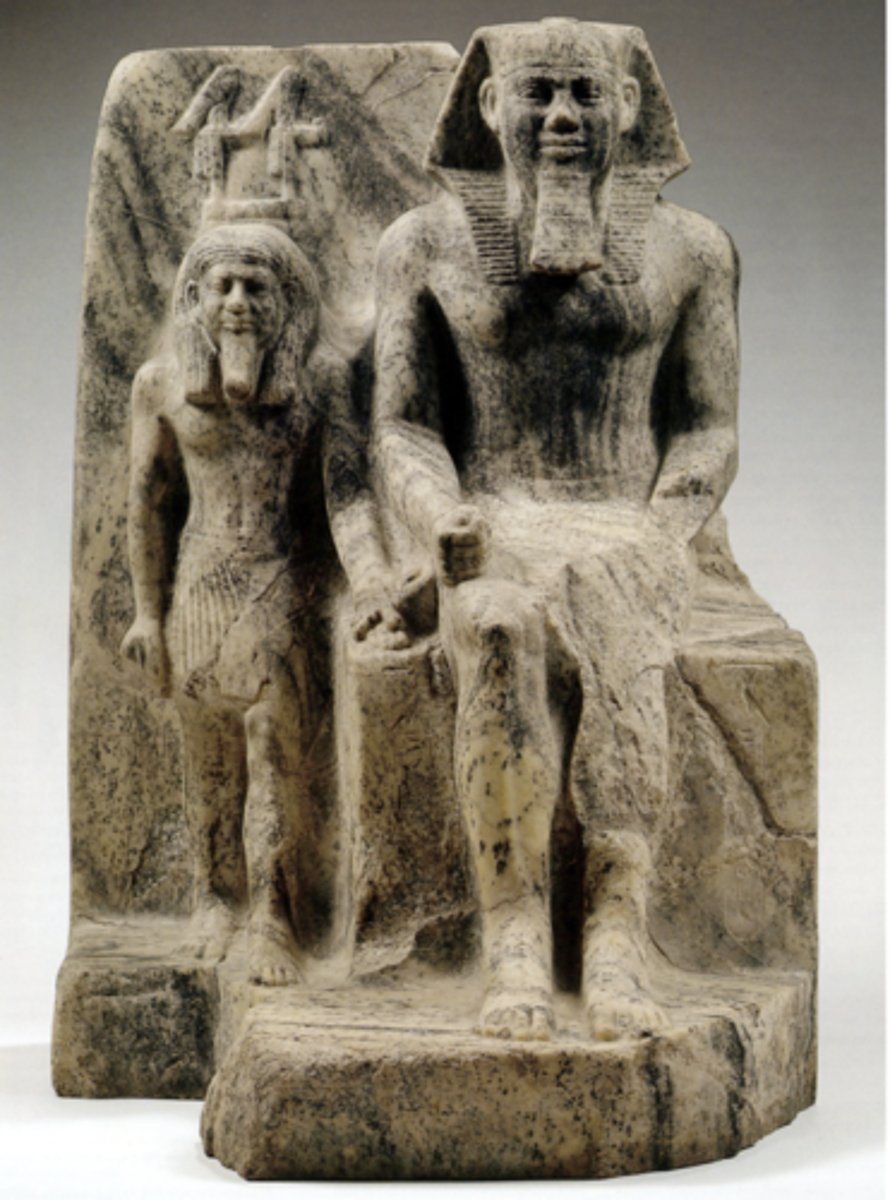

Copper statues of the king Pepi I (eyes inlaid), found in a secondary deposit in Hierakonpolis, ca. 2321-2287 BCE
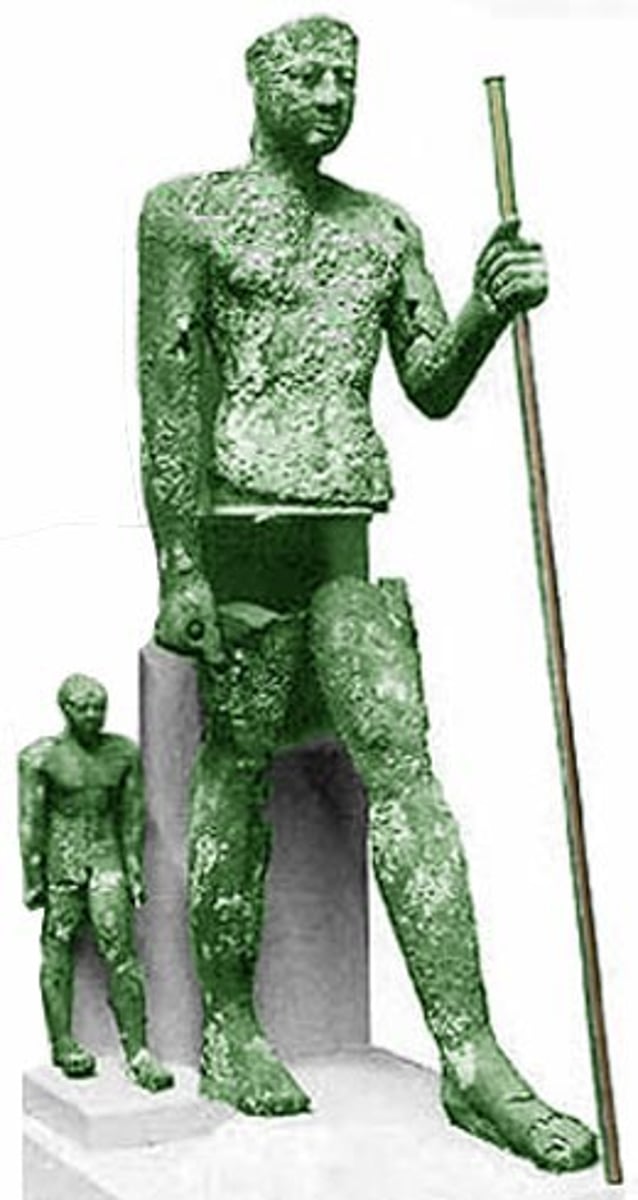

Seated queen Ankhnesmerira holding Pepi II on her lap,
made of alabaster, ca. 2270 BCE
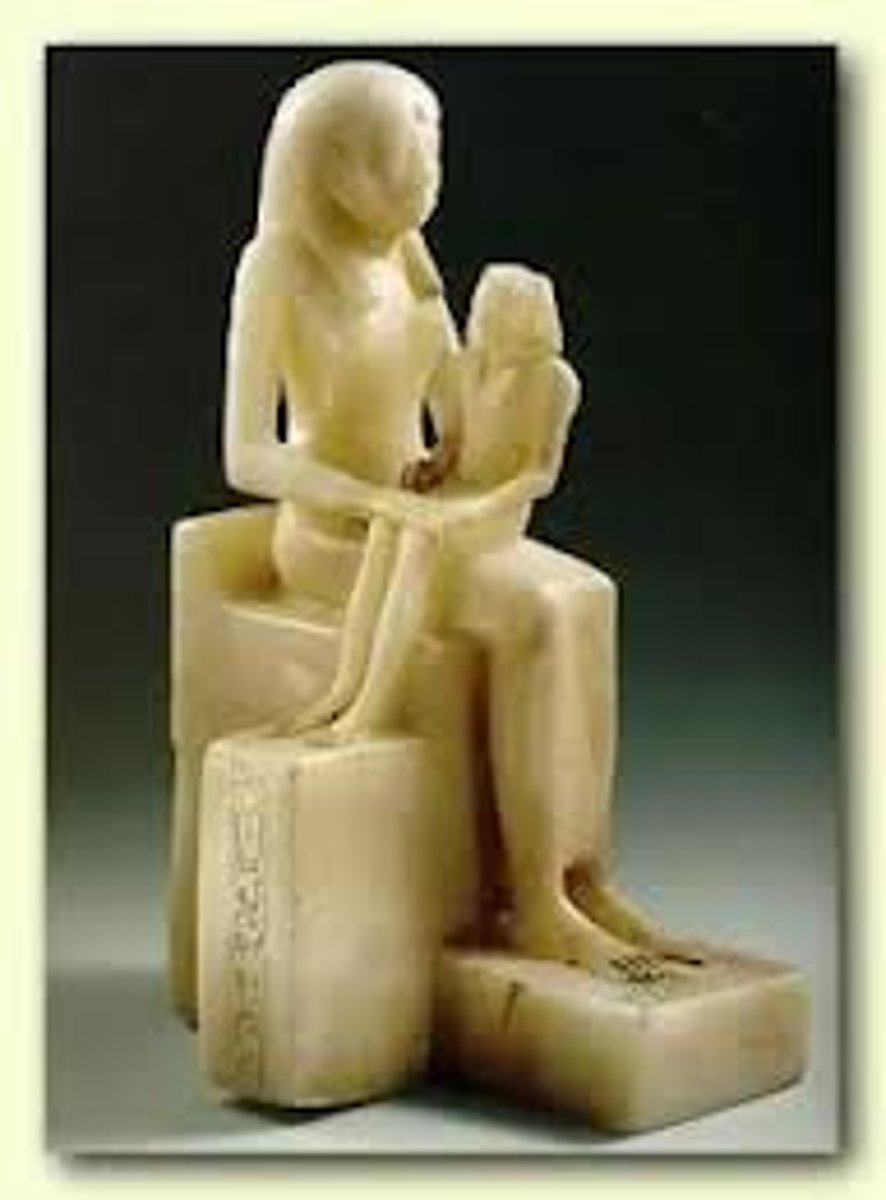

Tomb of Hemiunu and his seated statue out of limestone, Fourth Dynasty, the reign of Khufu, ca. 2589-2566 BCE
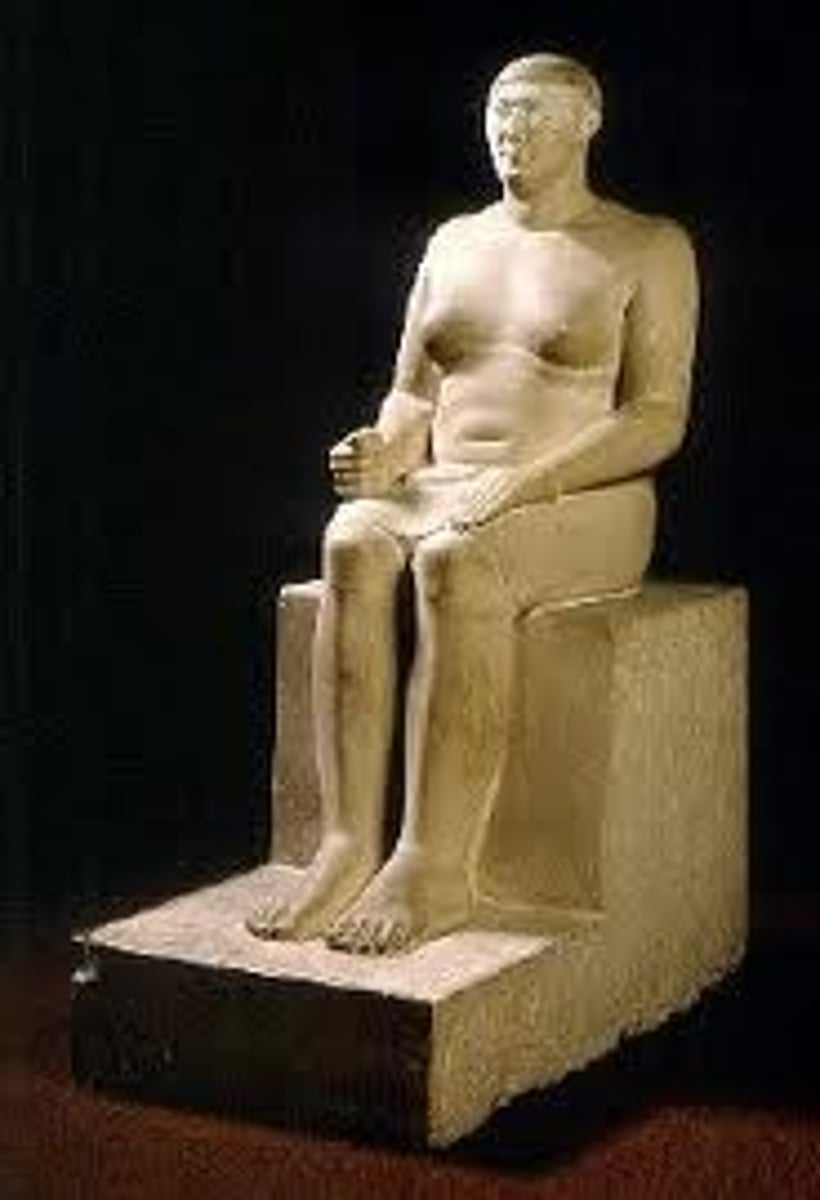

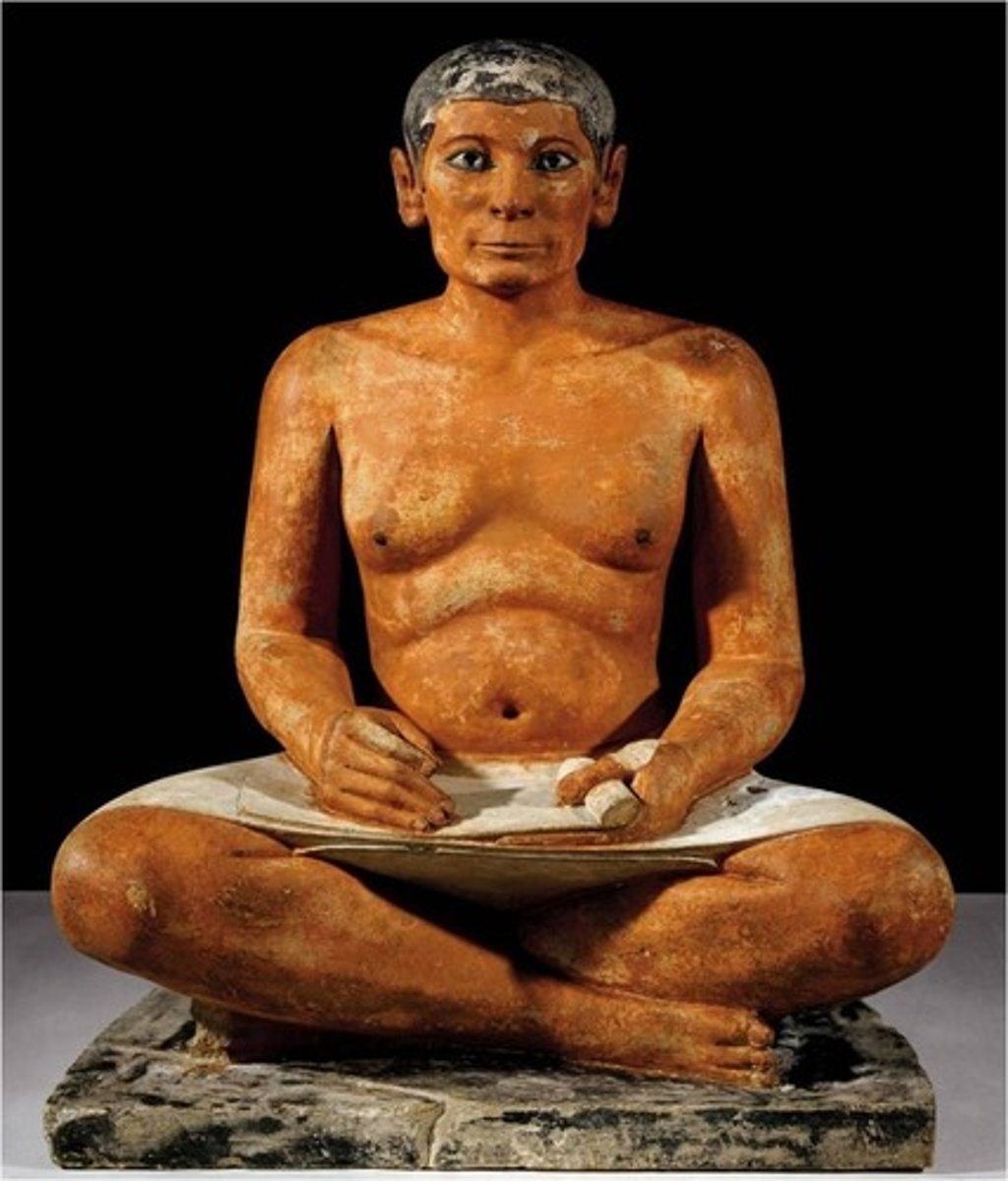
Scribe statue of the official Kai, from his tomb in Saqqara, Painted limestone, ca. 2450 BCE

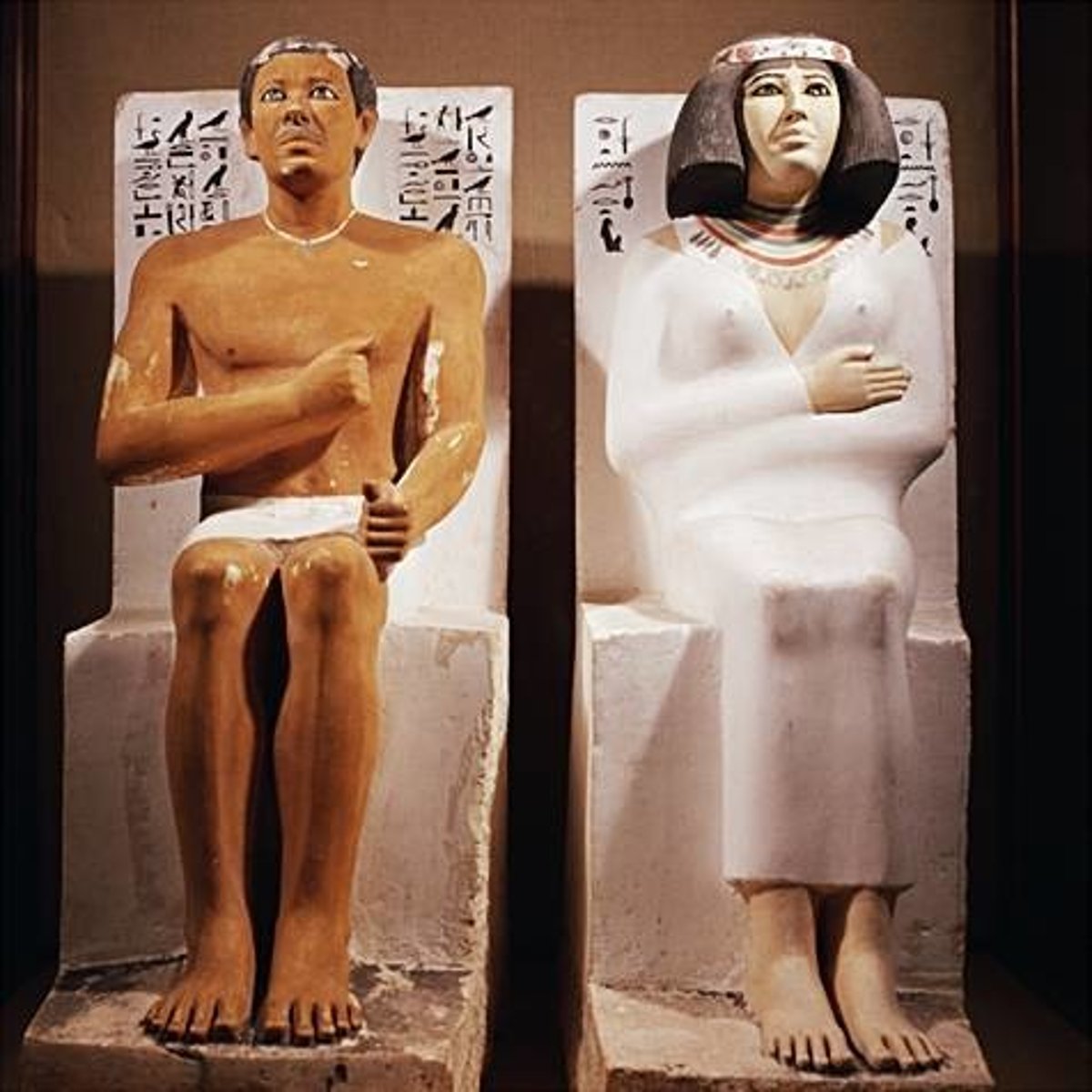
Painted limestone statues of Rahotep & Nefert from the tomb chapel of Rahotep in Meidum, Fourth Dynasty, ca. 26th century BCE.

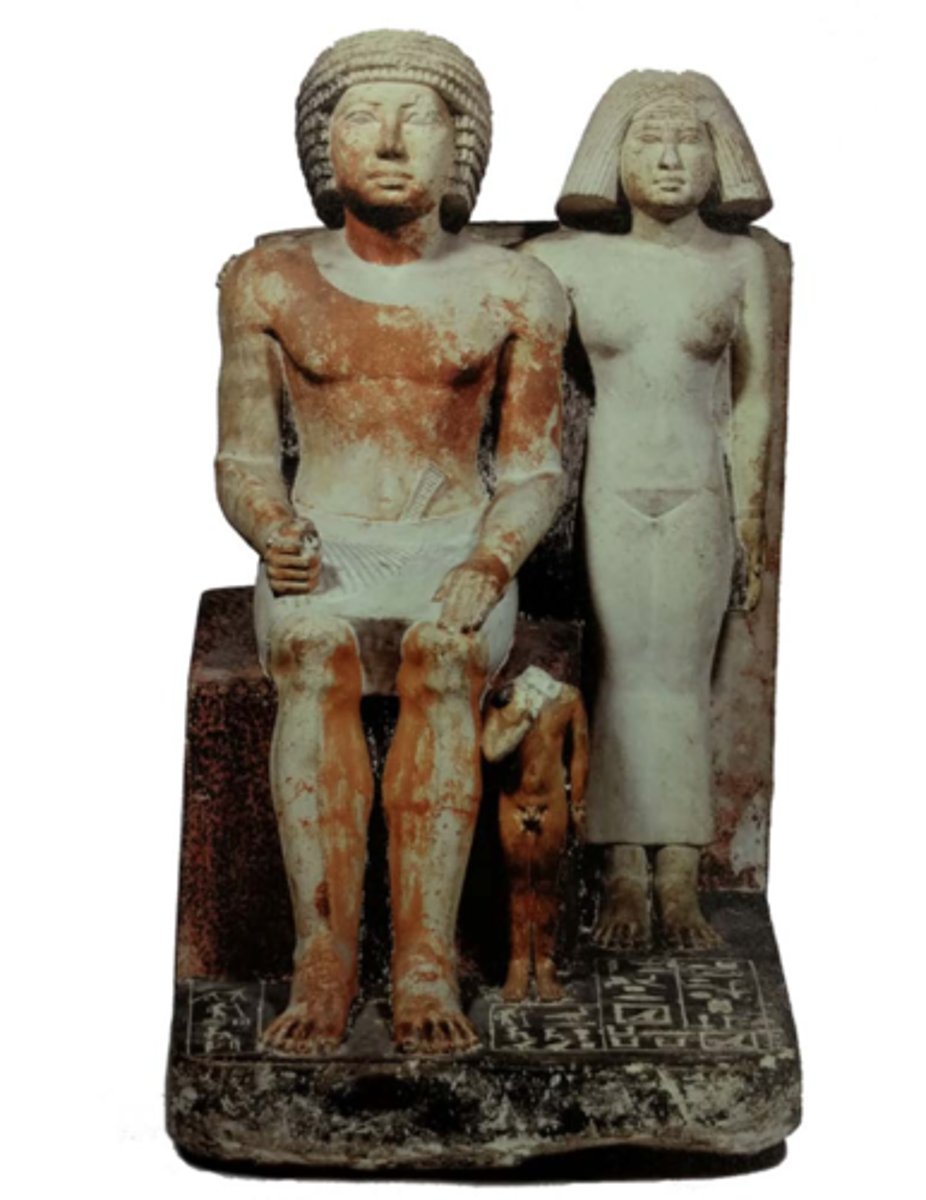
The official Shepsi, his wife Nikauhathor, and their son, painted limestone, from the serdab of their tomb chapel found in Saqqara, 5. Dynasty

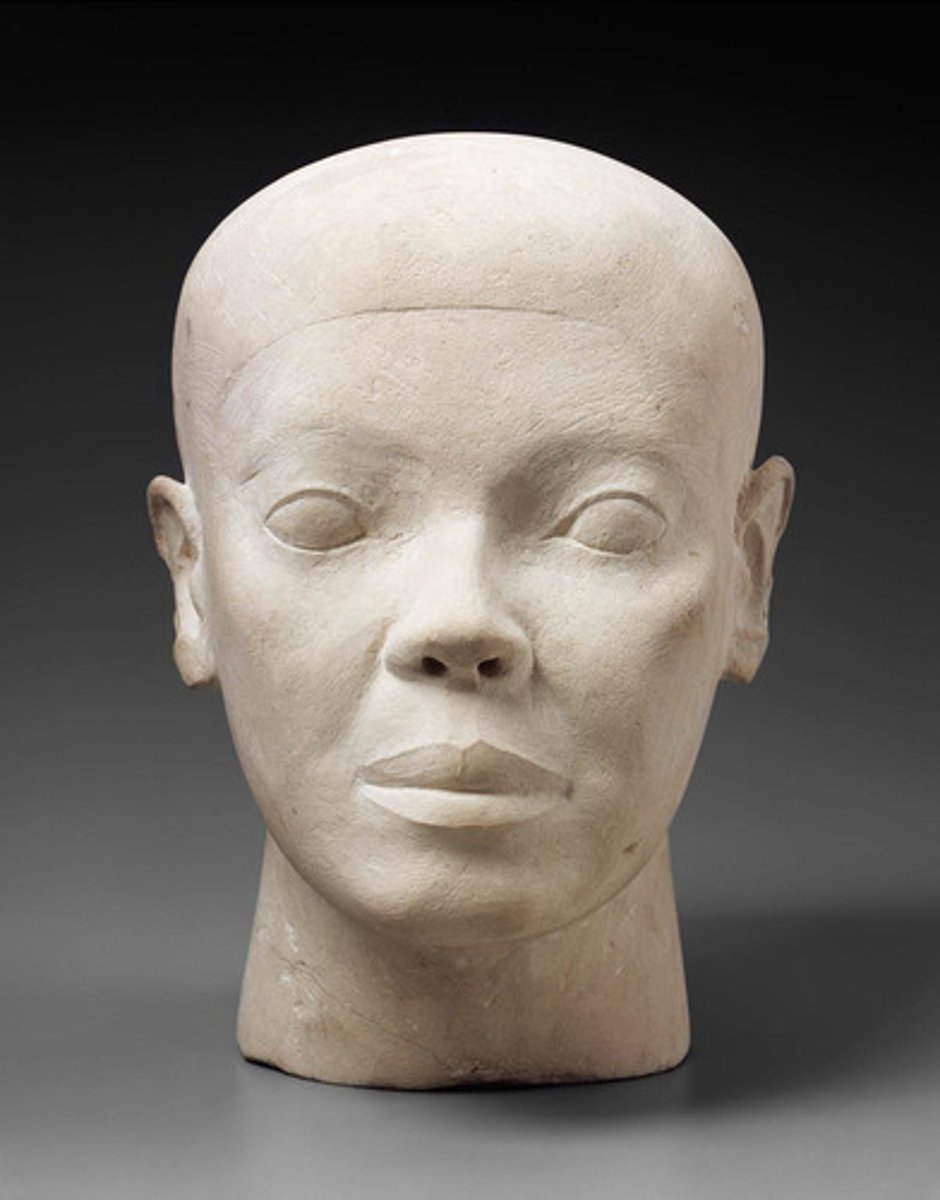
Reserve head, made of limestone, 4th Dynasty, ca. 2589-2566 BCE

Falsedoor of Ptahshepses, Saqqara, made of limestone, ca. 2440 BCE
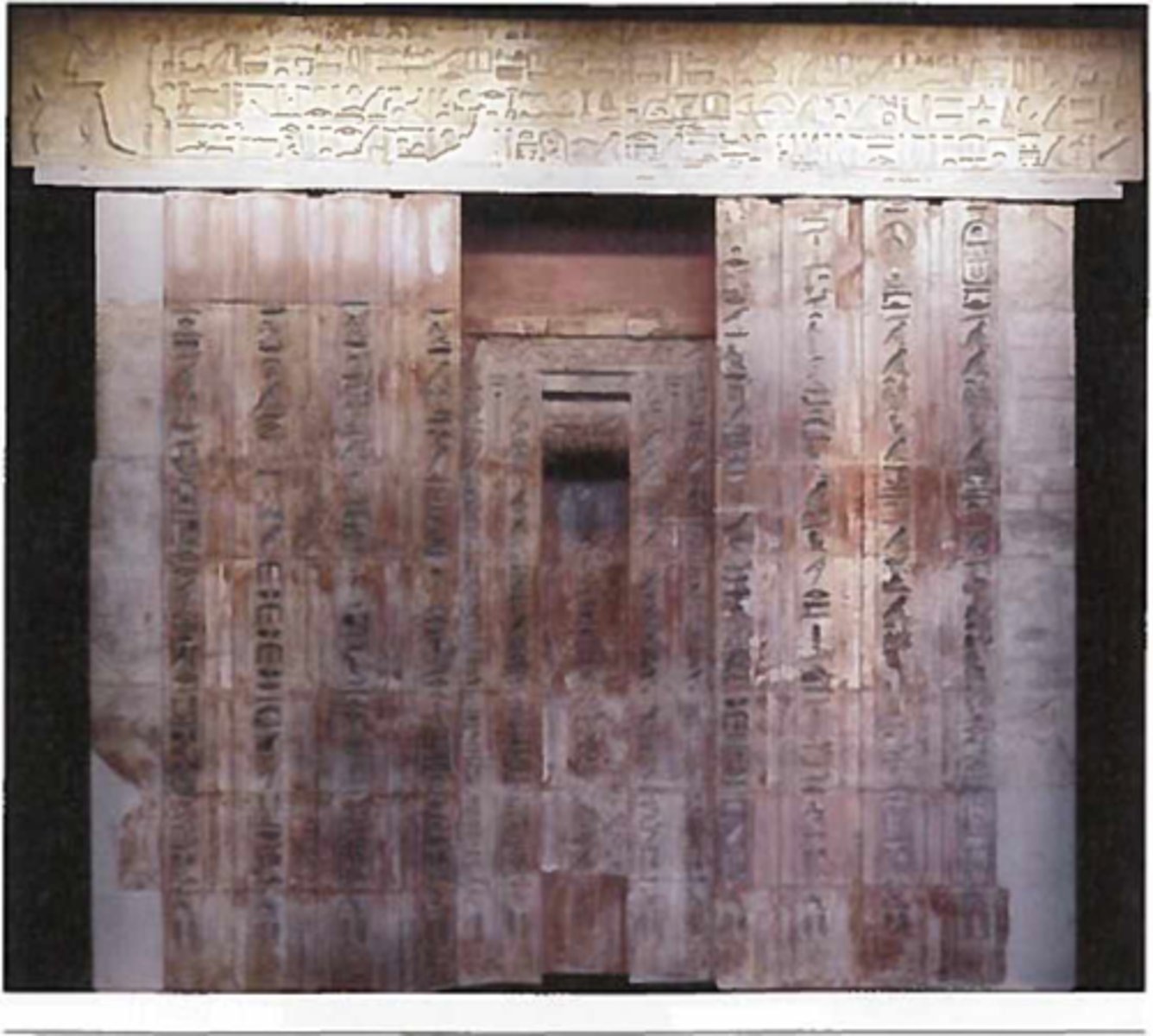

Drawing of the false door in the tomb of Werirenptah, priest, and his wife Khentkauses, From Saqqara, Fifth Dynasty
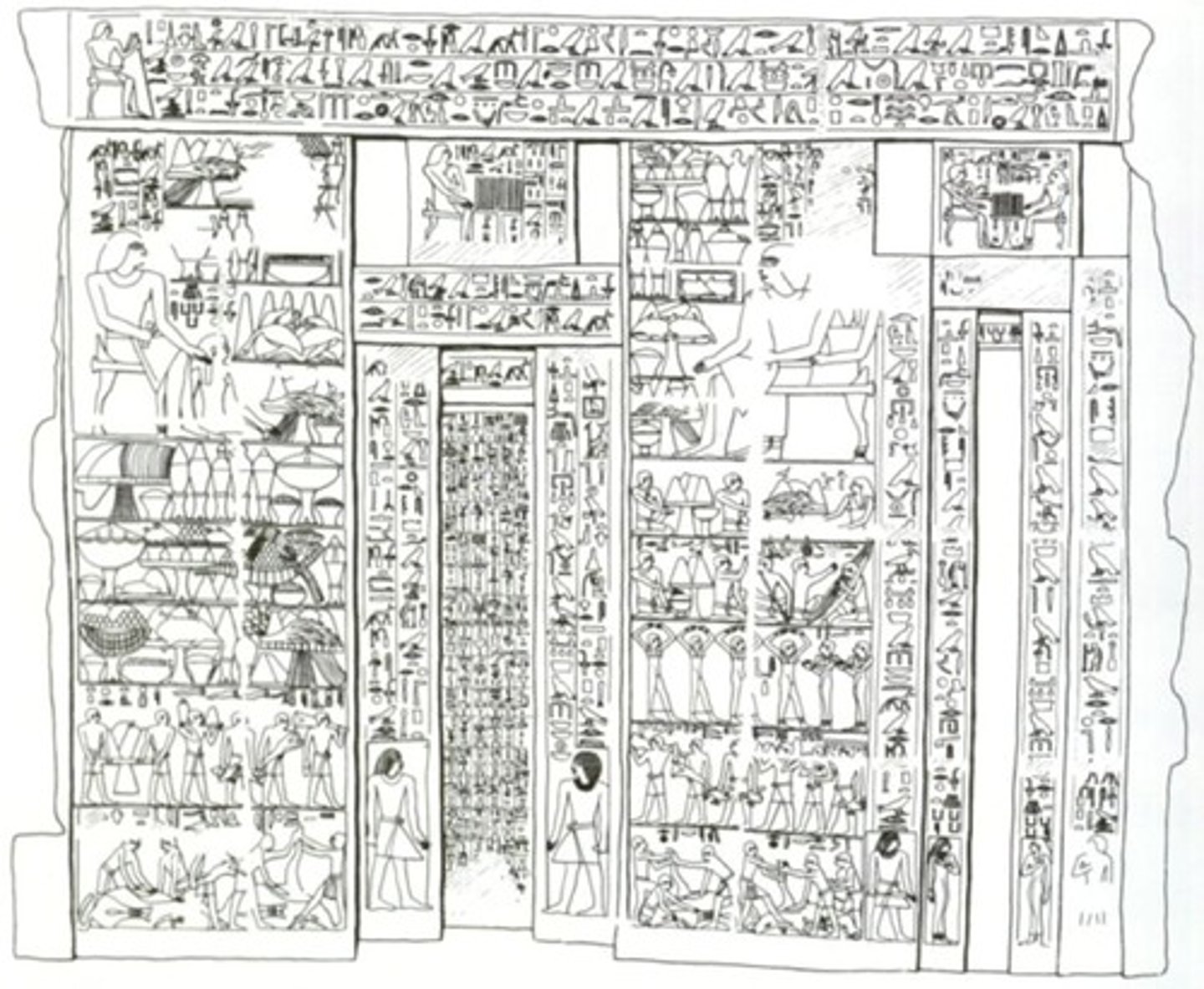
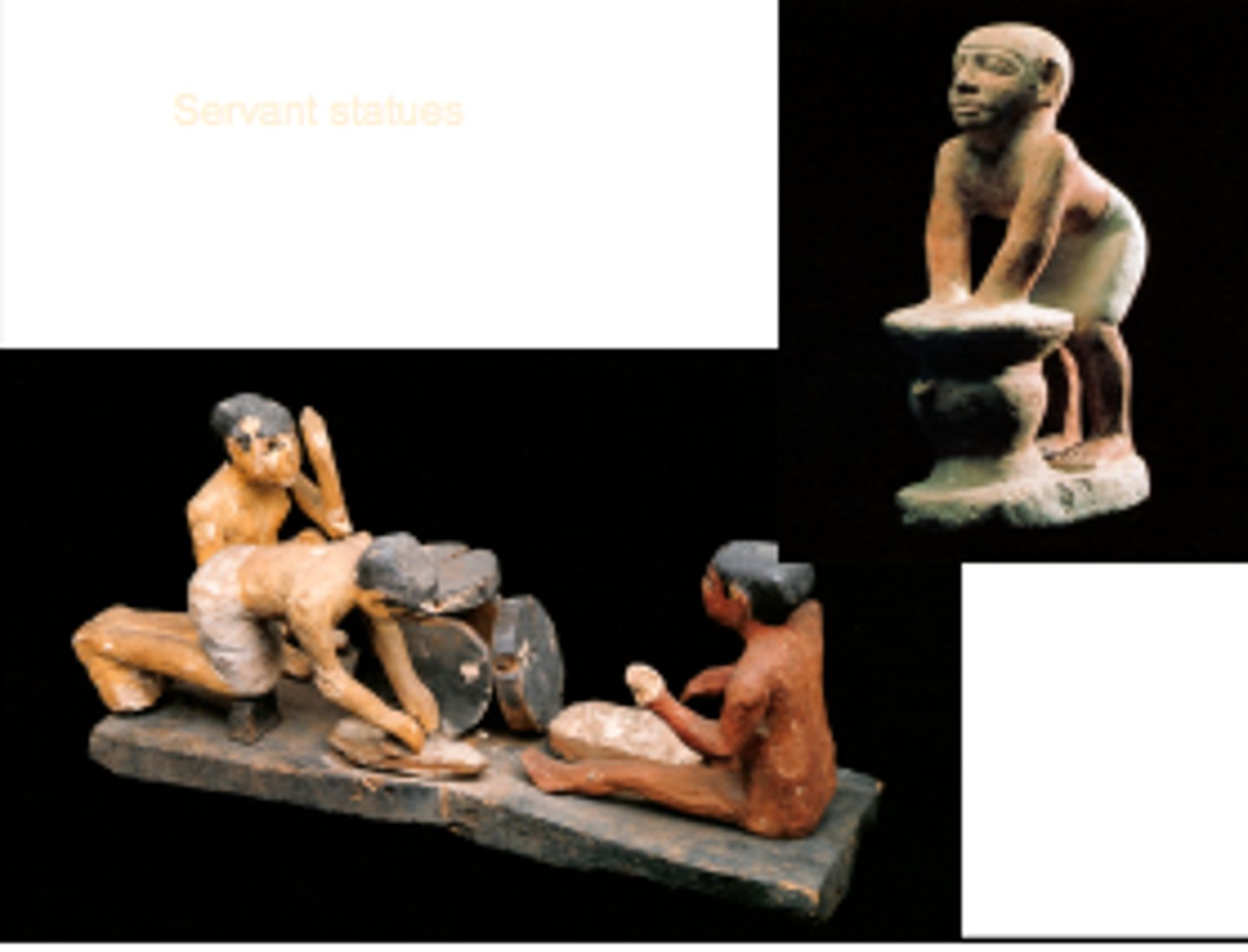
Servant Statues: Male brewer on the left & servants grinding grain and baking on the right, Made out of painted limestone, from the tomb of Merirahashetef, 6th Dynasty

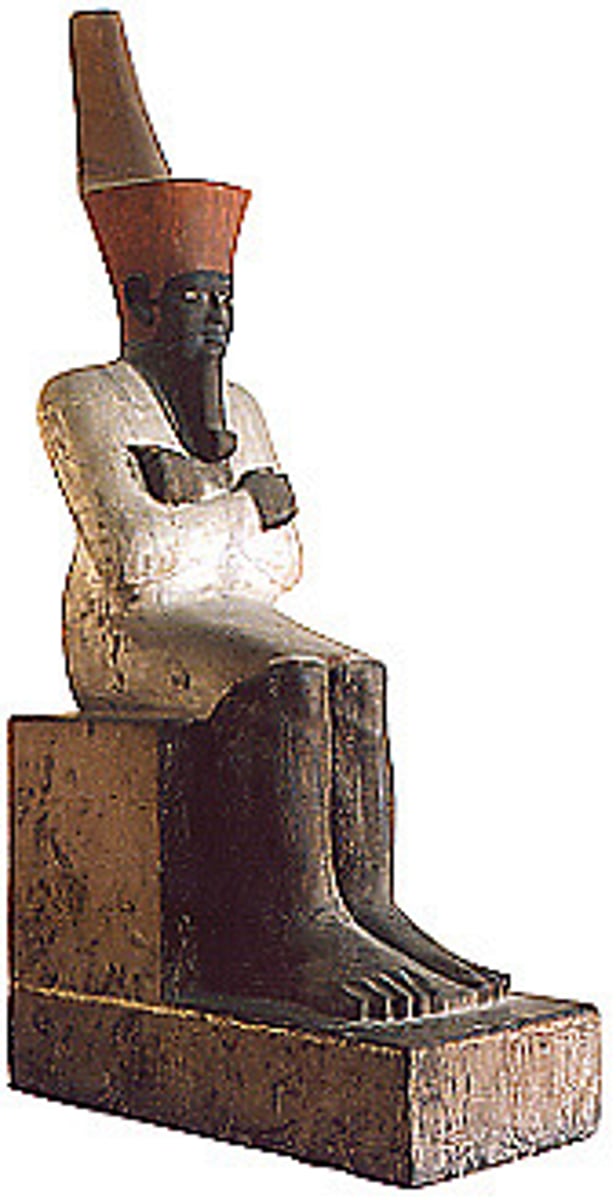
Statue of Nebhepetre-Montuhotep, Painted limestone, from his mortuary temple, in Deir-el-Bahri nearby Thebes, ca. 2055-2004 BCE
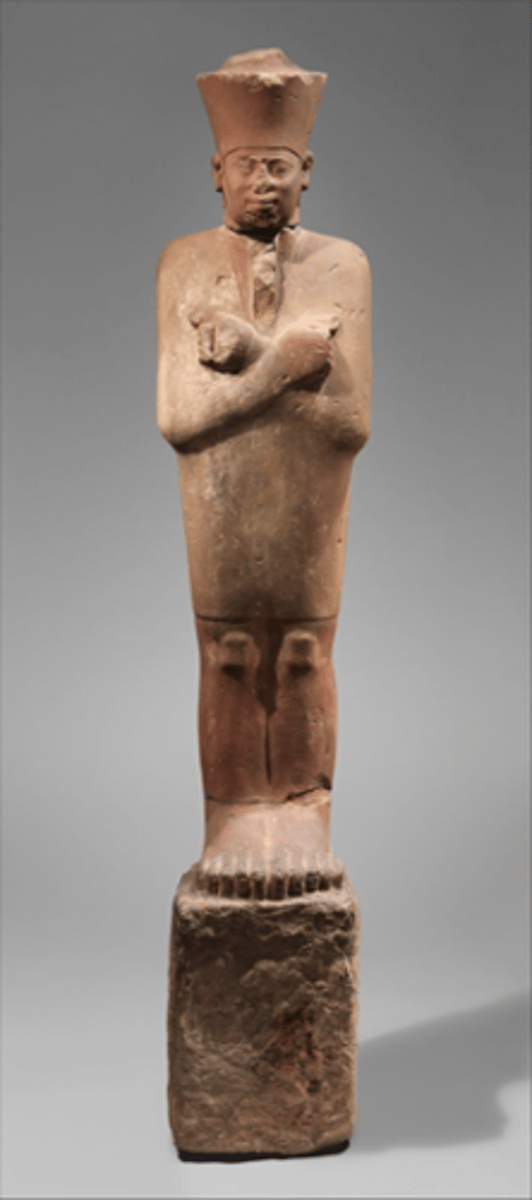

Funerary statue of Nebhepetre-Montuhotep, Deir el-Bahri, painted sandstone, ca. 2055-2004 BCE

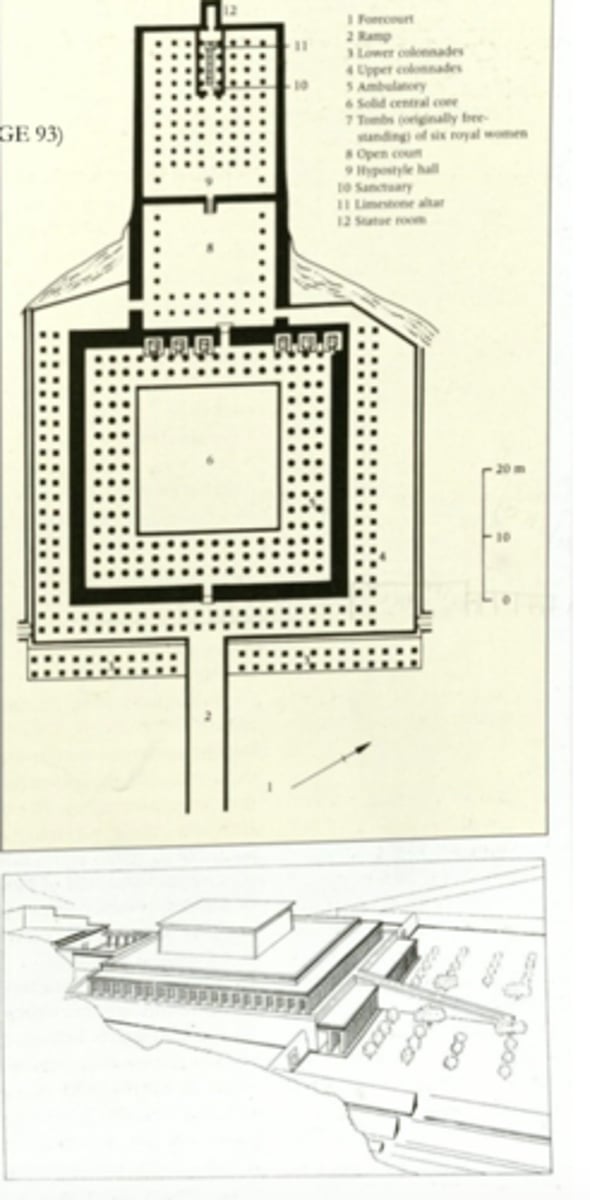
The funerary temple of Nebhepetre-Montuhotep, Western Thebes, ca. 2000 BCE
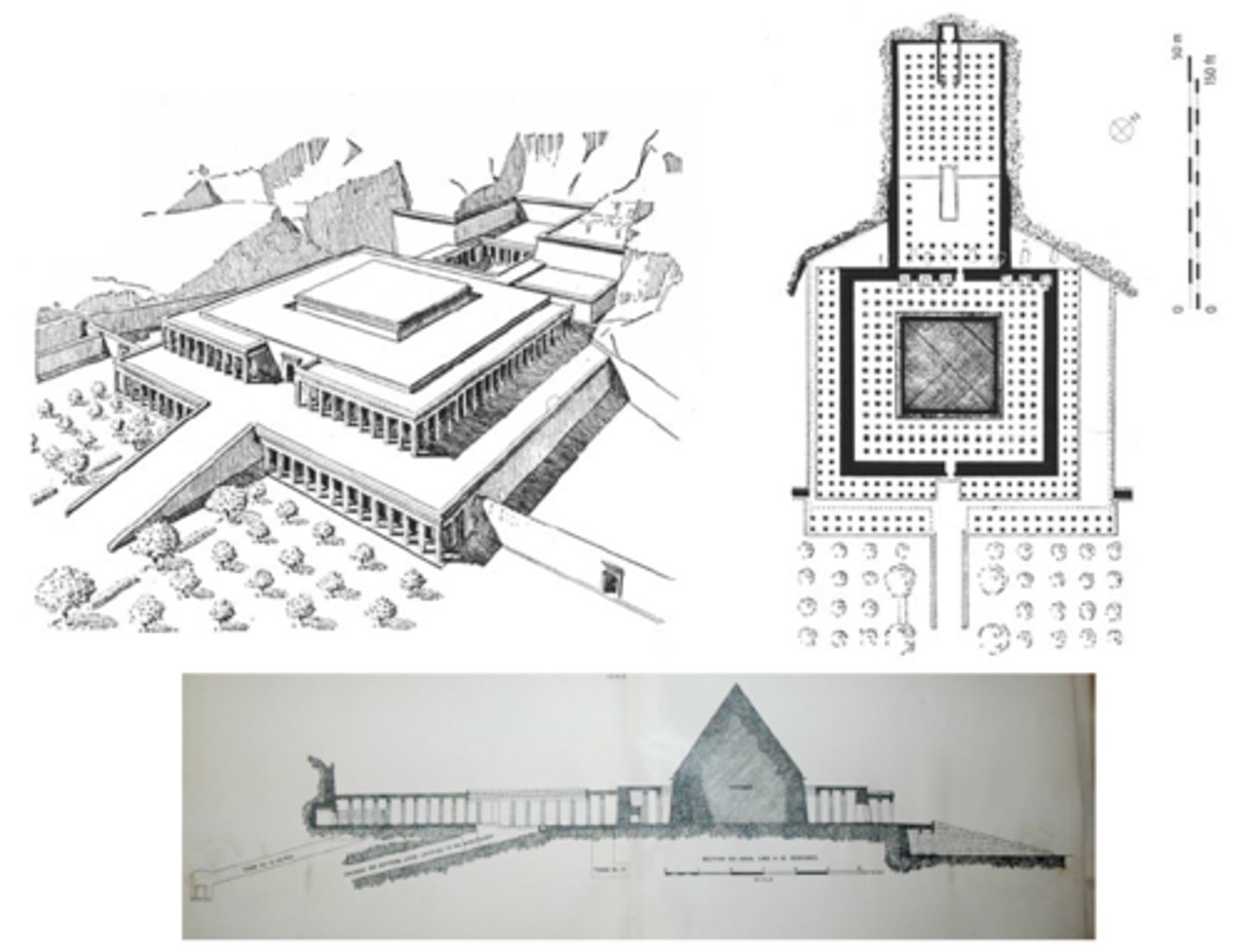
The funerary temple of Nebhepetre-Montuhotep, Western Thebes, ca. 2000 BCE
Reconstruction of the mastaba of the vizier Khnumhotep at Dahshur,
Twelfth Dynasty, reign of Senwosret III (ca. 1878-1840 BCE)

Pyramid of Menkaure, 4th Dynasty, Giza, ca. 2500 BCE
(little one)

Pyramidion (capstone) of Amenemhat III, made of basalt,
12th Dynasty, ca. 1859-1813 BCE

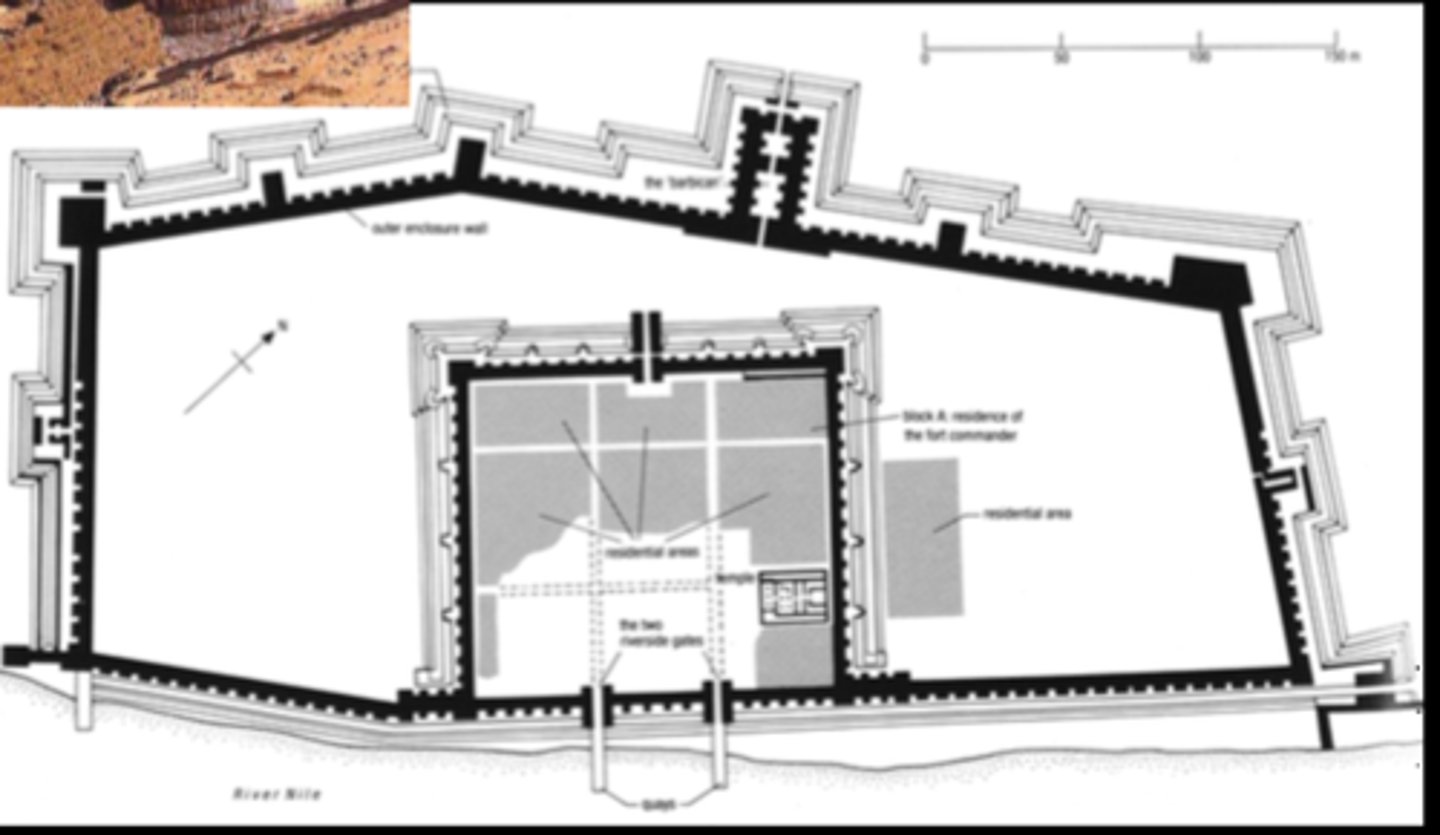
Fortress of Buhen in Nubia, south of Egypt, Constructed by Senwosret III, mudbrick architecture, ca. 1840 BCE
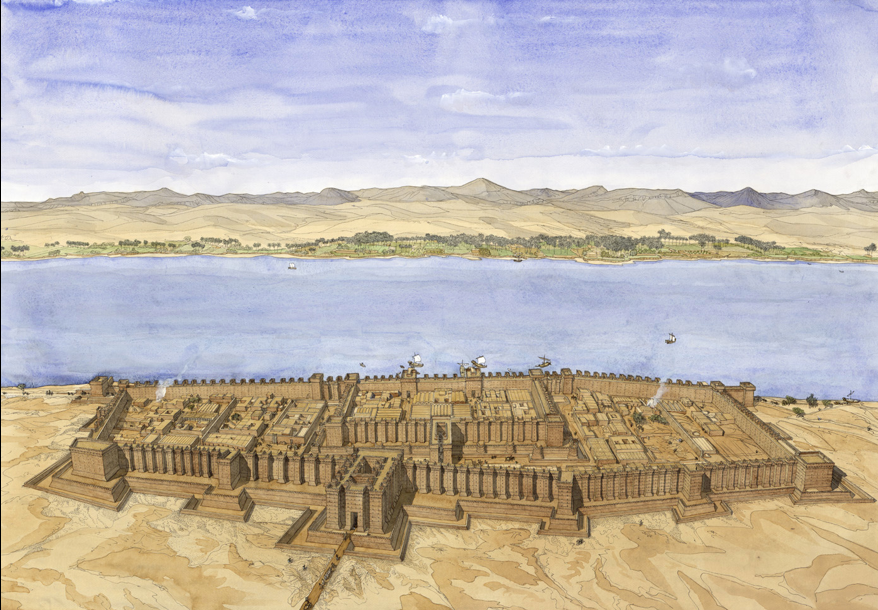

Fortress of Buhen in Nubia, south of Egypt, constructed by Senwosret III, mudbrick architecture, ca. 1840 BCE
Elevation of the Amun-Re Temple in Karnak, Twelfth Dynasty, Senwosret I, limestone, ca. 1961 - 1917 BCE
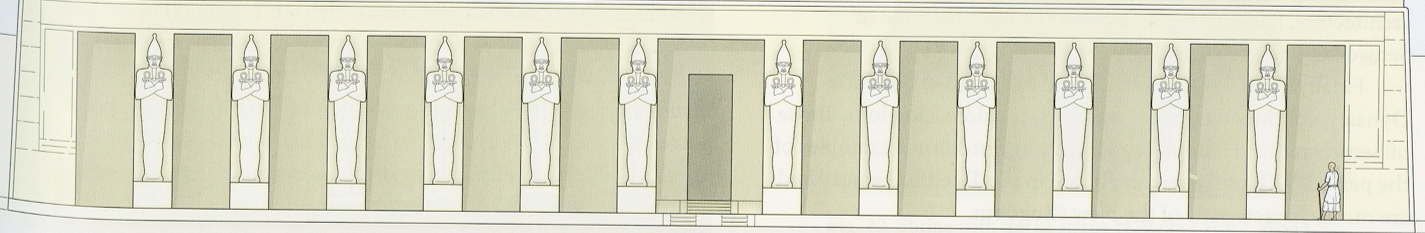
The White Chapel of Senwosret I, Limestone, ca. 1971 - 19326 BCE
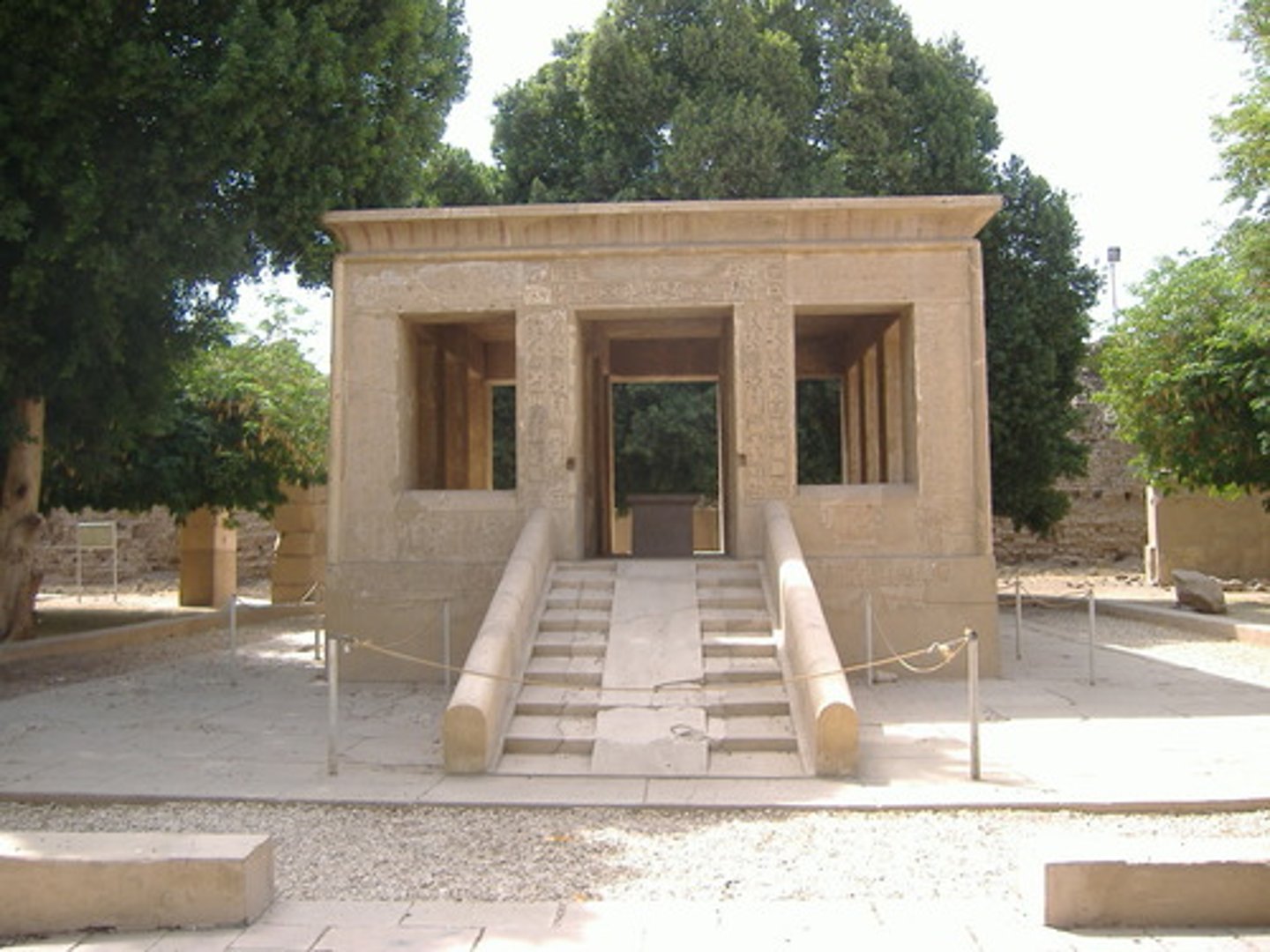

Reliefs from the White Chapel, Limestone, ca. 1971 - 19326 BCE
(not exactly this, but similar)

Canonical grid of eighteen squares from the While Chapel
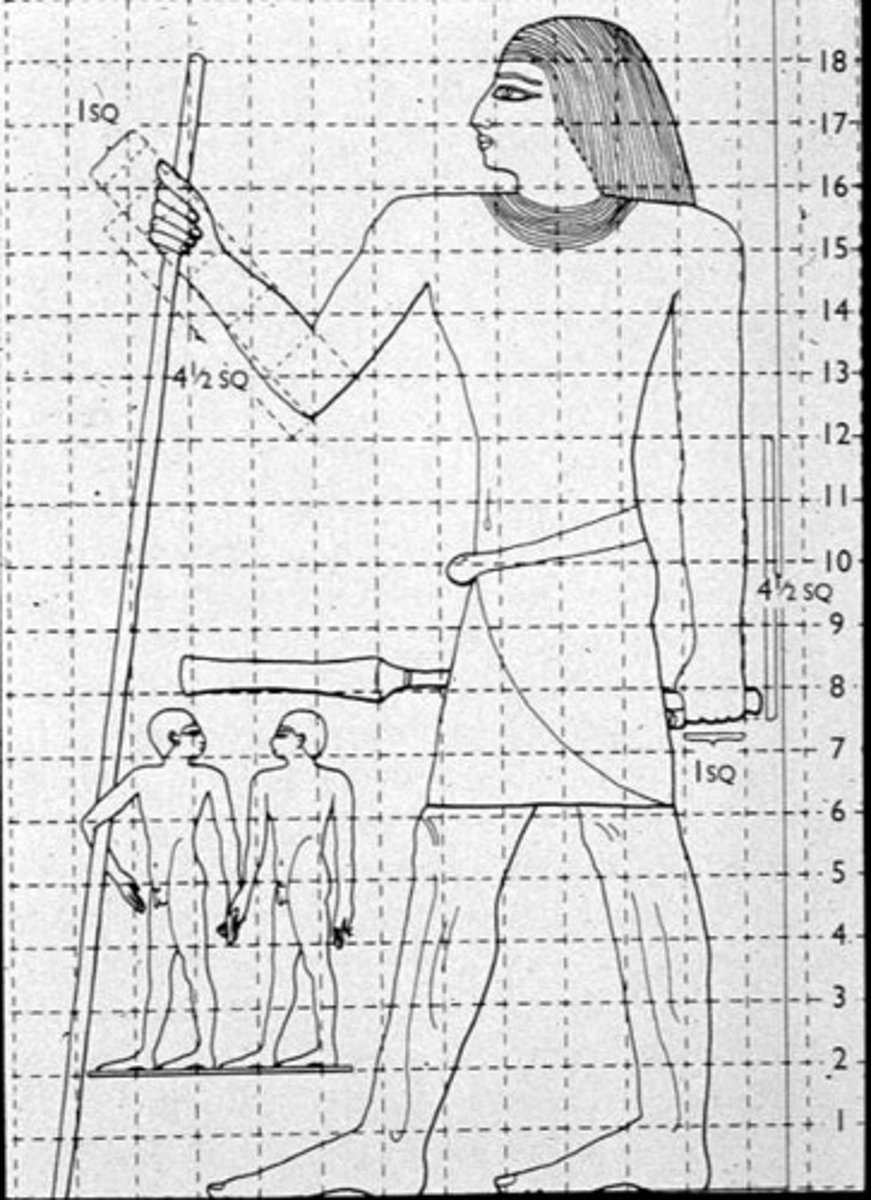
Senwosret III interacting with the gods, White Chapel, Karnak, Thebes, ca. 1870 - 1831

Face of Senwosret III, quartzite, 1878-1841 BCE
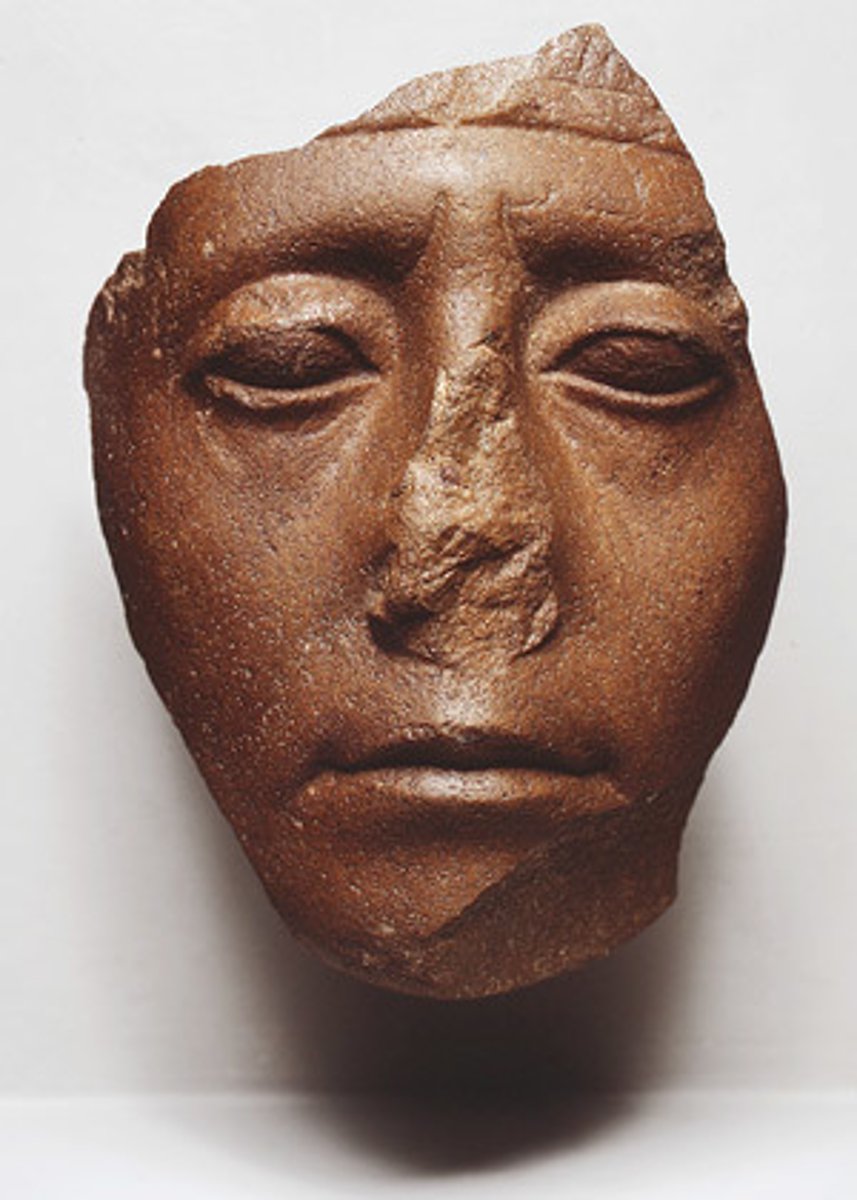

Head of Senwosret III, quartzite, 1878-1841 BCE
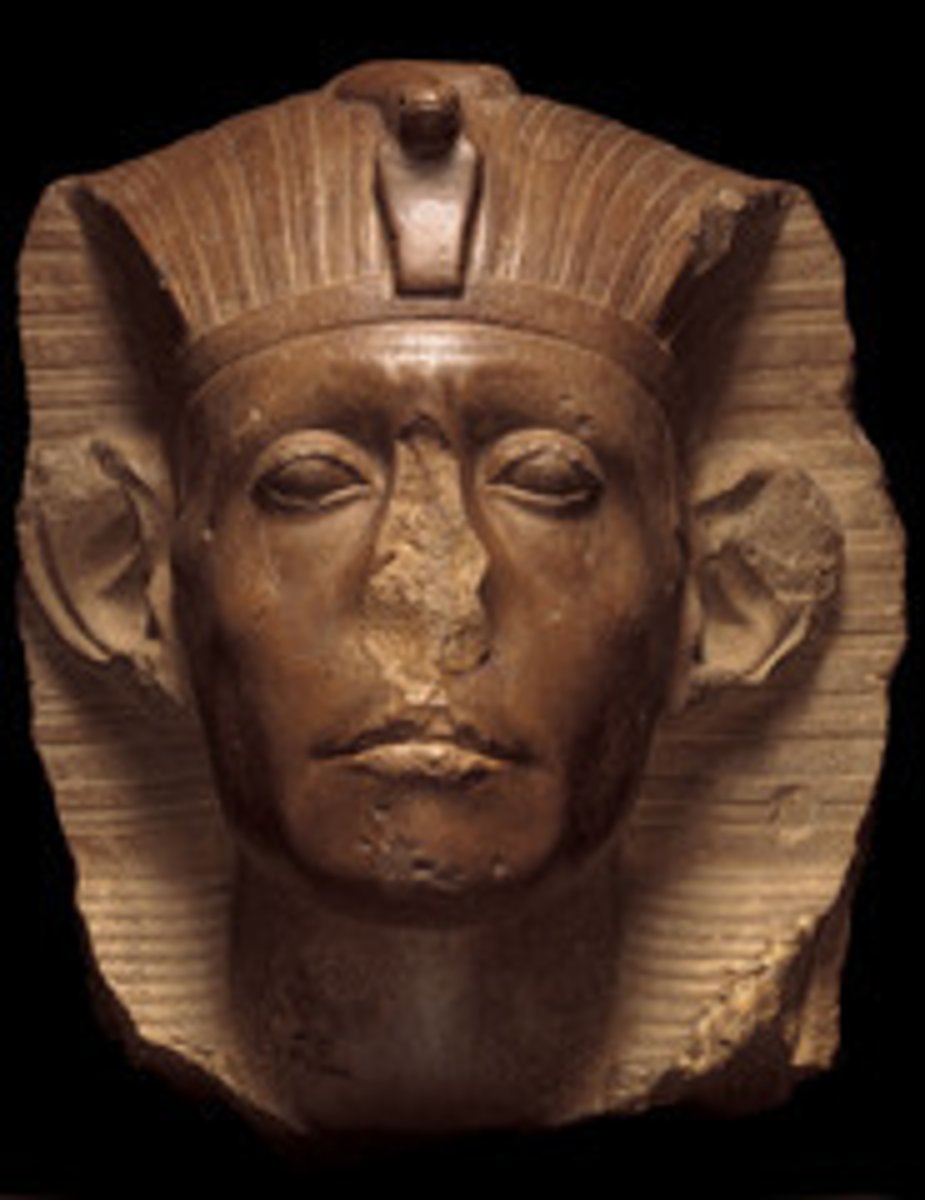

Statue of Senwosret III in devotional pose, Found in mortuary temple of Nebhepetre-Montuhotep, granodiorite, ca. 1878-1841
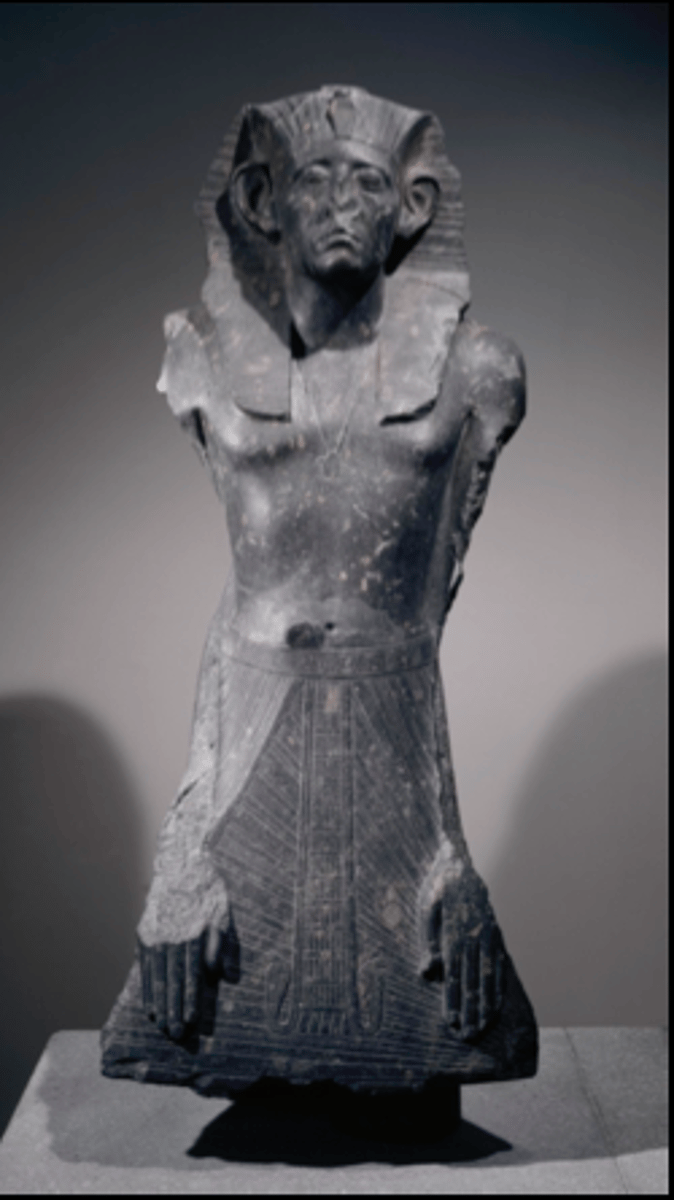

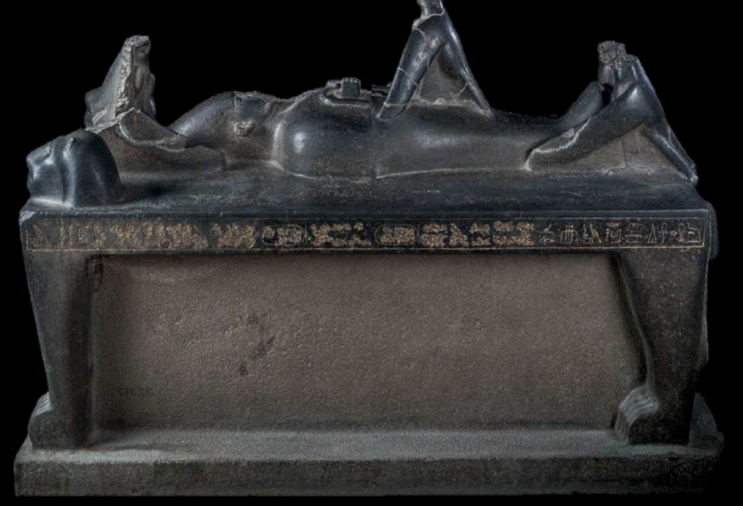
The Osiris Bier, found in the Early Dynastic tomb of Djer at Abydos, Dedicated by a Thirteenth Dynasty pharaoh, ca. 1773 - 1650 BCE, Made of diorite

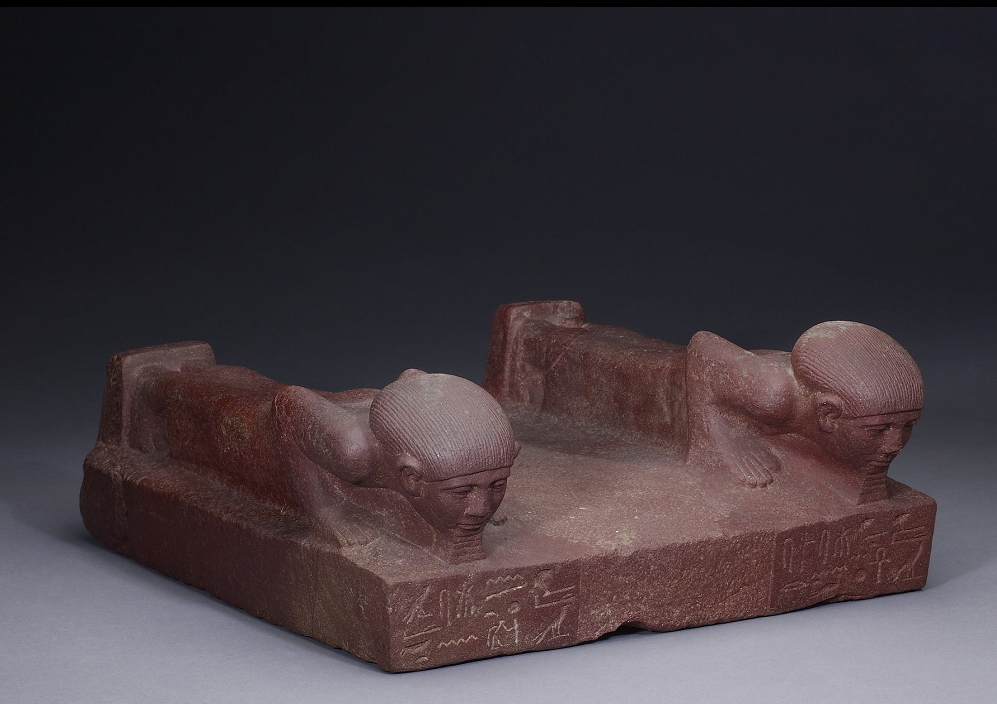
Base with two male figures, made of red quartzite, ca. 1880 BCE

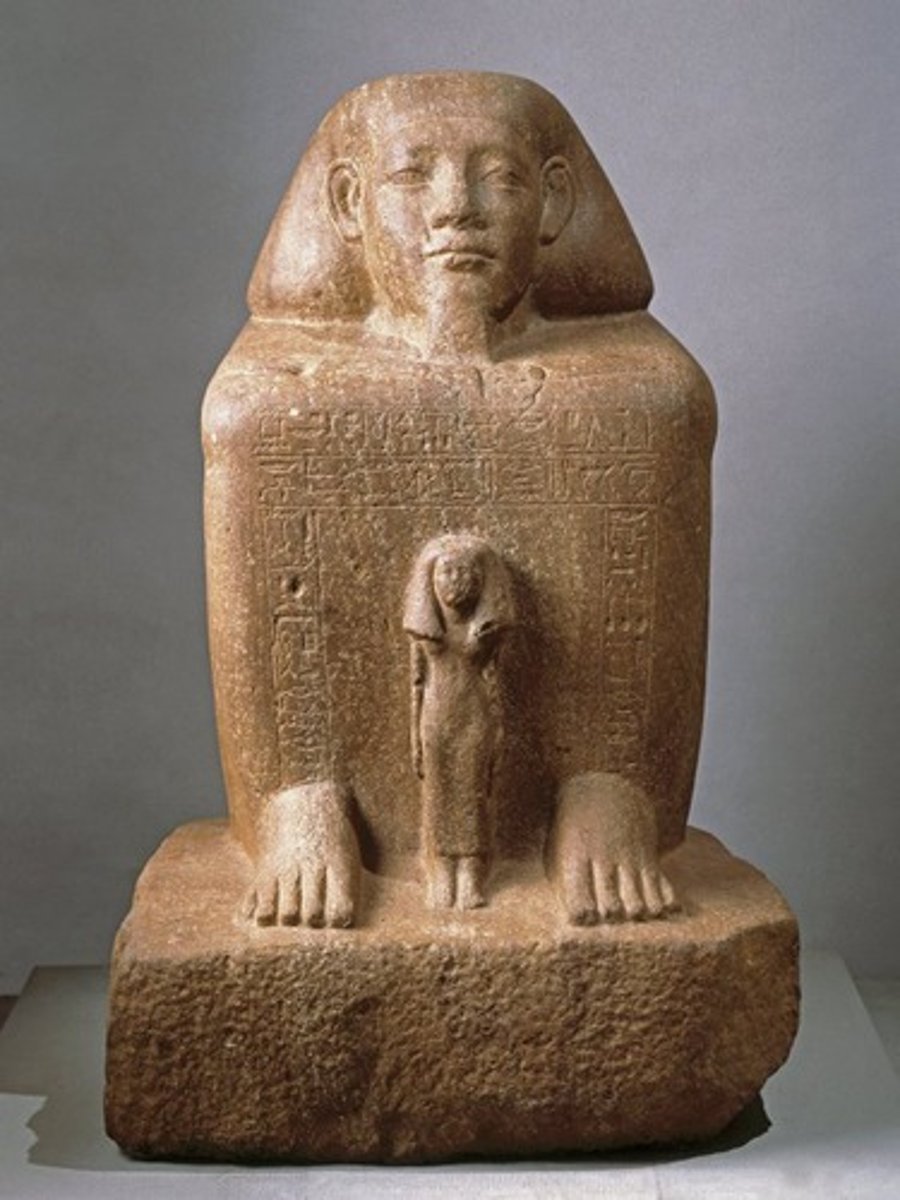
Block statue of Senwosret-senbefni & his wife,
Quarzite, ca. 1850 BCE

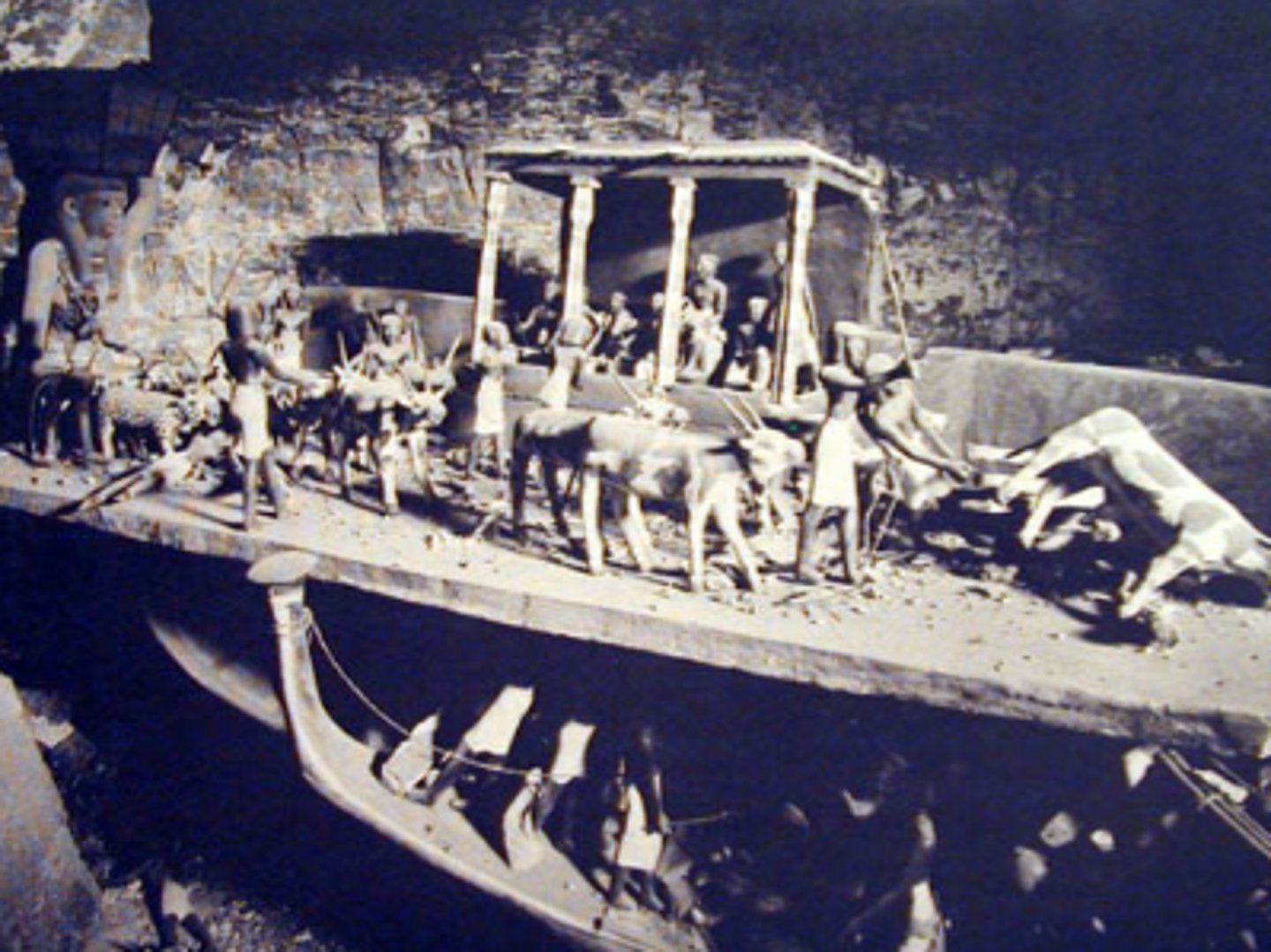
Private Tombs of the Middle Kingdom: The tomb of Meketre along with models, the vizier of Amenemhat I, Twelfth Dynasty, carved into the cliffs nearby Thebes, ca. 1981-1975 BCE

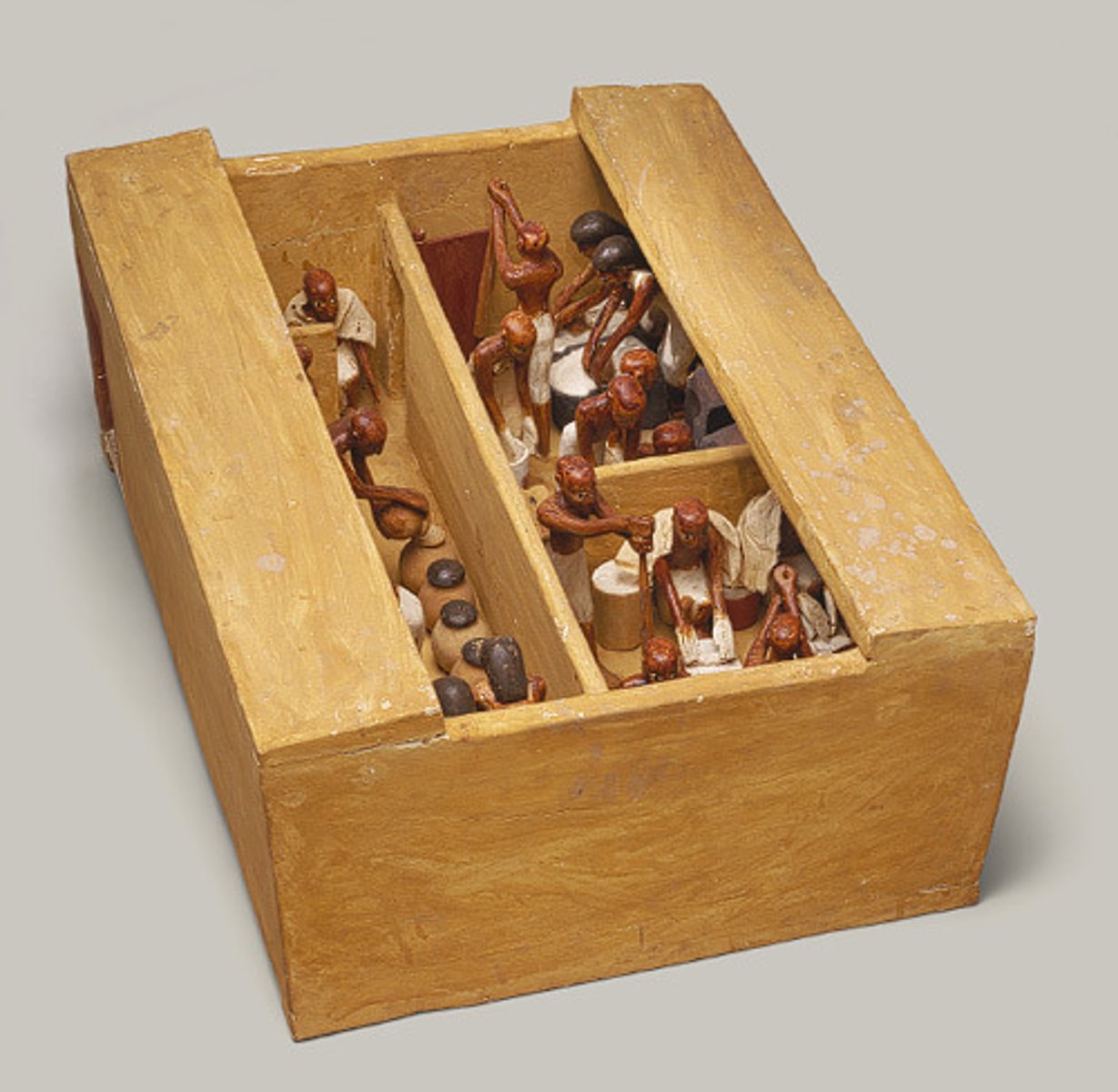
Model bakery & brewery- Models from the tomb of Meketre, the vizier of Amenemhat I, Twelfth Dynasty, from Thebes, ca. 1981-1975 BCE

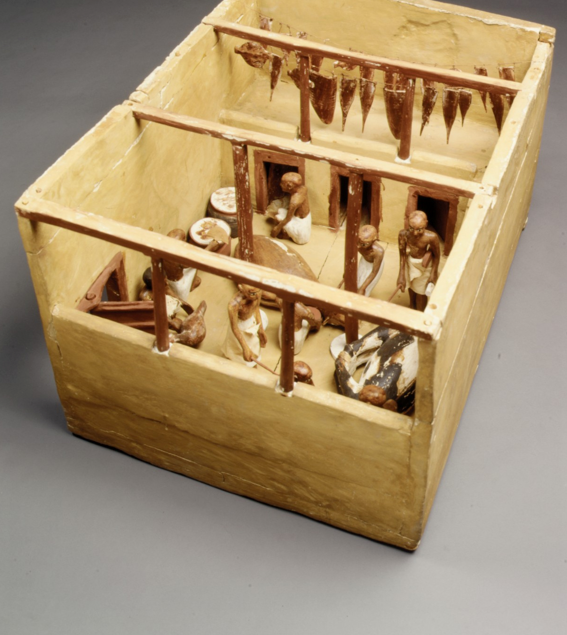
Slaughterhouse, plastered & painted wood- Models from the tomb of Meketre, the vizier of Amenemhat I, Twelfth Dynasty, from Thebes, ca. 1981-1975 BCE

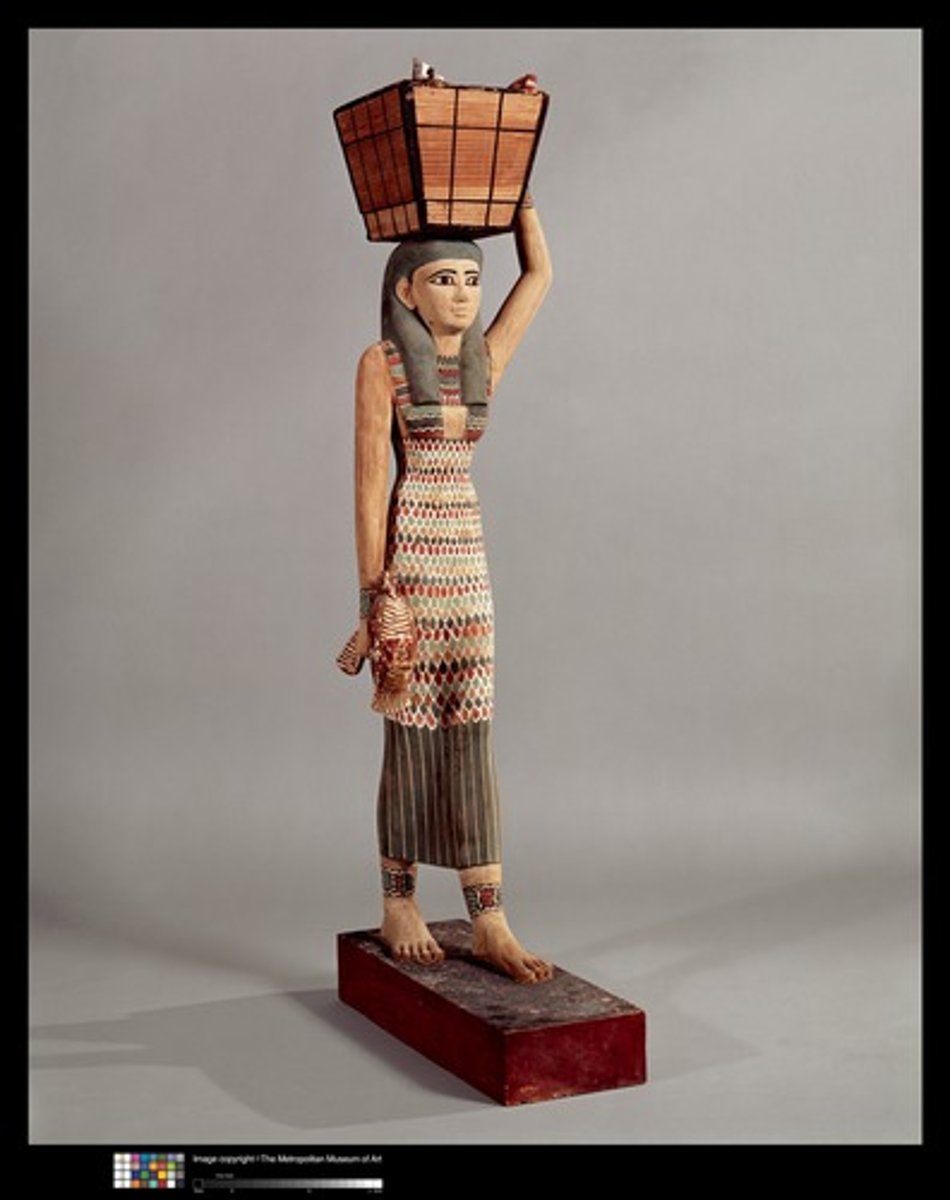
Female offering bearer from the tomb of Meketre, the vizier of Amenemhat I, from Thebes, wood & paint, ca. 1981-1975 BCE

Ancient royal burial ground for Egypt's first pharaohs, a major cult center for the god Osiris, and the location of the Abydos King List
Abydos
Heliopolis was an ancient Egyptian city, meaning "City of the Sun," which was the religious center for the cult of the sun god Ra
Heliopolis
The main city of the twentieth district of Upper Egypt
Heracleopolis Magna
The religious and political capital of Upper Egypt at the end of prehistoric Egypt (united egypt?)
Hierakonpolis
A stela is an upright monument containing information in the form of texts, images or a combination of the two. Stelae have been used to commemorate people or events, to delineate physical spaces or as objects through which to access the dead or divine.
Stelae
Used during the Old Kingdom, the serdab was a sealed chamber with a small slit or hole to allow the soul of the deceased to move about freely
Serdab
Nemes consisted of pieces of striped head cloth worn by pharaohs in ancient Egypt.
Nemes
One of the most significant ancient Egyptian deities who served many functions, most notably as the god of kingship, healing, protection, the sun, and the sky. Depicted as Falcon
Horus
The god of fertility, agriculture, the afterlife, the dead, resurrection, life, and vegetation in ancient Egyptian religion. The first king of Egypt and later the king of the afterlife
Osirus
The ankh or key of life is an ancient Egyptian hieroglyphic symbol used to represent the word for "life" and, by extension, as a symbol of life itself.
Ankh
A material similar to thick paper that was used in ancient times as a writing material. Plant of lower Egypt
Papyrus
A ceremonial palette was a stone slab used for grinding and mixing cosmetics in ancient Egypt, but unlike a standard cosmetic palette, its intricate carvings distinguished it as a ritual object for religious ceremonies or as a historical monument.
Ceremonial Pallete
Mastaba, rectangular superstructure of ancient Egyptian tombs, built of mud brick or, later, stone, with sloping walls and a flat roof. From the word bench.
Mastaba
Memphis was the ancient capital of Egypt during the Old Kingdom and a major religious and administrative center.
Memphis
Thebes was a major ancient Egyptian capital and cult center, located on the Nile River where modern Luxor now stands. It was the capital during the Middle and New Kingdoms, known for the worship of the god Amun.
Thebes
Egyptian obelisks are tall, four-sided, monolithic stone shafts with a pyramid-shaped top, originally created as part of solar worship, especially for the god Ra
Obelisk
Primarily built as elaborate tombs for pharaohs and their consorts during the Old and Middle Kingdom periods.
Pyramid
A system of writing that uses pictorial characters
Hieroglyph
a symbolic representation of a royal palace, which was used in hieroglyphs and tomb art.
Palace facade (Serekh)
the flooding of the river that began in late June, peaked in late September, and left behind fertile silt essential for ancient Egyptian agriculture and life
Indundation
Lion body and human head, a guardian symbol, often representing divine kingship and protection
Sphinx
The first pharaoh of the Fourth Dynasty of Egypt, during the earlier half of the Old Kingdom period. He introduced major innovations in the design and construction of pyramids, and at least three of his pyramids survive to this day.
Snefru
The Fourth king of the Fourth Dynasty, during the earlier half of the Old Kingdom period. Son of Khufu and owner of the second pyramid of Giza
Khafre
The second pharaoh of the Fourth Dynasty, in the first half of the Old Kingdom period. Son of Sneferu and owner of first pyramid of Giza
Khufu
An architectural feature in a tomb or temple, mimicking a real door but serving as a symbolic portal for the deceased to the afterlife. It allowed the deceased's spirit (ka) to communicate with the living, receive offerings, and pass between the worlds of the dead and the living.
False Door
God of the sun and creator god. He was believed to travel across the sky in his solar bark.
Re/Ra
The principal god of Ancient Egypt during the New Kingdom, eventually becoming known as the king of the gods and the creator deity after merging with the sun god Ra to become Amun-Ra
Amun
An Egyptian priest who wrote a history of Egypt in Greek, probably commissioned by Ptolemy II/listed dynasties and kings
Manetho
The name of the desert (the red land)
Desheret
The name of ancient Egypt from the Egyptians (dark soil/black earth)
Kemet
An ancient Egyptian pharaoh, the sixth ruler of the Eleventh Dynasty. He is credited with reuniting Egypt, thus ending the turbulent First Intermediate Period.
Mentuhotep II
An oval with a line at one end tangent to it, indicating that the text enclosed is a royal name.
cartouche
First king to unite all of Egypt (3000 - 2972 BC); Narmer
Menes