Tissues & Membranes
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
19 Terms
Tissue
Group of cells that have similar structure and that function together as a unit.
Intercellular Matrix
Intercellular matrix (nonliving) fills the spaces between the cells.
Abundant in some tissues and minimal in others
May contain special substances like salts and fibers and are unique to a specific tissue and gives distinctive characteristics.
Four Main Body Tissues
Epithelial
Connective
Muscle
Nervous
Epithelial Tissue
Form the covering of all body surfaces, line body cavities and hollow organs, and are the major tissue in glands.
Functions: Protection, secretion, absorption, excretion, filtration, diffusion, and sensory reception.
Tightly packed together - little intercellular matrix. The cells have one free surface that’s not in contact with other cells.
Cells are attached to underlying connective tissue by non-cellular basement membrane
Membrane is a mix of carbs and proteins secreted by epithelial and connective tissue cells.
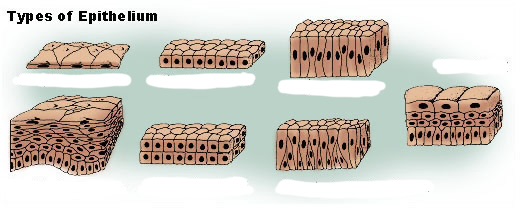
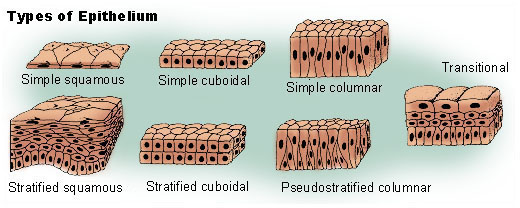
Types of Epithelium
Simple squamous
Thin, single layer of flat cells that line various surfaces in the body + helps the movement of gases between lungs and blood vessels.
Simple cuboidal
In glandular tissue and the kidney tubules
Simple columnar
Lines the stomach and intestines
Transitional
AKA urothelium + specialized type of stratified epithelium that lines the urinary tract: bladder, ureters, and urethra.
Stratified squamous
Protection against mechanical stress, abrasion, and microbial invasion
Stratified cuboidal
Protection in large exocrine glads, and helps with secretion
Pseudo-stratified columnar
Lines portions of the respiratory tract and some of the tubes of the male reproductive tract
Transitional
Can be distended or stretched
Glandular
Specialized to produce and secrete substances
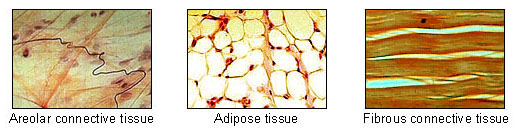
Connective Tissue
Functions
Bind structures together
Forms framework and support for organs and that body as a whole
Store fat
Transport substances
Protect against disease
Help repair tissue damage
Characteristics
Abundance of intercellular matrix with relatively few cells
Cells reproduce but not as rapidly as epithelial cells
Most have good blood supply but some don’t
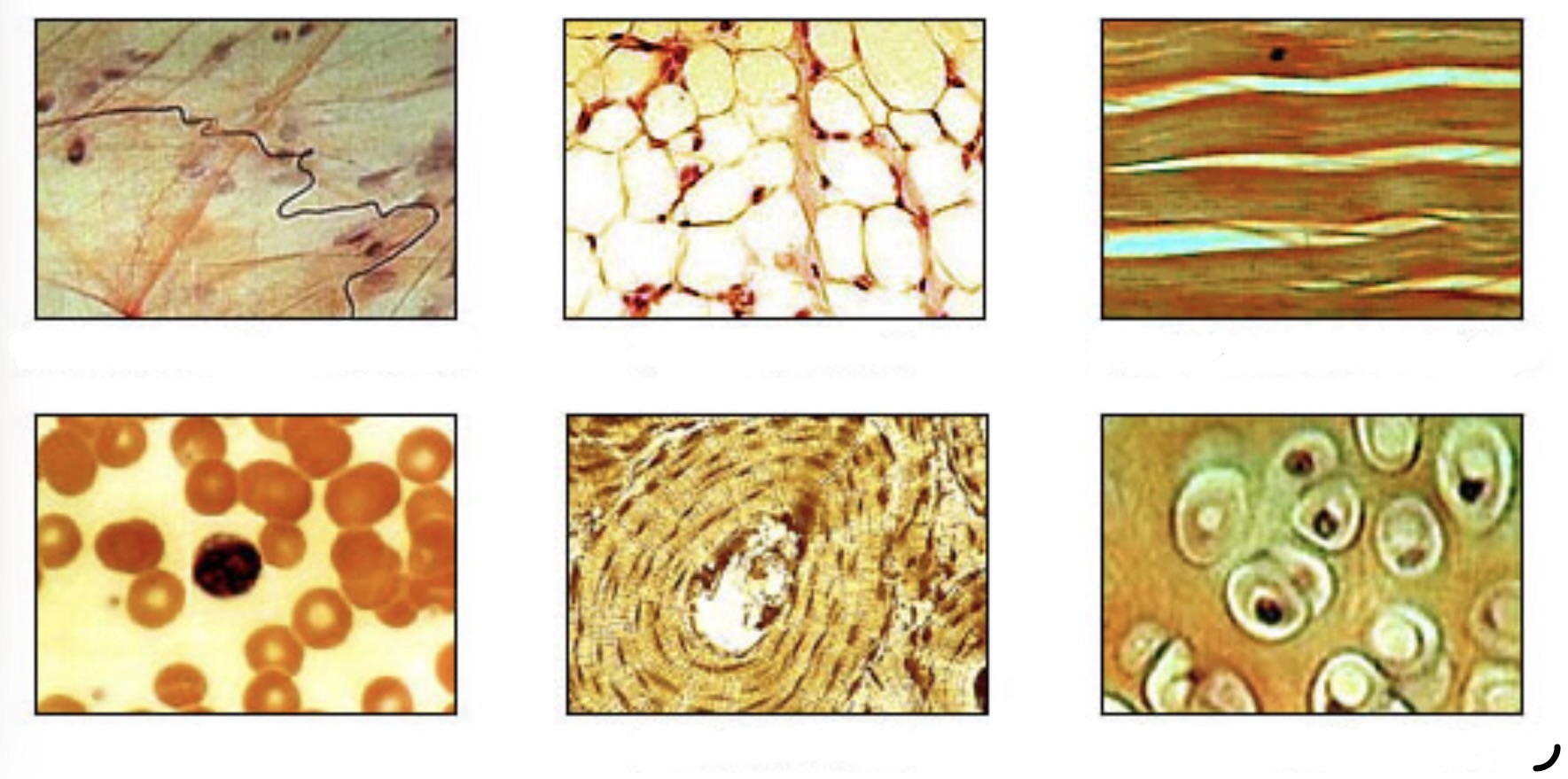
Connective Tissue Cell Types
Fibroblast
Macrophage
Mast Cell
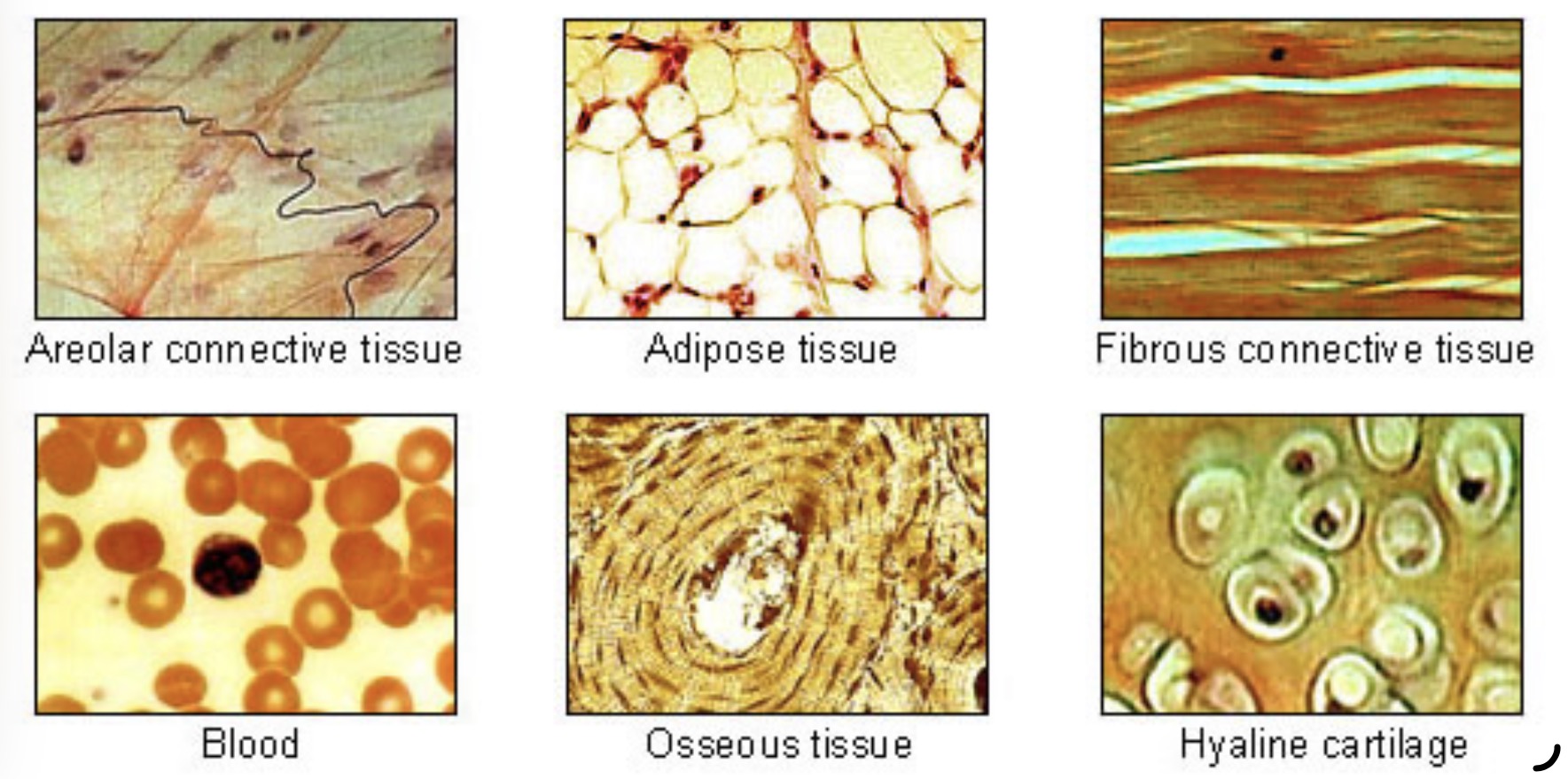
Includes:
Loose connective tissue
Adipose tissue
Dense fibrous connective tissue
Elastic connective tissue
Cartilage
Osseous tissue (bone)
Blood
Muscle Tissue
Composed of cells that have the special ability to shorten or contract to produce movement of the body parts
Tissue is highly cellular and is well supplied with blood vessels
Cells are long and slender
Sometimes called muscle fibers
Usually arranged in bundles or layers surrounded by connective tissue
Actin and myosin are contractile proteins in muscle tissue
Muscle tissue can be categorized into:
Skeletal muscle tissue
Smooth muscle tissue
Cardiac muscle tissue
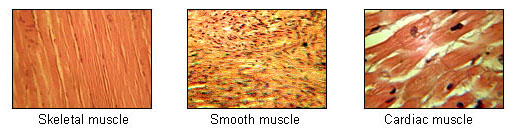
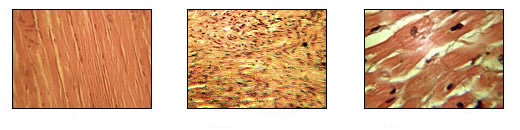
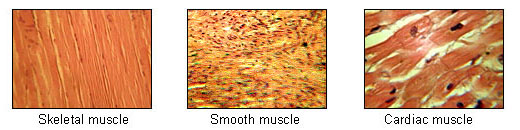
Muscle Tissue Types
Skeletal muscle fibers
Cylindrical
Multinucleated
Striated
Under voluntary control
Smooth muscle cells
Spindle shaped
Single centrally located nucleus
Lacks striations
Cardiac muscle
Branching fibers
One nucleus per cell
Striations
Intercalated disks
Contraction is not under voluntary control
Nervous Tissue
Found in the brain, spinal cord and nerves
Responsible for coordinating and controlling body activities
Stimulates muscle contraction
Creates awareness of environment
Plays major role in emotions, memory, and reasoning
Cells in nervous tissue need to be able to communicate with each other by way of electrical nerve impulses
Neurons (nerve cells) generate and conduct impulses
Three principle parts:
Dendrites
Cell body
Axon
Cell body is the main part of the cell and carries general functions
Nervous Tissue Cells
Three principle parts:
Dendrites
Extensions or processes of cytoplasm that carry impulses to cell body
Cell body
Main part of the cell and carries general functions
Axon
Extension or process that carries impulses away from the cell body
Cells that do not transmit impulses but support the activities of neurons:
Glial cells (neuroglial cells) Together the neuroglia
Supporting or glia cells bind neurons together and insulate neurons
Some are phagocytic and protect against bacterial invasion
Others provide nutrients by binding blood vessels to neurons
Membranes
Body membranes are thin sheets of tissue that:
Cover the body
Line body cavities
Cover organs within the cavities in hollow organs
Can be categorized into epithelial and connective tissue membrane
Types of Membranes
Epithelial Membranes
Mucous Membranes
Serous Membranes
Connective Tissue Membranes
Synovial Membranes
Meninges
Epithelial Membranes
Consist of epithelial tissue and the connective tissue that it is attached to.
Two main types of epithelial membranes are the mucous membranes and serous membranes
Mucous Membranes
Epithelial membranes that consist of epithelial tissue attached to underlying loose connective tissue
Membranes (mucosae) line the body cavities that open to the outside
Digestive tract is lined with this
E.g. respiratory, excretory, and reproductive tracts
Serous Membranes
Line body cavities that do not open directly to the outside
Cover organs located in those cavities
Covered by a thing layer of serous fluid secreted by the epithelium
Lubricates the membrane and reduces friction and abrasion when organs in the thoracic or abdominopelvic cavity move against each other or the cavity wall
Have special names given according to location
E.g. Lining the thoracic cavity and covers lungs is called pleura
Connective Tissue Membranes
Contain only connective tissue
Synovial membranes and meanings belong to this category
Synovial Membranes
Connective tissue membranes that line the cavities of the freely movable joints such as the shoulder elbow and knee
Line cavities that do not open to the outside
Do not have a layer of epithelium
Secrete synovial fluid to joint cavities to lubricate the cartilage on ends of bones so they can move freely w/o friction
Meninges
Connective tissue covering on the brain and spinal cord
Is within the dorsal cavity
Provide protection