Respiratory histology
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
34 Terms
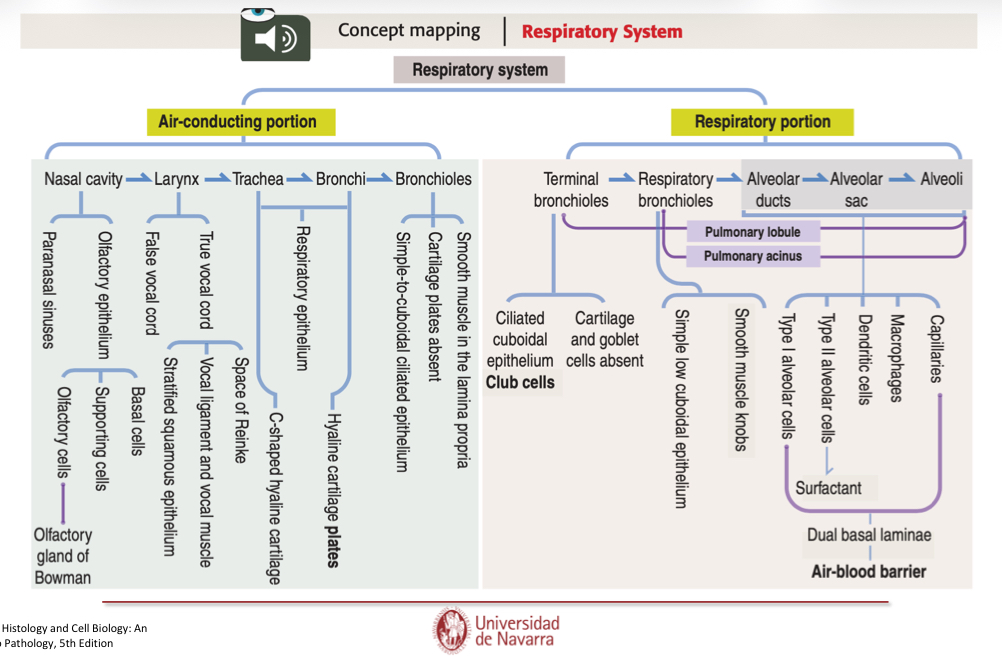
What is the Respiratory system structure?
Upper respiratory system (Conducting portion):
conducts air to lungs
Covered by respiratory epithelium
Includes: Nose, phrynx, trachea, bronchi, bronchioles and terminal bronchioles
Lower Respiratory system (Respiratory portion)
main site of gas exchange
Covered by alveolar epithelium
Includes: Respiratory bronchioles, alveolar ducts, alveolar sacs, and alveoli.

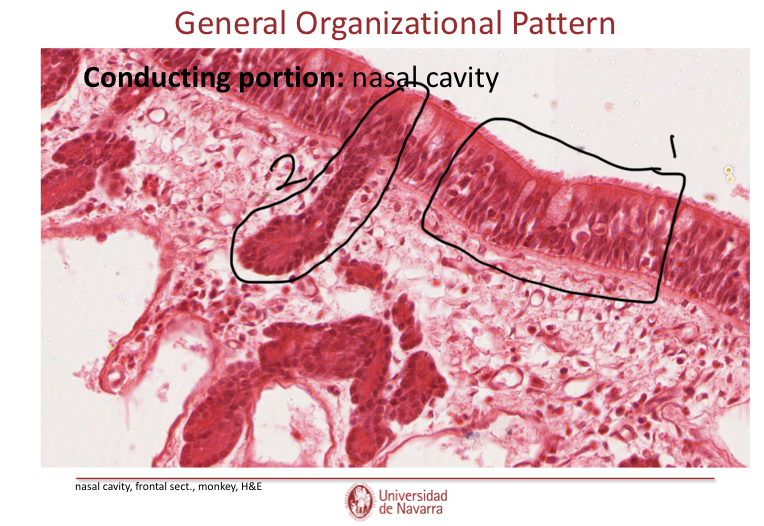
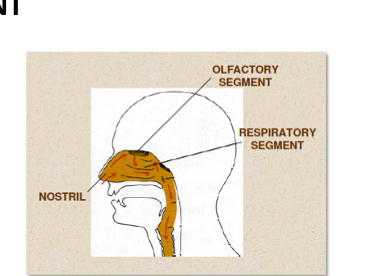
Label the image and explain whee it is. Also, what type of epithelial cells does it have?
It is the nose. Epithelium changes from keratinized stratfied squamous epithelium to pseudostratified columnar ciliated epithelium.
Sinus: Warm up the air upon entry
Nasal cavities
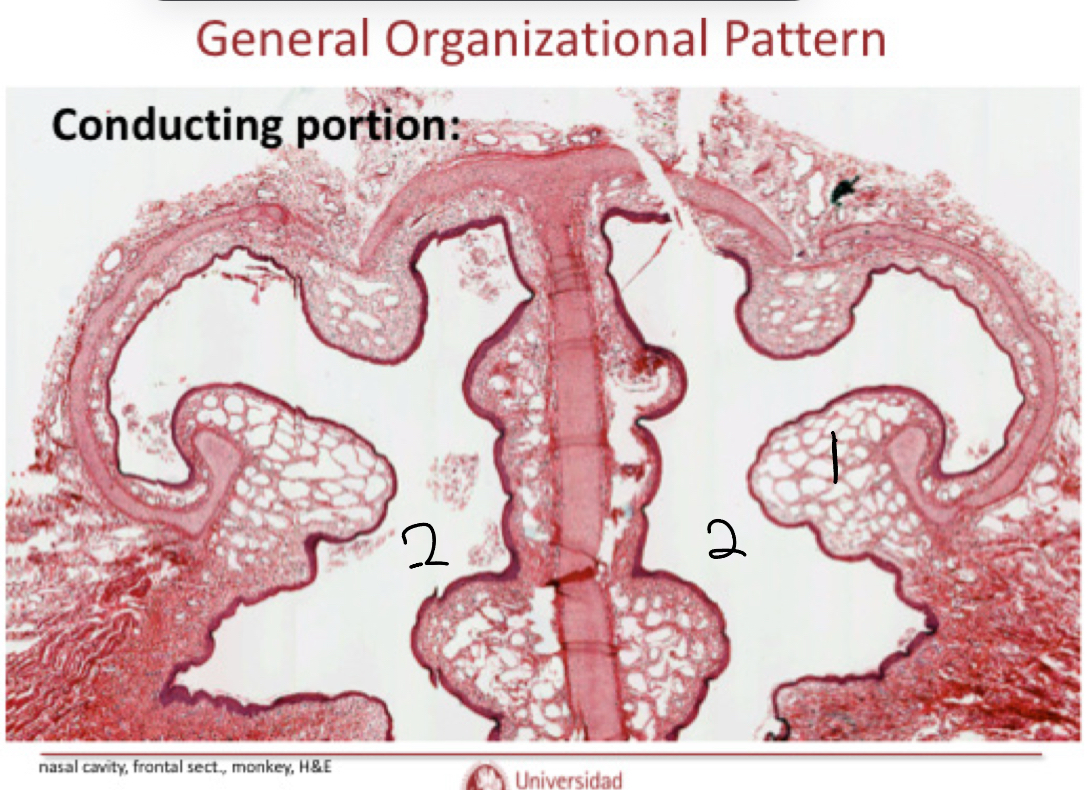
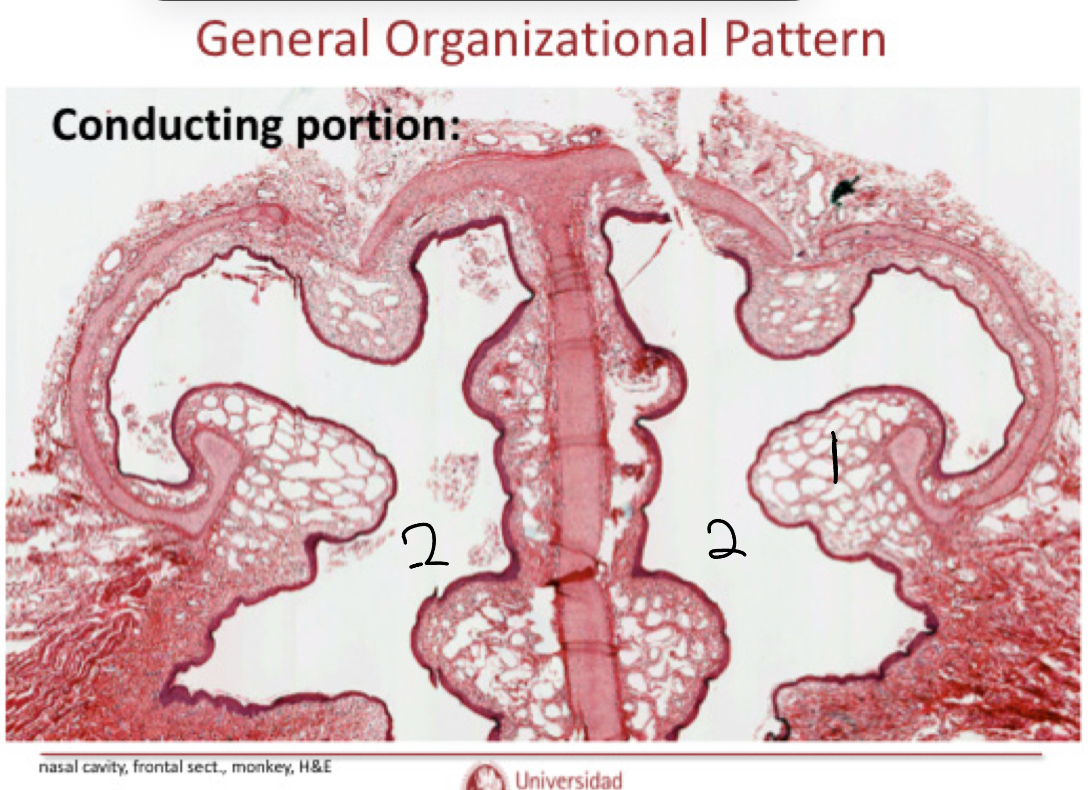
Label this image in the nasal cavity and explain what the structures do.
Columnar pseudostratified with goblet cells.
Serous gland that allows for olfactory processes:
The process ocurs at the top of the nose
The gland secretes water
The water traps molecules
Molecules go to olfactory receptors.

Explain the general organization of the conducting portions.
Mucosa: repiratory epithelium (luinal epithelium sheet)+lamina propia (loose fibroelastic CN)
Submucosa: not alaways present, serous or mixed glands may be present
Muscularis externa: may be smooth, cartilage, or bone
Adventitia or serosa, absent in nasal cavity.
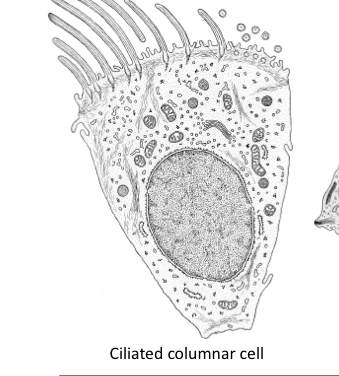
What do ciliated columnar cell do?
They move mucus up to the throat to be swallowed.. smoking kills cila and allows for entry of bacteria- infection.
What do goblet cells do?
Secrete mucus
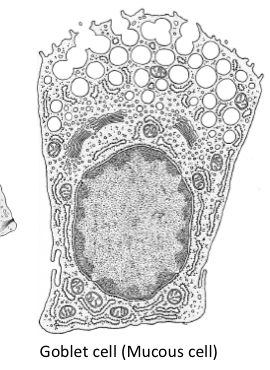
What do basal cells do?
Replace damaged cells
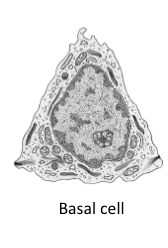
What are brush cells?
Sensory receptor cells
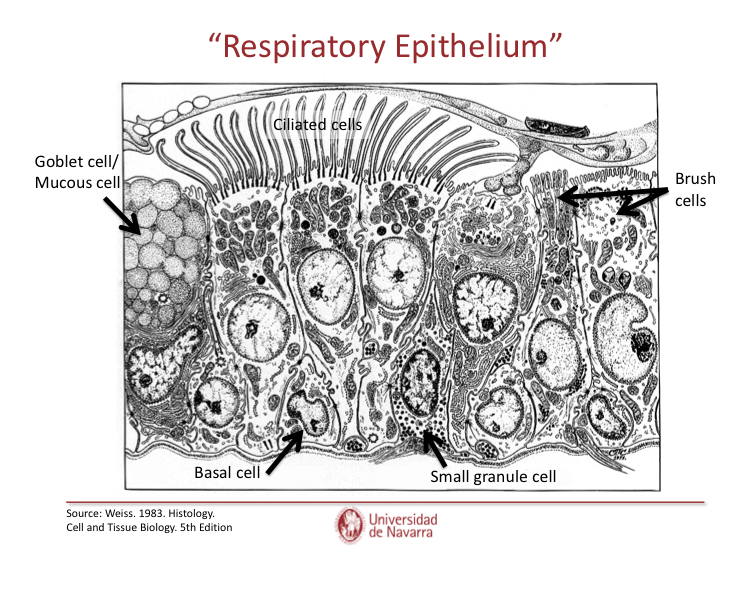
What are dense core granule cells?
Small granule cells that are endocrine cells
What are Clara cells?
In tracheea and bronchi, they are protein secreting cells and secret surfractant, they’re found deep in the lungs. They’re secretory vesicles show up as a lighter color in microscopy
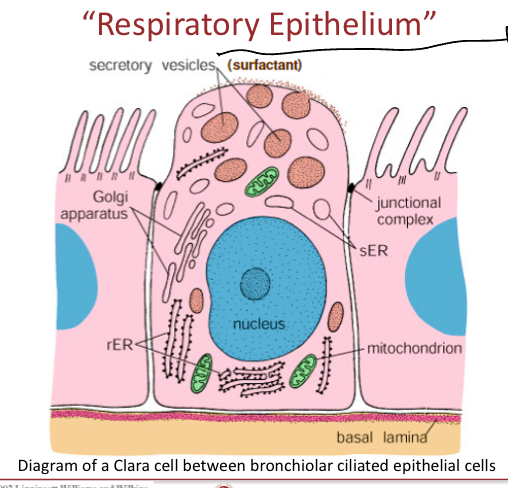
What is surfactant?
fatty substance
Compounds that lower surface tnesion of a liquid to allow interfacial tension between two liquids or that between a liquid and a solid.
May act as detergents, wetting agents, emulsifiers, foamin agents, and dispersants
Helps maintain inflation of the alveoli between inspirations.
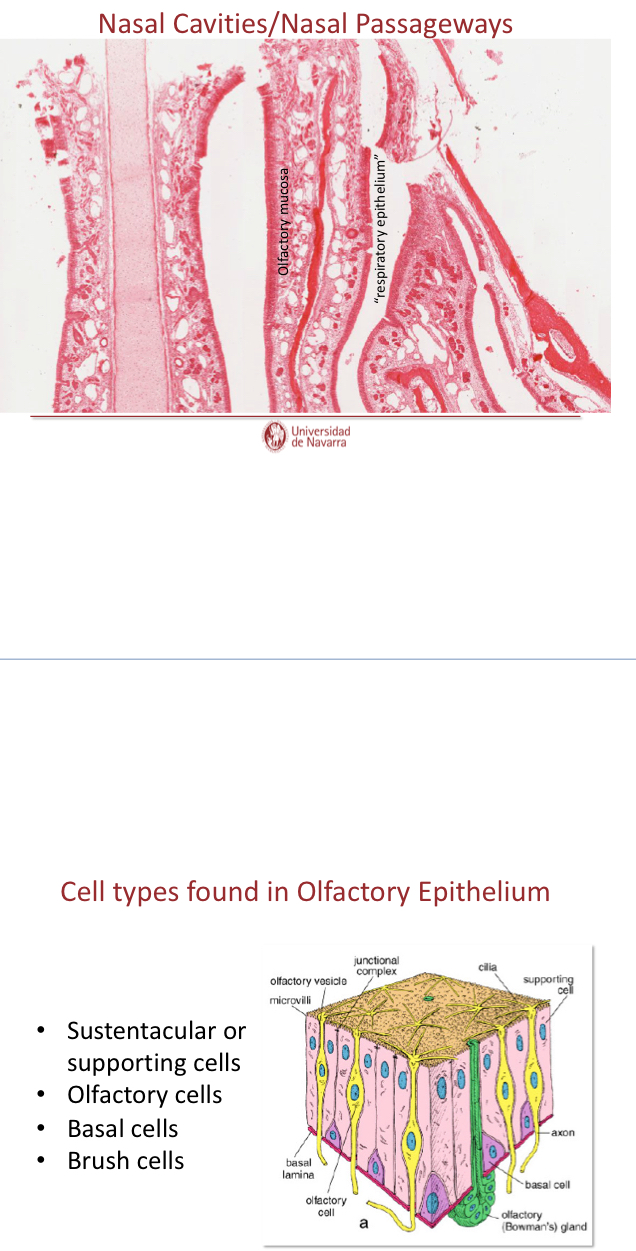
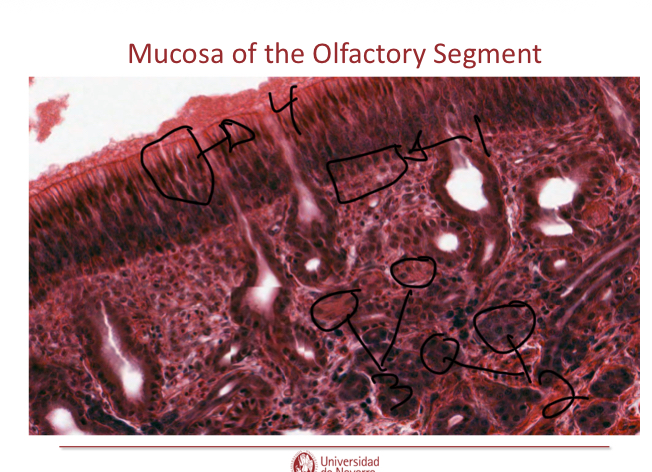
What cells are found in olfactory epithelium?
LACKS GOBLET CELLS
Many nerve fibers branched from olfactory nerve
SPecialized olfactory glands (Bowman’s glands)
Watery secretions
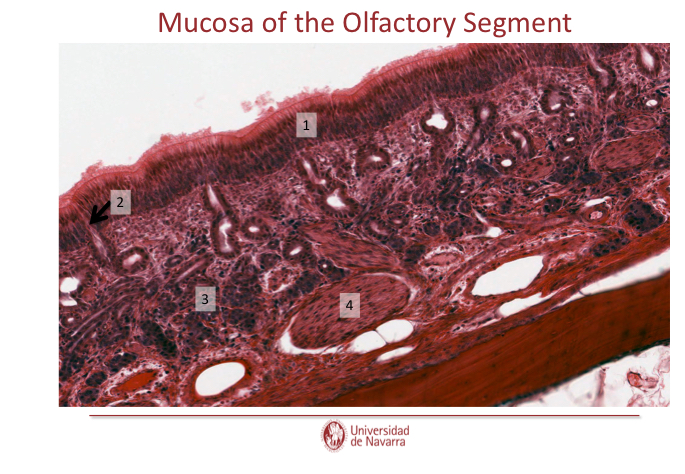
Label this
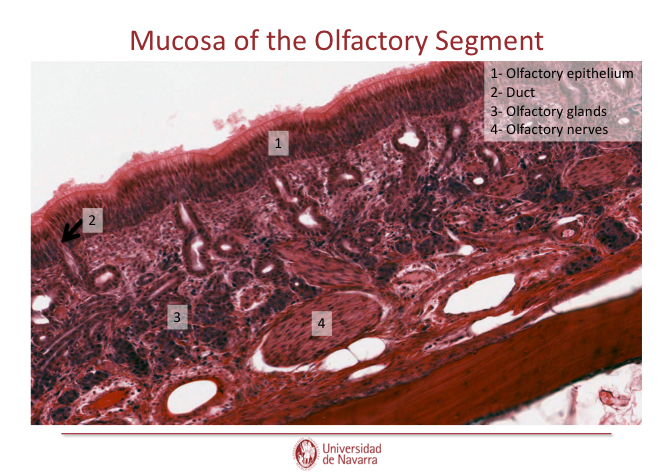
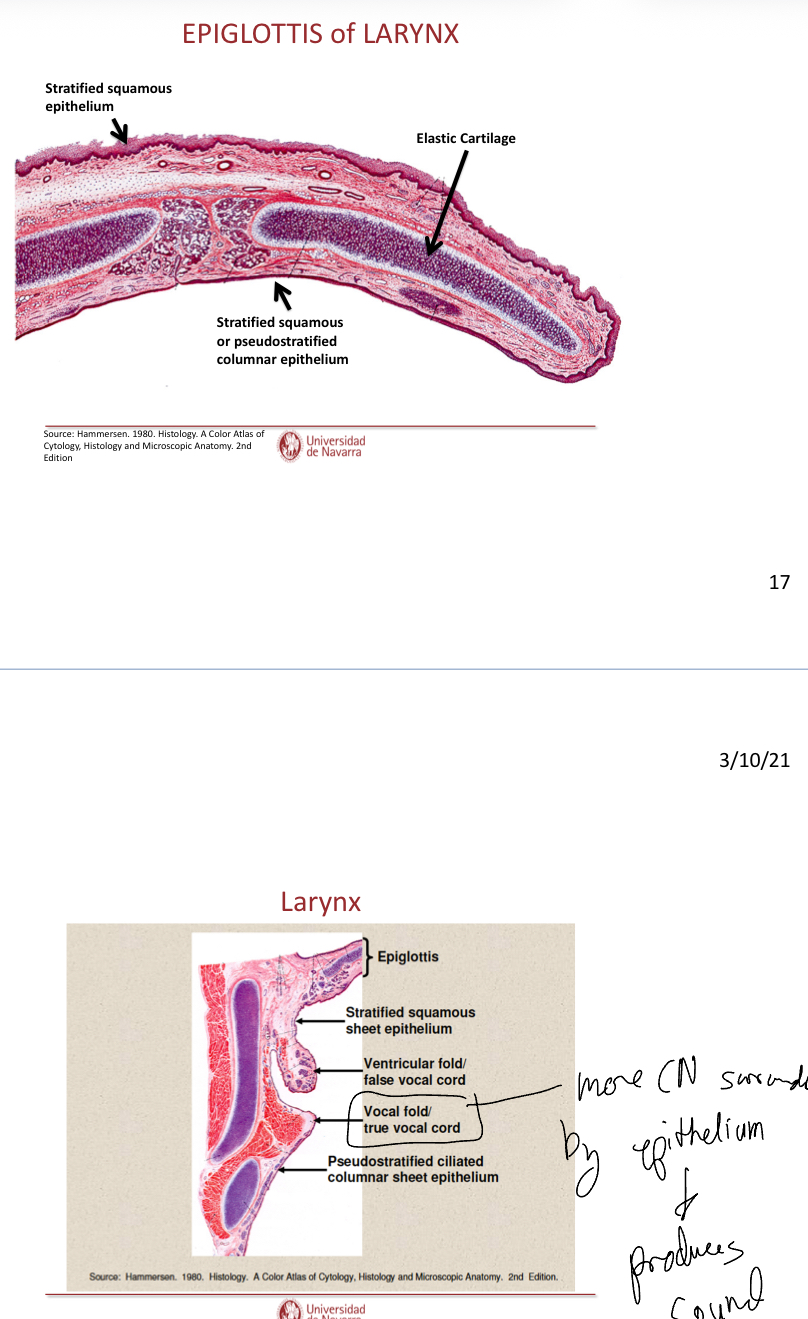
Label this


Label these images
The vocal fold is surrounded by more excess connective tissue and epithelium that prodcues sound.
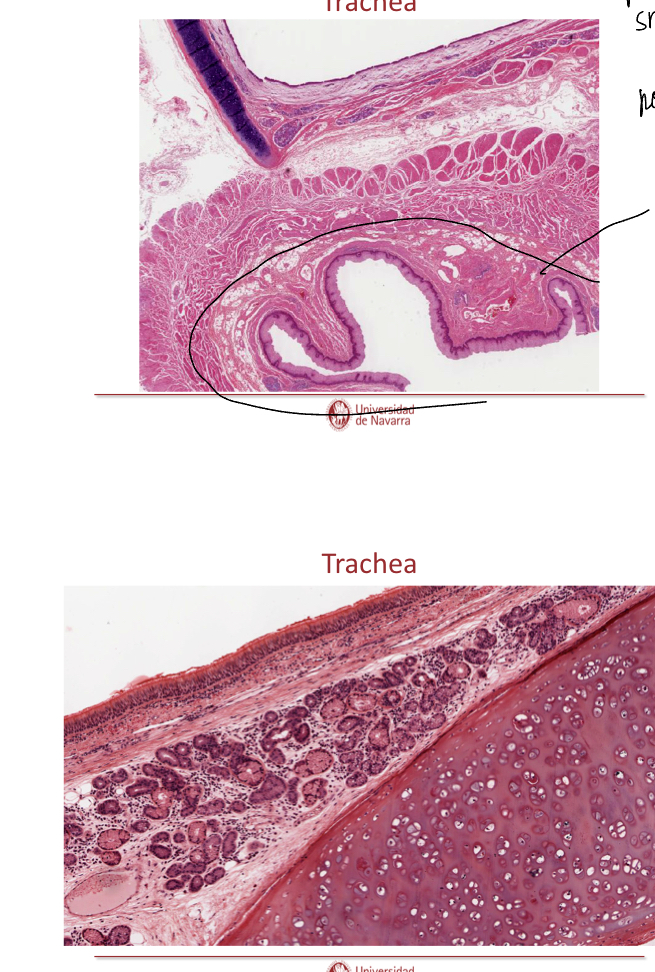
In the top image, since the top caivity is the trachea (can be seen with its cartilage) then what is the cavity under and how do you know?
It is the esophagus, you can tell because it has no cartilage surroudning it unlike the trachea, the esophagus has smooth muscle instead of cartilage
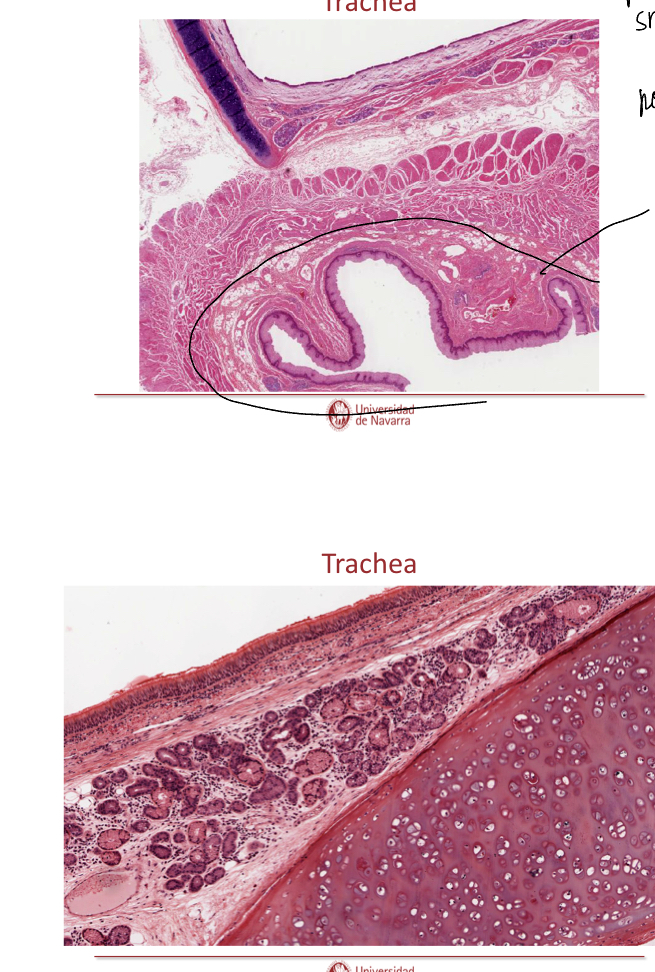
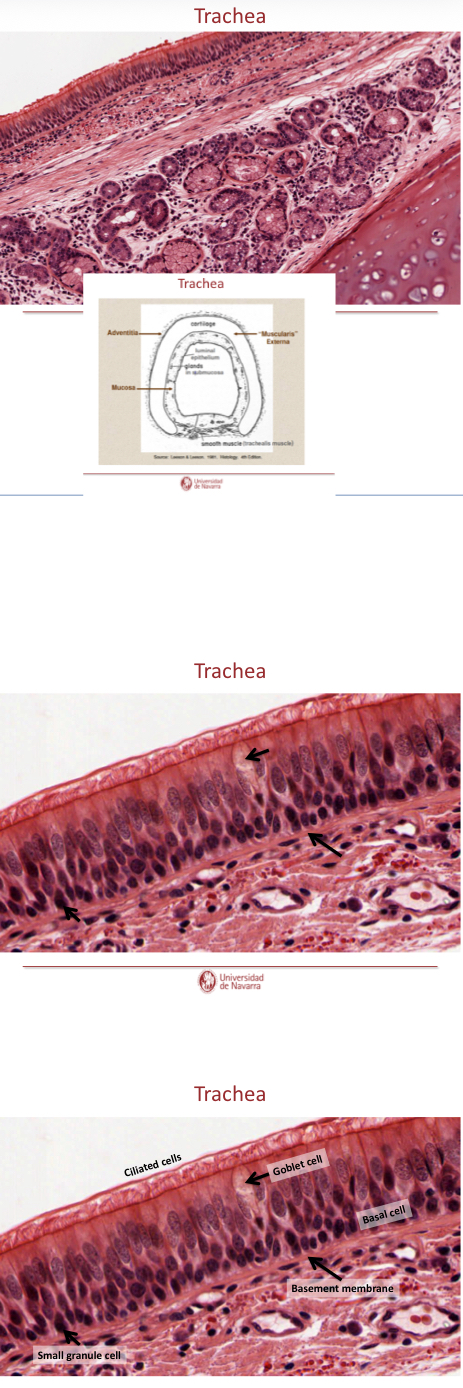
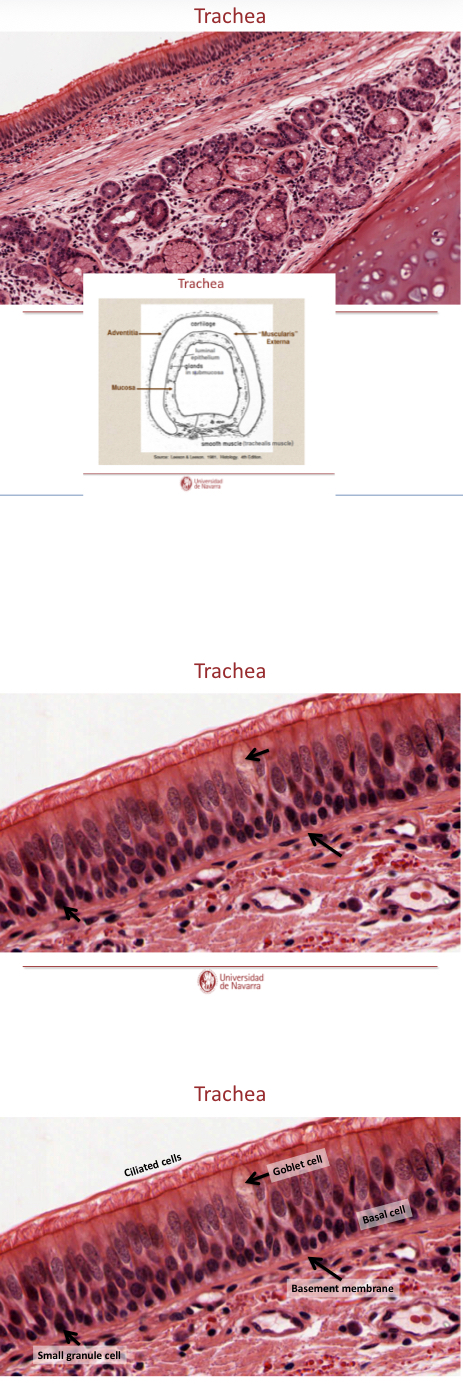
Explain th elayers of the trachea
Mucosa: respiratory epithelium with Clara cells and lamina propia of loose fibroelastic CT
Submucosa: loos to moderatly dense Fibroelastic CT (denser than lamin propia), may contain seromucous glands
Musuclaris externa: hyaline cartilage, smooth muscle across open ends of cartilages (where no cartilage— smooth muscle). Moderalt loos firboelastic CT
Adventitia: loos fibroelastic CT

Explain Bronchi and their layers
Trachea bifurcates into two primary bronchi which enter the lung and then branch sveeral times to give rise to smaller secondary and tertiary bronchi, the bronchi however, have plates rather than rings of cartilage and therefore have smoothmuscle betwen the lamina propia and Submucosa where there isn’t cartilage.

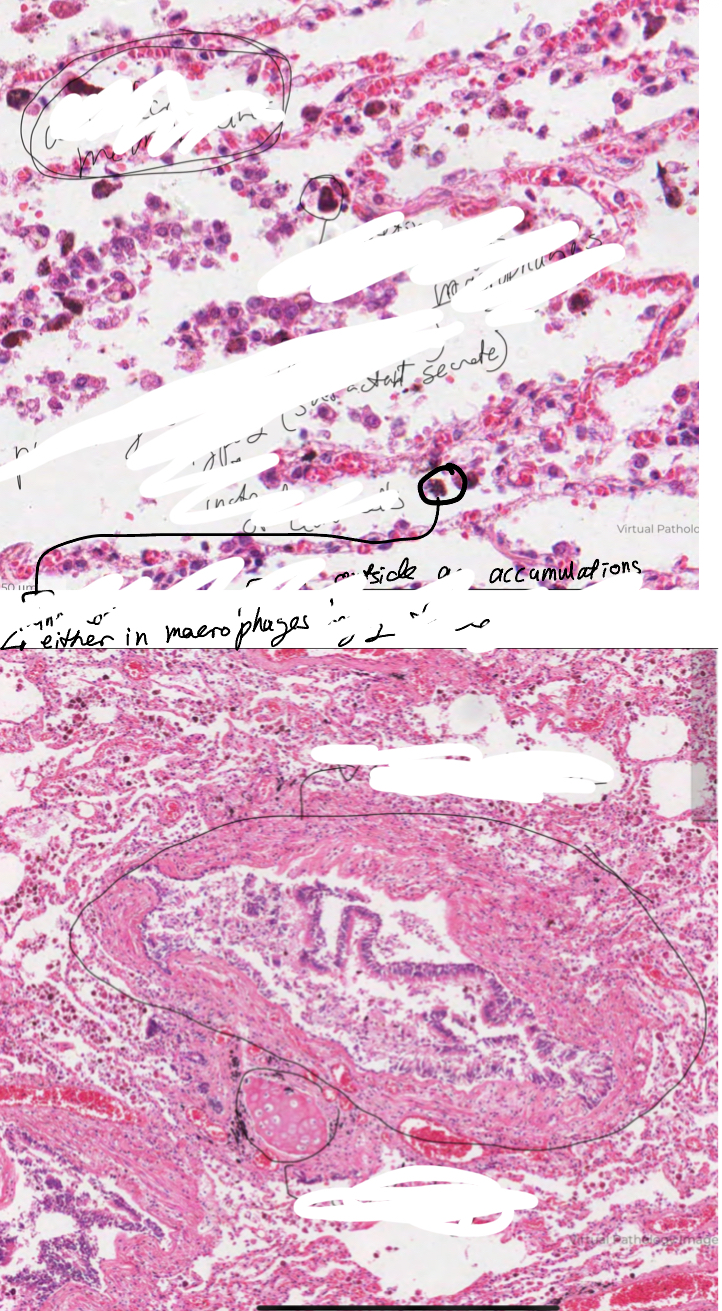
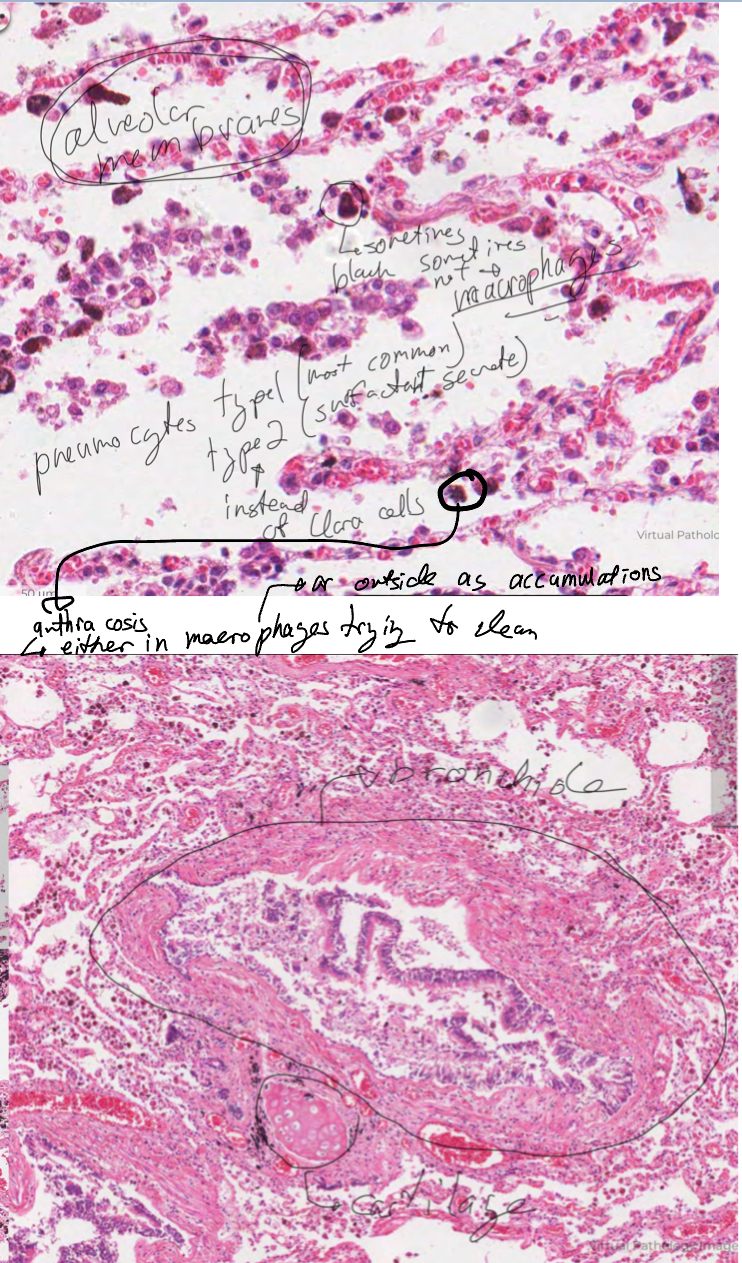
Label this image and explain them.
Bronchiole
No cartilage so no goblet cells
Have ciliated and clara cells
Bronchi
Have patches of cartilage
Psuedostartified, ciliated epithelium with goblet cell and cartilage
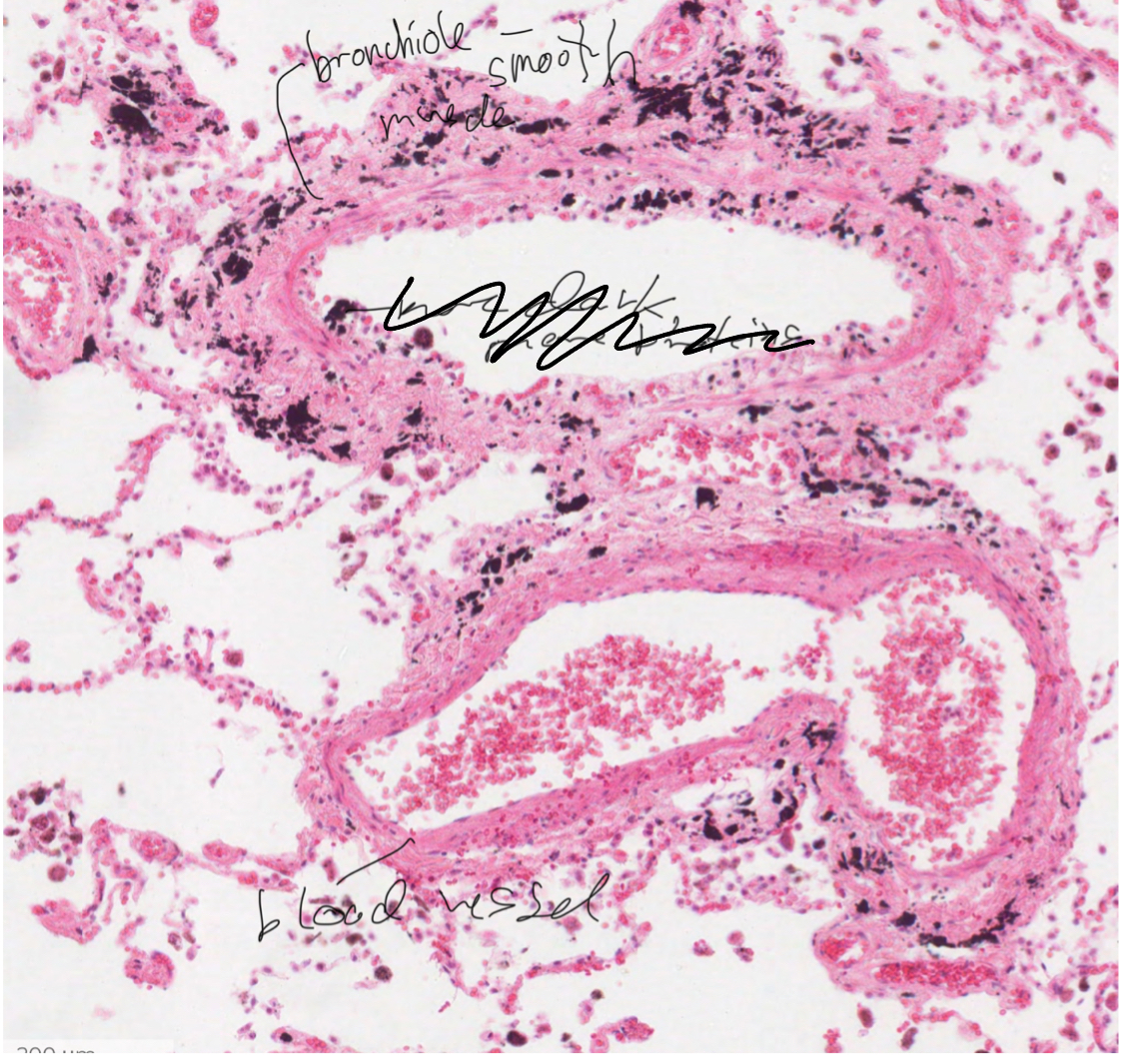
Capillaries
Lined by endothelium, this forms the gas exchange membrane.
Lung Parenchyma
(Part of lung parenchyma) Membranes that allows gas exchange
(Part of lung parenchyma) Alevolar cavity.

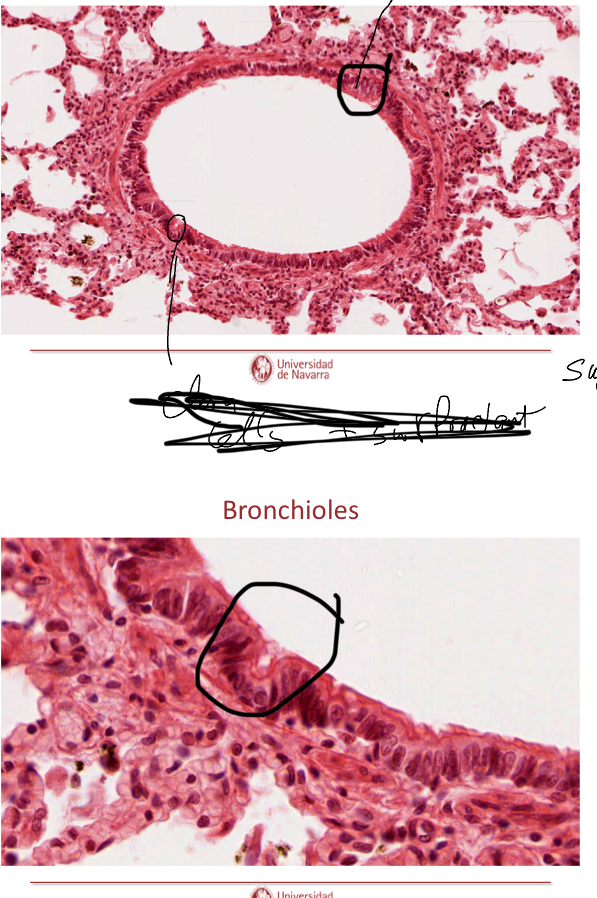
What is circled in the image?
Top circle: simple ciliated epithelium, no goblet cells, smooth muscle layer, and since no cartilage it can have clara cells.
Botoom circle: Clara cells with surfactant.
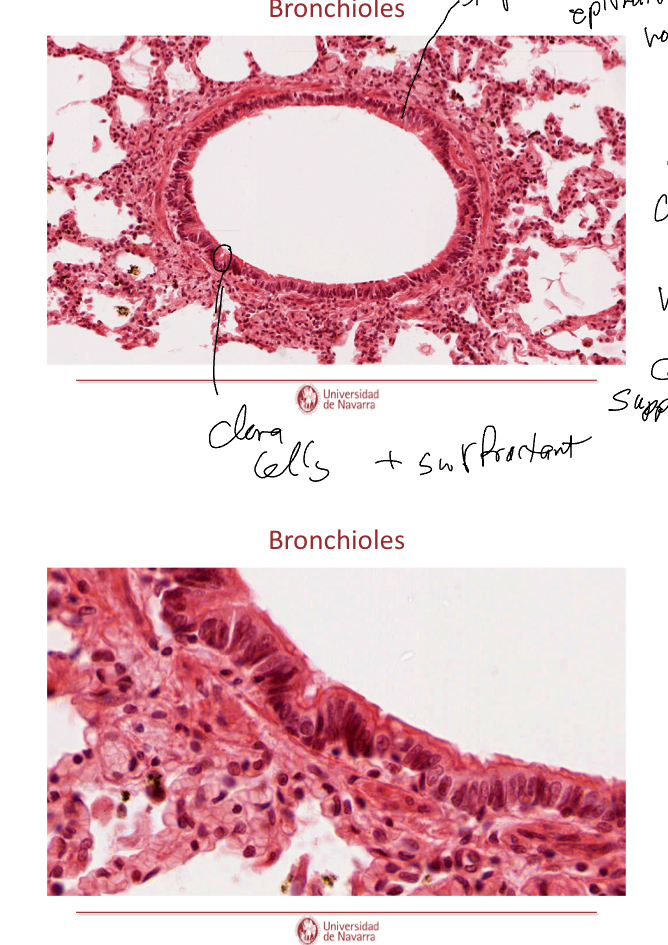

What are the indicated cells?
Clara cells.
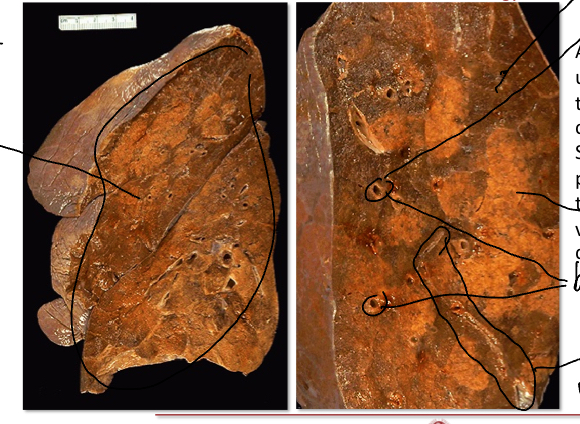
identify the structures in the image


What are the circled structures’

What are the circled structures?

What are tehse two structures?
Describe the gas exchange surface in alveoli
Alveolar space inside alveoli-avelar membrane with pneumocyte type 1 and 2, brush cells and pulmonary macrophages-basal membrane-epithelium of capillary


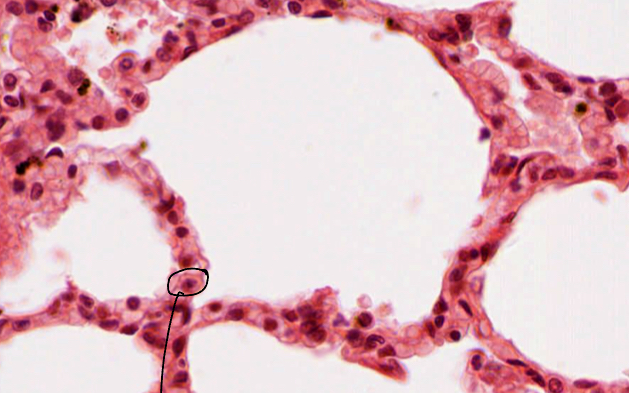
What si the cell circled in the image And explain its function
It is a pneumocytes type 1, identifiable by the fact that it is elongated and flat. These are found in alveolar membranes and allow gas exchange with the blood.
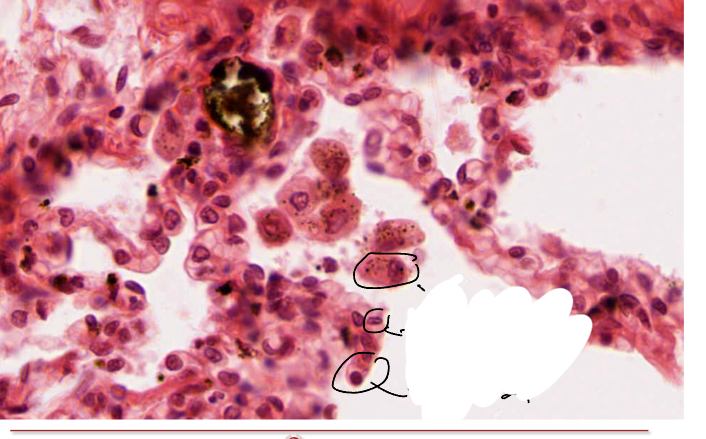
What si this cell and hwta is its function?
When not long/flat (indictaing it would be a pnuemocyte tye 1) this cell is instead round and large, found in the alveolar membrane t is a pneumocyte type 2 which secrets surfactant which can be seen in the image as a white substance
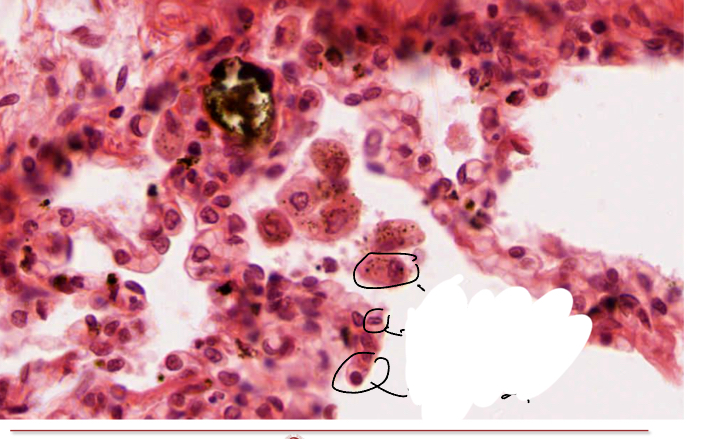
What are the cellsindicate here and what is the uppermost’s function?
The aveolar macrophage’s purpose it to clean up the lungs.
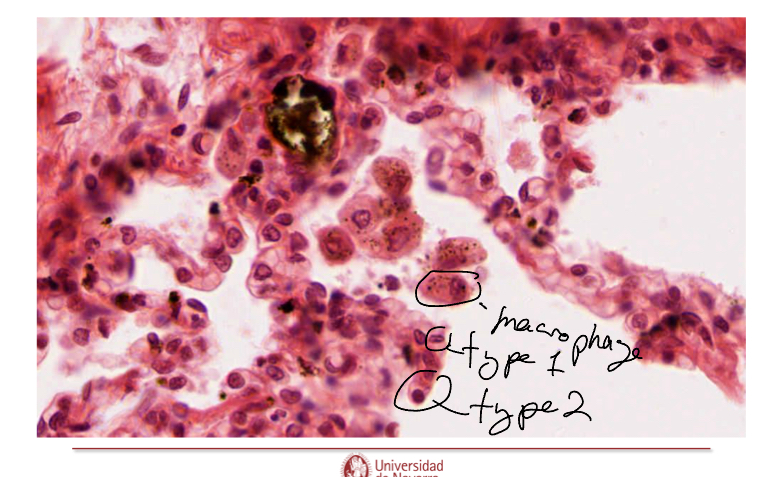

What are these
Macrophages
Keep in mind
What kind of epithelium is pleura?
Simple columnar squamous?
What is abestes
Stick like structure that ends up in the lungs by inhaling it in… causes no inflamation/causes no immune reaction. Alowly damages epithelial and other cells in lung periphery. Likely to cause mutations-may cause tumor formation.