Biology( Blood Sweat & Air)
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
39 Terms
What is Glucose
Simple sugar that serves as the primary fuel source.
Glucose
Its chemical bonds store energy, which is released through a series of reactions to generate ATP, the cell's main energy source.
Where does Glucose occur?
Occurs in glycolysis
ATP ( ? )
Adenosine Triphosphate
ATP
High energy molecule that stores and transfers energy.
ADP (?)
Adenosine diphosphate
ADP
Energy Storage Molecule
Mitochondria
Organelles in the cells eukaryotic body that generate most of the cells supply of chemical energy.
Aerobic Respiration
Occurs with oxygen/ Includes the Krebs Cycle and ETC
Anaerobic Respiration
Occurs without Oxygen/ Includes Latic acid and Alchoholic Fermentation.
Lactic Acid
Produced during latic acid fermentation/ too much may lead to muscle soreness.
Pyruvate
3 carbon molecule that is the final product of glucose.
O2
Oxygen
H2O
Water
CO2
Carbon dioxide
Glycolysis
First step of cellular respiration/ occurs in the cytoplasm.
Creates 2 ATP molecules and 2 NADH
Glycolysis
Citric Acid/ Krebs Cycle
2nd step of aerobic respiration/ occurs in the cells matrix
Produces 6 NAHD, 2 ATP, 2 FADH2, 4 CO2 Molecules
Krebs cycle
ETC
Final step of cellular respiration/ occurs in the cells membrane.
Creates 34 ATP
ETC
Feedback mechanism
Uses feedback loops to identify if it is a negative or positive change.
Sensors
A structure that detects chemical or physical changes in the environment.
Effectors
A muscle or gland that produces a specific response to a stimulus.
Control Centers
A component that receives signals, processes it, and initiates a response to maintain homeostasis.
Hormones
A chemical messenger produced by specialized cells in the body that regulate physiological processes.
Nerves
Cells that carry out sensory information or send motor commands.
Homeostasis
Biological process of maintaining a stable Internal environment despite external changes.
Heart
Muscular organ that pumps blood throughout the body.
Heart rate.
The number of times a heart beats per minute to pump blood throughout the body.
Red blood cells
Responsible for carrying O2 from the lungs into tissues and CO2 back into the lungs.
blood vessel
A tubular structure which carries blood through tissues and organs (EX. Vein, Artery, ect).
pancreas
An organ behind the stomach which produces enzymes and hormones/ also made up of tissues.
Brain
An organ made up of soft tissue which works as the control center of the human body.
Macro-molecule
large molecule made up of monomers(lipids, carbohydrates, ect.)
organelle
Specialized subunit within a cell that preforms a specific function.
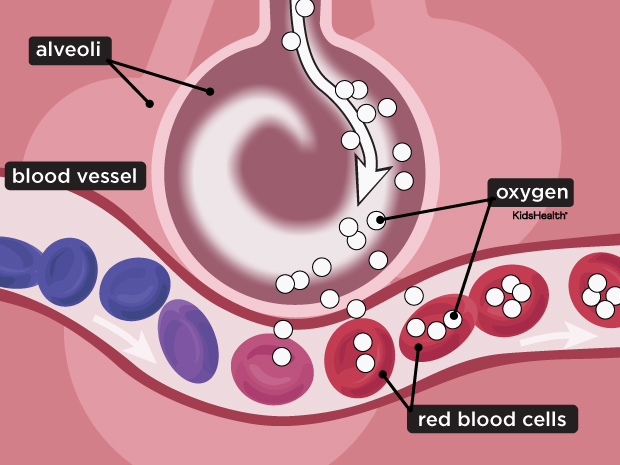
What is the Aveoli made up of?
Tissues

What enters the Aveoli sac from the blood stream (lungs)?
CO2

What turns the purple blood cells red?
O2 (Oxygen)