ecology unit 2
1/154
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
155 Terms
photosynthetically active radiation PAR
400-800 nm, spectra important to photosynthesis
photosynthetic photon flux (PPF)
photons per unit time
photosynthetic photon flux density (PPFD)
photosynthetic photons per unit time per area
photon flux density (PFD)
photons per unit time per area
autotrophs use _____ sources of _____ and energy
inorganic, carbon
photosynthetic autotroph uses _____ as a carbon source and ______ as energy
CO2, sunlight
chemosynthetic autotrophs use ____ _______ as a carbon source and energy
inorganic molecules
heterotrophs use _______ ________ as sources of carbon and energy
organic molecules
light propagates through space as a ______; interact with matter as a particle
wave
leaf area index (LAI)
total leaf area / projected ground area
photosynthesis reaction
6CO2 + 12 H2O —→ C6H12O6 + 6H2O
C3 photosynthesis
used by most plants
C4 photosynthesis
make up only 3% of terrestrial plant species but 25% of photosynthetic carbon gain
CAM photosynthesis
limited to succulent plants, very low rates of photosynthesis
herbivores have low ____ and ____ concentrations in plants
nitrogen and phosphorous
carnivores
consumes nutritionally-rich prey
predators act as “_____ ______” for refinement of prey
selection agents
aposematic coloring
warning signal in a form of bright colors on organisms
batesian mimicry
harmless species mimicking a dangerous specie
mullerian mimicry
when 2 or more harmful species evolve in similar appearances
detritivores
animal that feeds on dead organic material
photosynthesis ________ linearly with photon flux density at low light intensities, ______ more slowly with intermediate light intensities, and tends to _______ at high light temperatures
increases, rises, level off (stops progressing in a straight line)
optimal foraging theory
organisms are adapted to exploit resources as efficiently as possible
holling’s functional response model: type 1
feeding increases linearly with food density then levels off, little-to-no searching
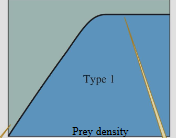
holling’s functional response model: type 2
feeding increases rapidly then slows (rises with food density → encounters searching → reach satiation)
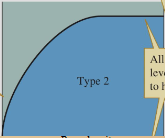
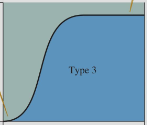
holling’s functional response model: type 3
S-shape, related to searching THEN handling (searching is the limiting factor at low food density, searching is reduced and handling is important at intermediate density, levels off due to handling at high density)
optimal foraging theory (animals)
energy is always limited, organisms allocate available energy, trade-off between searching/handling to optimize intake
darwin’s theory of natural selection
some individuals have a higher chance of survival than others in the same population due to physical/behavioral traits
johann gregor mendel
did the garden pea experiment
allele
alternate forms of genes (dominant or recessive)
genotype
genetic coding based on which alleles are present
phenotype
physical expression or function based on genetic coding
ecotype
populations living in separate locations with significant environmental differences (with almost no exchange of individuals)
ecotypes are still the same _____, but gene pools are genetically _____ from one other
same, distinct
ecotypes are more common in species with a broad _________ ________.
ecological range
hardy-weinberg principle
p² + 2pq + q² = 1.0
states that in a population, mating at random in the absence of evolutionary forces, allele frequencies will remain constant
each variable in p² + 2pq + q² = 1.0 is:
p = homozygous dominant frequency
pq = heterozygous genotype frequency
q = homozygous recessive genotype
fitness
measure of individual’s contribution of genes / number of offspring contributed by individual to future generations
stabilizing selection favors ______ phenotypes
average
directional selection favors ________ phenotypes
extreme (leads to changes over time)
disruptive selection favors ______ phenotypes over _________ phenotypes
2+, average (creates a bimodal distribution)
genetic drift
random processes that can change gene frequencies in populations (especially in small populations)
homozygosity refers to having inherited 2 __________ ______ of a particular gene or genetic marker (allele), one from each biological parent
heterozygous refers to having inherited _______ versions (alleles) of a genomic marker from each parent
inbreeding may be a major contributor to higher _______ rates in small populations
extinction
artificial selection is used to describe ________ breeding of domesticated organisms to produce/maintain desirable ______.
selection, traits
genetic engineering is the ________ / ________ of genes in domesticated organisms
introduction/deletion
evolutionary consequences of chemicals in agriculture
resistance among pests
behavioral ecology
study of social relations within organisms and the environment
sociobiology
study of social relations; can significantly impact fitness of individual/populations
females produce _____ gametes (eggs/ova)
larger
males produce _____ gametes (sperm, pollen)
smaller
hermaphrodite: organisms that contain ______ and ______ functions
male and female
sexual selection: differing reproductive rates resulting from_______ ________ ________.
differing mating success
intrasexual selection
one sex competes over other males for females (INTRA = within a group) (ex: deer fighting with antlers)
intersexual selection
mates express preferences and try to impress each other (INTER = between groups) (ex: colorful feathers)
intra prefix
within a group
inter prefix
between groups
endler’s natural selection study
3 different pond experiment w/ guppies: high predation, low predation, no predation
in endler’s natural selection study, it supports the hypothesis that predation ______ male “showiness” (spots) and moderates the effects of _______ selection
reduces, intersexual
evidence of non-random mating in both field and lab experiments are _______.
present
cooperative breeding
when a “helper” raises a baby that is not their own (by blood)
inclusive fitness us an organism’s genetic success is believed to be derived from ________ and ______ behavior
cooperation, altruistic
inclusive fitness
genetic relatedness x reproductive benefit > cost to helper
males that delay reproduction have ______ lifetime reproductive success
lower
females that delay reproduction have ____ lifetime reproductive success
higher
kin selection
evolutionary theory where an individual performs altruistic acts that benefit their genetic relatives (even at personal cost) to enhance survival and reproduction
eusociality has 3 parts: __________ care, multiple _______ co-habiting, and divisions of _______ and non-________ workers.
cooperative, generations, reproductive (ex: ant colony)
in a haplodiploid system, males develop from _________ eggs and are _______. females develop from __________ eggs and are _______. (FOR ANTS/BUGS)
unfertilized, haploid, fertilized, diploid
________ fitness and _______ selection are rational explanations for altruistic behavior in nature
inclusive, kin
density
number of individuals per unit of area
distribution
the shape, size, and location of the area a species occupies
abundance
the total number of individuals of a species in a specific area
a _____ summarizes the environmental factors that influence the growth, survival, and reproduction of a species
niche
the niche of a species is determined by the _____ in which it lives and its accompanying ______ adaptations
habitat, behavioral
grinnelllian niche: determined by the ______ and its accompanying _______ adaptations
habitat, behavioral
eltonian niche: a species’ response to and effect on environment; species grow/respond to environment based on ______, _______, ______.
resources, predators, climate
hutchinson niche: ___-__________ hypervolume, where the dimensions are environmental conditions and resources
n-dimensional
what happens to distribution patterns, organism interaction, and organism size as populations increase in density?
competition
random distribution
an individual has an equal probability of occurring anywhere in an area
in random distribution, there are ______ interactions between individuals, and between individuals and local environment
neutral
regular distribution
individuals are uniformly spaced through the environment
in regular distributions, there are _______ interactions between individuals and local depletion of resources
antagonistic
clumped distribution
individuals live in areas of high local abundance, which are separated by areas of low abundance
in a clumped distribution, there’s an ________ between individuals or of individuals to a common resource
attraction
for many species, organisms within populations are distributed not only in space, but also in ______
time (migration, mating strats, competition, growth
allelopathy: biological process where plants and microorganisms release ________ that impact the growth of other organisms
chemicals
in general, population density ______ with increasing organism size
decrease
commonness classification of rarity/vulnerability to extinction based on 3 factors:
1) ________ ________ ____ _________: extensive vs. restricted
2) ________ ________: broad vs. narrow
3) _______ _______ ______: large vs. small / broad vs. narrow
geographic range of species, habitat tolerance, local population size
abundant species usually ______ distributed, rarer organisms usually have _______ distributions
widely, small
rarity I: ________ habitat range, _____ habitat tolerance, _______ local populations
extensive, broad, small (ex: tigers) (ex
rarity II: _______ habitat range, _______ habitat tolerance, ______ populations
extensive, narrow, large (ex: pigeons)
extreme rarity
species close to extinction
extinction is a common ecological process, >____% of species are extinct
99
founder effect: genetic drift that occurs when a ____ ______________ is isolated from a bigger one
small population
phenotypic plasticity: when a single genotype produces different __________ (physical, behavioral), depending on their environment
phenotype
changes in population size formula
r = In(Nt/No)/t
geometric growth occurs in _______ generations (ex: reproduce once and die) before next generation begins breeding
discrete
exponential growth is a __________ process where growth rate proportional to the surrent size, leading to a faster _______ (decrease/increase) over time compared to geometric growth
continuous, increase
conditions for exponential growth is typically begin life in _________ environments, invasion of new territory, ________ of transient, favorable conditions
favorable, exploitation
exponential growth is limited by ______ __________.
carrying capacity (K)