Adult Pig and Ruminant GI
1/76
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
77 Terms
What toxin does C. perfringens proudce?
Beta toxin
What toxin does C. perfringens type A produce?
Alpha toxin
What is the only C. perfringens that matters for adult pigs?
C. perfringens type A
What is the main Clostridium type to cause infection in neonatal pigs?
C. perfringens type C
How do you inactivate C. perfringens toxin B?
Trypsin
Where is C. perfringens type A located
Normal soil and normal in the intestine
Why is significance of C. perfringens type A debated?
People are not sure how pathogenic it is, so isolation of C. perf type A alone does not count for diagnosis
What age does Lawsonia intracellularis infect?
3wks and older
What are the forms of Lawsonia intracellularis?
Proliferative form: Porcine intestinal adenomatosis or porcine proliferative enteropathy
Hemorrhagic form
Necrotic enteritis (ileitis)
What weight of pig increases the likelihood for hemorrhagic Lawsonia intracellularis?
>100kg
What is referred to as ileitis?
Lawsonia intracellularis
What species are affected by Lawsonia?
Pigs, horses, ferrets, rodents
What is the classic gross appearance of Lawsonia?
Enlarged small intestine
What is the pathogenesis of Lawsonia intracellularis?
Fecal oral contamination
Organism travels to distal ileal or colonic crypt epithelial cells
Endocytosed by epithelial cells
Marked mitotic and proliferative activity of infected cells
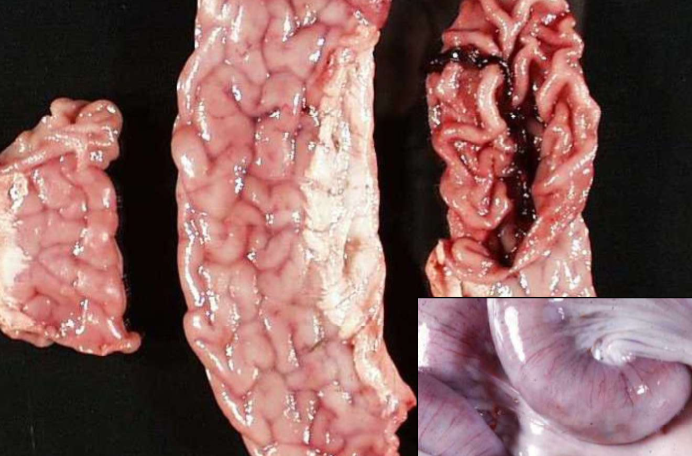
Proliferative Lawsonia
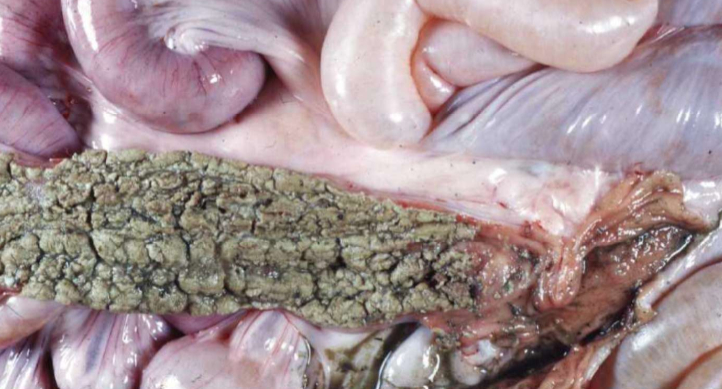
Necrotizing Lawsonia (cannot differentiate from Salmonella grossly)
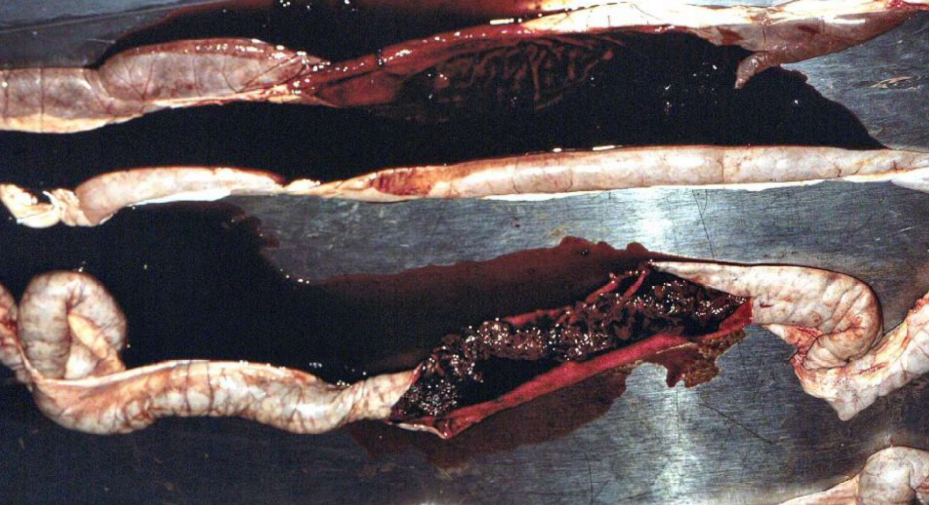
Hemorrhagic Lawsonia
How do you diagnose Lawsonia?
Histologic lesions
IHC
Silver stain
Why do we not culture Lawsonia?
It is difficult and not attempted
What is the causative agent of swine dysentery?
Brachyspira hyodysenteriae
Virulence of Spirochetes is based on what?
Production of Beta-hemolysin toxin
What does swine dysentery look like?
Hemorrhagic diarrhea in grow/finish pigs with fibrin and blood. Lesions are confined to large intestine
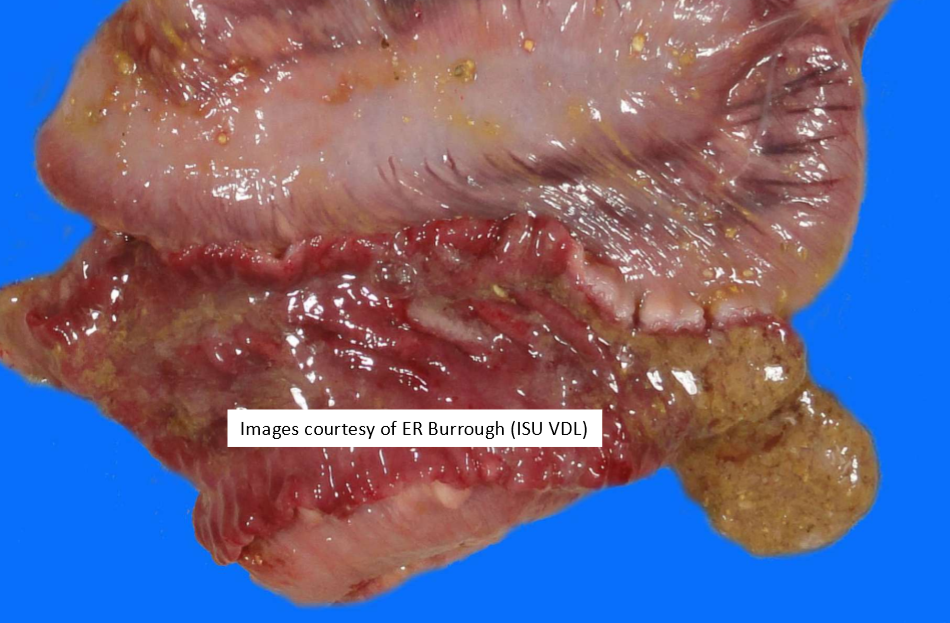
Brachyspira hyodysenteriae (swine dysentery)
Where is Brachyspira hyodysenteriae (swine dysentery) restricted to?
Large intestine
What is the pathogenesis of B. hyodysenteriae?
Proliferation in distal colon
Necrosis of colonic epithelium
Increased mucus secretion
Hemorrhage
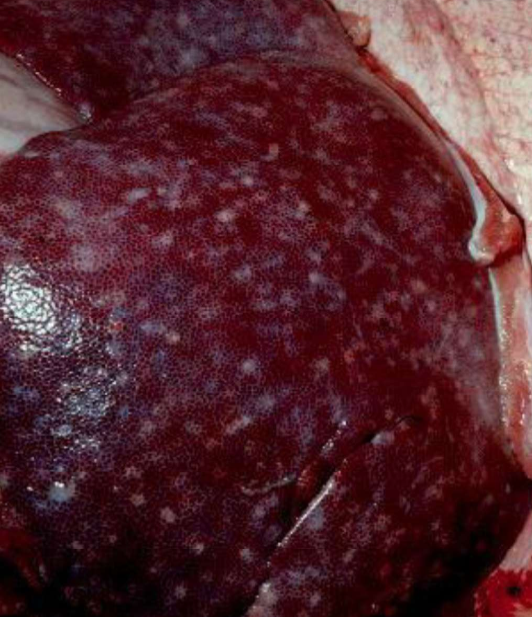
Milk spot liver
What does milk spot liver indicate?
Parasitic migration
What is the pathogenesis of Trichuris suis?
Direct trauma and hemorrhage in colonic mucosa
What does Trichuris suis look like?
Swine dysentery
T/F BVDV is a multisystemic disease?
True
What are the genotypes of BVDV?
1 and 2
What are the 2 main lesions of BVDV?
Epithelial necrosis and lymphoid necrosis
What are most cases of BVDV?
Mild transient cases
What is classical BVD?
High morbidity, low mortality with lethargy, anorexia, oculonasal discharge, oral ulcers
What is fetal infection BVDV?
Outcome depends on gestation stage you get either
PI calves
Mucosal disease
What are PI calves with BVDV?
Clinically normal with viremia, but no antibody causing constant viral shedding
Describe mucosal disease from a fetal infection of BVDV?
Occurs when PI animal is superinfected causing a low morbidity and high mortality
Where is the ulcers and necrosis of the GI system with BVDV?
The entire GI tract from esophagus to colon
What is the pathogenesis of BVDV lymphoid necrosis?
Infection
Lymphoid necrosis, epithelial necrosis
Peyer’s patch loss and necrosis
What is the pathogenesis of epithelial BVDV?
Crypt necrosis
Infect epithelial
Replicates in leukocytes
Necrosis and apoptosis of lymphoid tissue and epithelial cells
What is a major cause of diarrhea for nursery pigs?
Salmonella
What are the major causes of diarrhea for grow/finish pigs?
Lawsonia
Salmonella
Brachyspira
Parasitism (whipworms)
What is the pathogenesis of salmonellosis?
Fecal oral ingestion
Colonize small or large intestine
Secrete effector proteins
Necrosis of epithelium
Recruitment of inflammatory cells, fibrin
Disseminated via blood vessels
When should salmonella be you top ddx?
Fibrinonecrotizing enterocolitis in any location or species
Button ulcers
Ear tip necrosis
How does salmonellosis cause kidney lesions?
Endotoxemia
What toxins does C. difficile produce?
A and B
What are the lesions of C. difficile?
Diarrhea and fibrinous colitis in neonatal and older pigs
Mesocolonic edema
Where does C. difficile cause problems?
In the colon
How do you diagnose C. perf type C?
Seen in neonatal pigs. Genotyping is suggestive and toxin ID is confirmation
How do you diagnose C perf type A?
Genotyping, but you must rule out other causes before saying it is significant
How do you diagnose C. difficile?
Culture and toxin ID
How do you diagnose spirochetes?
Histologic lesions to suspect then feces or tissue culture with PCR is confirmatory
What are the lesions of PCV2?
Small intestinal granulomatous enteritis and lymphadenitis
What is the pathogenesis of PCV2?
Infection
Immunosuppression, lymphoid depletion and infection of macrophages
Proliferation in macrophages
How do you diagnose PCV2?
Multisystemic disease. Use histo lesions for suggestive then confirm with IHC or PCR
BVDV infection during days 30-120 of gestation results in what?
PI
BVDV infection after day 180 of gestation results in what?
Congenital infection where they are seropositive but clinically normal
How do you diagnose BVDV?
Antigen tests: IHC with an ear notch, ELISA, PCR
Antibody test with serology
What causes MCF?
Ruminant gamma-herpes virus (OvHV2)
What species get MCF?
Sheep
Describe the transmission of MCF
Sheep get it but are asymptomatic
Cattle get if from sheep and are symptomatic
What are the C/S of MCF?
Corneal edema, generalized lymphadenomegaly, ulcers in GI tract
Vasculitis
How do you diagnose MCF?
Histologic lesions, PCR, IHC, or ELISA
Vasculitis
What is MAP?
Mycobacterium avium paratuberculosis (Johne’s disease)
How is MAP (Mycobacterium avium paratuberculosis) spread?
Fecal oral
What is the progression of MAP?
Ingestion and passage to ileum in 20 hrs
Colonization of LNs in 1-4 months
Shed in feces for 1.5-3 years
Disseminated to other tissues 2-5 years
What is the morphologic diagnosis of MAP?
Granulomatous enteritis
What kind of diarrhea does MAP cause?
Malabsorption and protein loss diarrhea
What is the pathogenesis of MAP?
Fecal oral infections
Small intestinal and lymphoid infection
Macrophages get infected
Progressive granulomatous enteritis, malabsorption diarrhea
How do you diagnose MAP?
Culture, but it takes 16 weeks
Necropsy with lesions and acid fast staining help
Antemortem you can use PCR but it is inconsistent in early stages
What species does Clostridium perfringens type D infect?
Small ruminants
What toxin does C. perfringens type D produce?
Episolon toxin that is activated by trypsen
Describe episolon toxin from C. perfringens type D
Causes enterotoxemia in sheep in goats which leads to vasculitis and edema in brain, heart, kidney, and lung
Hemorrhage and necrosis in the colon in calves is caused by what?
coccidia or enteric coronavirus
What does coccidia do in goats?
Proliferation of epithelial cells
What does coccidia do in cattle?
Hemorrhage and necrosis in the colon
What does coccidia do in pigs?
Necrosis fibrin in small intestine