ETC8363-2020 BCCCP- Toxicology
1/141
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
142 Terms
What is the most common factor contributing to death in regards to toxic ingestion?
1. Loss of protective reflexes of airway due to flaccid tongue.
2.Aspiration of gastric contents into lungs.
3. Respiratory compromise (including arrest)
Hence primary treatment is (ABC) Airway, Breathing, Circulation.
What is a toxidrome?
Collections of symptoms that occur with particular classes of toxic agents. Help to ID toxic agents and assist in anticipating additional symptoms.
What is the mechanism of action and toxidrome for ingestion of Anticholinergic agents?
Competitive ANTAgonism of Acetylcholine at central and peripheral muscarinic receptors.
Mydriasis (Dilated Pupils)
Dryness (Anhidrosis, Dry mucus membran, urinary reten)
Tachycardia
Hyperthermia
Flushing
Delirium/Hallucinations/ mumbling speech
Altered mental status.
HYPO-active bowel sounds.
What are some common drug classes that cause Anticholinergic toxidrome.
Skeletal Muscle Relaxants.
Antihistamines/ Antipsychotics
TCAs
What is the mechanism of action and toxidrome for ingestion of CHOLinergic agents?
Inhibition of acetylcholinESTERASES = causing accumulation of acetylcholine = overstimulation of muscarinic and nicotinic receptors.
Acetylcholine is the main neurotransmitter of the "rest-and-digest" or parasympathetic nervous system
Miosis
Bradycardia
Hypertension
Bronchospasm/rrhea (making >100ml/day watery sputm)
CNS depression/ Confusion/ decreased mental status.
Diarrhea/Diaphoresis
Urination, Lacrimation, Salivation (wet mucus membrans)
Emesis
Muscle weakness/twitching
What are some common drug classes that cause a CHOLINERGIC toxidrome.
Organophosphates (insecticides)
Nerve Agent Exposure
Physostigmine
What is the mechanism of action and toxidrome for ingestion of Opioids?
Toxicity is due to stimulation of opioid receptors = decrease autonomic activity.
Miosis
Decreased respiratory rate/
Decreased consciuosness
Decreased bowel sounds
Sedation/Bradycardia/ hypotension
What are some common drug classes that cause a OPIOID toxidrome?
Heron, Morphine, Codeine, Synthetic opioids,
and dextromethorphan in large quantities.
What is the mechanism of action and toxidrome for ingestion of SYMPATHOMIMETICs?
Increase in sympathetic tone by:
1. Release of Catecholamines
2. Inhibition of re-uptake
3. Alterations in Neurotransmitter metabolism
4.Direct Receptor Stimulation
What is the toxidrome for ingestion of SYMPATHOMIMETICs?
Agitation
Delirium
Myoclonus (spasmodic jerking of muscles)
Mydriasis ( dilated pupils)
Tachychardia/Hypertension/Hyperthermia
Diaphoresis.
What are some common drug classes that cause a Sympathomimetic toxidrome?
Cocaine
Methamphetamine
Pseudoephedrine
Caffeine
When should we use Ipecac as a decontaminant?
NEVER, it has been removed from the U.S manufacturers due to INABILITY to improve pt outcomes and also due to safety concerns.
What is Gastric Lavage?
Must be within 60 min
When a large-bore catheter tube is inserted into the stomach. The tube has several holes at the distal end that delivers aliquots of warm water (or NS) in order to clear the aspirated fluid.
what is the efficacy and time frame which a gastric lavage should be used?
Efficacy is highly variable and diminishes over time. Optimally should be done within 60 min of ingestion.
(GL has NOT been proven to decrease severity of illness, HAS NOT improved recovery times or outcomes.
What are some contraindications for gastric lavage?
Craniofacial abnormalities
Head Trauma
UN-protected Airway
Risk of aspiration or GI hemorrhage/perforation.
What are some complications that can happen during or after gastric lavage?
Aspiration
Laryngospasm
Perforation of esophagus/stomach
arrhythmias
Fluid imbalance
Hyponatremia
What are cathartics intended to do?
NOT USED, DO NOT IMPROVE PATIENT OUTCOME
Reduce transit time of toxins (and absorption) +/- activated charcoal to decrease constipating effect.
Cathartics: What is the efficacy and how many doses do we need?
Conflicting data regarding efficacy ( no data on improved outcomes)
DO NOT USE, if you have to use limit it to one dose.
How does Activated Charcoal work?
Adsorbent that binds toxins via GI tract to reduce absorption.
NEEDS established airway/ protected airway
A patient has ingested an Acid/ Alkaline solution, can you use Activated Charcoal?
Should be avoided because the charcoal may cause vomiting = leading to injury to the esophagus
(Also charcoal is black = interferes with endoscopy)
A patient has ingested large amounts of alcohol, can you use Activated Charcoal?
Yes but Act. char binds poorly to alcohol so very large doses are needed which is hard to ingest
Cyanide poisoning, can you use activated charcoal?
Yes but cyanide will bind poorly to act char so normal doses of act. char will not work.
Hydrocarbon ingestion, can you use Activated Charcoal?
No, due to risk of aspiration
What are some complications and contraindications to activated charcoal?
Complications: Aspiration, admin into lungs, emesis, constipation GI obstruction
Contraindications: Unconscious state/ inability to maintain airway, recent GI surgery.
Is multi-dose activated charcoal better than single dose regimens?
Multi-dose has not been shown to be more effective in reducing morbidity and mortality than single doses.
Multi-dose Act Char only used in medications that undergo enterohepatic recirculation that make active enterohepatic metabolites.
What is a whole bowel irrigation?
strategy to cleanse bowels from potential toxin by giving osmotic polyethylene glycol solution.
When is the best time to use Whole Bowel Irrigation?
(not recommended for routine use) but...
Needs to be relatively close to time of ingestion.
1. Ingestion of Medications with long half-life, sustained release, or enteric coated formulations.
2. When activated charcoal has not worked or will not work ( lithium and iron)
3. Packers / Stuffers of illicit substances.
Can you use whole bowel irrigation AND Activated Charcoal at the same time?
No, if both used the charcoal will not work as well.
What are some Complications and contraindications to using a whole bowel irrigation?
Complications: anaphylaxis, lip angioedema, aspiration, Mallory-Weiss tear, esophageal perforation.
Contraindication: Bowel obstruction, perforation, illeus, recent bowel surgery. (use KUB radiograph to rule out)
Urine Alkalinization work how?
improves the elimination of toxins by increasing the urine pH to levels of 7.5 or more by giving sodium bicarb or sodium acetate.
When would you use the Urine Alkalinization strategy?
When ingestion involves weak acids with urinary clearance. (salicylates, phenobarbital, chlorpropamide)
What are some contraindications to urine alkalinization?
Acute/chronic renal failure
pre-existing heart failure.
What are some complications of urine alkalinization?
HYPOkalemia/calcemia
Hypernatremia
cerebral/coronary vasoconstriction
What happens to potassium when you induce alkalinization?
Potassium is pushed into the cell causing HYPOkalemia.
If pt has HYPOkalemia already, it will be impossible to alkalanize urine because low potassium will make kidneys excrete H+ ions = decreasing alkalinization.
Gastric Lavage: Pediatric and Adult Dose?
Must be within 60 min
Pediatric: 10ml/kg aliqots with equal amount of return
Adult: 200-300ml aliquots with equal amount of return
Cathartics: Pediatric and Adult Dose?
Magnesium citrate:
Pediatric = 4ml/kg Adult: 240ml
Sorbitol:
Pediatric=4.3 ml/kg(35% sol) Adult:1-2 ml/kg (70% sol)
Activated Charcoal: Pediatric dose?
Single dose: 0.5-1 g/kg
(0-1 year max of 25g)
(1-12 year max of 50g)
Multi-dose: 0.5-1 g/kg + 0.25-0.5 g/kg q 4 hrs.
Activated Charcoal: Adult dose?
(>12 yrs of age)
Single Dose: 25 -100 g
(doses of >50 g are high risk for vomiting)
Multi-Dose:
50 grams + 25-50 g q 4 hrs
Whole bowel Irrigation Pediatric dosing?
9 Months - 6 years:
500mls/hr
6 years - 12 yrs:
1000 ml/hr
Whole bowel Irrigation Adult dosing?
(>12 years)
500 ml/hr then doubled q 30 min to a goal of 2000ml/hr.
(PEG solution, dose until rectal effluent is clear)
Urine Alkalinization Pediatric and Adult dosing?
Peds:
25-50 mEqs IV for 1 hr
Adult:
225 mEqs IV for 1 hr
(NaBicarb in D5%-water BOLUSES can be given hourly or cont. infusion at this hourly rate to maintain pH of 7.5-8.5)
Which are the substances that cannot be decontaminated with Activated Charcoal?
Alcohols, Acids, Alkalis
Carbamates, Cyanide
Hydrocarbons
Metals
Organic Solvents/ Organophosphates
Examples of :
Alcohol
Acids
Alkalis
Alcohol:
Ethanol, Ethylene glycol, methanol
Acids:
Boric Acid, Mineral acids
Alkalis:
Bleach, cleaning solution, dishwasher detergent, lye
Example of:
Carbamates
Cyaninde
Carbamates:
Insecticides, neo/physo-stigmine
Cyanide:
Cyanogen Cl, Hydrogen/Potassium/Sodium Cyanide
Example of Hydrocarbons?
Gasoline
Kerosene
Petroleum oils
Example of metals?
Arsenic
Iron
Lead
Lithium
Mercury
Example of
Organic Solvents
Organophosphates
Organic Solvents:
Acetic acid, Acetone, Ethylene Glycol, Glycerin, Toluene
Organophosphates:
Antihelminthic (trichlorfon)
Insecticides (mala/para-thion)
Herbicides
In general what is the acute toxic dose for Acetaminophen in mg/kg for adults and children?
Adults:
150 mg/kg ( or 7.5g total)
Children:
200 mg/kg
What is the MOA for APAP toxicity?
Ingestion= Active metabolite of
N-acetyl-p-benzoquinoneimine (NAPQI) =
oxidant cell injury, Hepatic failure, death.
Only about 8-10% of medication is converted to NAPQI.
NAPQI is then converted to Cysteine conjugates by Glutathione. In toxic ingestions, sulfation and glucuronidation is saturated = glutathione depletion= NAPQI builds up.
What is the time frame and presentation of Phase 1 in APAP toxicity?
Within 24-hrs of ingestion.
MINIMAL/no signs of distress.
Some N/V, Diaphoresis, anorexia
What is the time frame and presentation of Phase 2 in APAP toxicity?
24-48 hrs after ingestion:
Damage to hepatocytes (right upper quadrant pain)
Elevated liver transaminases
Elevated Bilirubin
Prolonged PT/INR
What is the time frame and presentation of Phase 3 in APAP toxicity?
72-96 hrs post ingestion:
!!! PEAK !!! hepatotoxicity (Fulminant Hepatic Failure) as seen by jaundice, coagulopathies/hepatic encephalopathy, and hypoglycemia.
May also see:
Lactic acidosis
Acute Renal Failure/ Acute Pancreatitis
What is the time frame and presentation of Phase 4 in APAP toxicity?
1 week post-ingestion
this is the "recovery" phase
(if the pt makes it past Phase 3)
What requirements must be met for a pt to receive activated charcoal for APAP poisoning?
Ingestion needs to be <1hr ago
no vomiting
no alterations in mental status
What is the MOA of acetylcysteine?
Increases synthesis and bioavailability of Glutathione
Binds to sulfur group of NAPQI (inactivates it via sulfation) = non-toxic metabolism.
What is the time frame needed from ingestion of APAP that acetylcysteine can be used?
within 8 hrs of APAP ingestion if they are possibly or probably at risk for hepatotoxicity.
How do you determine if a patient is possibly or probably at risk for hepatotoxicity?
Use Rumack-Matthew nomogram.
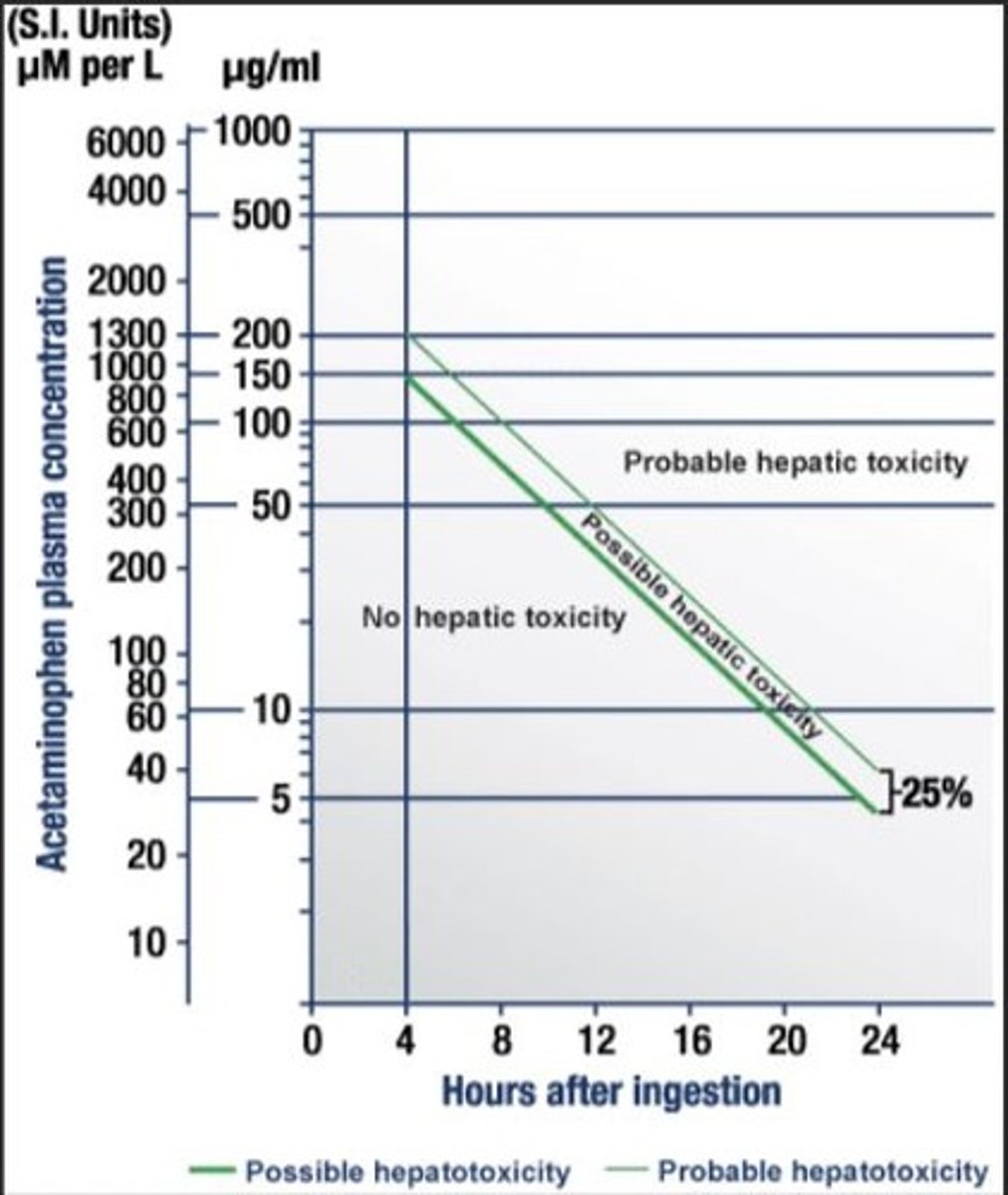
True or False?
If pt does not know ( or if time of ingestion ) not know. you cannot use acetylcysteine?
False, if time of ingestion is not known still give acetylcysteine if any of the following:
Increased ALT
APAP Level > 20mcg/mL
Hx of chronic ingestion > 4g/day + elevated ALT.
(Even if >24hrs post ingestion, with evidence of hepatotoxicity)
What are the limitations of the Rumack-Matthew Nomogram?
presentation >24hrs postingestion
Unknown or unreliable history of ingestion
OD with Extended-release formulation
Chronic/repeated supratherapeutic ingestions
Pts with hepatic disease, chronic alchohol use, concurrent meds metabolized by CYP system.
Which one is better, IV or oral Acetylcysteine?
IV is better because it takes less time for full regimen.
IV=21 hrs total vs. 72 hrs with oral.
also has less GI ADEs
(If IV is not available call Poison control to see if inhalation liquid can be made into IV)
If you decide to go with the oral version and the pt throws up, can we give another one or wait until the next dose?
if pt throws up within 1 hr of ingestion then dose must be repeated.
What is the criteria used by poison control for early discontinuation of acetylcysteine?
APAP level undetectable or <10mcg/ml
Normalized ALT (60 IU/L) or improving/ trending down
Pt clinically improved
INR of 1.3 or less.
What is the Acetylcysteine ORAL dosing regimen?
Loading dose : **actual BW**
140 mg/kg
Maintenance:
70 mg/kg q 4 hrs for total of 17 doses (72 hrs)
What is the IV Acetylcysteine dosing regimen?
Loading dose: **actual BW**
150 mg/kg (Max: 15 g) in 200 ml D5%W over 60 min
Maintenance:
50 mg/kg (Max: 5 g) in 500 ml D5%W over 4 hrs
+++PLUS+++
100 mg/kg (Max: 10 g) in 1000 ml of D5%W over 16 hrs
What is the mechanism of action for Salicylate Poisoning?
interferes aerobic metabolism = anaerobic metabolism= significant lactic acidosis.
Salicylates also directly stimulate respiratory center= Hyperventilation = respiratory alkalosis = compensatory metabolic acidosis.
What are the most common clinical presentation of ASA ingestion?
Hyperventilation
Tinnitus
GI irritation
Regarding the different levels of ASA what is the respective presentation for each tier?
<30 mg/dL: asymptomatic
15-30 mg/dL: therapeutic dose
30-50 mg/dL: Hypervent, N/V, Tinnitus, Dizzy
50-70 mg/dL: Tachy, Fever, Sweat, Dehydrate, Listless
>70 mg/dL: Coma, seizure, Hallucinate, cerebral edema
What is the difference between ACUTE vs CHRONIC salicylate poisoning?
Acute: GI symptoms, nausea
Chronic: CNS type symptoms.
When should you draw a salycilate level?
Full Absorption can take up to 36hrs if
-medication forms a bezoar (bulk of med)
-Formulation is enteric coated
What is the antidote for ASA poisoning?
No antidote, just limit the absorption and provide supportive care. (ventilate to prevent resp acidosis)
try to stay away from mech. vent, because it interferes with their ability to compensate and maintain pH.
One dose of activated charcoal can be used if N/V not present.
Try urine alkalinization (recommended)
give potassium / glucose if necessary
Urine alkalinization with NaBicarb in salicylate poisoning dose?
250 mls of NaBicarb 8.4% over 1 hr + 50 mls as needed to maintain urine pH at 7.5-8.5
150 mls NaBicarb (8.4%) in 1L D5%W @ 2-3 ml/kg/hr
goal: urine output 1-2 ml/kg/hr ( keep pH > 7.4)
Oral NEVER used / not recommended since it may ENHANCE salicylic acid absorption. while IV bicarb helps with acidosis and elimination.
When should you stop the NaBicarb drip when used for Salicylate poisoning?
When serum salicylate level is < 30mg/dL
(or resolution of symptoms)
What are the most common symptoms of opioid OD?
Respiratory Depression (<12 breaths/min)
Coma
Miosis (pinpoint pupils)
Hypoactive Bowel Sounds
Treatment for opioid overdose?
Stabilize airway ( RSI if needed)
IV Crystalloids to maintain BP
Activated Charcoal ( if <1hr of ingestion + no N/V)
Whole Bowel Irr (if extended release formulation is found or pt is packing/stuffing-especially fentanyl patches)
Narcan
Naloxone (Narcan)
Mechanism of action
Onset + Duration
Dosing Adult and Pediatric
MOA: COMPETITIVE Antagonist at opioid receptor.
Onset= 2 min ++++++++ Duration: 30-120 min
Adult: (IV is preffered but also IM, ET, IN, Inh, IO, IP)
0.04mg>>3min increase to 0.5mg>> 2mg>> 4mg>> 10mg>> 15mg (q3min)
IM/SUBq = sporadic use last.
Pediatric:
0.1mg/kg dose.
(Intra-nasal: attach atomizer to 2mg/2ml syr and spray in 1ml to each nasal fossa)
You managed to reverse an opioid OD with narcan, now what do you do?
Start narcan drip at two-thirds of the effective bolus dose / hour (0.04-4mg/kr) to sustain effect.
Why do people ingest high doses of loperamide?
For its euphoric effect. but at high doses Loperamide can stimulate Mu-opioid receptors in GI tract and block intestinal Ca+ Channels.
(Also blocks Na+&K+ channels in the heart = QTc prolongation and widening of QRS= life-threatening dysrhythmias and cardiac death)
What can be given for a loperamide OD?
Crystalloids
Activated Charcoal
Naloxone
Sodium Bicarbonate 1-2 mEq/kg IV
Mag+ & K+ (since it blocks Na+ & K+ channels)
What commercially available products have METHANOL alcohol?
windshield fluid
Antifreeze
brake/carburetor fluid
cooking products
What commercially available product contains Ethylene Glycol?
antifreeze\de-icing solutions
refrigerants
brake fluid.
Mechanism of action of the toxicity that develops with methanol and ethelyne glycol
Methanol> formaldehyde>formic acid = anion gap acidosis and ocular toxicity.
Ethylene glycol> glycoaldehyde> Glycolic acid>Oxalic acid = anion gap acidosis & CNS/ renal toxicity (calcium oxalate crystals)
What is one very unique presentation of Ethylene Glycol not seen in methanol ingestion?
Ethelene Glycol: sometimes may present with tetany due to hypocalcemia.
What is the formula for osmolar gap?
(Sodiumx2) +(glucose/18)+(BUN/2.8)
What is the formula for osmolar gap with ..
Ethanol
Methanol
Ethylene Glycol
(Sodiumx2) +(glucose/18)+(BUN/2.8) +
Ethanol/4.6
Methanol/3.2
Ethylene Glycol/6.2
What is the formula for Anion Gap?
Na- (Cl-HCO3)
What is the preferred antidote for ethenol/ethylene glycol and methanol ingestion?
Mechanism of action?
Dose?
Fomepizole.
COMPETITIVE inh of alcohol dehydrogenase
15mg/kg bolus
10mg/kg every 12hrs x 4 doses
15mg/kq every 12hrs until meth/ethanol conc <20mg/dL
(past 48hrs fomepizole induces its own metabolism)
How does HD affect fomepizole?
HD clears fomepizole much faster. Hence needs to be given every 4 hrs.
10mg/kg q 4hrs.
What other agent can you use for ethanol/methanol ingestion that isn't fomepizole?
Ethanol diluted in 95% alcohol for IV, PO, Per-tube. to compete for alcohol dehydrogenase.
not used due to difficulties in dosing and adverse effects
What is the dose for ethanol used for methanol poisoning?
600-700mg of 10% followed by
66mg/kg/hr (154mg/kg/hr in chronic alcoholics)
goal is to maintain serum ethanol conc of 100mg/dL until symptoms have diminished or methanol/ethanol glycol conc are undetectable.
What other therapies can be used in methanol poisoning that are not fomepizole and ethanol?
Pyridoxime + thiamine= decreases toxic metabolites
folinic acid (folic acid)= cofactor in metabolism
Dextrose
Magnesium (1-2g IV esp is chronic alcoholic)
Anti-seizure meds: Benzos (DOC), Phenobarb, propofol, phenytoin
What is the time-line for someone who is going thru alcohol withdrawal?
symptoms appear within 8-hrs of BAL conc decrease
Peak symptoms at 72hrs
significant decrease in symptoms 5-7 days out.
What are some of the common symptoms of alcohol withdrawal?
Tremors
Diaphoresis
N/V
HYPER-tension, HYPER-thermia
TACHY-cardia and TACHY-pnea.
What are the symptoms that lead us to believe a person has MODERATE- SEVERE withdrawals
Alcoholic hallucinations (audio, visual, tactile)
Tonic Clonic Seizures (within 72hrs)
Life-threatening Delirium Tremens- (within 72hrs)
What is the primary agent used for alcohol withdrawal?
Benzodiazepines ( esp Lorazepam and Diazepam) binds to GABA receptor and hyperpolarizes it which stabilizes membrane.
When do you use Phenobarbital vs. Benzodiazepine in alcohol withdrawal?
When there is a high probability that GABA substance is depleted. Phenobarbital does not require GABA to be effective. Phenobarbital binds to GABA receptor directly as well but used as a 2nd line treatment. used AFTER Benzo has failed.
How does Clonidine work in regards to alcohol withdrawal?
Alpha-2 receptor agonist that controls catecholamine surge during alcohol withdrawal that causes elevations in BP & HR
How does propofol work in pts with alcohol withdrawal?
GABA receptor agonist + NMDA receptor antagonist
(CHRONIC alcoholics have increased NMDA receptors)
Useful in controlling delirium and prevention of seizures
How does Dexmedetomidine work in regards to alcohol withdrawal and where does it fit in the treatment regimen?
Alpha-2 receptor agonist (controls BP & HR)
reduces overall Benzo use
RECOMMENDED when clonidine is contraindicated
Suggested starting dose and Interval/Infusion dose for Diazepam and Lorazepam in alcohol withdrawal?
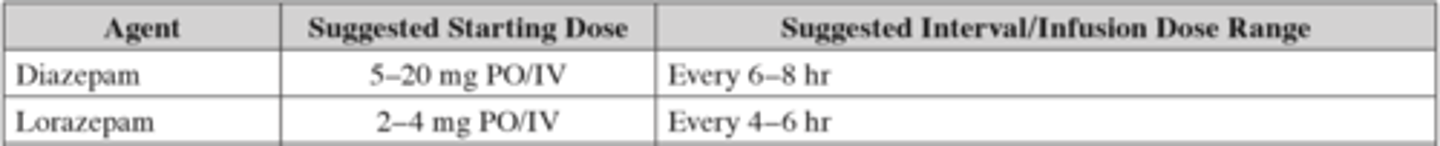
Suggested starting dose and Interval/Infusion dose for Phenobarbital in alcohol withdrawal?
