Globalisation
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
Globalisation
the increasing interdependence between countries through flows of capital, trade, goods and services as well as culture and ideas.
Causes of Accelerated Gobalisation and the Shrinking World
Economic
volume and influence of transnational companies (TNCs) has increased and use international outsourcing and offshoring to lower costs
online purchasing between countries has become more common
stocks are traded across countries and countries invest in eachother (FDI)
some financial businesses (pension funds, investment banks) trade large amounts of currencies to make profit
Political
trade blocs (NAFTA, EU) have become more influential and reduced tariffs and other protectionist measures
IGOs (international governmental organisation) e.g. IMF, WTO, World Bank work to harmonise econmoies whilst promoting democratic ideology
political views and ieaology are expressed in worldwide media outlets (BBC, CNN, Fox)
deregulation (removing state regulations) policies allow markets to grow with an international reach
Social
international migration has led to extensive family netwroks living across the globe, leading to spread of culture and finance through remittance
international tourism has increased due to lower transport costs
global NGOs and charities are involved in the global improvement of education and health (e.g. World Health Organisation, Amnesty International)
Flow of Commodities
goods can be easily transported increasing countires interdependence on one another
volume of manufactured goos has increased rapidly due to low cost countries such as Bangladesh
Cultural
exposure to media sources such as teevision and social media allow a recognition and understanding of other cultures
ability to travel internationally lets people experience other cultures
individuals have greater awareness and understanding of world events due to education and news sources
westernisation - the domination of western cultural traits in non-western areas
Technology
internet has rapidly allowed the spread of info and knowledge
social networking sites have become popular
networks can allow the spread of culture, idealolgy and opportunities for migration and tourism
enormous server farms exist which store lots of data
Impacts of Globalisation
lengthening of connections - people can now travel further afield and goods are brought in further away
the deepening of connections and penetrating more aspects of life
faster speed of connections with improvement of technology
Interdependence
Economic
countries are dependent on flows of labour, products and services entering the country in order for the economy to grow
labour provides workforce
services mean countries can develop
Social
migration has caused social interdependence as there are now diasporas (groups of migrants of the same origin living in another country) all over the world hat are dependent on he place they live in
countries rely on each other for leisure activities, e.g. TV programmes
Environmental
all nations are affected by each others’ emissions
meaning all countries rely on each other to protect the environment
e.g. the nuclear fallout from Chernoybl disaster in Ukraine reached the UK and France
Political
international political isues require countries working together in order to solve them
Increasing Globalisation through History
19th and 20th Century
steam power - 1800s Britain was leading in use of steam technology which allowed Brits to move their goods and armies very quickly into key areas like Asia and Africa
jet aircraft - newer and more efficient aircraft have allowed goods to be transported quickly between countries
increasing competition between affordable airlines has led to more people being able to travel abroad
containerisation - all sorts of goods are transported around the world, lower cost of travel beneficial for both business and consumers (200 million + container movements every year)
telegraph - first telegraph cables were laid across the Atlantic in 1860s, which allowed for quicker, easier communication
21st Century
telephones - mobile phones revolutionised global ommunication
broadband and fibre optics - since 1990s large amounts of data can be transferred very quickly via cables laid out along the ocean floor
introduction of fibre optic cabling for domestic use has accelerated telephone, internet and television speeds for home
GPS - satellites have allowed companies and people to track goods across the world
internet - now extremely important 40% of the world’s population has access to it, social media incredibly influential and has led ot rapid flow of news
Dimensions of Globalisation
when countries share things with each other it is known as flows. flows can be physical like people and products or ideas and concepts like services and informations. different flows are dimensions of globalisation and are the reason sglobalisations exist
FLOWS:
Capital | movement of money for the purpose of investment, trade or business production |
|---|---|
Labour | movement of people that go to work in another country |
Services | footloose indstries which can work anywhere without constraints of resources or other obstacles. services flow because they can be produced in a different country to where they are received (e.g. international call centre) |
products | flow of physical goods from one country to another |
information | any type of info can flow from one place to another via internet, phone calls etc |
Governance & Decision Making
switched off areas are excluded from global flows and these countries are generally left behind whilst other countries prosper and benefit from globalisation
Reasons for switched off
Environmental
landlocked countries cannot be independent in trade and must rely on neighbours to travel through
poor fertility of land, mountainous or arid conditions, limited land space can all reduce capacity for a country to produce a commodity for trade
some are vulnerable to climate change and natural environment could change to unfavourable conditions (sea level rise, desertification)
Political
political agenda and governance of a country may limit flows of people and culture (anti-migration policies, North Korea)
terrorism and active conflict can be detrimental o global connectivity
corruption within government means money is lost rather than invested
Economic
LEDCs with little extra finance cannot afford to invest in ports infrastructure, incentives for TNCs nor education to improve skills of labour force
countries with unstable markets or weak currencies will deter investment and business
In some countries global flows may be seen as a threat because
importing raw materials and commodities may hurt domestic suppliers
migrants from aborad may cause unwanted tensions
foreign information could be seen as a threat (China’s Great Firewall)
Inter-Governmental Organisations (IGOs)
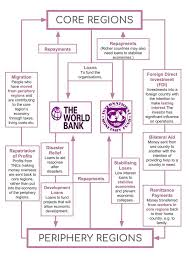
IMF - International Monetary Fund
based in Washington
loans money to poorer developing nations
one of the key conditions for recipient nations is that the country opens up its market from governemnt control which then leads to privatisation
TNCs can now enter easier
LEDCs fall into debt with industries privatised, leads to proftis leaving the country and enviromental and workforce exploitation
countires struggling to pay debts have to cut back spending on educatioon, healthcrae, infrastructure which further damages economy and welfare
The World Bank
loans money to developing nations
similair to IMF and often critisised for increasing LEDCs debts and limit their government’s sovereignity
World Trade Organisation (WTO)
based in Switzerland
aims to liberalise trade by removing tariffs, subsidies and quotas
critisised as it failed to prevent EU and USA from implementing protectionist measures like subsiddies
has been unsuccesful in creating equal trade opportunities for all
Attitudes and Actions of Governements- Encouraging Globalisation
free market liberalisation
belief that government intervention in markets hinders economic growth and development long term
banking and finance sectors deregulated in UK as a result which led to London becoming one of the worl’ds leading financial centres
privatisation
the transfer of assets from the public (government) sector to the private sector
until 1980s important assets in the UK, like railways and utilities were owned by the government
Thatcher privatised these state-owned industries so private companies bought and ran these services which has continued to present day
allowed governemnt to raise lots of money
some believe privatisation comproises quality of services
encouraging business start ups
incentives are provided by governments in order to attract business (grants, tax breaks, infrastructure constructed)
foreign direct investment (FDI)
TNCs increase ecomonic or industrial activity in a country
offshoring = TNCs set up production facilities in developing countries which have large, cheap work forces
foreign mergers = TNCs from different countries join to form one larger company
foreign acquisitions = a TNC aquires another company abroad often in a hostile way (may involve local job less, lack of interest in enivornemnt etc)
transfer pricing = TNCs channel their profits through subsidaries in tax havens (e.g. Ireland)
Attitudes and Actions of Government - Limiting Globalisation
censorship
givernemnt restricts flow of information and knowledge through state controlled media outlets and internet restrictions
limiting migration
most countris have some sort of border control and migration monitoring
with rise of right wing and extremist views many countires adopted stricter restrictions
trade protectionism
subsidies, tariffs and quotas which help a country protect domestic industries
Free Trad Blocs
to trade mroe freely governments sign agreements with each other in order to reduce restrictions of the flow of capital and goods
Benefits:
businesses have larger potential market to sell to, so larger potential revenue to make
business cater to larger demand by increasing volume of production, other businesses can benefit by providing raw material, skilled workers, outsoucing opportunities = positive feedback loop
trade of essential materials or services is more reliable within a trade bloc as less economic risk and better pathways for imports
Disadvantages:
interests of countries within major trade blocs are focussed on themsels
outside trading countries become excluded and find it difficult to join trading
foreign industries and suppliers can be directly damaged as a result of competition or lack of opportunities due to blocs forming
trade blocs don’t guarantee fair treatment within, e.g. relationship between Mexico and USA has not improved through trade bloc NAFTA
Trade Restrictions
tariffs = a tax for importing goods
non-tarif barriers:
quotas = limit/fixed number of goods
requirements
bans on products or country imports/exports
To lower the cost of trade countries can enter trade agreements which work to benefit al lparties invoved. The WTO looks over all agreements to make sure they are fai. In these agreements certain restrictions are removed or lessened. NAFTA reduced tariffs on imports and exports between Canada, USA and Mexico.
Measures of Globalisation
KOF Index
measures of globalisation of countries based on following factors combined. measured on a scale from 1 - 100, where 100 is most globalised nation.
composite measure produced annually by the Swiss Institute for Business
political (39% weighting on overall score)
membership of international organisations and trade blocs like EU, WTO, IMF, NAFTA
participation in international treaties
number of foreign embassies located in a country
economic (37% weighting on overall score)
long distance flow of goods, services and capital
flows of FDI
social (24% weighting on overall score)
personal contact through international phone calls
toursit numbers
information flow through internet users
cultural proximity through thinks like number of McDonalds
each indicator is converted to an index value
small but developed European countries top the list, because unlike the USA which has large amounts of trade within the country, smaller countries are forced to participate in international trade
AT Kearney Index
measure of globalised cities, by a London business using following indicators, uses 12 indicators spread across 4 categories
economic integration
imports and exports
FDI
personal contact
telephone traffic
travel and tourism
remittances
technological advances
internet users
internet hosts
secure servers
political engagement
membership of international organisation
signatories to international treaties
number of embassies
Other Measures
simple measures are only based on one factor
GNI = gross national income, value of goods and services by country, takes into account overseas earnings
PPP = purchasing power parity, expenditure of a country’s population reflects cost of living
GDP = gross domestic product. measures total value of goods and services produced in a country, doesn’t take into account overseas earnings, may be inaccurate as it doesn’t include any informal earnings or black market economies
income per capita = mean average income per person. average can easily hide inequality; few high earners have a larger influence of GDP than majority of low income earners, measured in USD so cna vary as exchange rates vary
composite measure consider a range of factors and are more raliable
economic sector balance
considers all four main economic sectors; primary, secondary, tertiary and quaternary and describes composition of a country’s industry
as a country develops primary industries usually decline whilst secondary and tertiary increase (according to Clarke Fisher Model)
Gender Inequality Index = measures female participation and treatment within society and considers
reproductive health = maternal mortality ratio
empowerment = proportion of parliamentary seats held by women
employment = labour force participation rates of women
Human Development Index = measure of social development considers;
life expectancy
wealth (GDP per capita)
education (literacy levels, average number of years in education)
Winners and Losers - TNCs
TNCs and Trans National Corporations and are companies that operate across multiple countries
have their headquaters, production and sales in different countries
crucial aspect of globalisation
provide raw materials, products, manufactured goods, services or information - they exist in different inudstries
TNCs make products, create jobs, invest in countries and some are powerful and have political influence
2016 top 200 TNCs accounted for 25% of the world’s economic activity but only employed 1% of the population
headquarters usually located in HICs
majority of headquaretrs in USA, Europe, Japan and a few in China
TNCs create links between countriesand with other companies:
links through FDI = TNCs create links with other countries by investing in htem which benefits the country as this creates jobs and contributes to economy
links through intergration = TNCs often expand their company by creating links between other companies. two types of tntergration:
horizontal intergration: taking ownership of part of the supply chain
vertical intergration: taking ownership of another company, often one in the same industry. happens a lot in the food industry
outsourcing = TNCs that provide tartiary industry products (services) will often outsource tasks to other companies in order to save money and time , e.g. Apple outsource manufacturing
offshoring = companies that make manufactured products will often have their factories in LICs due to lower labour costs, better taxes, weaker regulations for workers and environement, although this leads to much dispute over ethical issues
DIsadvantages
TNC’s need for interdependence and global logistics can have major implications on global markets
natural disasters can disrupt supply chains
collapse of factories, e.g. Rana Plaza in Bangledesh 2013 impacted many garment TNCs
exploit workers and have lack of regard for local environment
Glocalisation
adaption of goods or services by TNCs to meet local needs or tastes
Bangladesh supermarkets don’t wrap veg becasue customers choose based on fel
McDonalds created meal without any beef or pork in India, due to large Muslim population
Global Shift
how manufacturing and industrial activity has shifted from different parts of the world
prior to 1960s naufacturing industries were located in west Europe and USA but then it shifted to East countries due to large unskilled workforce and lower labour costs
decline of many secondary and primary industries in USA and West Europe
many companies also outsource services to India as many citizens can speak fluent english and Indian government invested in infrastructure like large broadband capacity
Outsourcing
Benefits
workers receive middle class wages which mean incomes have increased
other businesses have seen more customers and more spending - positive multiplier effect
increased profit for businesses that outsource
Costs
may workers exploited with log hsofts, poor pay, poor working conditions
employees become demotivated due to repetitiveness of work
inequality between richest and poorest increasing because poorest are not well educated and cannot benefit from outsourcing jobs
Outsourcing of Manufacturing to China
in 1990s many Chinese cities offered investors a large pool of cheap labour for manufacturing anf other secondary employment
sweatshops = previiously accelaerated China’s global status have now becom eless popular due to cheaper labour elsewhere and bad reputation Chinese products have. Instead sweatshops are moving elsewere whilst technological outsourcing offers more opportunities to China, offering higher wages
Benefits:
new production methods and techniques brought by TNCs noe been adopted by loal companies causing local economic devlopment
locals, especially those in rural communities who woud have had to rely on subsidence farming are now earning a wage
Costs:
many employees have been exploited with poor pay, dangerous working conditions, long shofts
environemnt has been degraded - rivers and waterways polluted with arsenic, lead and other dangerous chemicals
air polluted with particles that increase asthma and pollution-related fatalities
Deindustrialisation
during 1970s many factory workers in Europe and USA lost their jobs due to global shift of manufacturing to the East. triggered a set of social and economic impacts
derelection and contaminsation = many factories when closed became deelect and other areas suffered from chemical and industrial waste which infiltrated soil and waterways
rates of unemployment increase = can lead to depopulation, depirvation of areas, crime rates increase
Rural → Urban Migration
growth of megacites (city with a population of over 10 million), in 1970 there 3 megacities, today there are 34
since 2007, over half of the world’s population live in urban areas
Urban Pull Factors - migrants are attracted to the city for
employment opportunities
large businesses and TNCs provide a wide range of jobs with the opportunity for advancement to better roles with higher wages
services
better access to services in urban cities as distance to travel is reduced and tehre is more likely to be specialised facilities in the city than in rural areas
infrastructure
better transport links in cities
may be less congestion than in a small village
better internet and broadband
street lights and more people out, make people feel safer to go out at night
Rural Push Factors - migrants pushed out of rural areas
poverty
people may not be able to earn enough due to decreasing earning of farming, seasonal toursit employment and few job opportunities in rural regions
conflict
may be scarcity of resources which can cause conflict between groups as they fight for resources like land, water or natural resources
e.g. Darfur, Sudan
land reform
locals can’t prove they own the land they claim to own so tNCs cliam the land instead, very common in indigenous communities
agricutural mordernisation
increase in advancement of agricultural machinery has meant less people are required on farms, causing risisng unemployment and forcing economic migration of the unemployed
climate and natural disasters
droughts or crop falures force migration in search of food and water
regions frequently affected by volcaos, earthquakes, storm surges atc families may feel pressured to move elsewhere to avoid economic loss or fatalities
Challenges Faced by Growing Cities:
strain on services like education and healthcare
overcrowding and development of slums
rising crime rates
poor sanitation due to open sewers and defecating outdoors
lack of green space
high levels of congestion, causes air pollution
International Migration
elite international migrants = generally very skilled, or very wealthy people with the ability to move global hubs
e.g. Russian Oligarchs who pay investor visas and purchase elite propertyin London, and have caused UK house prices to increase, questions trickle down theory that thier taxs and business would eventually improve other UK citizens
economic migrants = many big cities attract workers who work for very little and are skilled in a prticular profession (e.g. contruction) and can fill skill gaps and advance a country’s development, but unless monitored could lead to increase in escalating urban populations and rise of illegal immingrants
Host Country | Source Country | |
|---|---|---|
Benefits | -can help fill skill gaps working -migrants contribute to the conomy by paying taxes and buying goods + srvices -increase in cuktural diversity -young migrants can help to balance an ageing population over time -businesses have a larger pool of potwntial employees or customers | -migrants send back remittances which can aid development and reduce poverty without government intervention -migrants become skilled and can come back and start up their own businesses encouraging local economic grwth and employment opportunities (like Addy) -reduced services spending for government as population reduces |
Costs | -rise of far right movements, hate crime and racial tensions if lack of understanding between migrants and original population -could be strain on services -house price inflation due to higher demand | -migrants tend to be young so elderly family left behindcan become isolated -brain drain due to skilled workers leaving -decline in services due to low customer numbers -agricultural land not maintained with potential derelection |
Culture and Social Globalisation
historically cultural imperialism and governemnt control over religion has been nessecary for succesful imperial control. However, through invreasing interconnectivity a global culture is emerging.
Culture composed of:
language - national languages, dialects, accents
traditions - behaviours manners passed on generations
religion
food - diets reflect local crops and animals
culture can be influenced by media, TNCs, migration, businesses and social media
China - Cultural Change
BAD
traditional asian diets low in meat
as china develops middle class growing
adapt diets to western influences introduced by western TNCs like McDonalds
from 1990s to 2015 meat consumption per capita rose from 5kg to 50kg
obesity has increased
rise in cattle rearing has led to a rise in methane emissions which in turn is increasing global warming
GOOD
research suggests only 25% of disabled people in China are employed which suggests discrimination in China against disabled people
2012 china won paralympics
paralympics show how global attitudes changed positively towards disabled people
Cultural Erosion
communities exposed suddenly to a new culture can face sudden change or reduction to their own culture, young people especially vulnerable to cultural erosion or diffusion
resiting cultural change - examples
France
french government attempts to reduce globalisation by limiting freign language media so 40% of all broadcasts must be in French
China
the great firewall of china prevents information unfavourable to the governemnt or foreign media outlets
Iran
early 2000s government banned barbie dolls as they woeren’t seen as appropriate for the Islamic State
Widening Equality Gap
average incomes have risen across all continents since 1950s but the poorest parts of Africa have seen little or slow growth
increase pf wealth in Europe and North America has widened gap between richest and poorest in the world
absolute poverty fallen overall but still high
Winners of Globalisation
most billionaires made their wealth through tNC ownership, e.g. Jeff Bezos owns Amazon
developed countries are able to maintain their wealth
factory and call centre workers in developing countries have a reliable income and opportunities that did not exist before
Losers of Globalisation
workers in sweat shops are exploited, work in poor conditions for low pay
workers in industrial cities in HICs have lost jobs when manufacturing relocated (deindustrialisation) e.g. Rust Belt USA
income inequality (Gini Coefficient)
Gini Coefficient
measures the inequality wealth shared across a population and scores a country from 0 to 100
0 represents perfect equality wheere everyone has the same income
100 represents perfect inequality where one person has all the income
Globalisation Causing Growing Conflict
social
in Europe intolerance growing and far right movements gaining popularity
has excelerated since expansion of EU in 2004 (8 eatern european countires added) leading to increased flow of migrants
germany accepted highest amount of migrants out of any EU country which led to rise of Pegida (far right extermist movement)
france the National Front received 25% of votes during national election (nationalist far right party)
political
increasing conflicts between China, Myanamar, Laos, Cambodia and Thialand which share Mekong River over fossil fuels, rivers, islands for naval bases, land for living and farming
protecting cultural identity
sme communties have strengthened their identity
tousrists attracted to come observe their lifestyle
despite TNCs threat to drill for oil within their territories inidigineous communtities remain strong in Canada, Siberia and Alaska
Sustainability and Localism
globalisation linked to many environmental issues
growing insecurity over energy food and water
increasing middle class and growing global population will increase demand
TNCs developed global production networks to minimise cost and maximise profits, but many environmental costs (e.g. high CO2)
Localism is reduction of globally sourced goods instead purchasing locally sourced products to protect environment and vulnerable individuals
METHODS used by local commmunities to reduce environmental impacts:
local sourcing
grow your own
transition towns
ban plastic bags
recycling
allow local protest groups
ADVANTAGES:
local suppliers can generate more revenue and can provide jobs for locals while keeping money in local economy
lower carbon emissions as food miles are reduced
deliveries quicker and shorter so less expensive
national scale policies and initiatives can be promoted by local action
DISADVANTAGES:
foreign suppliers in developing countries lose out and jobs may be lost abroad
overall cost is higher due to higher wages and manufacturing costs in developed countries
low income families simply cannot afford produce
locally grown vegetables may be worse for the environment (heated greenhouses) than just importing them from warmer countries
TRANSITION TOWNS
Totnes, Devon world’s first transition town
Totnes Pound encourages spending in local stores
benefits local economy
aim to support local economies and promote:
reducing consumption through reusing and recycling
reducing waste, pollution and environmental damage
meeting local needs through local production
FAIRTRADE
fair trade aims to secure better pay to producers and growers
coffee, cacao, bananas
fairtrade certification provides consumer confidence that suppliers are being paid fair price for what they produce
as scheme grows increasingly difficult to ensure profts are distributed properly to growers and producers
Impacts of Globalisation on the Environment
NEGATIVES:
deindusutrialised areas experience dereliction and contamination
globalisation of manufaturing industry whith global shift to many Asian countries, which increases pollution and environmental amage in those areas
lengthening food distribution networks, increased food miles, increased carbon footprint, water insecurity, use of fertilisers which will eventually result in eutrophication (dense growth of plant life in rivers) and species loss
trade blocs and other international organisations encourage global trade which is facilitated by transport and developments in ICT communications, increase of fossil fuels
economic development often means growth in personal wealth for everybody, so more cars, homes abroad, air travel for holidays etc
pollution oftn spreads across boundaries e.g. acid rain, global warming
POSITVES:
some countries have pursued a sustanable path to development, e.g. Costa-Rica ecotourism, Denmark’s investment in renewable energy
Wealthy countries having “exported” their pollution-creating industries (factories) are able to invest in improving and protecting habitats and cleaning up rivers
Many TNCs have taken major steps to reduce their environmental impacts,
cutting supply chains and reducing packaging, for example.
ICT improvements may reduce travel, as Skype etc. allow remote
conferencing, reducing carbon footprints.