Monopoly Ch. 15
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
14 Terms
Monopoly
A market structure characterized by a single seller or producer who controls the entire supply of a product or service without close substitutes and has significant pricing power (price setter).
Why monopolies arise
Monopolies can arise due to high barriers to entry for other firms, control over essential resources, government regulation granting exclusive rights, or significant economies of scale that make it inefficient for competitors to enter the market.
monopoly demand curve
typically downward sloping, indicating that a monopolist can set prices above marginal cost.
Marginal Revenue for a monopoly
The additional revenue generated from selling one more unit of a good or service, which declines as output increases due to the downward sloping demand curve. MR<P
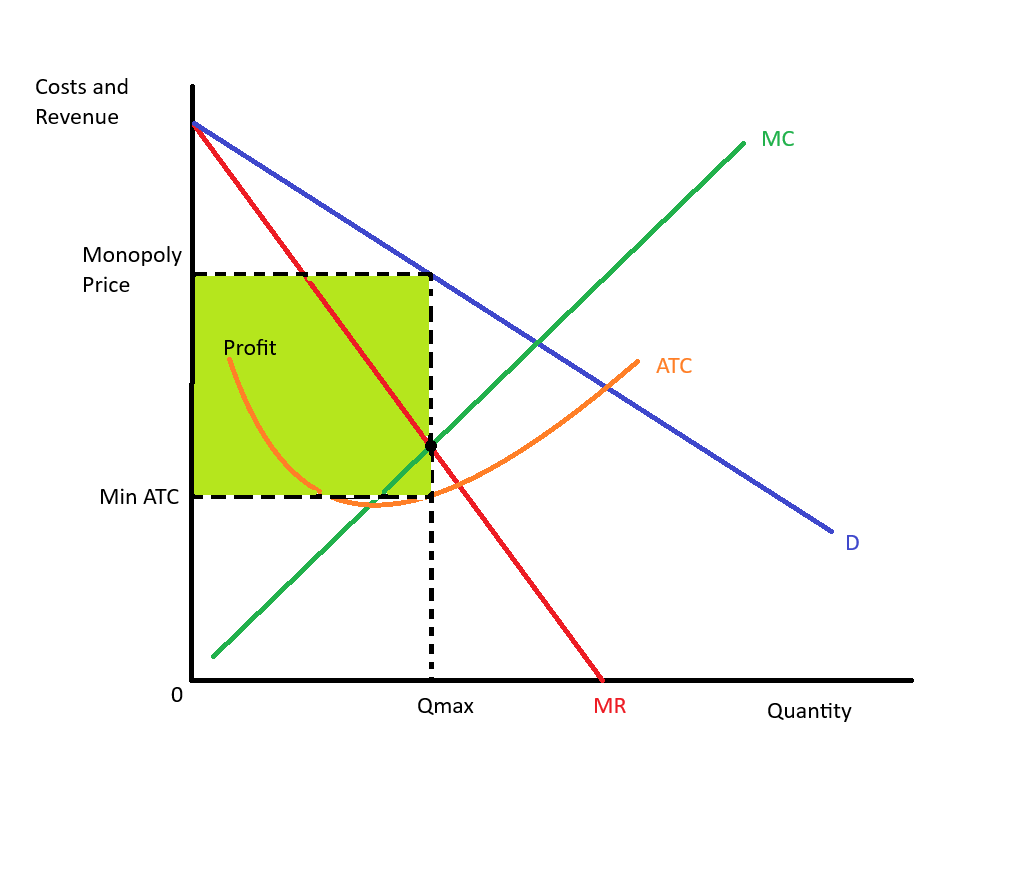
Profit-maximizing for monopoly
occurs where marginal cost equals marginal revenue, allowing the monopolist to maximize its total profit.
Competition Law
Regulations that promote competition and prevent monopolistic practices in markets, ensuring fair trade and protection against anti-competitive behavior.
Government Regulation of Monopolies
Government agencies regulate the price a monopoly may charge, usually P = MC to ensure fair pricing and promote consumer welfare.
Public Ownership
A situation where the government or collective owns and manages a resource or service, aiming to provide equitable access and prevent market monopolies.
Price Discrimination
A pricing strategy where different prices are charged to different customers for the same product or service, often based on willingness to pay.
perfect price discrimination
A type of price discrimination where a seller charges each customer the maximum they are willing to pay, capturing all consumer surplus.
second degree price discrimination
A pricing strategy where customers are charged based on the quantity purchased or the form of the product, often through discounts for bulk buying or product versions. Also called multi-part or block pricing.
third degree price discrimination
A pricing strategy where different prices are charged to different consumer groups based on identifiable characteristics, such as age or location.
Monopoly supply curve
A monopolist does not have a supply curve due to the price-setting nature of its market power.
Monopoly price/quantity diagram