Organic analysis
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
What is acidified potassium dichromate K2Cr2O7 used for? and how does it work
Used to distinguish between primary, secondary and tertiary alcohols
Oxidises primary and secondary alcohols
How can you identify primary and secondary alcohols?
They both give the same colour change
Collect the products produced from the oxidation of both alcohols via distillation
Test the products for aldehyde (primary alc) and ketone (secondary alc)
How does Fehling’s solution work?
Its an oxidising agent
Wille oxidise aldehydes not ketones
How do use Fehling’s solution?
Put Fehling’s solution in test tubes with the substances you want to test
Put it in a warm water bath
Results from Fehlings test
Brick red precipitate for aldehydes (Cu2O)
Ketones remain blue
How do you make tollens reagent?
Silver nitrate solution(colourless)
Add few drops of NaOH
Pale brown precipitate forms
Add a few drops of dilute ammonia until precipitate dissolves
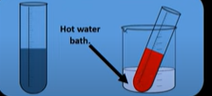
How do you use tollens reagent
Add ketones/aldehydes to tollens reagent
And place in hot water bath
Why don’t you use a Bunsen burner to heat up aldehydes and ketones?
Both are flammable
Results for tollens reagent
Tollens reduced to silver which coats the inside of the flask for aldehydes
No silver precipitate formed for ketones
Test for alkenes
Add bromine water to alkene in a test tube
Swirl it
If alkene is present solution will become colourless from brown
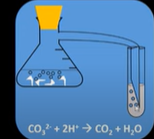
Test for carboxyclic acids
React the acid with a carbonate (sodium carbonate)
If acid is present it will begin to fizz
Will produce carbon dioxide and water
Carbon dioxide will react with limewater turning it cloudy
What is the problem with testing for carboxylic acids?
All acids not just carboxylic acids will react the same way with a carbonate
What is mass spectrometry used for?
To find the relative molecular mass (Mr) of a compound
What does the M+ peak show?
Known as the molecular ion peak
Molecular ion peak is the same relative molecular mass of the molecule
What is high resolution mass spectrometry used for?
Useful when identifying different molecules with the same Mr rounded to the nearest whole number
How do high resolution mass spectrometers measure the relative mass?
To several decimals
E.g. Instead of H=1 it will use H= 1.0078
How does infrared spectroscopy work?
Uses infrared radiation to increase the vibrational energy of covalent bonds in a sample
What does the frequency of infrared radiation absorbed by a covalent bond depend on?
The atoms that are either side of the bond
Position of the bond in the molecule
What is the fingerprint region used for?
Allows you to identify specific molecules
As it is different for all molecules
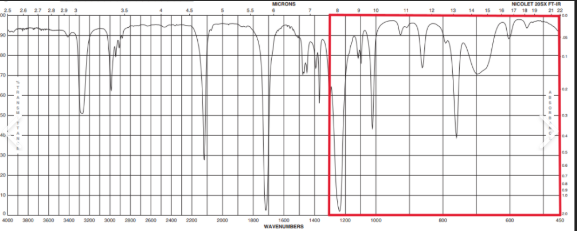
How can you use the fingerprint reigon?
Compare the fingerprint region generated against a known library of spectra to identify the molecule
What do extra peaks in the fingerprint region indicate?
Impurities in the sample
What do greenhouse gases in the atmosphere do?
Absorb infrared radiation form the sun
Examples of greenhouse gases
Co2
water vapour
Methane (CH4)
How does the greenhouse effect occur?
Electromagnetic radiation from the sun reaches the earth and is absorbed by the land and the sea
Some of this radiation is re-emitted as infra red
Greenhouse gases absorb this radiation and re-emit this back towards earth-Greenhouse effect
(The covalent bonds in the greenhouse gases absorb the radiation)
Human activities such as burning fossil fuels has increased the levels of….
Greenhouse gases in the atmosphere
Causing the gradual warming of the earth-global warming