Red Cell Suspension (RCS)
1/28
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Immunohematology | Laboratory
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
Red Cell Suspension
This provides the appropriate SERUM TO CELL RATIO to allow for grading and interpretation of tests results.
To remove the unwanted plasma proteins including antibodies that might interfere in the reactions.
To provide the appropriate serum to cell ratio to allow for grading and interpretation of tests results.
What is the purpose of preparing RCS?
Washed RBCs
These are RBCs that had most of the plasma, platelets, and white blood cells removed and replaced with saline or another type of preservation solution.
Plasma
Platelets
WBC
What components are removed from Washed RBCs?
Saline
Other preservative Solutions
What replaces the removed components in Washed RBCs?
Repeatedly suspending the whole blood in NSS
Mixing
Centrifuging and Decanting the supernatant completely
The preparation of Red Cell Suspensions involves:
0.9% Normal Saline Solution
This is used because it is ISOTONIC with the RBC Cytoplasm.
RBC Cytoplasm
NSS is isotonic with the ___________.
0.9%
What percentage or concentration of NSS is used in preparing RCS?
Water will neither go in nor go out of the RBC
What is the effect of the ISOTONIC NSS on RBCs?
Water will move out of the cell via osmosis;
Crenated RBCs
What is the effect of a HYPERTONIC solution to RBCs?
Water will go in the cell;
Swelling & Hemolysis
What is the effect of a HYPOTONIC solution to RBCs?
FALSE
Many procedures require demonstration of antigen and antibody reactions in vitro.
TRUE or FALSE
Many procedures done in the laboratory do not require demonstration of antigen and antibody reactions in vitro.
2-5%
What percentage of RCS is universally employed as an indicator to display antigen-antibody reactions?
Agglutination is difficult to visualize
Weak Positive can fail to be detected
What is the effect of using a concentration of RCS that is TOO LOW?
It may mask weak agglutination
What is the effect of using a concentration of RCS that is TOO HIGH?
"“ADCR” - RCS
ABO and Rh Typing
Direct Antiglobulin Test
Compatibility Testing (Cross-Matching)
Red Cell Phenotyping
Give four (4) uses of Red Cell Suspension
“ADDR” - 2-5% RCS
ABO and Rh Typing
Direct Antiglobulin Test and Auto Control
Donor Unit Compatibility (Cross-Matching)
Red Cell Phenotyping
Give four (4) uses of 2-5% Red Cell Suspension
“DDII” - 0.8% RCS
Direct Antiglobulin Testing
Donor Unit Compatibility (Cross-Matching)
Indirect Antiglobulin Test
Identification Panel Test Cells
Give four (4) uses of 0.8% Red Cell Suspension
Whole Blood in EDTA
What specimen is used in preparing RCS?
Normal Saline Solution (0.85% - 0.9% NaCl)
Phosphate-Buffered Saline (PBS)
Low Ionic Strength Solution (LISS)
Other enhancement media
What reagents are used in preparing RCS?
Centrifuge
Serological Pipettes (1 mL, 3 mL, or 5 mL)
Graduated Pipettes or Micropipettes with Disposable Tips
Test Tubes (10 x 75 mm or 12 x 75 mm)
Test Tube Rack
Wash Bottle or Dropper for Saline or PBS
List the six (6) laboratory equipment used in preparing RCS.
Transfer 3 mL of EDTA blood in a test tube
Fill the test tube with NSS (3/4 of the tube)
Centrifuge for 1 minute at 3,400 rpm
Decant the supernatant saline solution in a quick manner
Avoid disturbing the PRBCs
Repeat 3-5x (steps 2-5)
Label clean test tube with patient’s name and desired concentration of RCS
Deliver 300 uL of washed patient’s red cells + 9,700 uL NSS in a test tube (TV: 10 mL)
Properly mix the suspension to achieve tomato red color (preferred)
Enumerate the nine (9) steps in performing RCS.
3/4
How much of the test tube should be filled with NSS?
3-5 times
How many times is the cell washing performed in RCS preparation?
3400 rpm for 1 minute
What is the centrifuge setting for RCS preparation?
Quick manner without disturbing the PRBCs
How will you decant the supernatant saline solution?
Tomato Red
What is the preferred color of the finished RCS procedure?
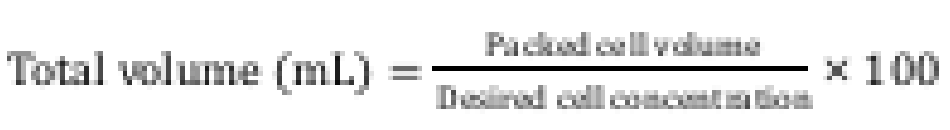
What is the formula to obtain the Packed Cell Volume?