Ch II : Entry into M phase and MPF
1/8
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
9 Terms
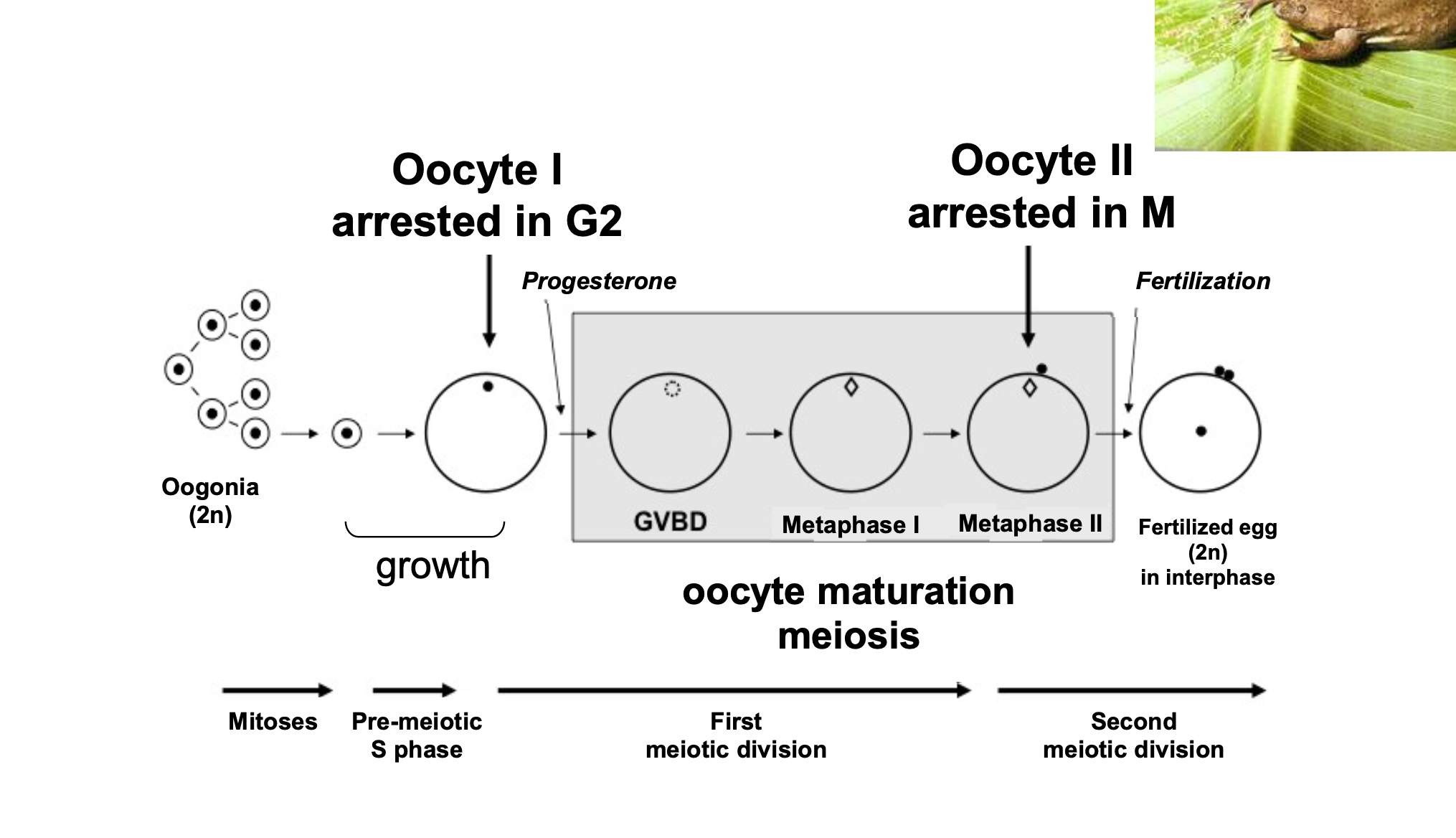
meotic maturation and fertilisation of the xenopus egg
oogonia (2n cells) enter ore-meiotic S phase
oocyte grows to accumulate resources for fertilisation and oocyte I stops in G2/prophase I meiosis
progesterone released by neighbouring cells to oocyte I, resuming meiosis and enters reduction division
GBVD germinal vesicular break down —> nuclear break down of oocyte
oocyte asymmetric divises into 2 daughter cells
oocyte II arrested in metaphase II
fertilisation of oocyte II will allow second meitoic divison
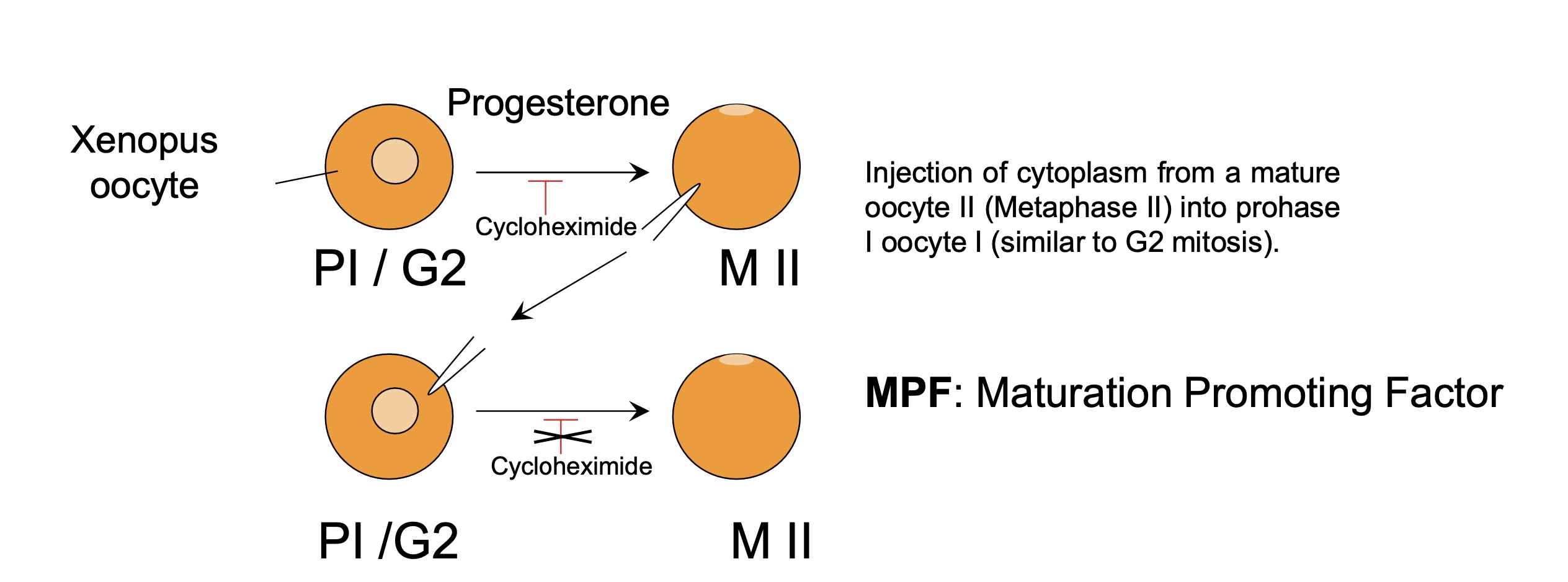
discovery of MPF by observing xenapus oocyte I and II
injection of cytoplasm from oocyte II (metaphase II) into oocyte I (prophase I) and inhibition of cycloheximide removed
oocyte I become oocyte II
MPF maturation promoting factor active in oocyte II and enough to induce maturation of oocyte I
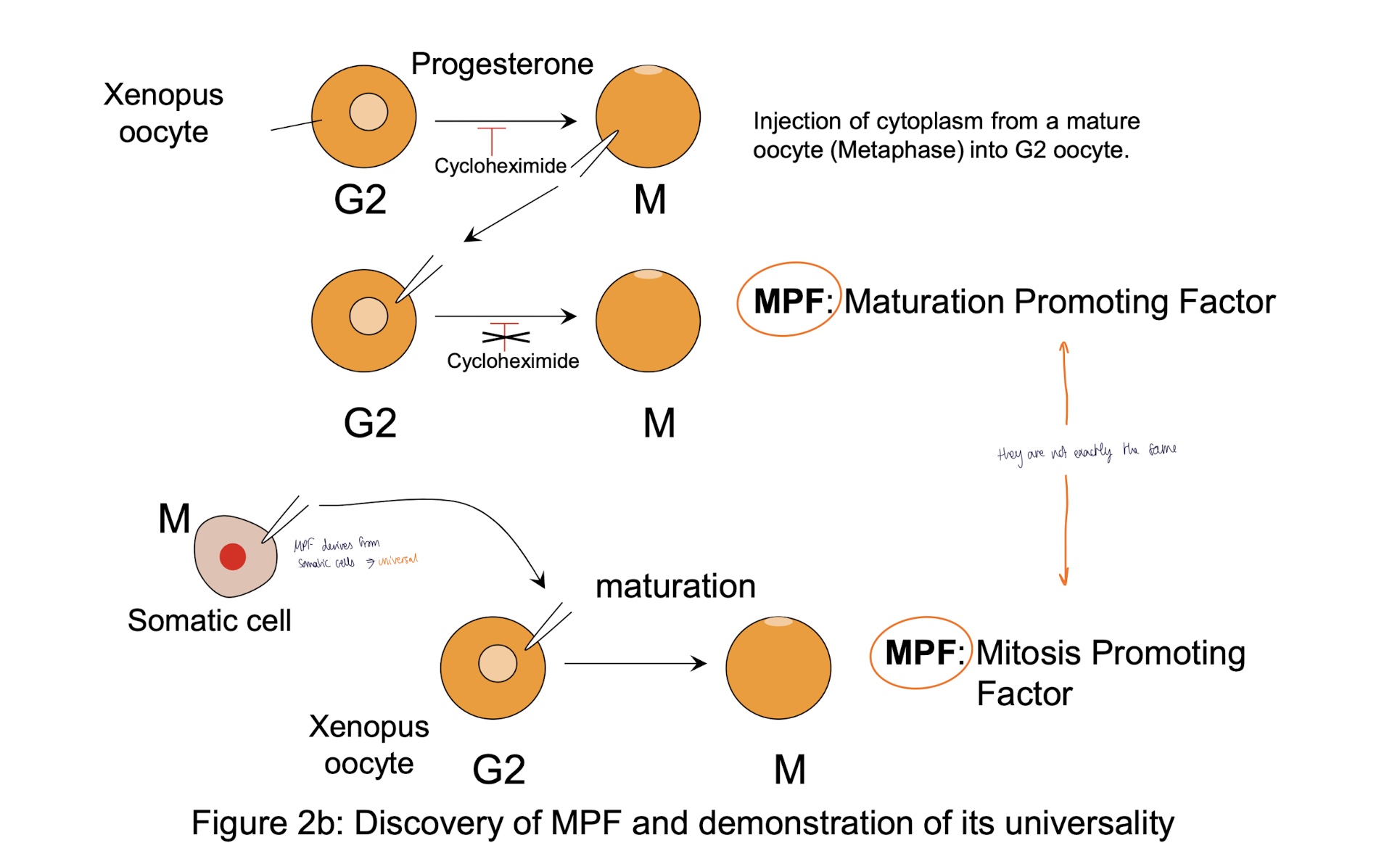
discovery to determine if MPF universel (somatic cells)
injection of cytoplasm from somatic cell in Mitosis to xenopus oocyte
maturation of oocyte I to oocyte II
MPF = mitosis promoting factor —> universal
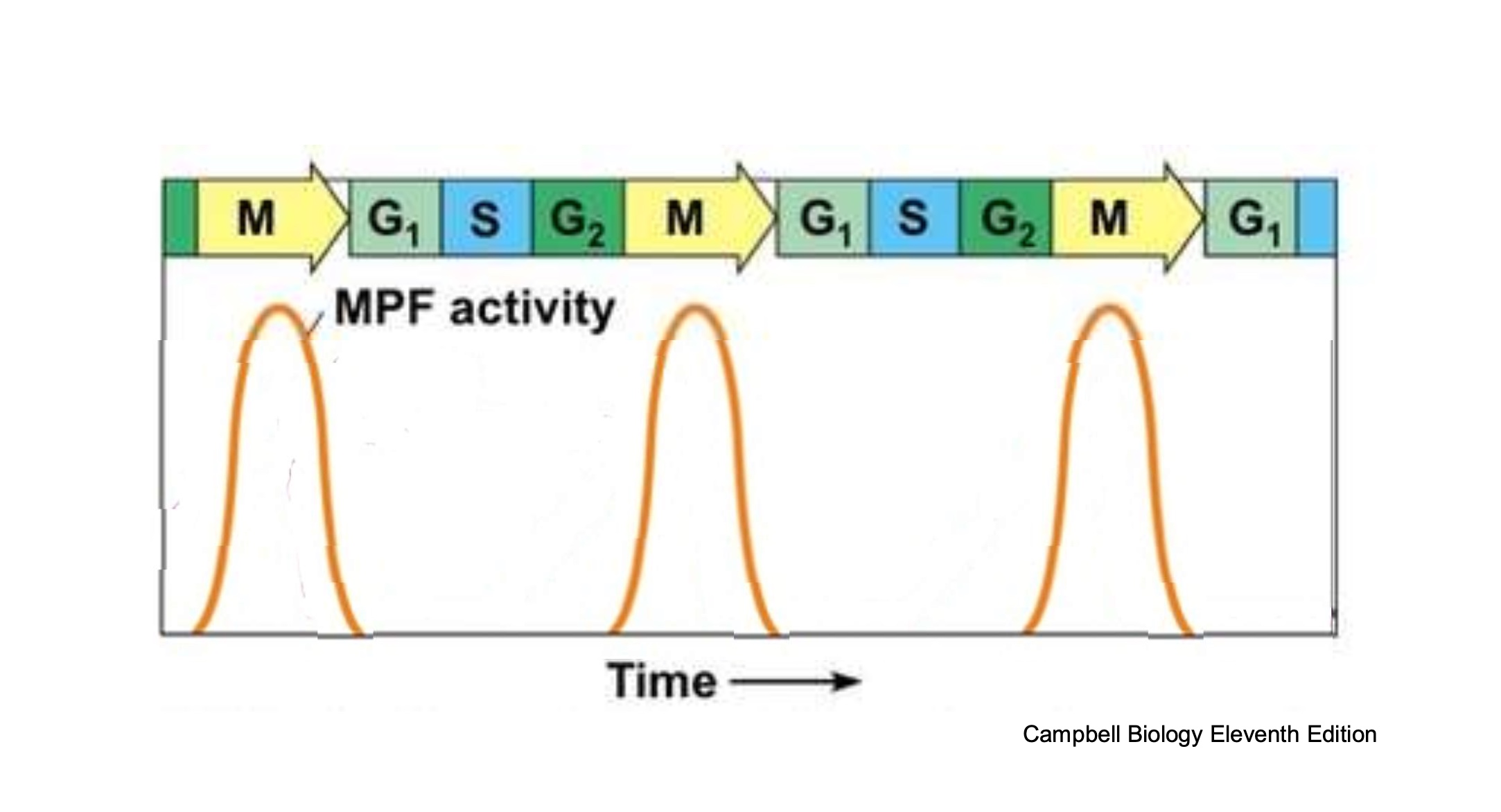
xenopus model also reveals when MPF is active, so when is it active ?
MPF is rapidly activated at the end of G2/beginning of ad decreases rapidly at the end of telophase
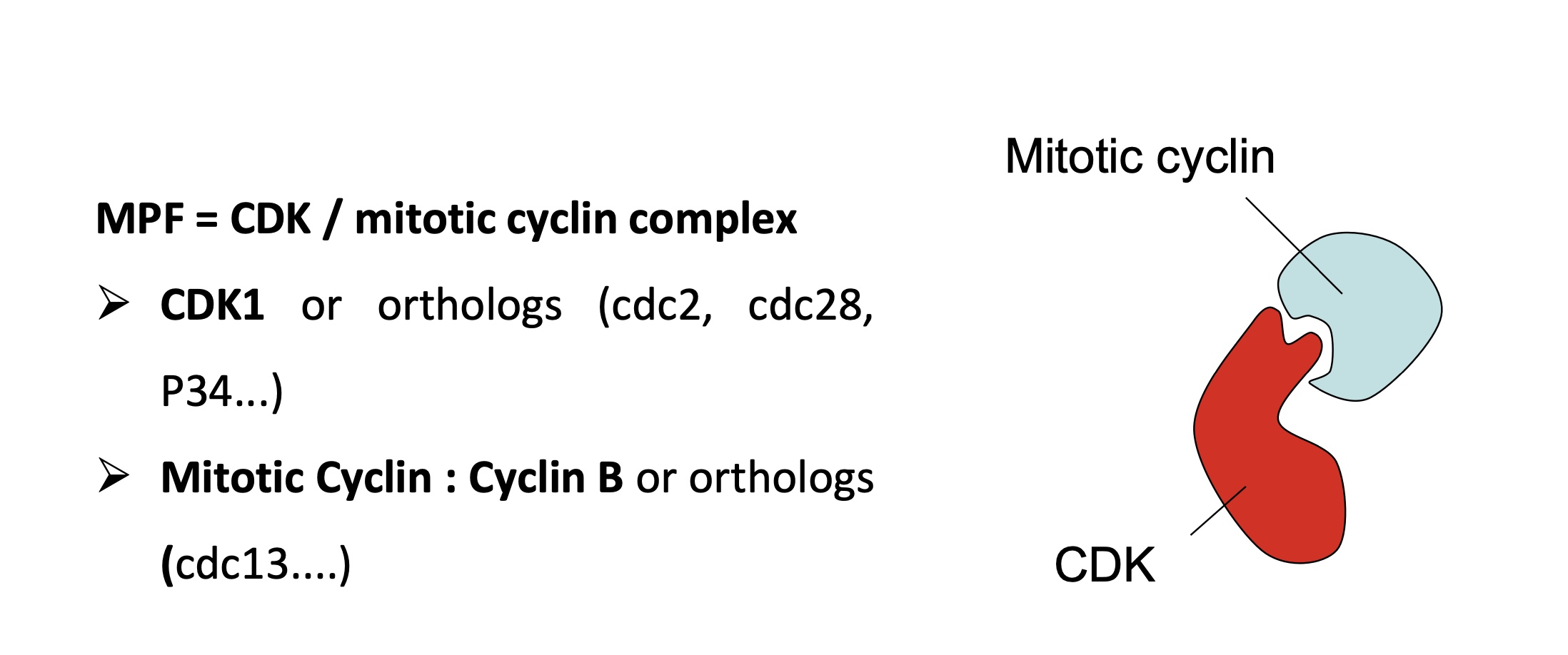
structure of an MPF
MPF = CDK/Mitotic Cyclin complex
CDK1
cyclin B (mitotic cyclin)
however cyclin B is not sufficient for CDK1 activity
phospho-substrate + ATP required
CDK1 has 2 binding sites for these molecules
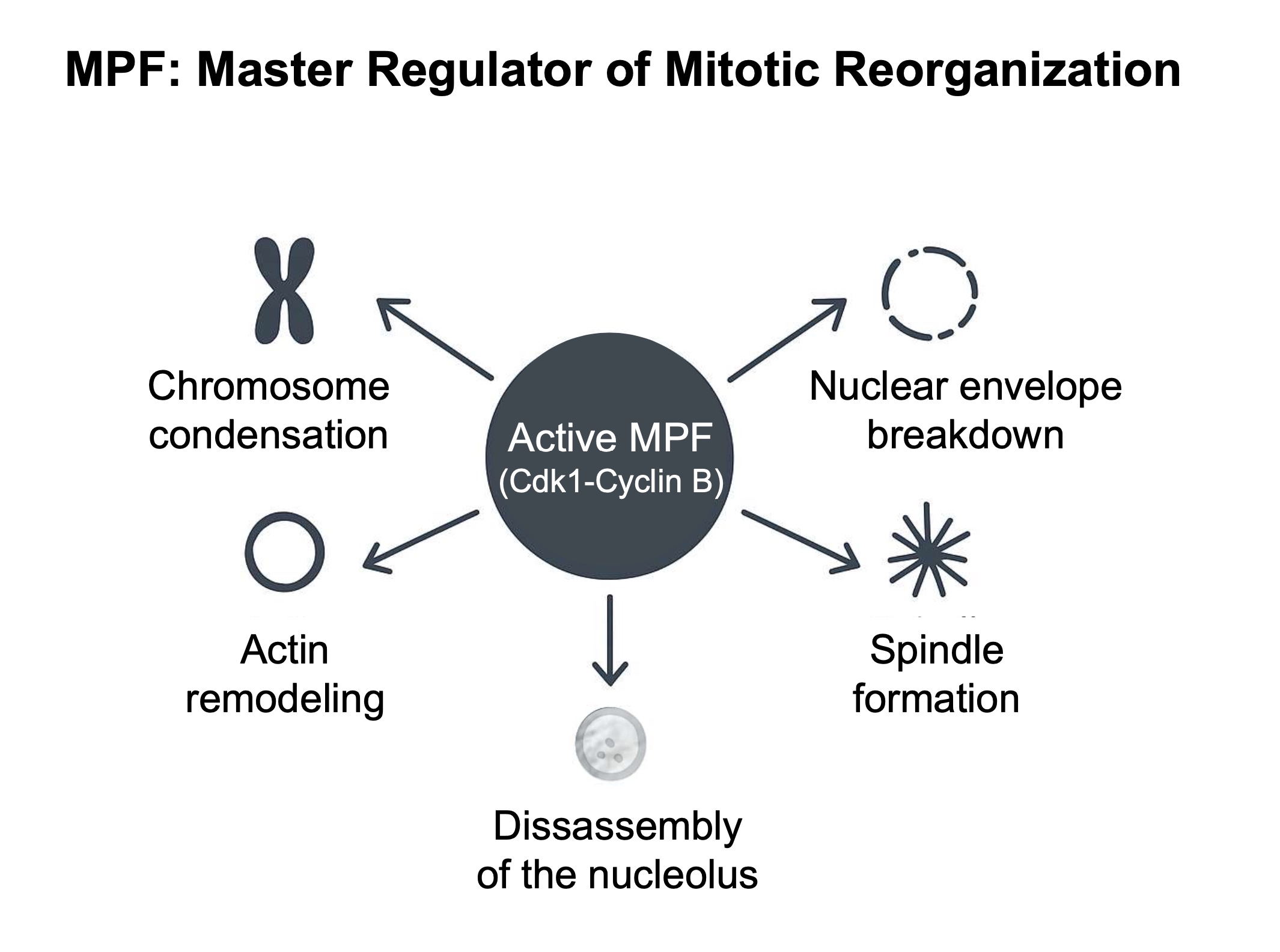
what is MPF responsible for ?
nuclear envelope breakdown
spindle formation
disassembly of the nucleus
chromosomes condensation
actin remodelling
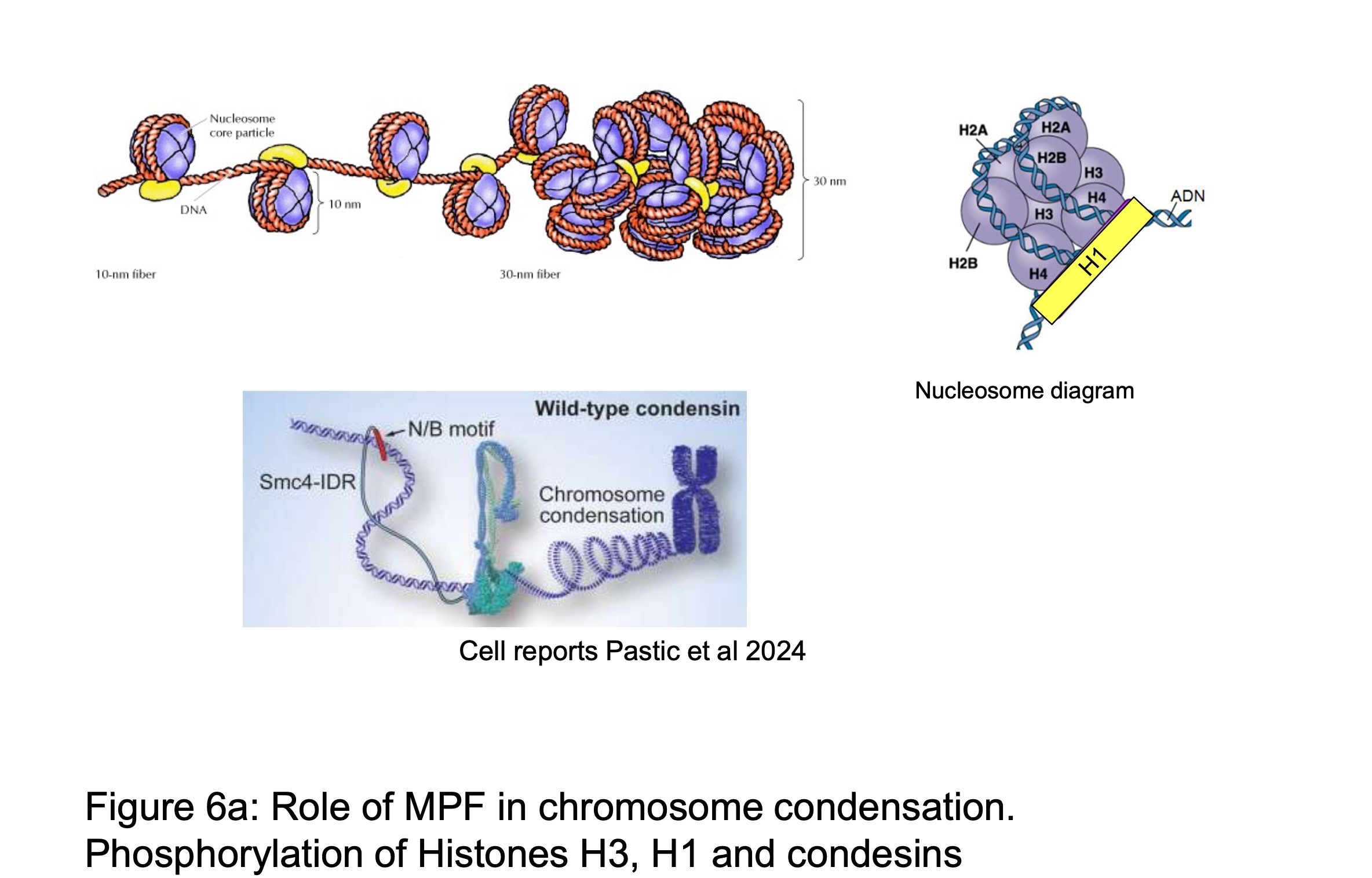
how does MPF play a role in chromosome condensation by phosphorylation of histone 3,1 and condensins
MPF controls phosphorylation :
A. condensins - bind to DNA and promote DNA coiling
B. Histones -
H1 → stabilises nucleosome structure, when phosphorylated its electrical charge changes and theres a reduction in DNA affinity (required for condensation
H3 → when phosphorylated it becomes an epigenetic mark that promotes recruitment of condensing factors
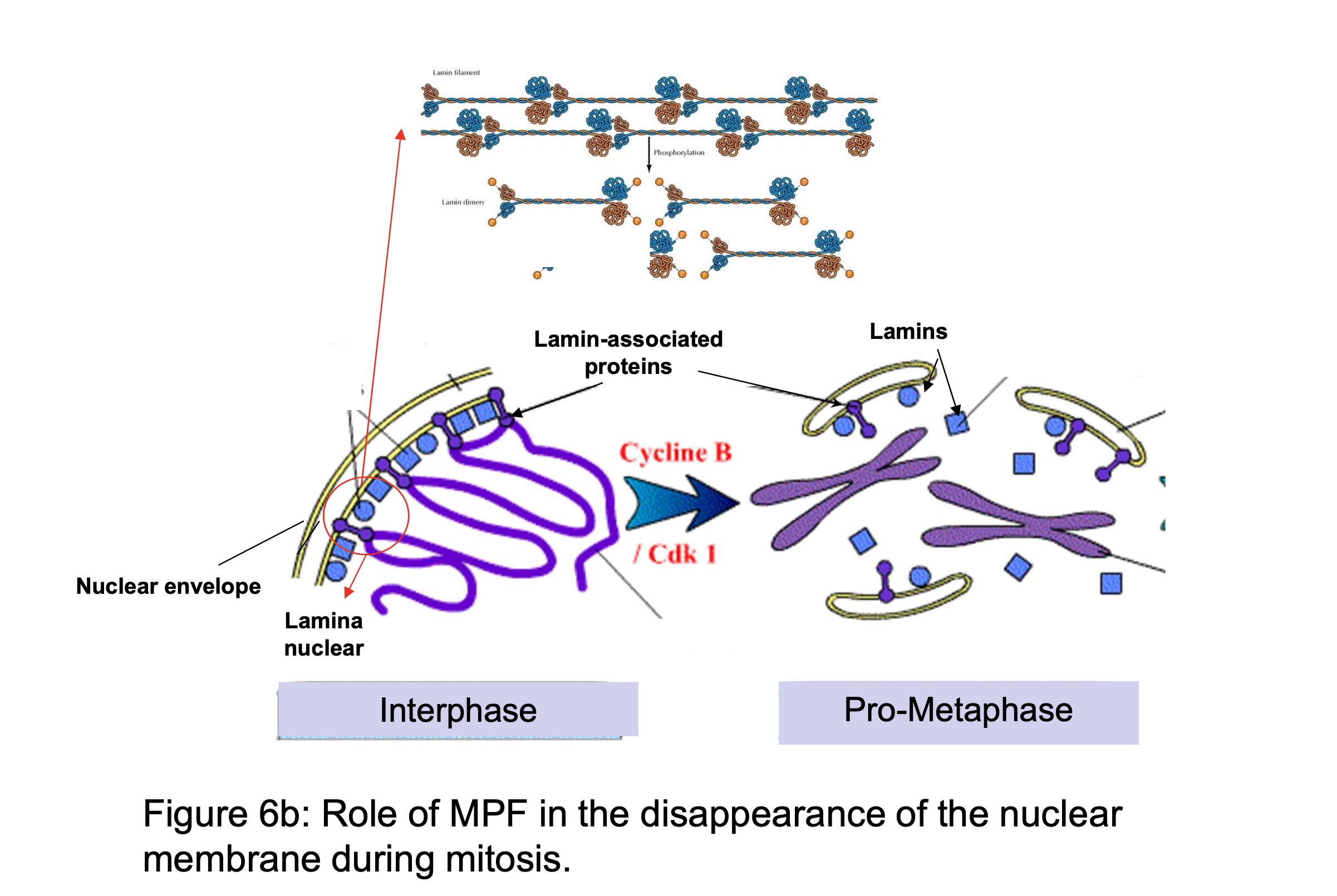
what is role of MPF is the disappearance of the nuclear membrane during mitosis
MPF phosphorylates Lamines (= supporting structure) and Lamine associated proteins (= junction between chromatin and inner nuclear membrane):
→ Lamine no longer interact w/ each other so dissociation of nuclear lamina and nuclear membrane fragments
→ physical association of chromatin w/ nuclear membrane by lamine is released and the chromatin is free to condensed
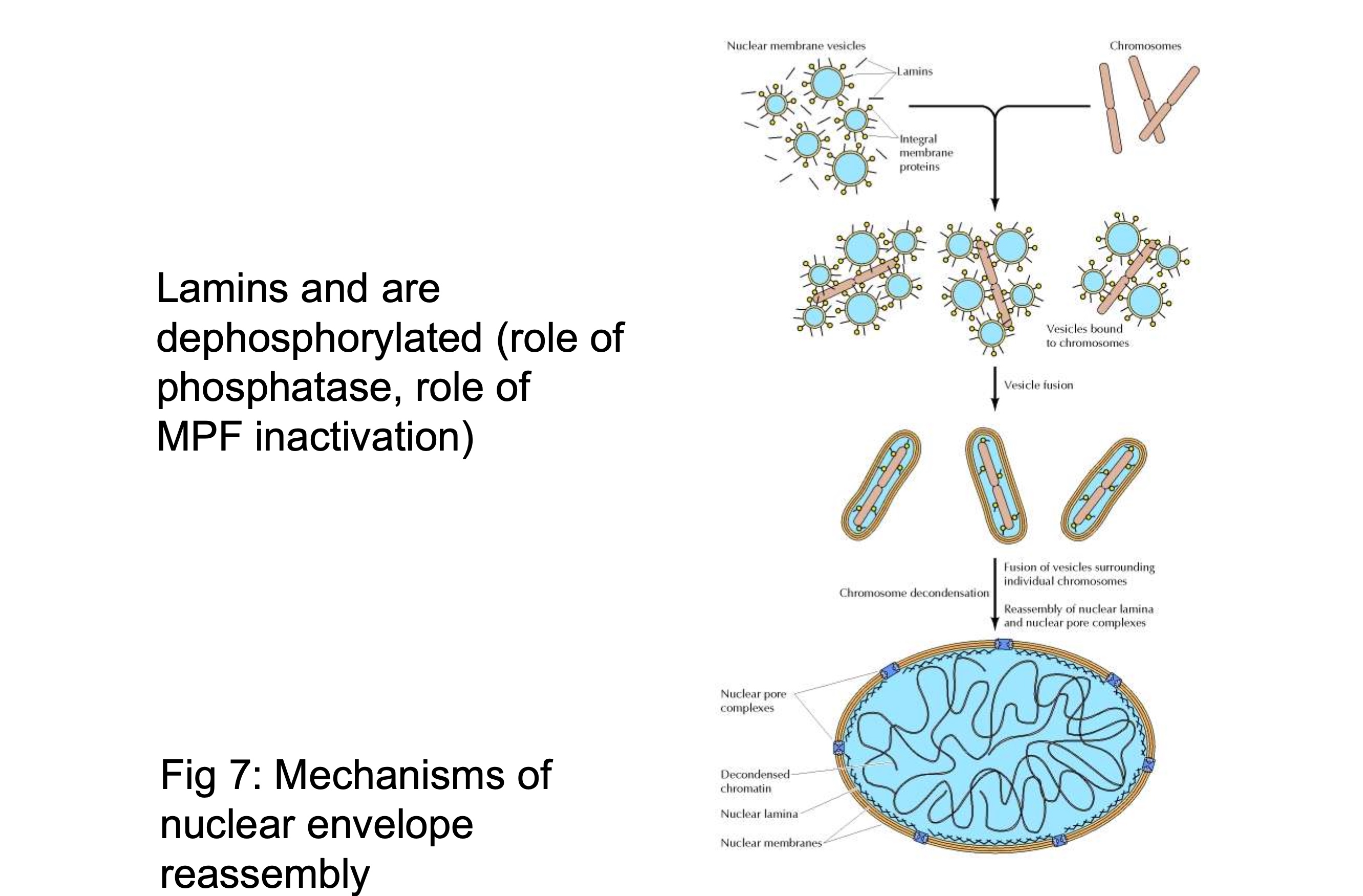
mechanism of nuclear membrane assembly
MPF inactive
the nuclear membrane vesicles bind to chromosomes
vesicles fuse around the chromosomes to form envelope
fusion of vesicles surrounding each chromosome
chromsome de-condensation