Neural Control of Basic Drives: Thirst and Hunger
1/11
Earn XP
Description and Tags
These flashcards cover key concepts related to the neural control of thirst and hunger, including hormones, brain regions, and feedback mechanisms.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
12 Terms
What are the two main drives regulated by the hypothalamus in response to hydration and energy balance?
How are they detected ?
Hunger and Thirst.
Directly by nutrients and BP
indirectly by sensing hormones and neuropeptides - mainly by specialised neurones in hypothalamus and circumventricular organs CVOs
Which part of the brain contains specialised neurons that detect hunger and thirst stimuli?
The hypothalamus. and CVOs
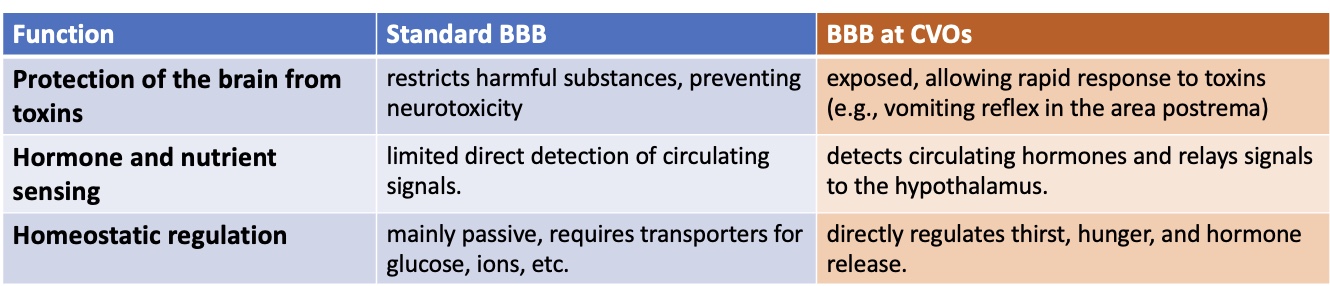
What role do Circumventricular Organs (CVOs) play in hunger and thirst regulation?
what and where are they ?
How ?
-They monitor blood composition and facilitate blood-brain communication. Plays a key role in the detection of hunger and thirst signals.
they are small leaky areas in blood brain barrier located around the third and fourth ventricles of the brain, allowing them to detect changes in blood chemistry.
capillaries lack endothelial tight junctions, so allow movement.
What hormone is known as the ‘hunger hormone’?
Ghrelin.
How does leptin function in appetite regulation?
Leptin inhibits NPY/AGRP neurons and activates POMC/CART neurons to induce satiety.
Which receptors does Angiotensin II target to regulate thirst?
It targets receptors in the Subfornical Organ (SFO) and Organum Vasculosum Laminae Terminalis (OVLT).
What feedback mechanism inhibits thirst when water balance is restored?
Restored blood volume and decreased osmolality serve as negative feedback responses.
What is the significance of the arcuate nucleus in appetite regulation?
It serves as both a hunger and satiety centre, responding to various internal cues.
Which type of internal cue is associated with inducing hunger?
Orexigenic signals.
What is the effect of insulin on appetite regulation?
It inhibits NPY/AGRP neurons and activates POMC/CART neurons to suppress hunger.
function of the blood brain barrier