Ana300 - Articulations and Axial Skeleton
1/156
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
157 Terms
Articulations
Where two bones meet
Not all articulations allow _______
movement
Articulations classified ________ or _______
structurally, functionally
Synarthroses allow _______
no movement
Amphiarthroses allow _______
little movement
Diarthroses allow _______
free movement
Fibrous synarthroses are joined by _________, ie. _____ and _____
dense irregular CT, suture, gomphosis (between tooth and gum)
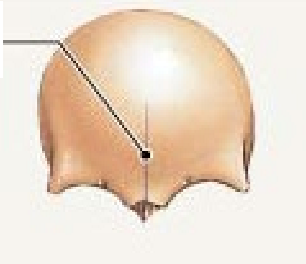
Cartilagenous bones joined by ______ ie. _______ ()
cartilage, synchondrosis, epiphyseal plate of growing bone
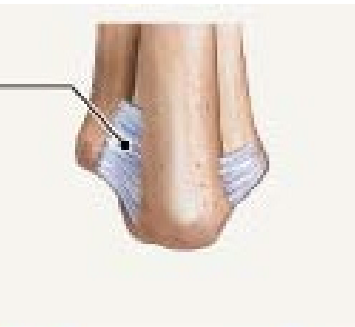
Bony fusion ie:
Fusion of two bones
Syntosis
Skull
Sacrum
Hip bones
Sternum
Vertebrae
Long bones
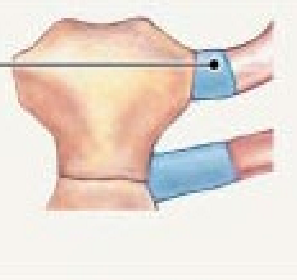
Fibrous amphiarthrosis joined by _____ or _____ ie.
ligament, band of CT, syndemosis, (distal tibiofibular joint)
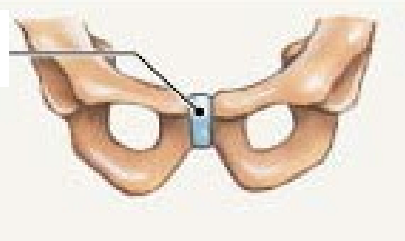
Cartilaginous amphiarthrosis bones joined by ______ ie.. ()
wedge of cartilage, symphysis (intervertebral disk), symphysis pubis
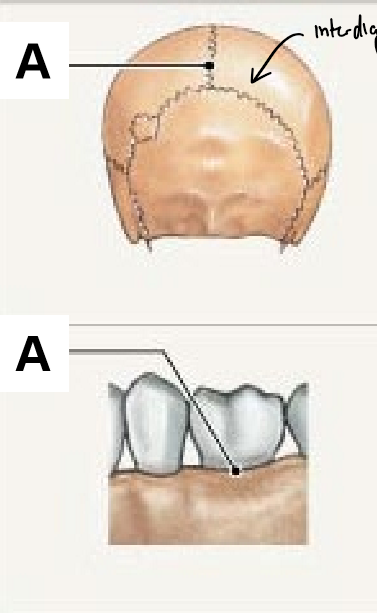
Fibrous synarthrosis
Cartilaginous synarthrosis
Bony fusion
Fibrous amphiarthrosis
Cartilaginous amphiarthrosis
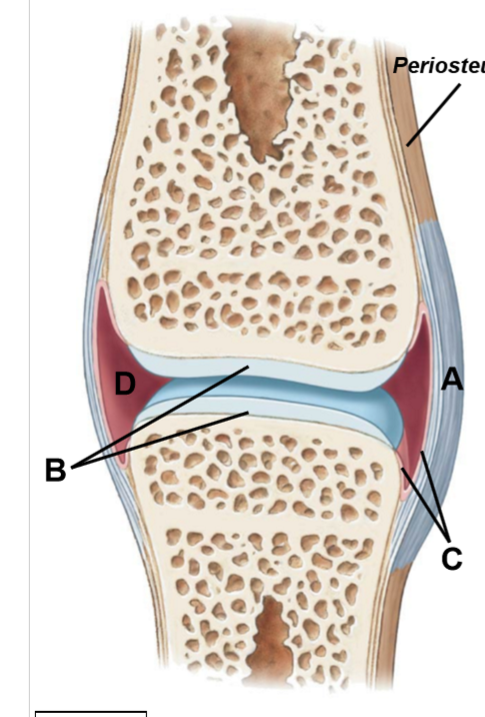
A-D
A: Joint capsule
B: Articular cartilage
C: Synovial membrane
D: Joint cavity
Fibrous joint capsule encloses _________
joint space
Synovial membrane encloses all ____, ______, and secretes _________
internal, nonarticular surfaces, synovial fluid
Joint cavity contains _____, is a _____, _____and a medium for _________
synovial fluid, lubricant, shock absorber, solute transfer between blood & cartilage
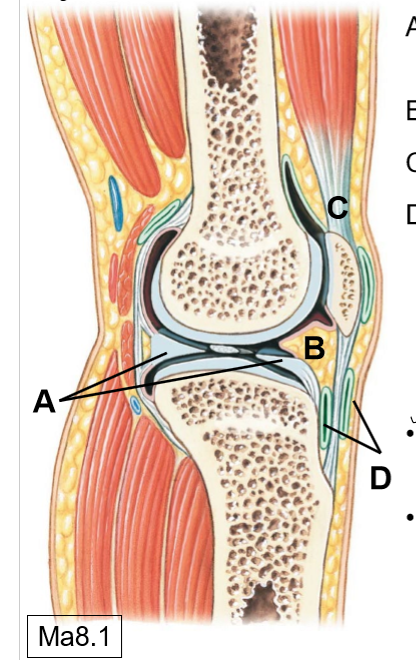
A-D
A: Articular discs/menisci
B: Fat pads
C: Tendons
D: Bursae
Purpose of articular discs
Stabilize joints
Fat pads accommodate _____
joint movement
_______ stabilize the joint
tendons
Bursae are sacs of ________ containing ________, facilitating ________
synovial membrane, synovial fluid, relative movement between structures
bursae can be ____ or ______
subcutaneous, subtendinous
When bursae are inflamed, causes ______
bursitis
____________ are thickenings of the joint capsule across certain aspects of the joint
intrinsic ligaments
__________ separate from joint capsule
extrinsic ligaments
Stability and mobility is influenced by (5)
Shape of articulating surfaces
Capsule
Ligaments
Tone of surrounding muscles
Other tissues around the joint
Linear motion
Gliding
Angular motion
Uniaxial, biaxial, triaxial
Circumduction
Angular motion around 2 axes
ROtation
Angular motion around long axis
6 types of joints
Gliding joint
Hinge joint
Pivot joint
Ellipsoidal joint
Saddle joint
Ball and socket joint
Example of gliding joint
Intercarpal joint
Example of hinge joint
Elbow(uniaxial)
Example of pivot joint
Atlantoaxial joint (uniaxial)
Example of ellipsoidal joint
Radiocarpal joint (biaxial)
Example of saddle joint
Metacarpal of thumb (biaxial)
Example of ball and socket joint
Shoulder (triaxial)
Axial skeleton includes (7)
Skull
Vertebral column
24 vertebrae
Sacrum
Coccyx
24 ribs
1 sternum
Appendicular skeleton consists of
Pectoral girdles & upper limbs
Pelvic girdle & lower limbs
Skull includes _____ that form the cranium and ____ facial bones
8, 14
Internally, the _____ houses the brain
cranial cavity
externally, the cranium provides ________
muscular attachment
The cranium articulates inferiorly with the ________
vertebral column
Facial bones surround entrance to ____ and ______
digestive, respiratory tracts
Facial bones provide muscular attachment for muscles of ____ and _______
facial expression, mastication
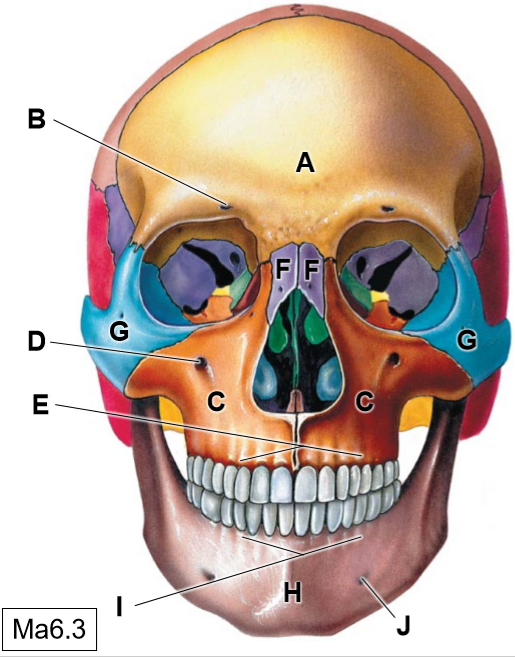
A
Frontal bone
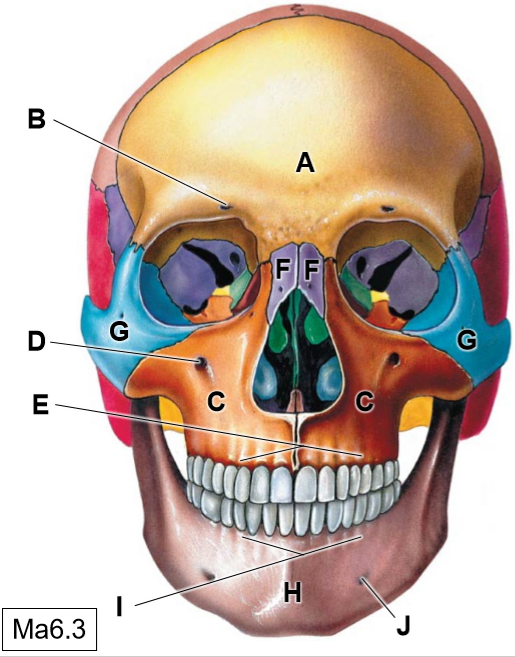
B
Supraorbotal foramen
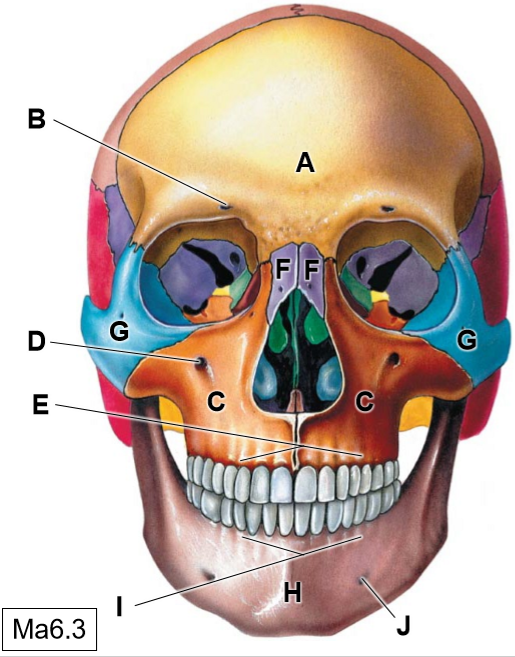
C
Maxillae
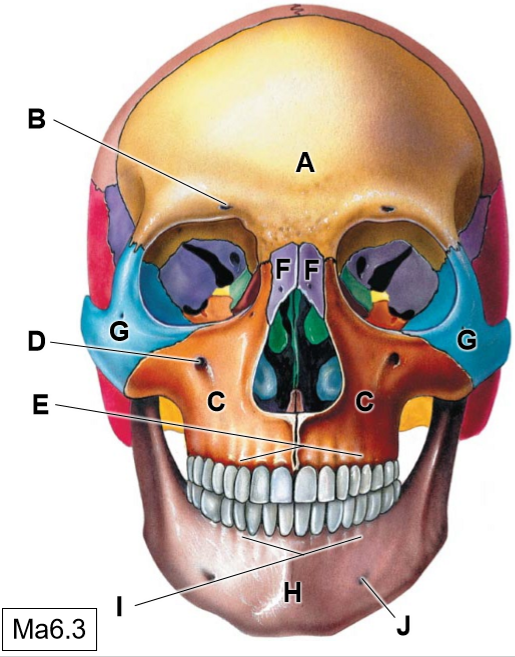
D
Infraorbital foramen
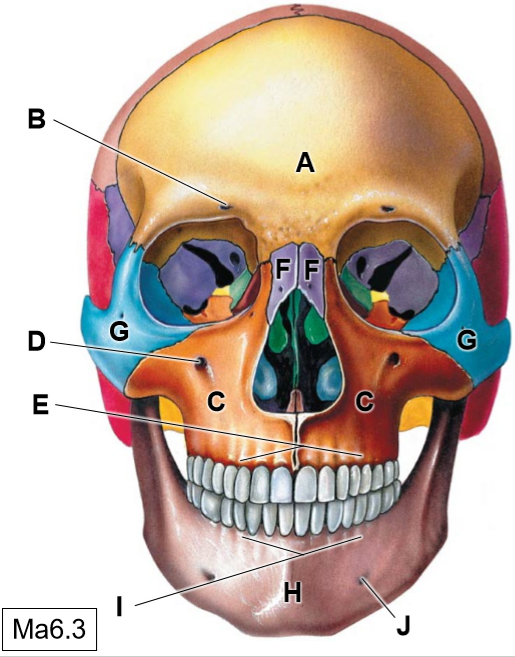
E
Superior alveolar process
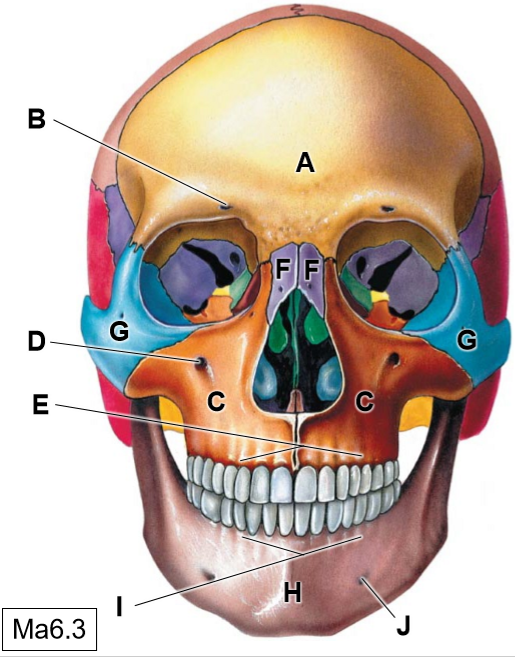
F
Nasal bones
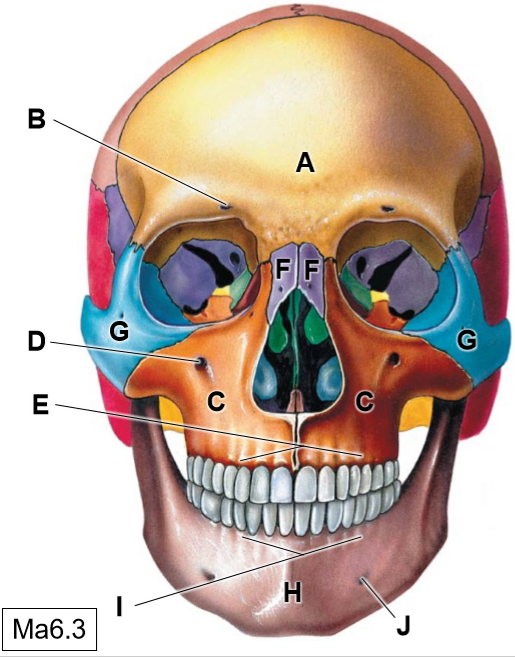
G
Zygomatic bone
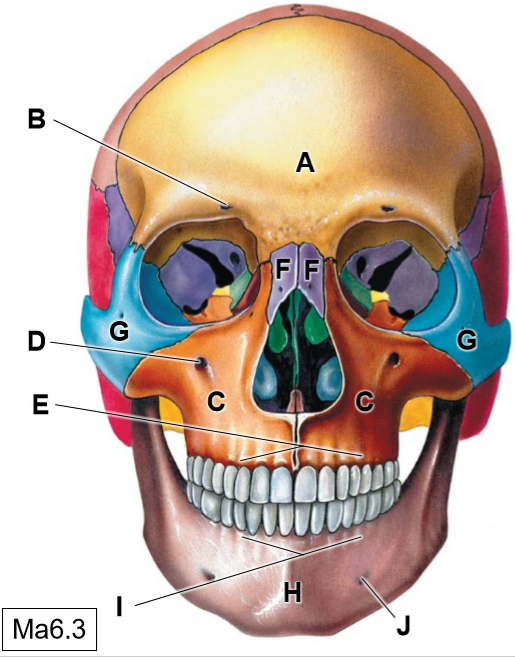
H
Mandible
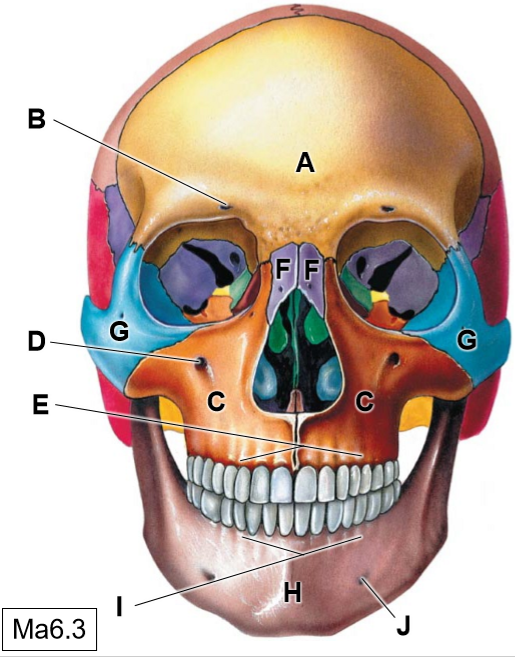
I
Inferior alveolar process
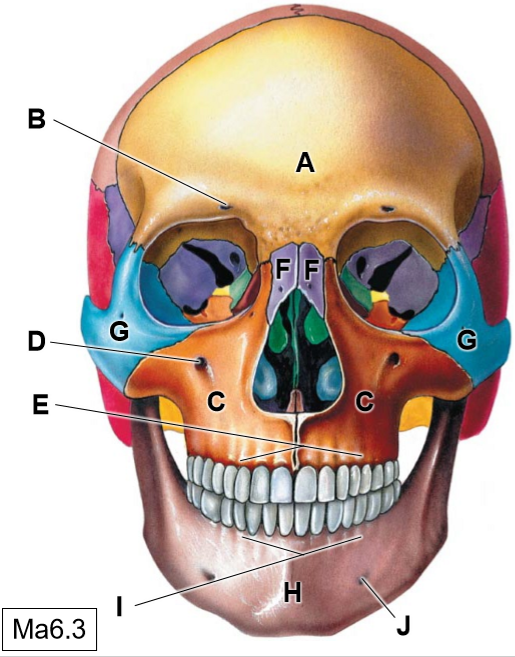
J
Mental foramen
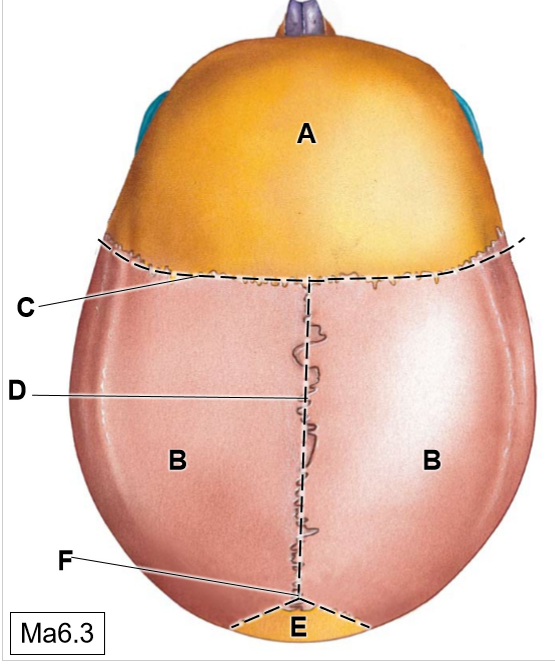
A-F
A: Frontal bone
B: Parietal bones
C: Coronal suture
D: Sagittal suture
E: Occipital bone
F: Lamboid suture
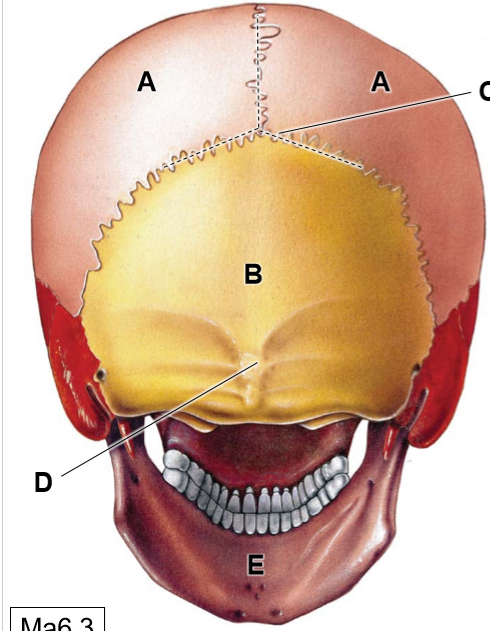
A-E
A: Parietal bones
B: Occipital bones
C; Lamboid suture
D: External occipital protuberance
E: Mandible
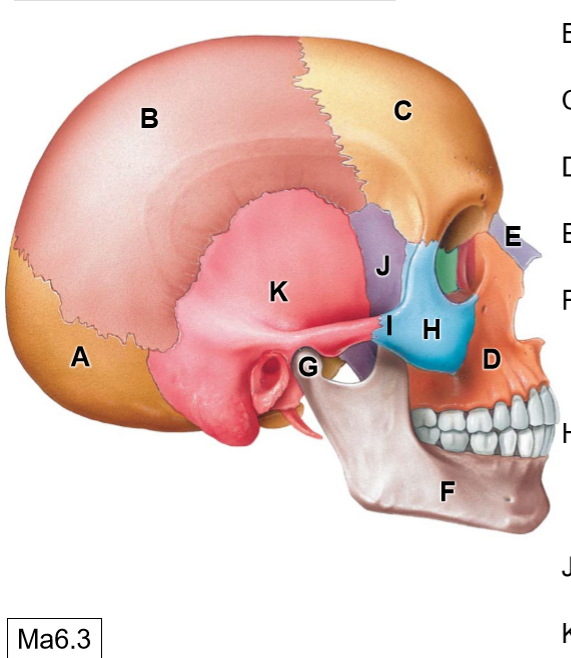
D
Maxilla
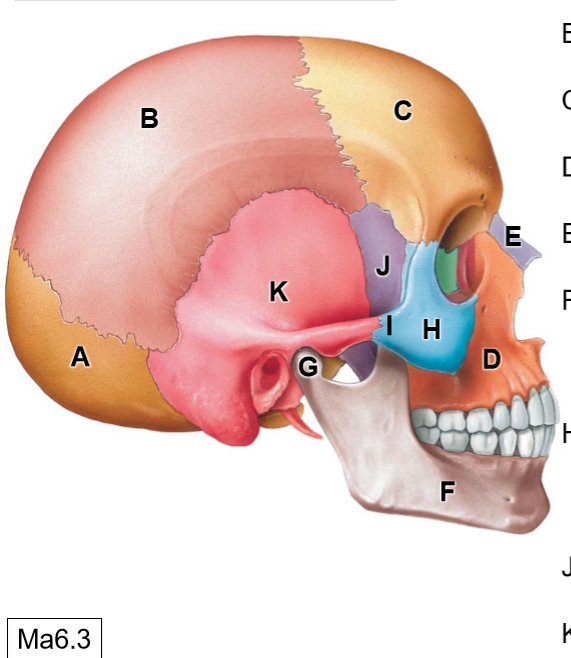
E
Nasal bone
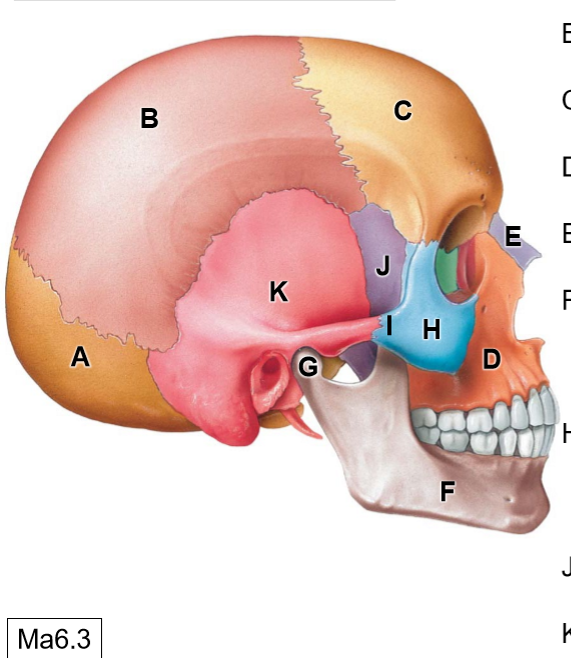
G
Head of mandible
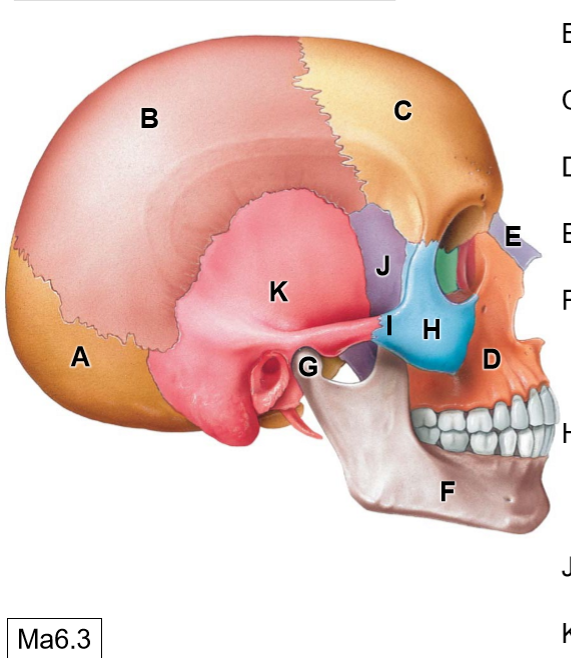
H
Zygomatic bone
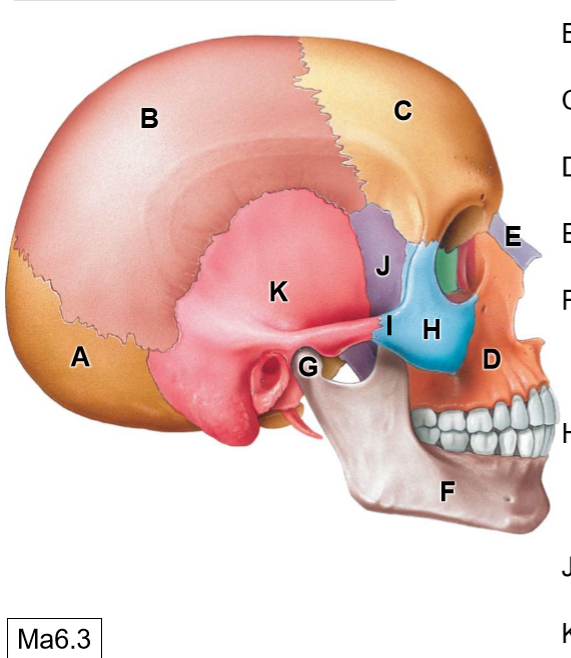
I
Temporal process of ZB
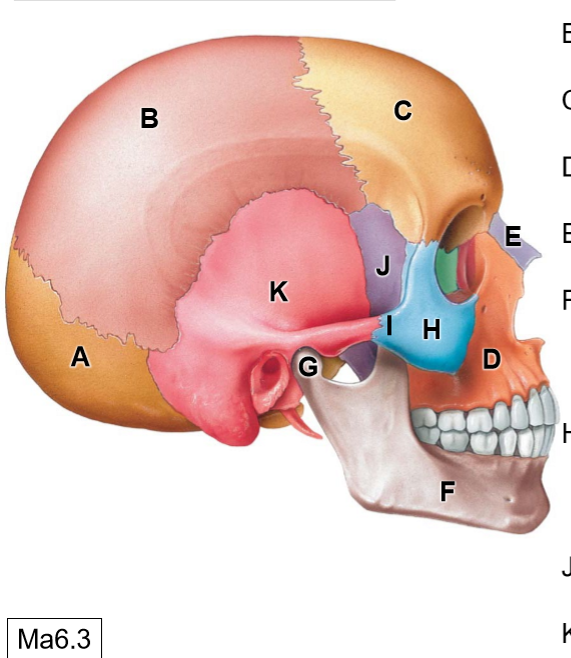
J
Sphenoid bone
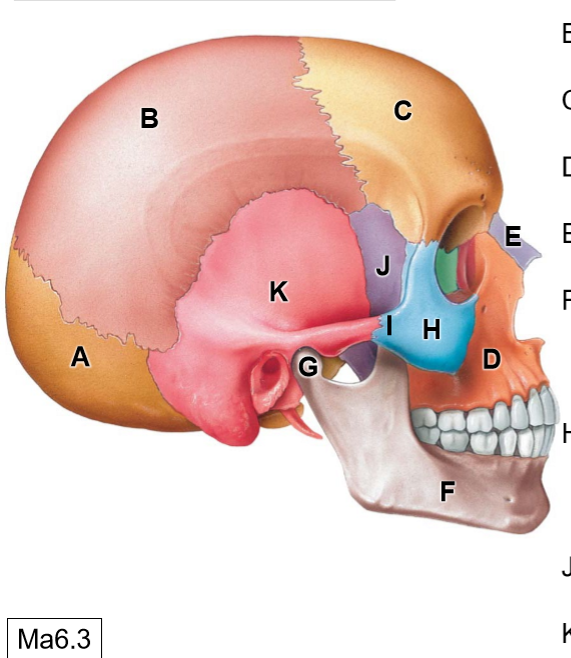
K
Temporal bone
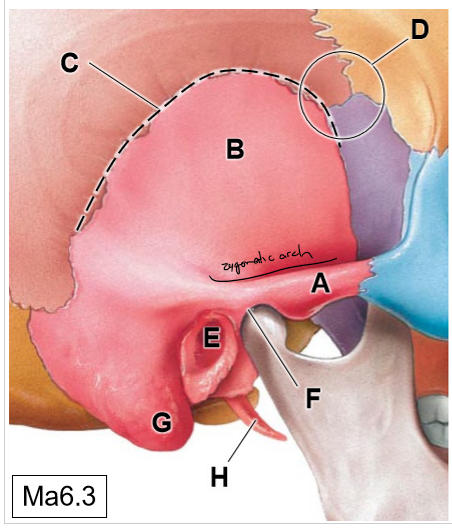
A
Zygomatic process of TB
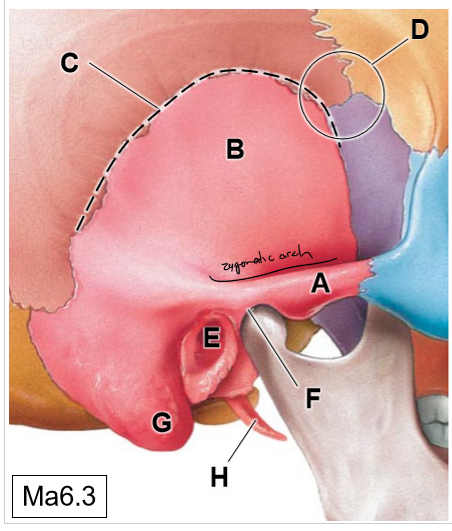
B
Squamous part
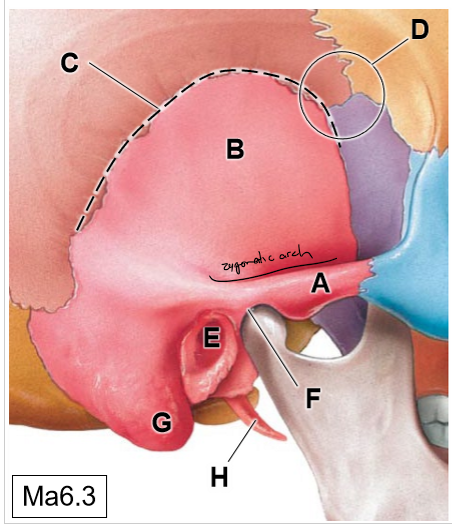
C
Squamous suture
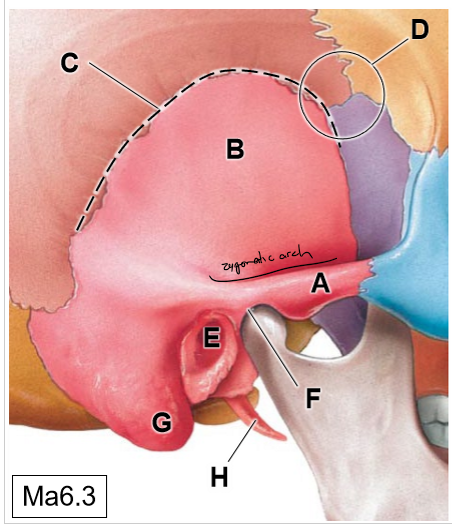
D
Pterion (thinnest region of the skull)
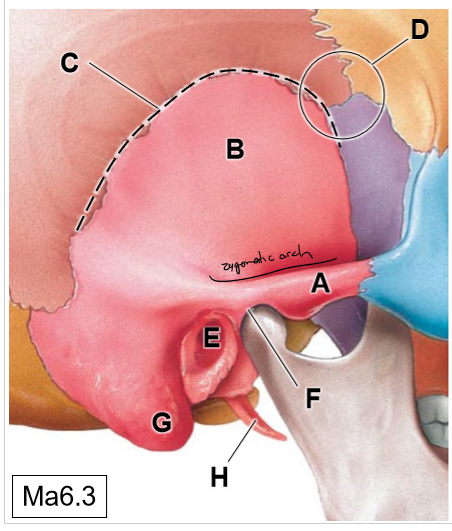
E
External acoustic meatus
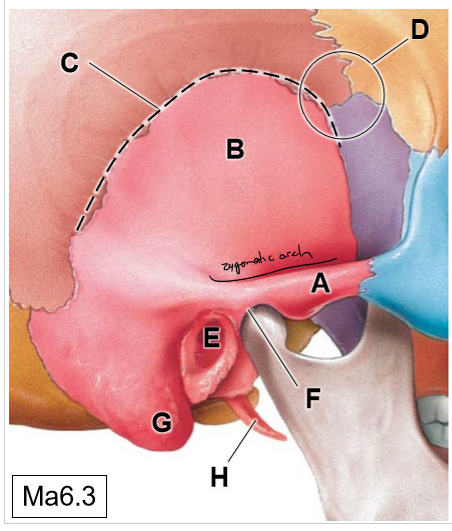
F
Temporomandibular joint
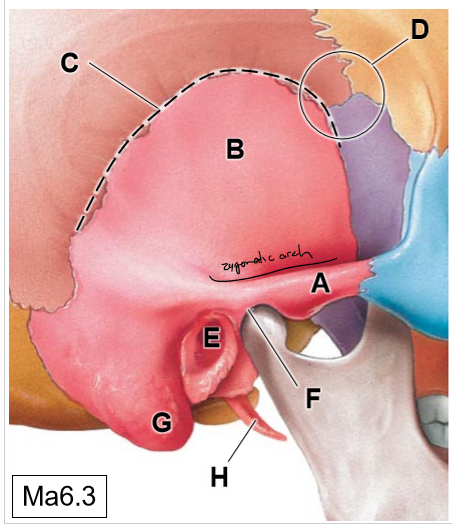
G
Mastoid process (mastoid air cells)
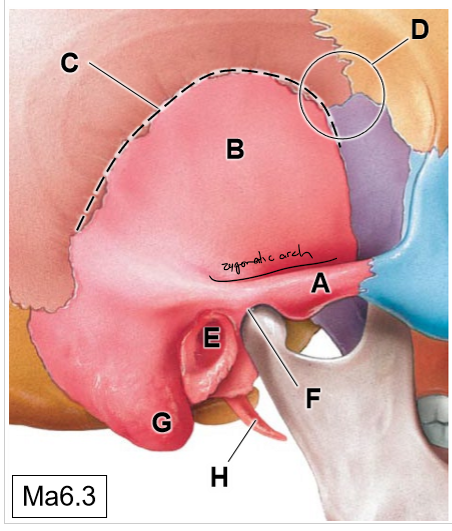
H
Styloid process
B
Occipital condyles (articulates with C1)
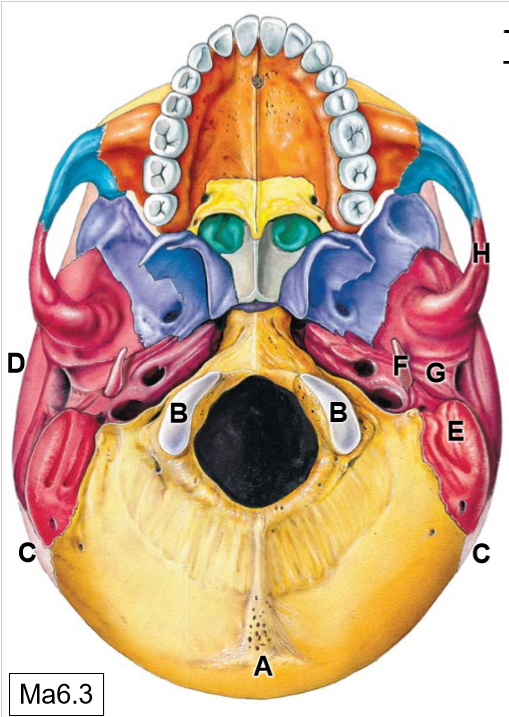
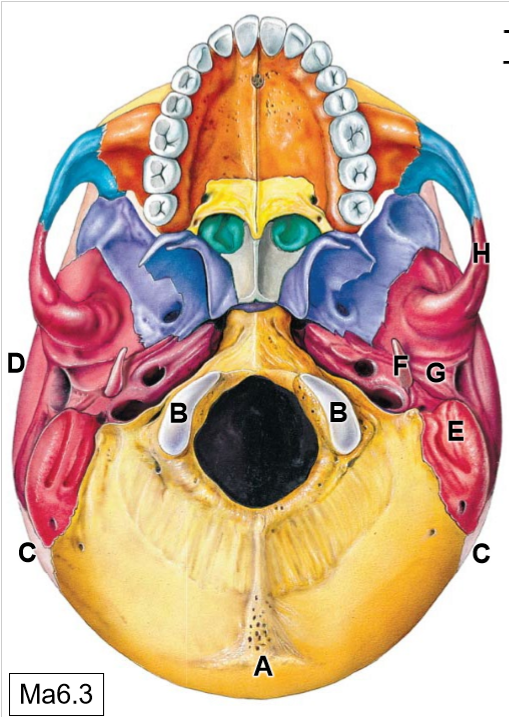
C
Parietal bones
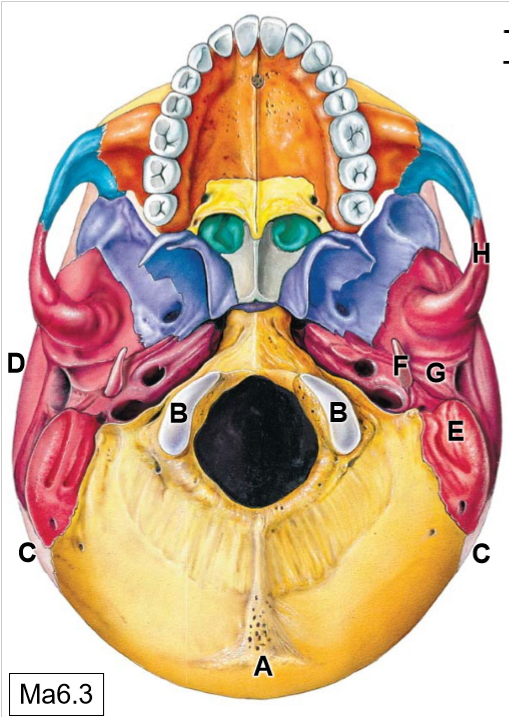
D
Temporal bones
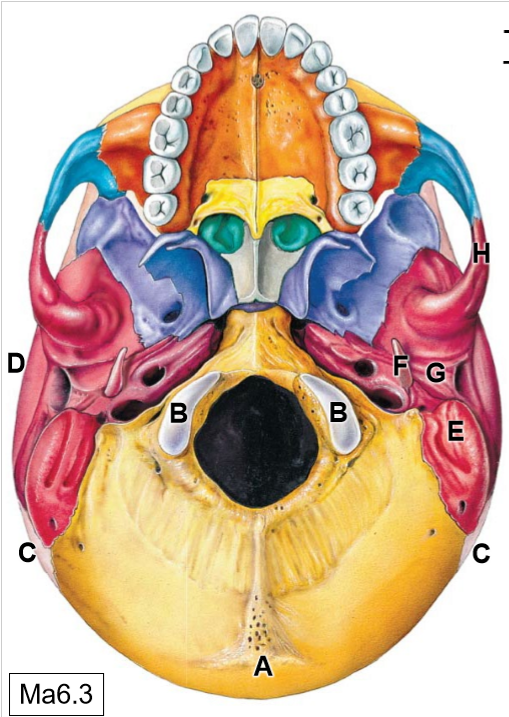
E
Mastoid process
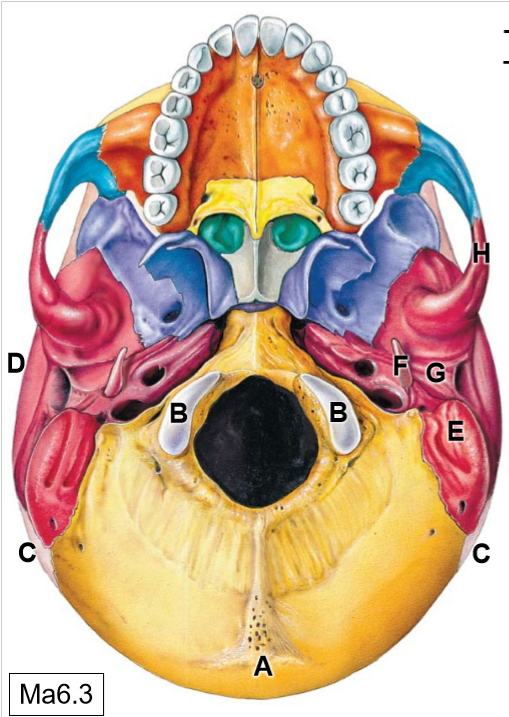
F
Styloid process
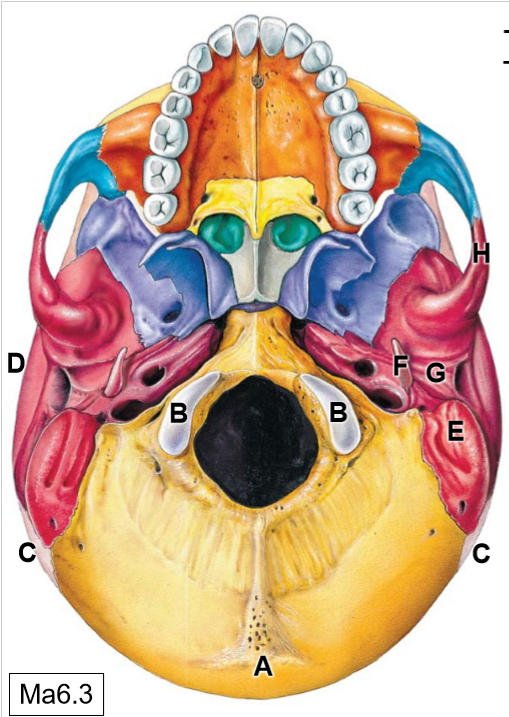
G
Mandibular fossa
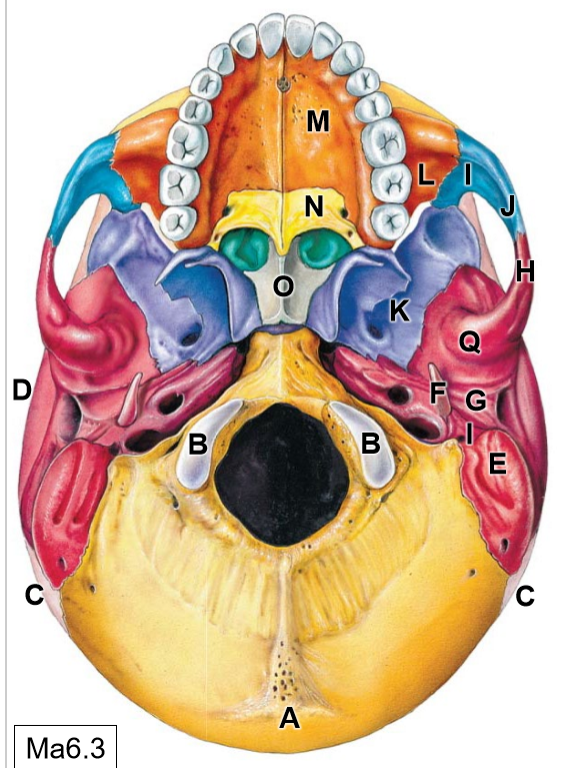
K
Sphenoid bone
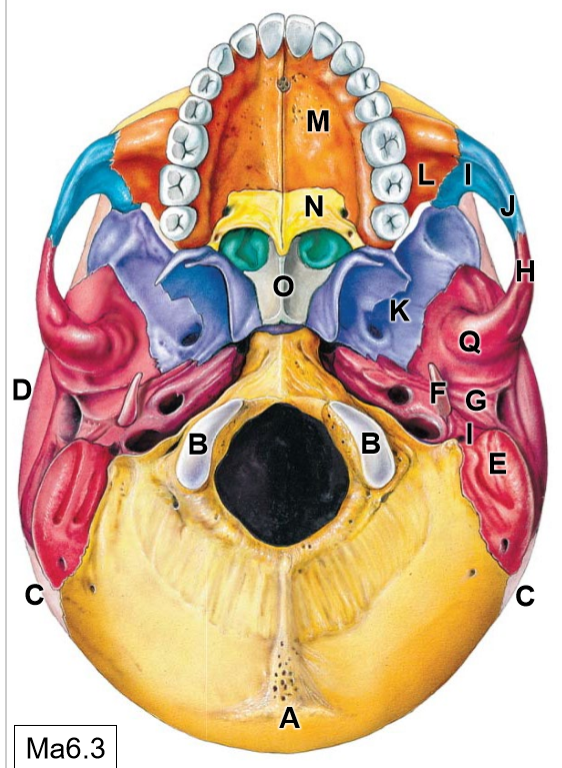
L
Maxilla
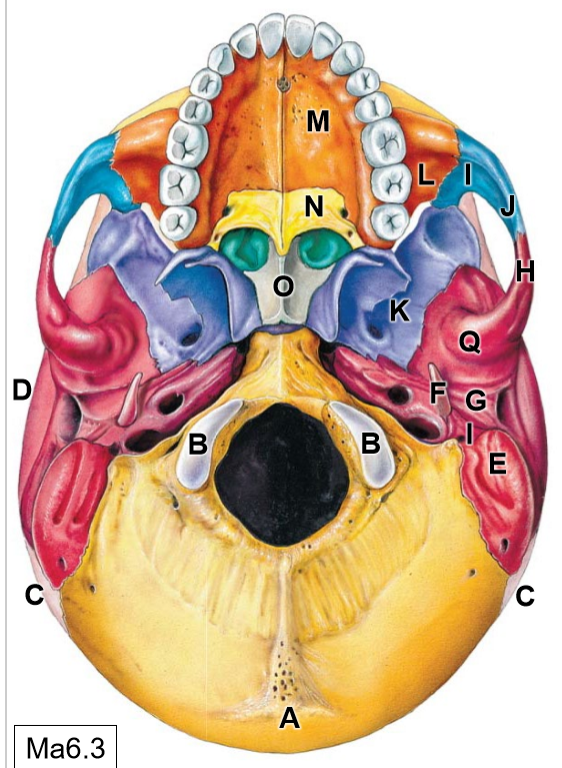
M
Palatine process
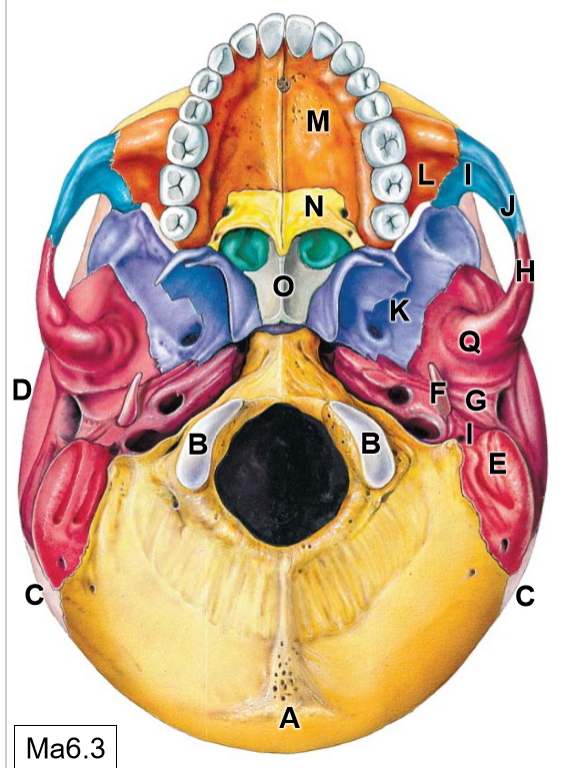
N
Palatine bone
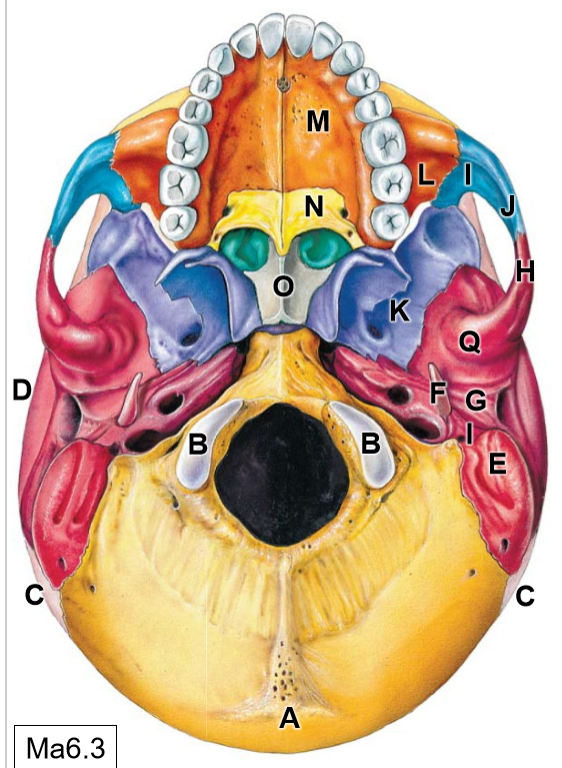
O
Vomer
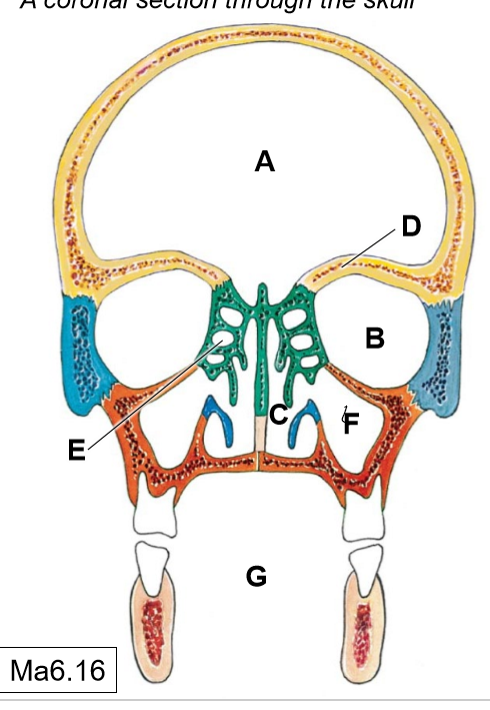
A
Cranial cavity
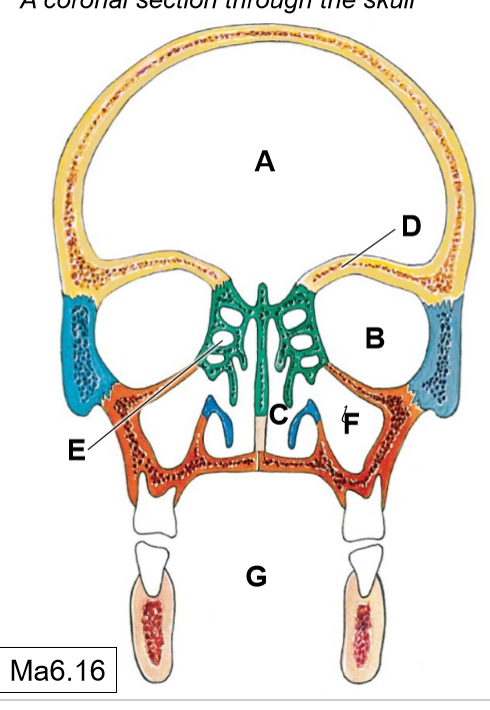
B
Orbits
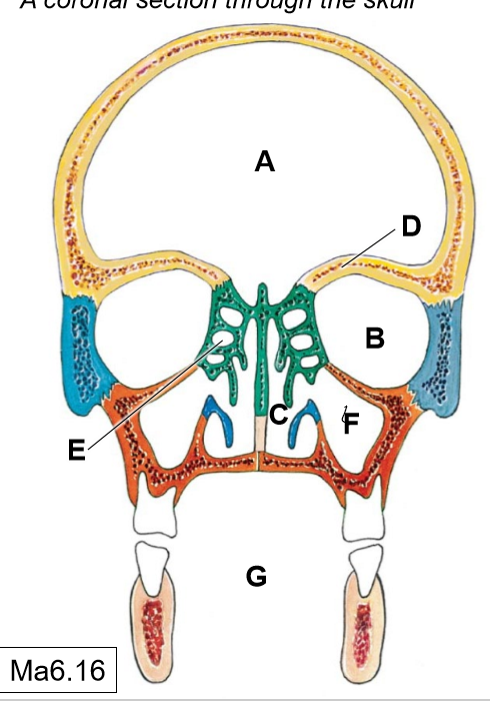
C
Nasal cavities
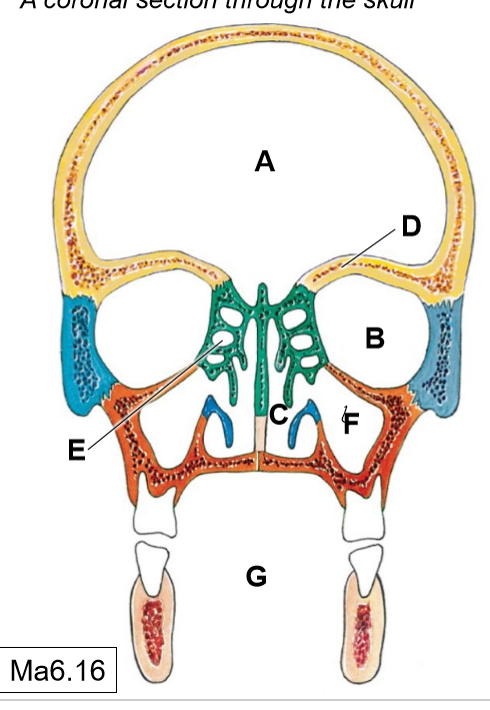
D
Frontal paranasal air sinus (not pictured)
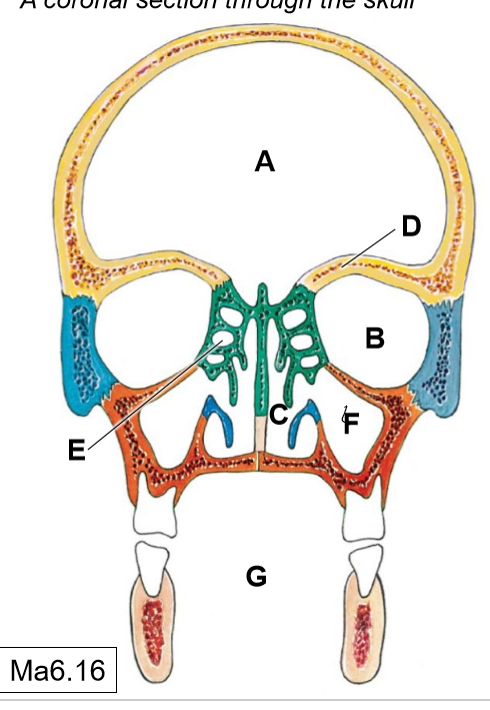
E
Ethmoidal air cells (continuous with each other)
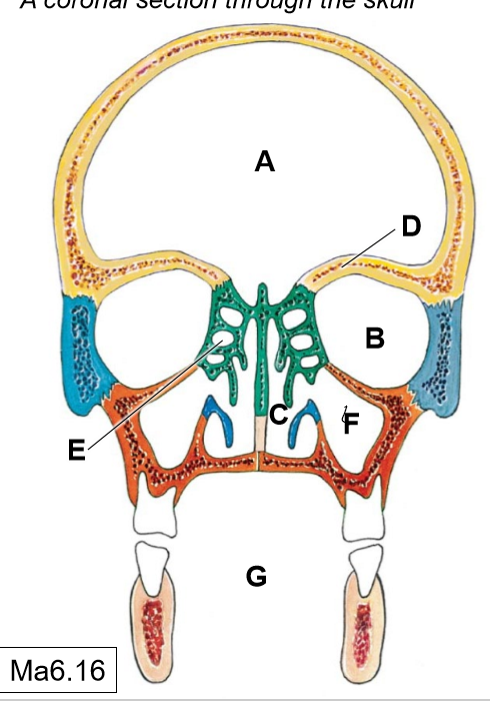
F
Maxillary (sphenoid) paranasal air sinus
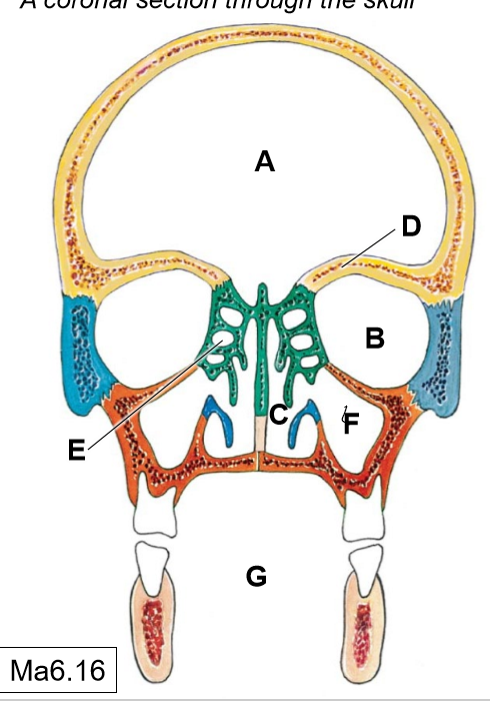
G
Oral cavity
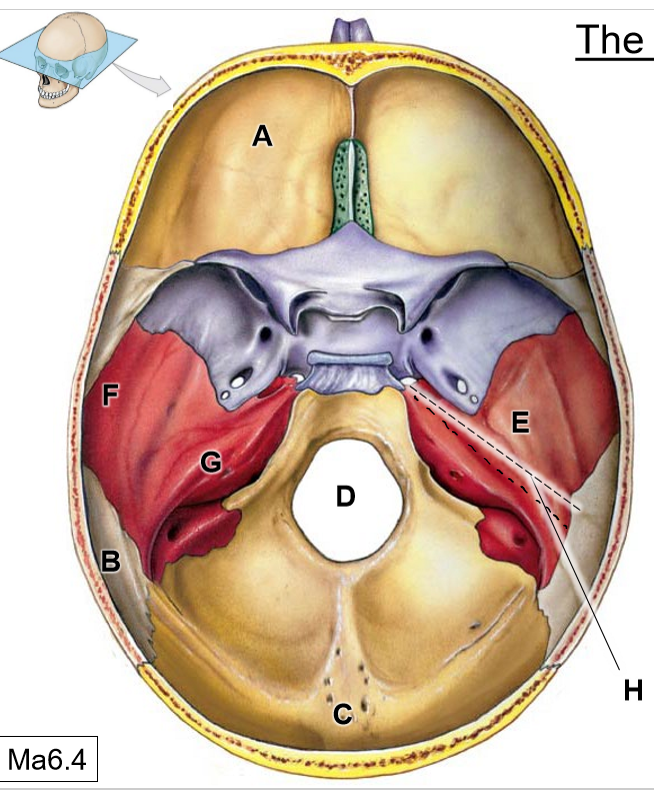
A
Frontal bone
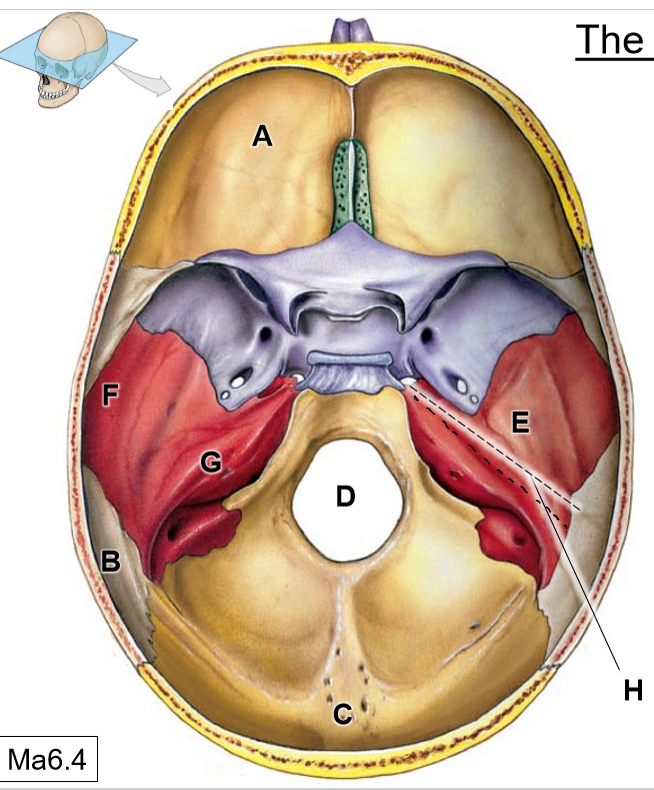
B
Parietal bones
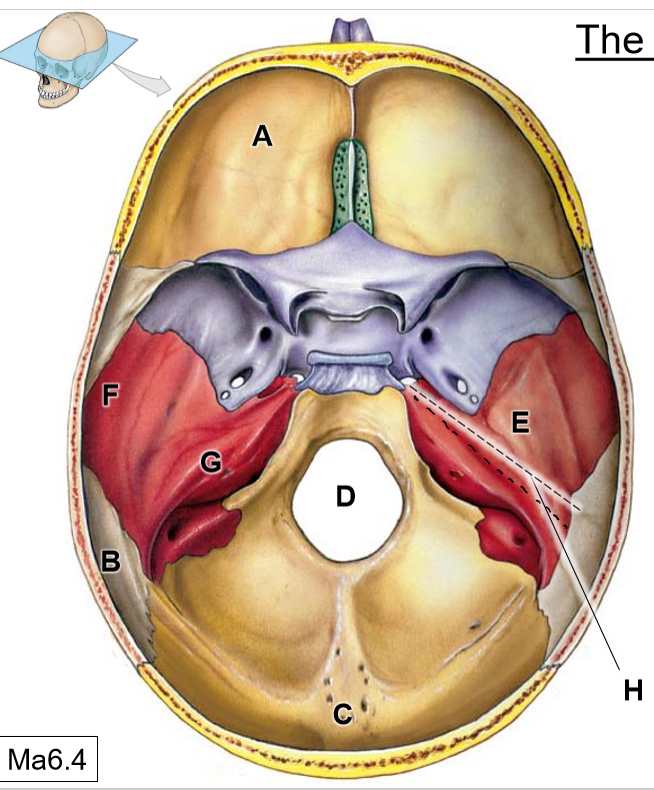
C
Occipital bone
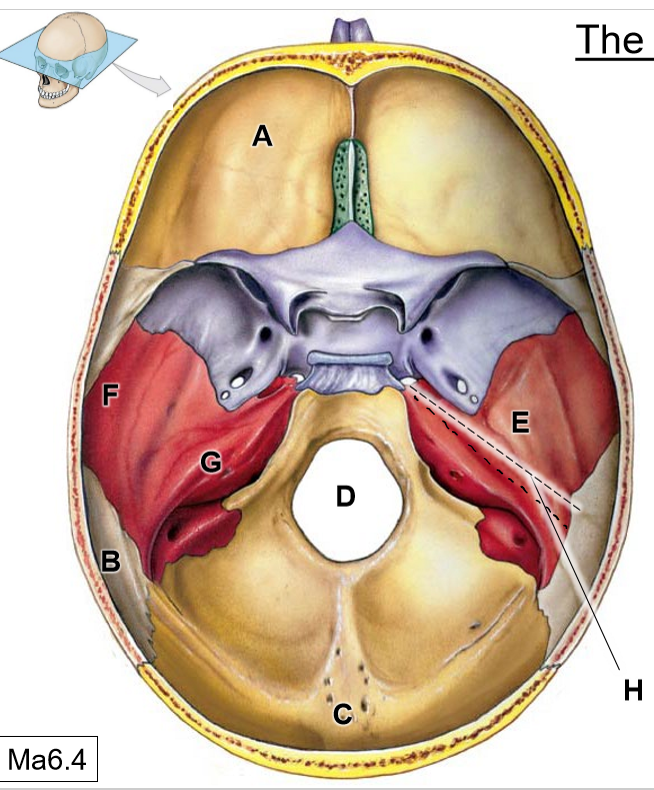
D
Foramen magnum
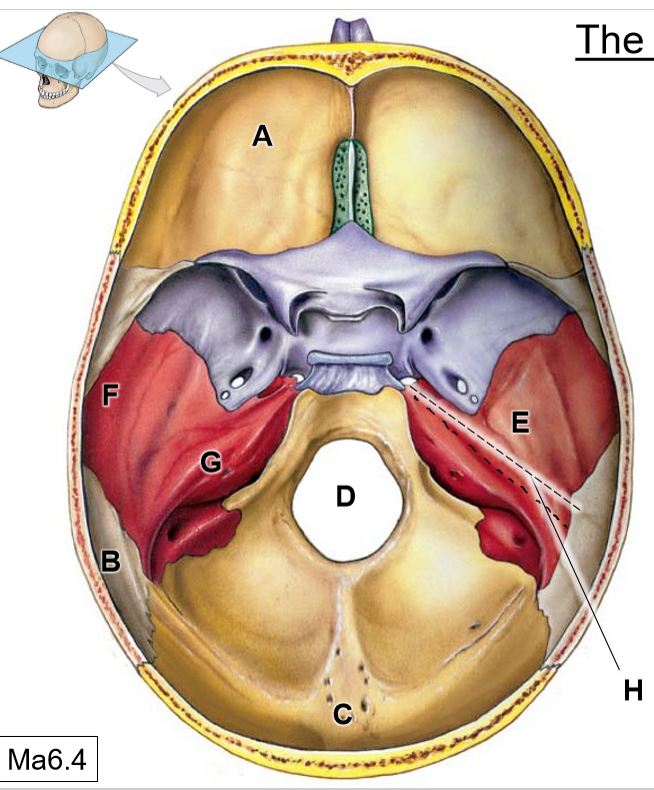
E
Temporal bone
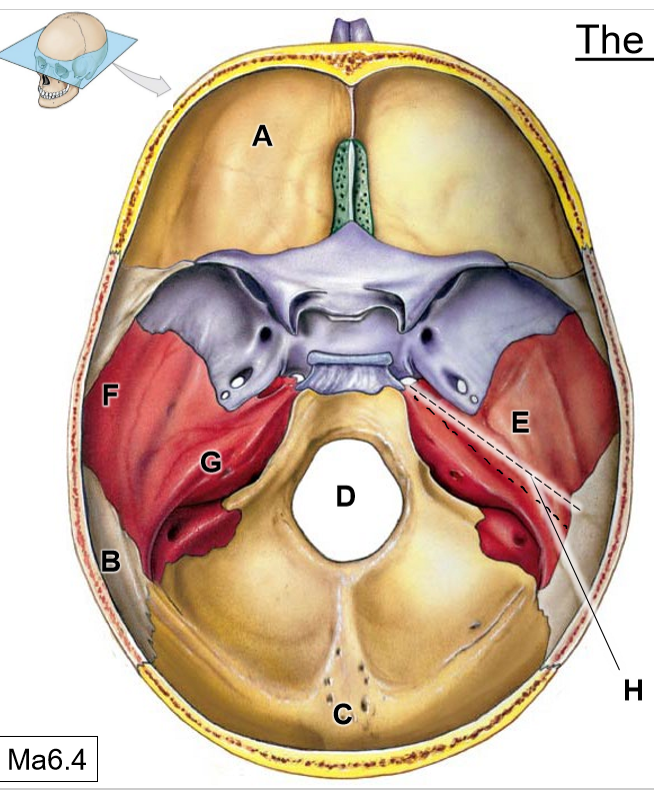
F
Squamous part