Human Anatomy and Physiology 1 (MATC) Lecture Exam 1
1/116
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
117 Terms
covalent bond
multiple atoms combined to fill the valence shells
molecule
two or more atoms held together by covalent bonds
ionic bond
when atoms in a molecule have charges (different number of protons and electrons). attraction of a pos./neg. ion.
chemical reactions
the making and breaking of chemical bonds, leading to changes in the composition of matter. generally reversible.
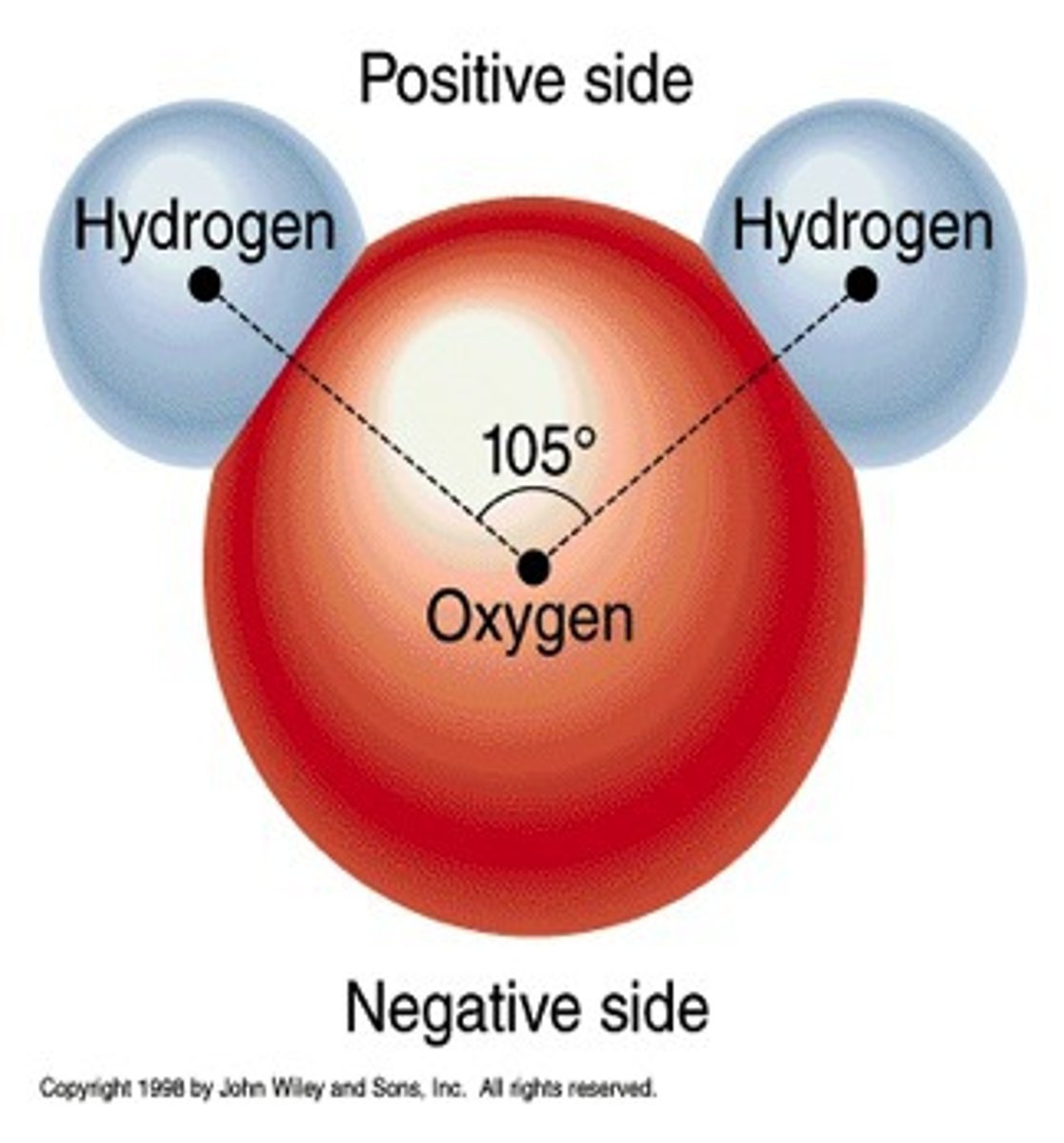
hydrogen bond
weak attraction between a hydrogen atom and another atom.
ex: H20 - so many protons in O, H's electrons spend more time with O so O takes on a negative charge and H takes on a positive charge - more so between molecules than atoms
ions
charged particle (atom or molecule).
dehydration reaction
formation of large molecules (polymer) by the removal of water
monomer
small chemical unit that makes up a polymer
hydrolysis
A chemical process that splits a molecule by adding water. (breaking of a covalent bond through an enzyme)
macromolecules: carbohydrates
monomers of carbs are simple sugars.
monosaccharide - one sugar
Glucose: C6H12O6 1:2:1 ration
starch: where does it store? what does it store?
store glucose in plants
glycogen: where does it store? what does it store?
store glucose in animals
polymer of glucose
stored in liver and muscles, in blood for a ready supply
macromolecules: PROTEINS - what are their monomers? what are they when hydrogen comes off in water?
amino acids are monomers
(small molecules) they are acids.
acids:
substances that release hydrogen ions when dissolved in water, leaves electron behind.
components of protein
carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen
The sulfur-containing amino acids (cysteine and methionine) are generally considered to be
nonpolar and hydrophobic
All amino acids contain an amino(-NH2) group(bonded to the Alpha-Carbon), which contains Nitrogen.
However, there are some Amino Acids, including Lysine, Arginine, Histidine, which contain more Nitrogen than the others
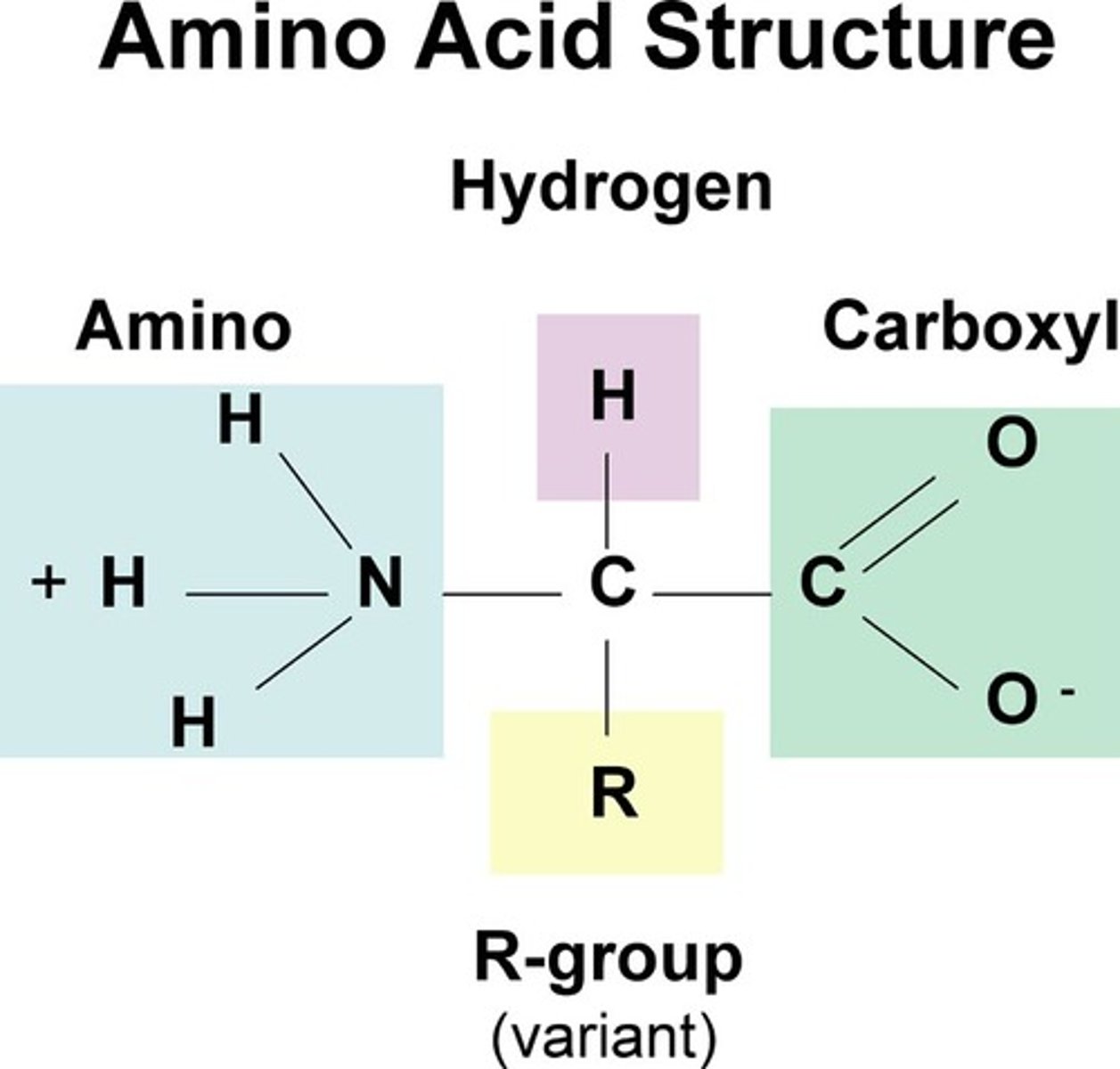
amino acids, which are small organic molecules that consist of an
alpha (central) carbon atom linked to an amino group, a carboxyl group, a hydrogen atom, and a variable component called a side chain. The largest group of amino acids have nonpolar side chains.
carboxyl group
A functional group present in organic acids and consisting of a single carbon atom double-bonded to an oxygen atom and also bonded to a hydroxyl group. (-COOH)
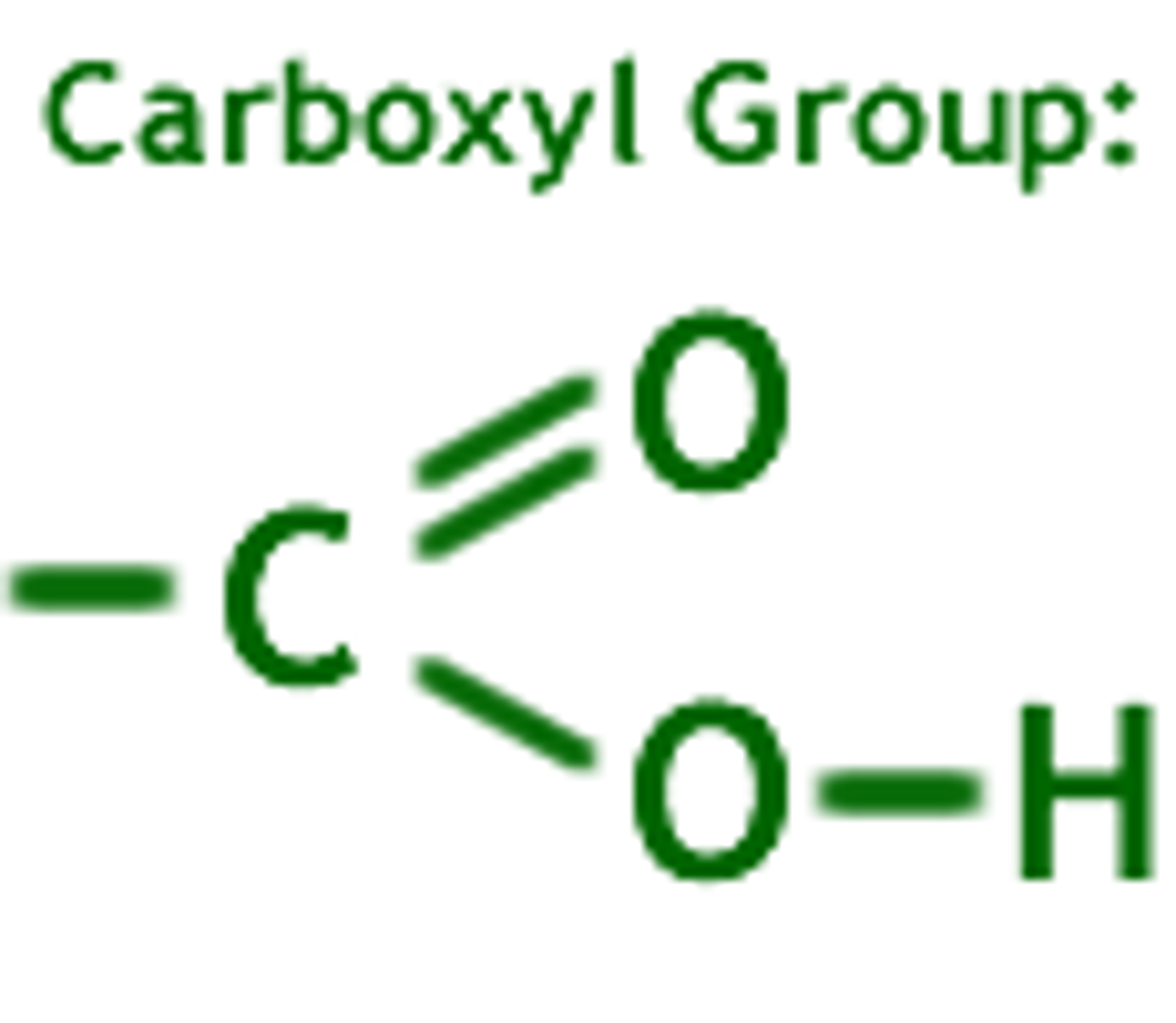
amino group
A functional group that consists of a nitrogen atom bonded to two hydrogen atoms (-NH2)
Hydroxyl
OH-
R means variable group
amino acids are ___ (charge) and have a ________ because of one ____ side and one ____ side
polar. one negative side and one positive side
why is it important to check the polarity of side chains
polar side groups of amino acids form hydrogen bonds
carbons NEED ____ bonds (number)
4
amino group have 2 components
amine group (+)
gain electron (-)
always nonpolar
amine group
the nitrogen-containing portion of an amino acid (NH2)
always nonpolar because of
amine group (+)
gain electron (-)
side chains
the atoms extending beyond the universal H3N+-CH-COO- core of all amino acids and determine their chemical properties
determining side chain polarity
if side chain has a (+) or (-) - polar
sometimes side chains don't have charges - nonpolar
OR
a lot of carbons - nonpolar
many oxygen - polar
side chains are on the___ which are ______ which assemble to make proteins
amino acids, monomers
polypeptides are
polymers of amino acids
polar side chains (+), (-) or many O's can make ____ bonds
hydrogen
polar molecule
a molecule in which one side of the molecule is slightly negative and the opposite side is slightly positive
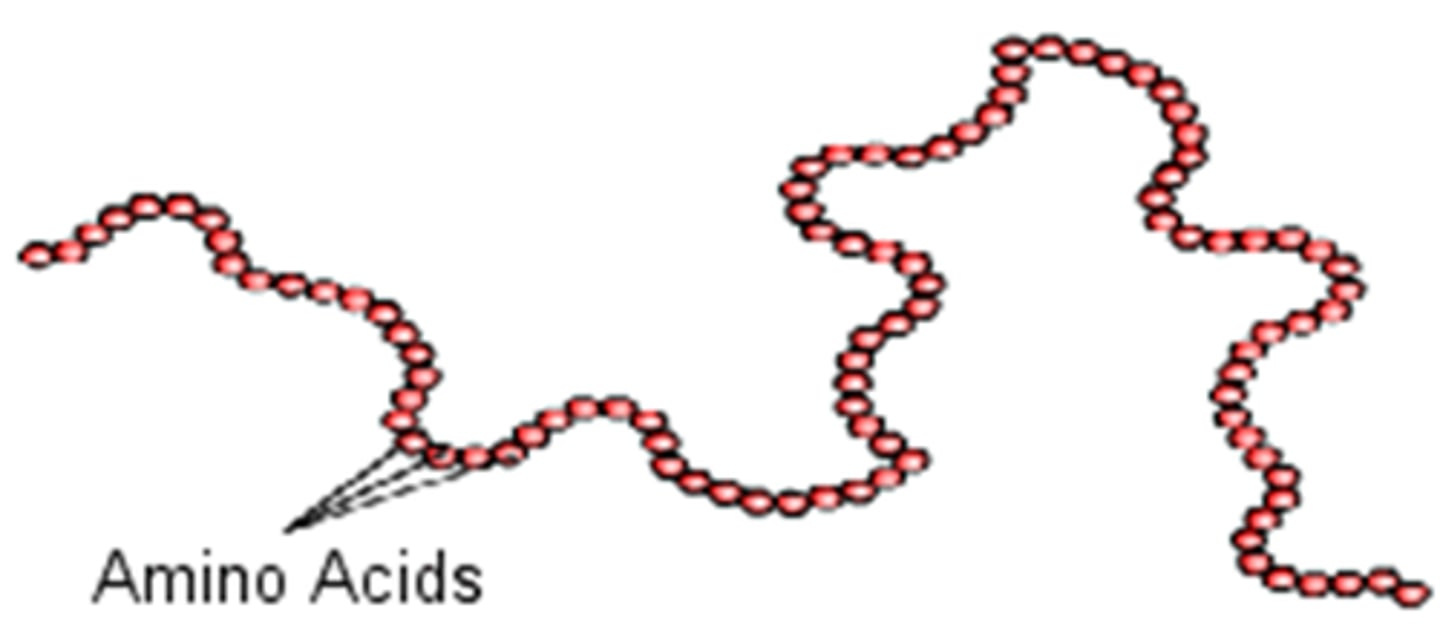
polymer
large compound formed from combinations of many monomers
amino acids strung together through dehydration rxn
polypeptide bonds
w/ a dipeptide with amino group on one side and acid on the other side
primary structure
sequence of amino acids

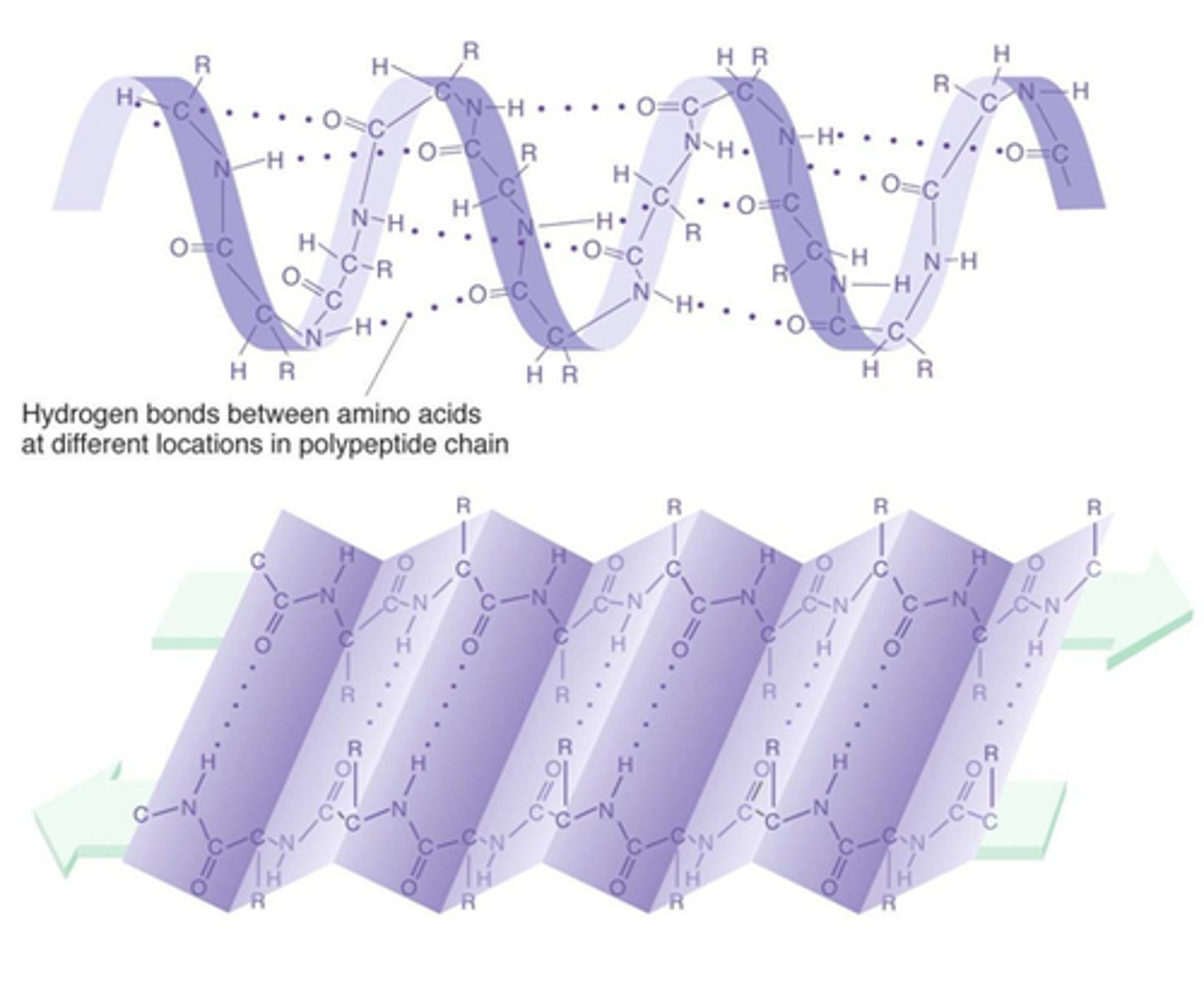
secondary structure
Either an alpha helix or beta pleated sheet.
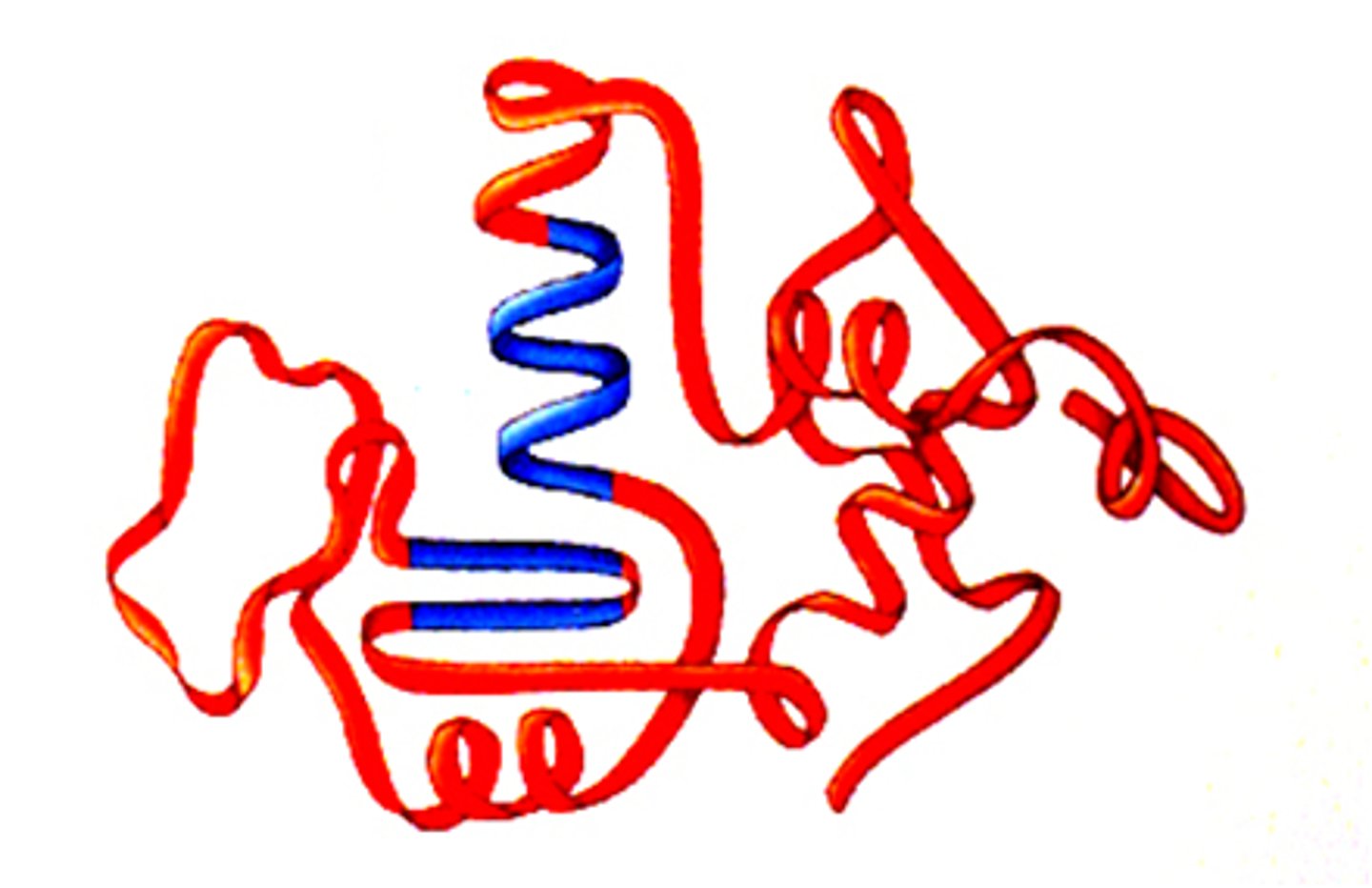
tertiary structure
The third level of protein structure; the overall, three-dimensional shape of a polypeptide due to interactions of the R groups of the amino acids making up the chain.
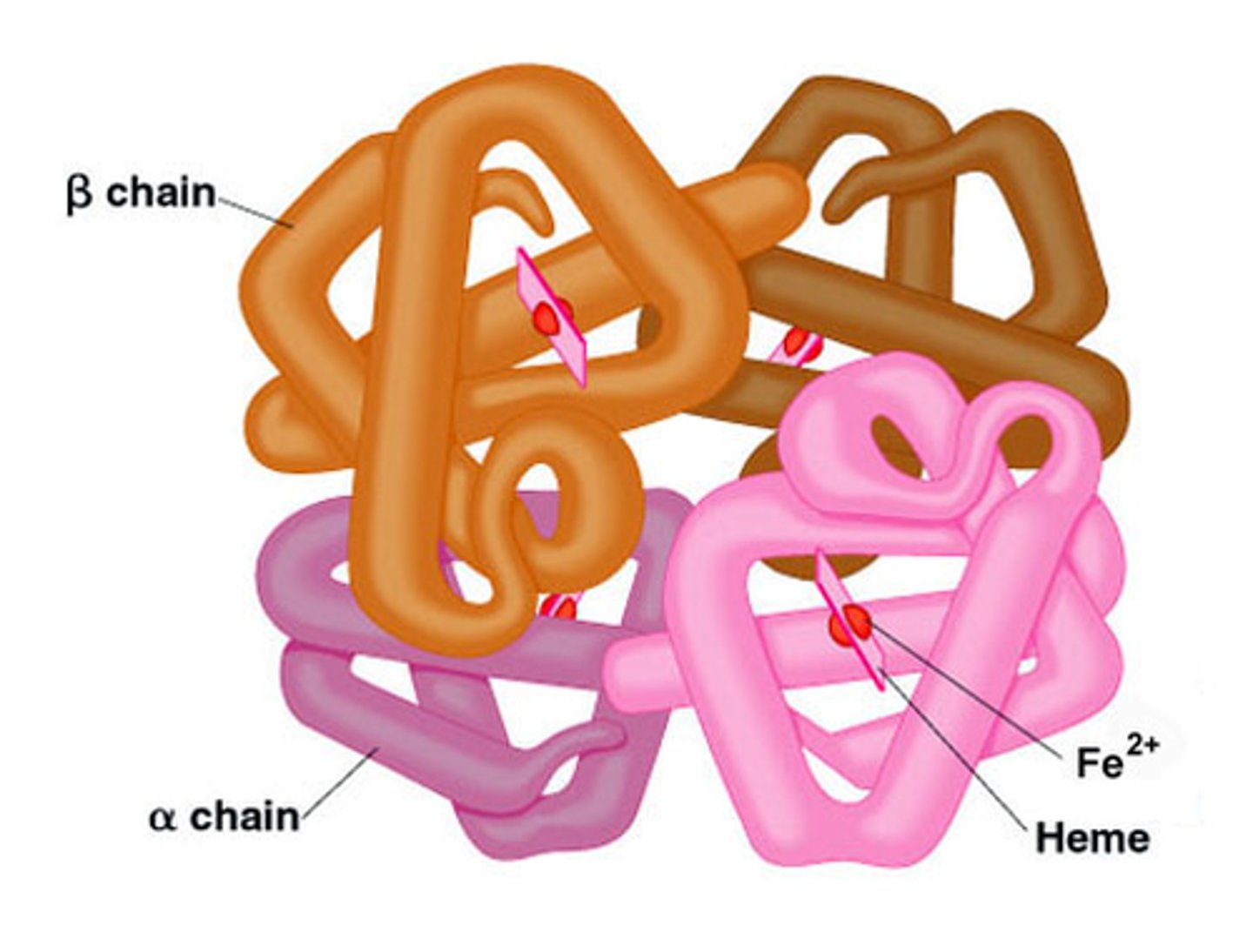
quaternary structure
The fourth level of protein structure; the shape resulting from the association of two or more polypeptide subunits.
polypeptides are
polymers of amino acids
proteins are polypeptides with
more complex 3D structures
polypeptides are polymers of amino acids.
polypeptides are the chain, proteins are the folded 3D shape
how to change a protein
apply heat
remove water
change pH (how many H ions are present)
protein function (1) ENZYMES
catalyze chemical reactions
protein function (2) CELL MEM. CHANNELS
allow materials in or out
protein function (3) CELL RECEPTORS
in membrane or within cell, bind to hormones or other signalers and initiate or stop chemical reactions within the cell
protein function (4) SUBCELLULAR STRUCTURE
organelle membranes, support DNA structure
other functions of protein
support, connective tissue
muscle function
hair and fingernails
energy source
macromolecule: LIPIDS
carbon atoms bonded covalently with hydrogen atoms
C-C
C-H
share equally, no ionization, non polar, hydrophobic
components of lipids
C, H, O
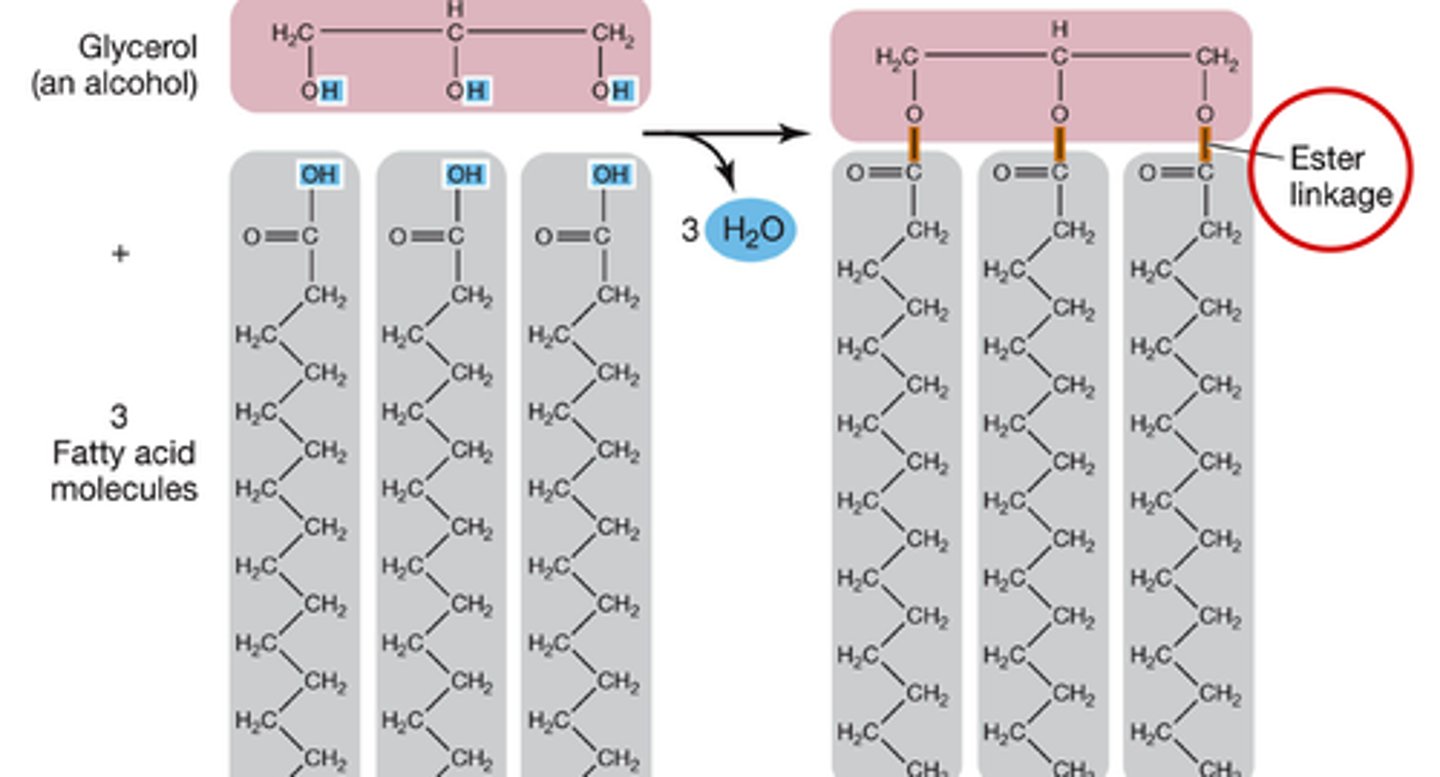
fatty acids, glycerol
fatty acids and glycerol
Building Blocks of Lipids
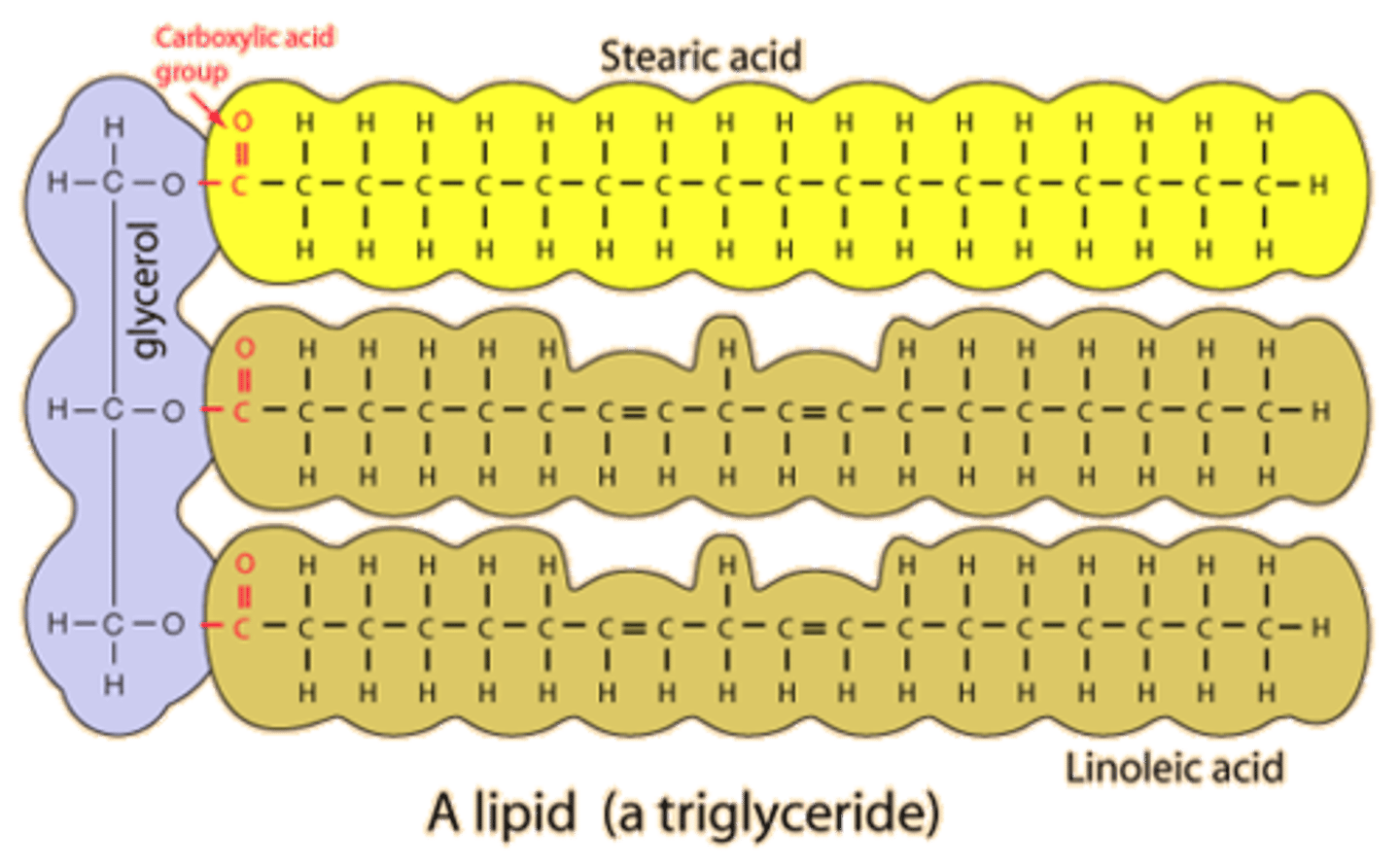
3 fatty acids and glycerol
fat molecule and 3 H20's after dehydration rxn
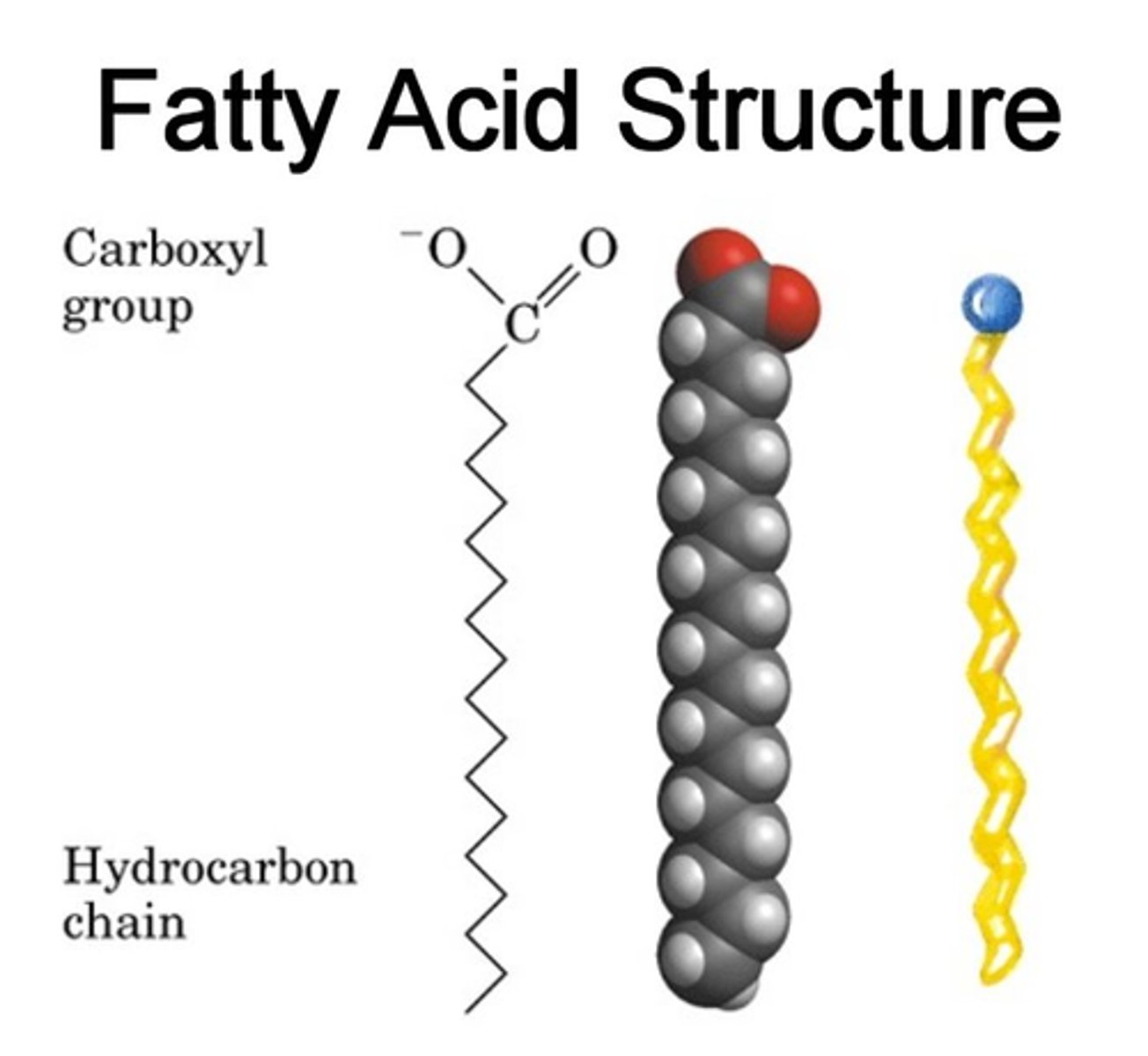
fatty acids
chains of carbon atoms bonded to hydrogen atoms
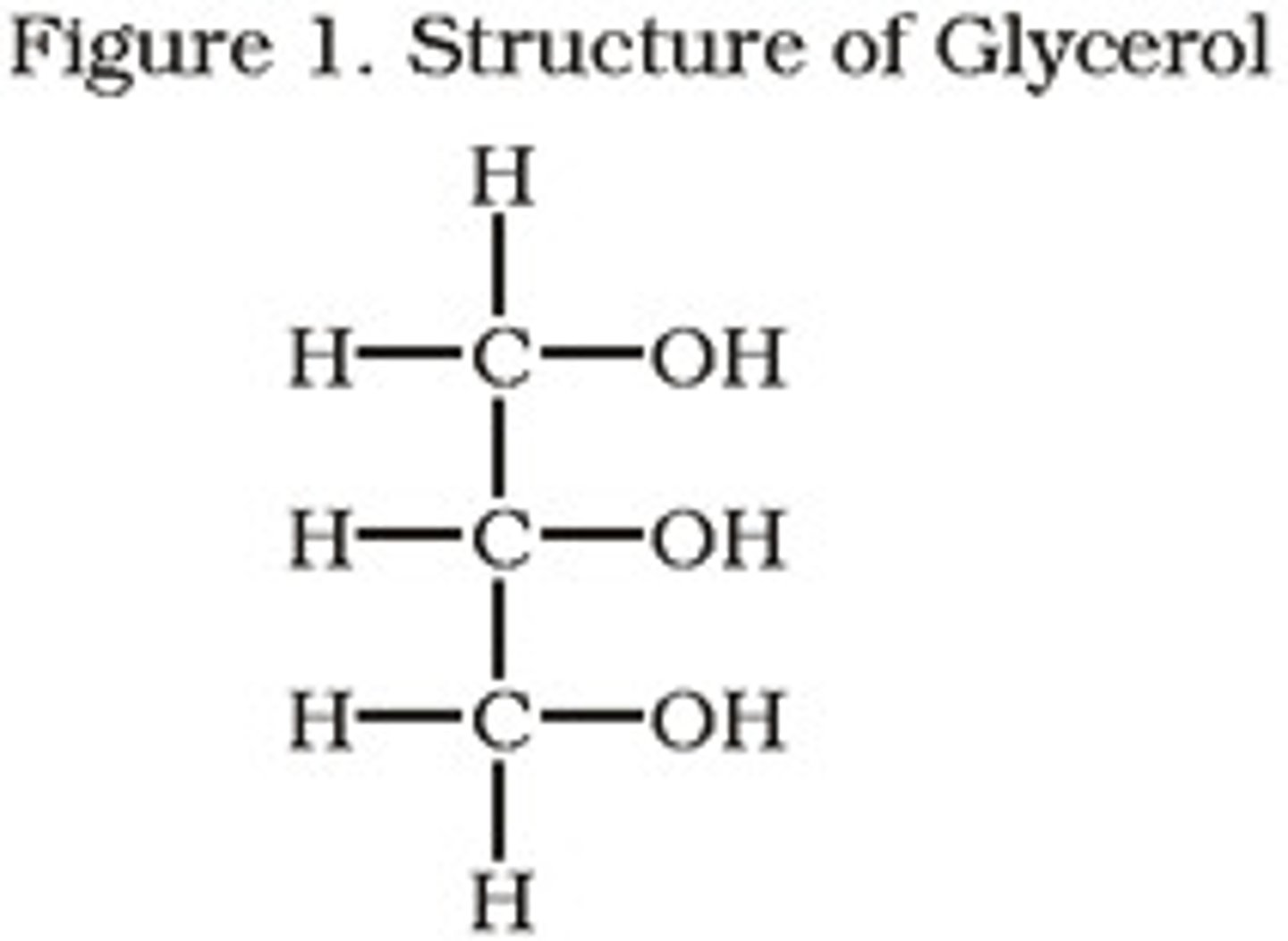
glycerol
A three-carbon alcohol to which fatty acids are covalently bonded to make fats and oils.
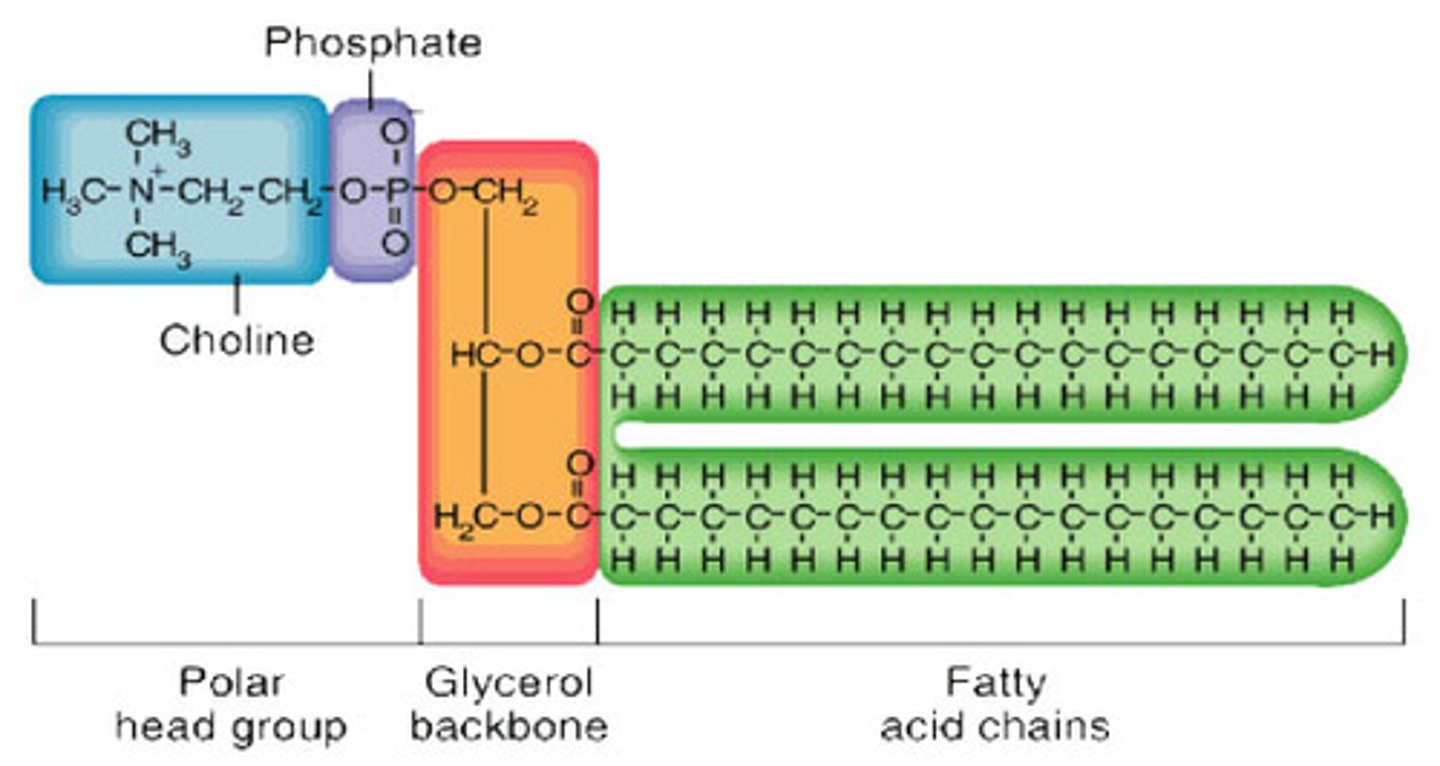
Phospholipids
a lipid consisting of a glycerol bound to two fatty acids and a phosphate group.
phosphate group - very polar (philic)
with loads of oxygens - hydrophilic
polar is
hydrophilic
nonpolar is
hydrophobic
lipid characteristics
hydrocarbons - make a chain or ring shape
nonpolar , C-H bonds
easily converted but not much variety
C-C-C-C-C-C-C backbone
lipids are often found bound to
polar molecules such as proteins, glycerol and amino groups.
CANNOT exist without attaching to a polar molecule
lipid functions (5)
cell membrane
steroid hormone
energy storage (adipose tissue)
cushioning (knee joints)
yellow bone marrow
macromolecules: NUCLEIC ACIDS
polymers of monomers. monomers are nucleotides
Nucleotides
Basic units of DNA molecule, composed of a sugar, a phosphate, and one of 4 DNA bases
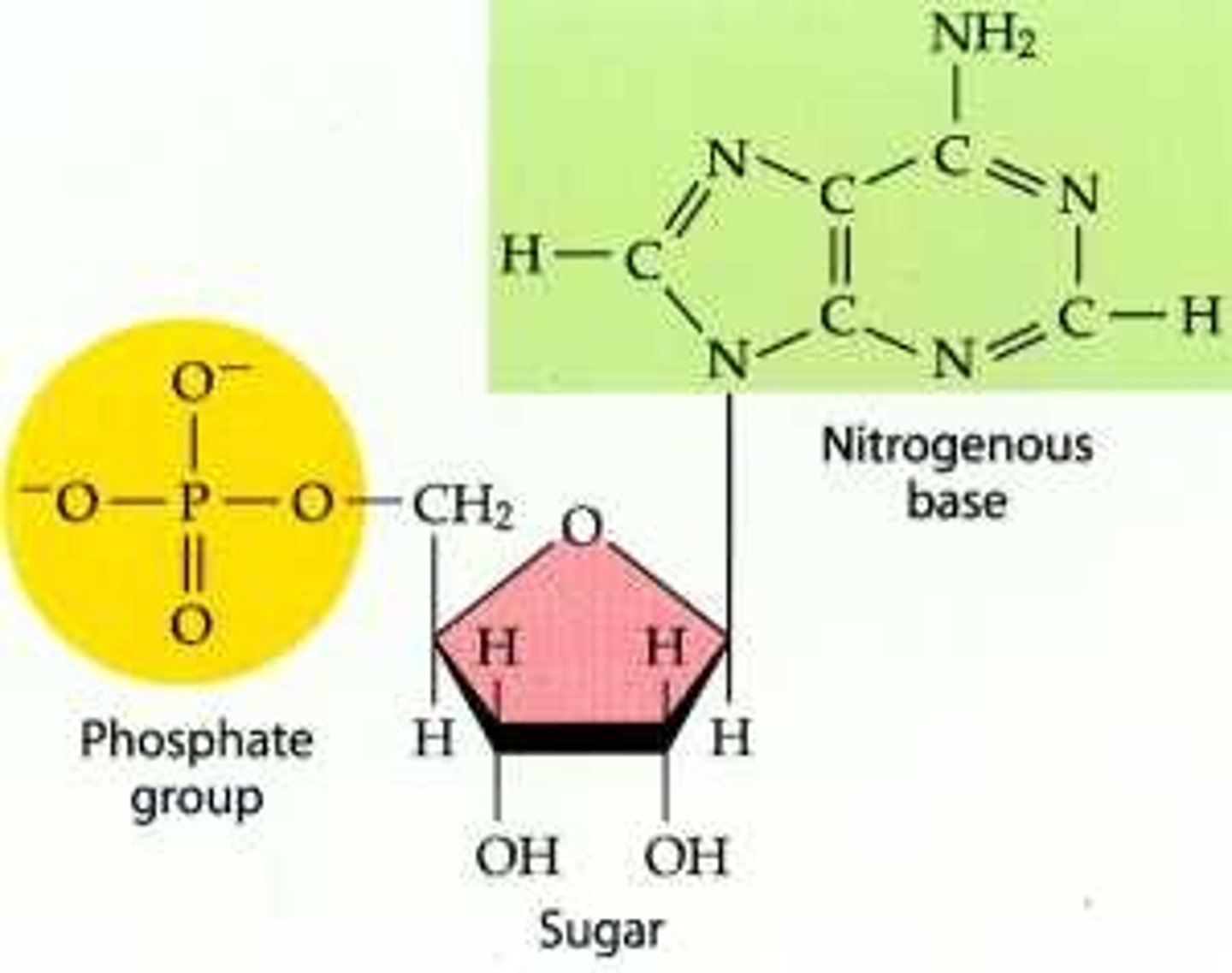
nitrogenous base
An organic base that contains nitrogen, such as a purine or pyrimidine; a subunit of a nucleotide in DNA and RNA.
DNA nitrogenous bases
Adenine, Thymine, Cytosine, Guanine (AT GC's)
RNA nitrogenous bases
Adenine, Uracil, Guanine, Cytosine (GUAC)
DNA: Good at _____ bonds. ______ because of O and N
Hydrogen Bonds. Polar.
Double Stranded, helix.
RNA is a
single-stranded nucleic acid that passes along genetic messages
how to count 5 carbons
5' at top, go counterclockwise, 4,3,2,1
Function of DNA: DNA replication
store genetic information. unzip, expose nitrogenous bases, formation of 2 strands
. DNA polymerase
Enzyme involved in DNA replication that joins individual nucleotides to produce a DNA molecule
DNA replication occurs
ONLY in preparation for cell division.
Nucleic Acid function
storage and transfer of genetic information
ATP - short term energy within a cell adenosine triphosphate
Aqueous environments constitute
45-60% of bodies in plants and animals
Properties of water (5 including acid/base def)
- polar solvent
- hydrogen bonding
-adhesion, cohesion, tension
-thermal stability
-acid/base, pH
- proton donor (acid)
- proton acceptor (base)
water resists heating and ____ (2)
hold heat well, insulates well
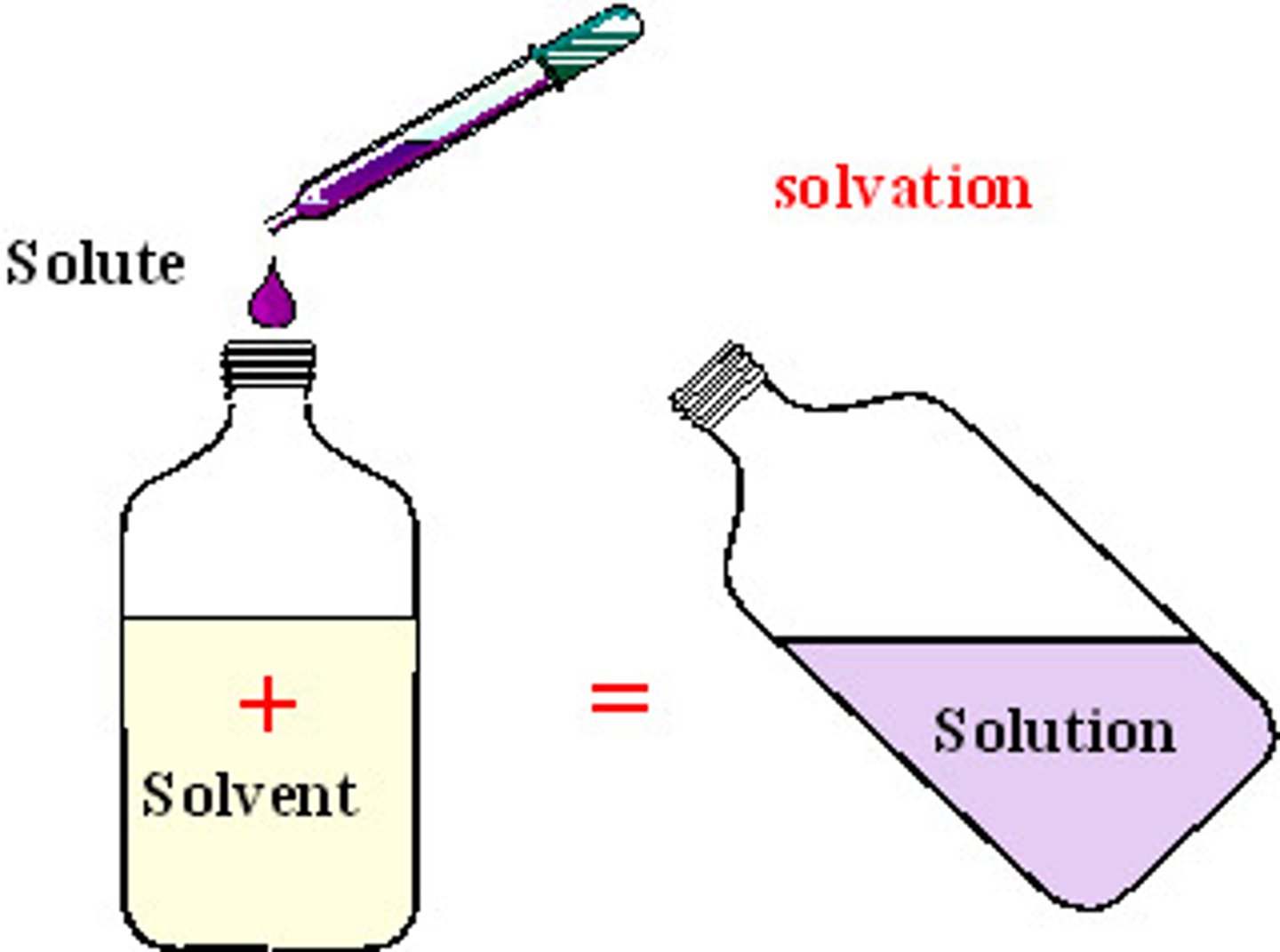
solution
A homogeneous mixture of solute and solvent
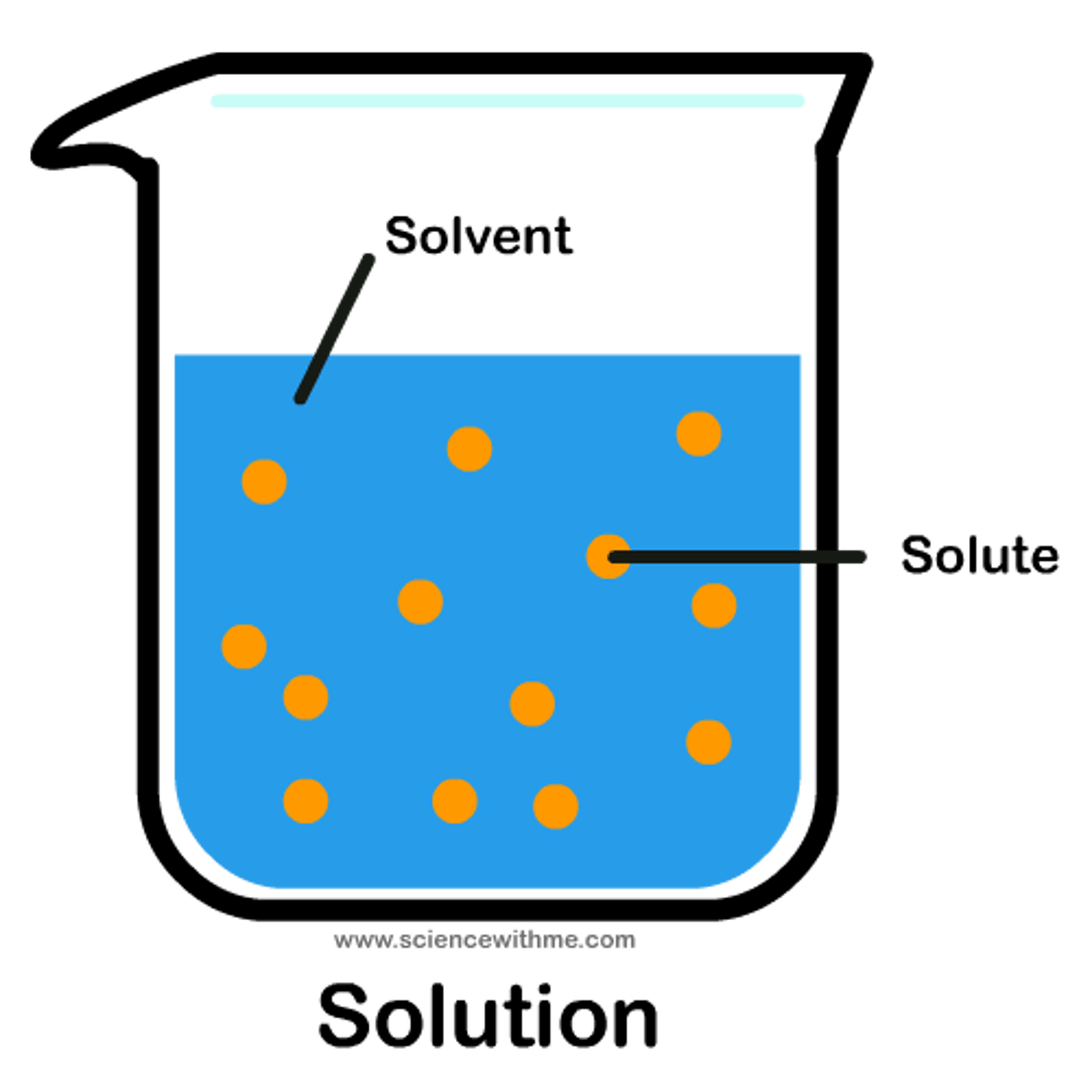
solute
Substance being dissolved
solvent
substance that does the dissolving
salt
An ionic compound made from the neutralization of an acid with a base. ( research more )
colloid
A mixture containing small, undissolved particles that do not settle out.
ex: flour in water

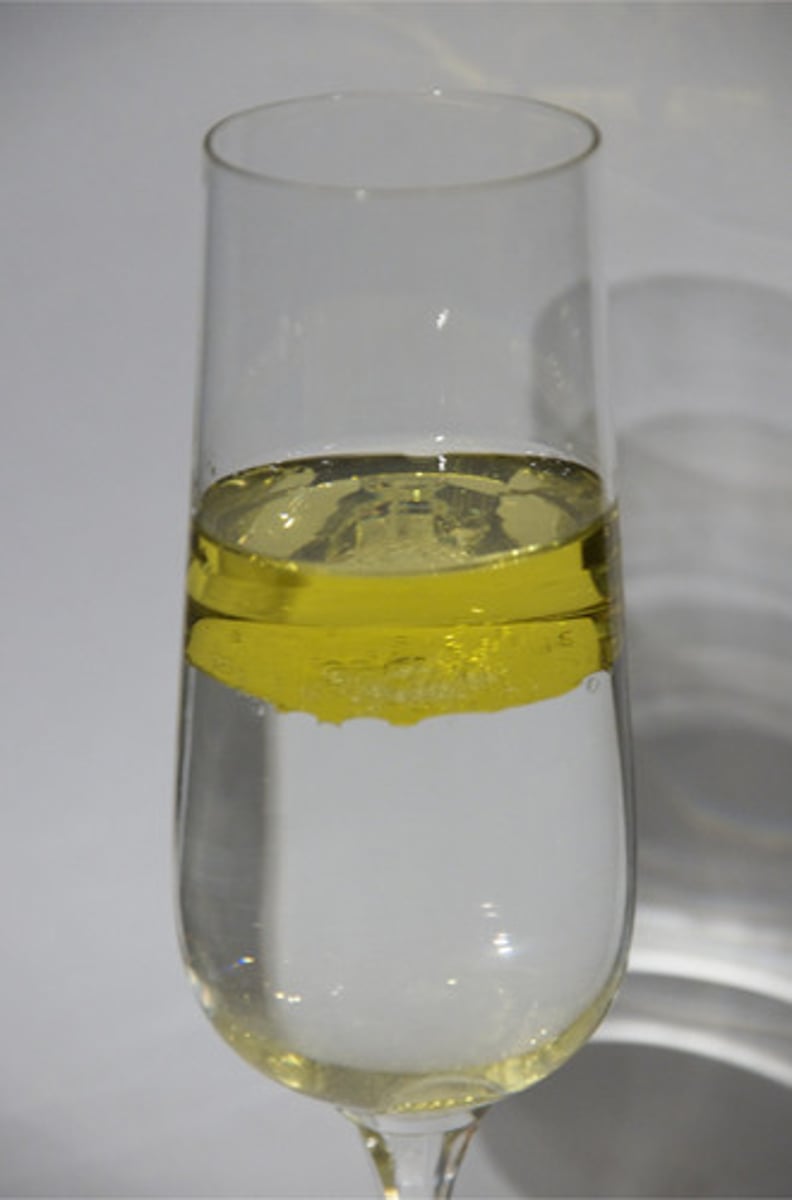
emulsion
any mixture of two or more immiscible liquids in which one liquid is dispersed in the other
ex: oil/water

suspension
A mixture in which particles can be seen and easily separated by settling or filtration. cloudier than a colloid
most fundamental acid base rxn is the
dissociation of water
H20 -- H+ + OH-
[ ] means
concentration
highest pH
14

lowest pH
1
pH of pure water
7 (neutral)
strong acid
ionize freely, easily give up H+
weak acid
ionizes slightly, keeps H+ bond
strong base
strongly binds H+
weak base
weakly binds H+
buffer
A chemical substance that resists changes in pH by accepting hydrogen ions from or donating hydrogen ions to solutions - weakening acids and bases
pertaining to nucleic acids: gene
sequence of DNA nucleotides that determines the order of amino acids in a polypeptide
pertaining to nucleic acids: locus
location of a chromosome where a gene is found
pertaining to nucleic acids: pyrimidine base
single ringed, thymine, cytosine, uracil
pertaining to nucleic acids: purine base
double ringed, adenine and guanine
Transcription
specific part of a DNA molecule unzipped and RNA nucleotides are added by RNA polymerase. RNA transcript is then processed - complementary bases, not a copt
DNA --> RNA what does the arrow represent
the flow of information. Guided by the DNA "blueprint", transcribed by RNA. no chemical changes. the process is transcription.
DNA to primary RNA to mRNA
see notes page 21
DNA contains information for ____ to make ______ --> Proteins
for amino acids to make polypeptides ---> proteins
the genetic code
collection of codons of mRNA, each of which directs the incorporation of a particular amino acid into a protein during protein synthesis
universal to all living things
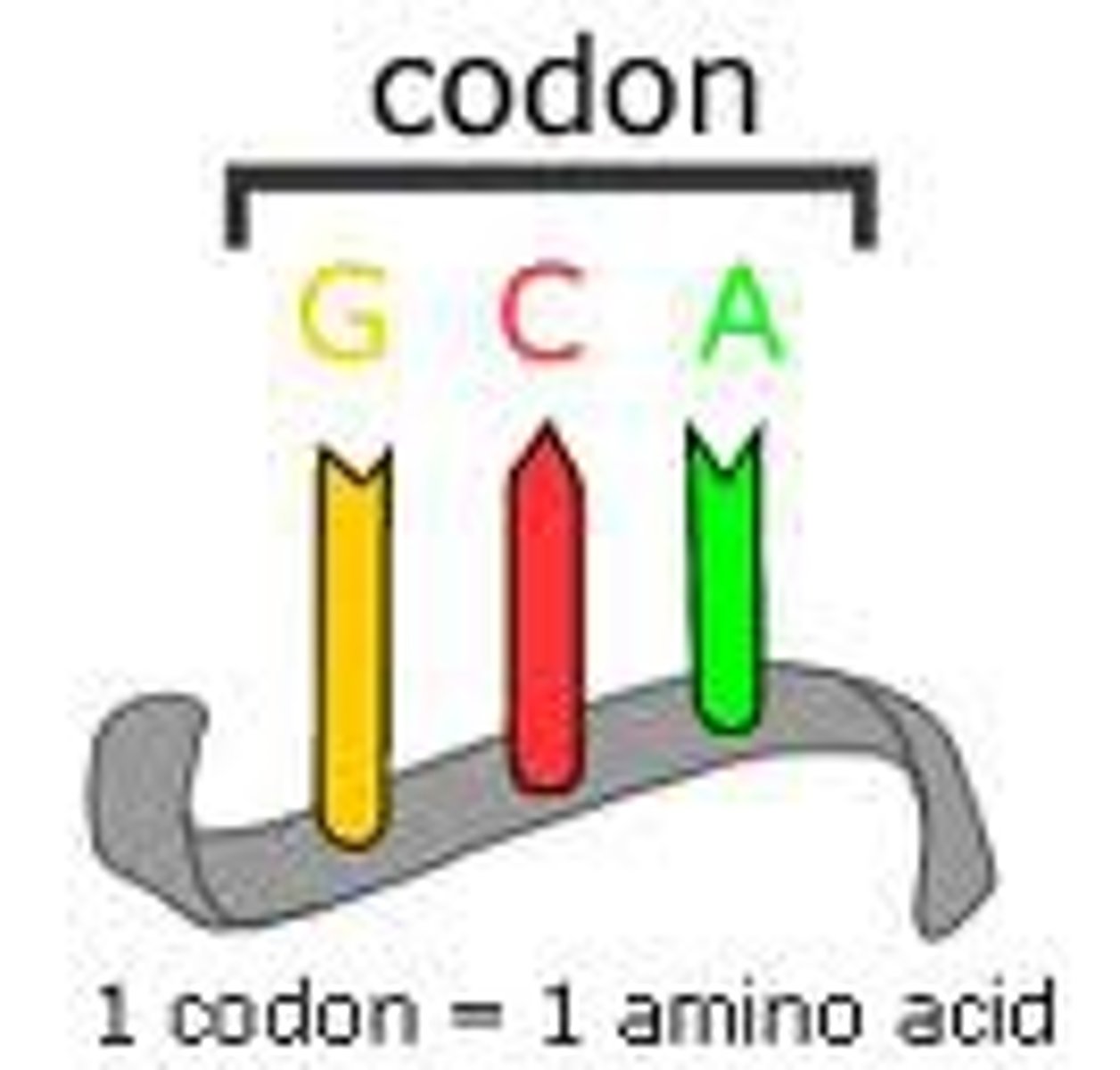
codon
A specific sequence of three adjacent bases on a strand of DNA or RNA that provides genetic code information for a particular amino acid