Cheat sheets 8/9 Molecular Genetics pt.1 and 2
1/65
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
66 Terms
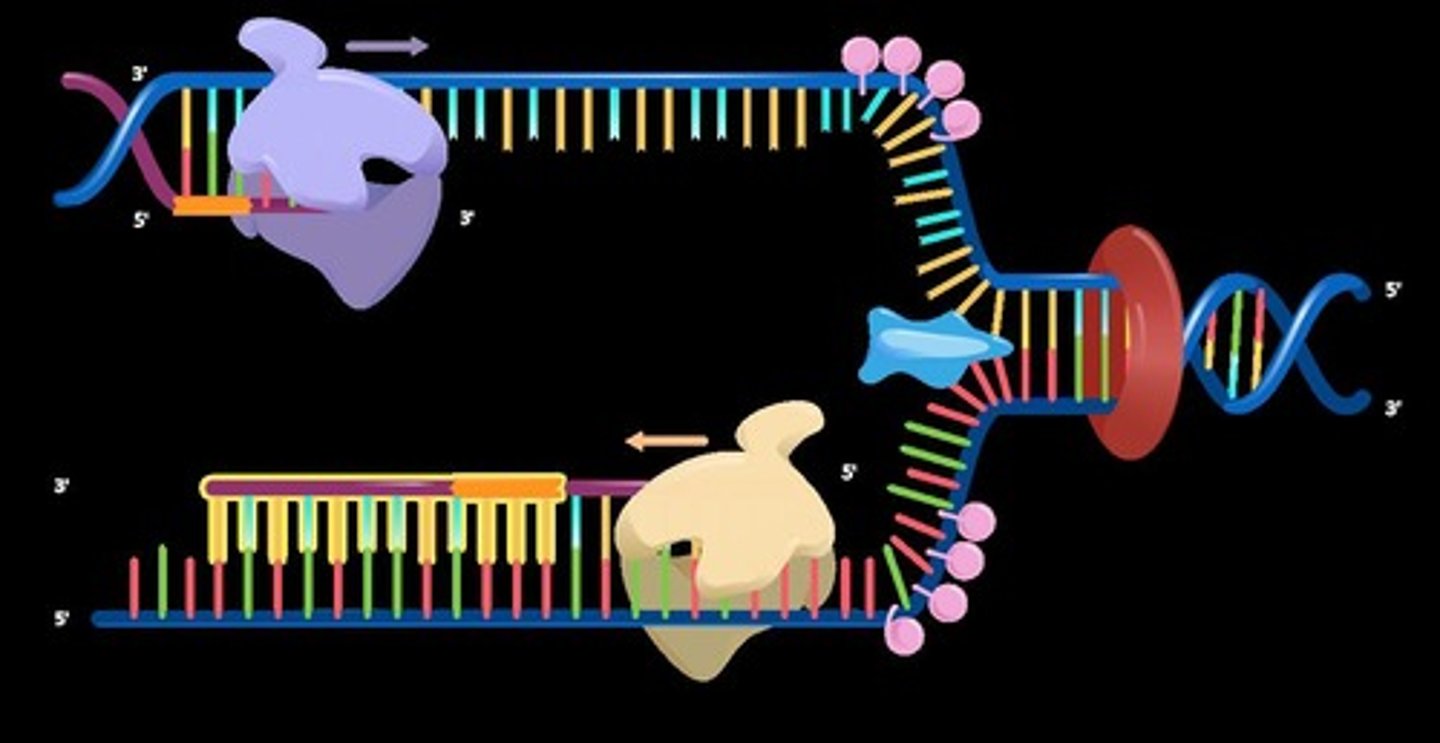
The process of copying genetic information in cells to produce two identical DNA molecules.
DNA Replication
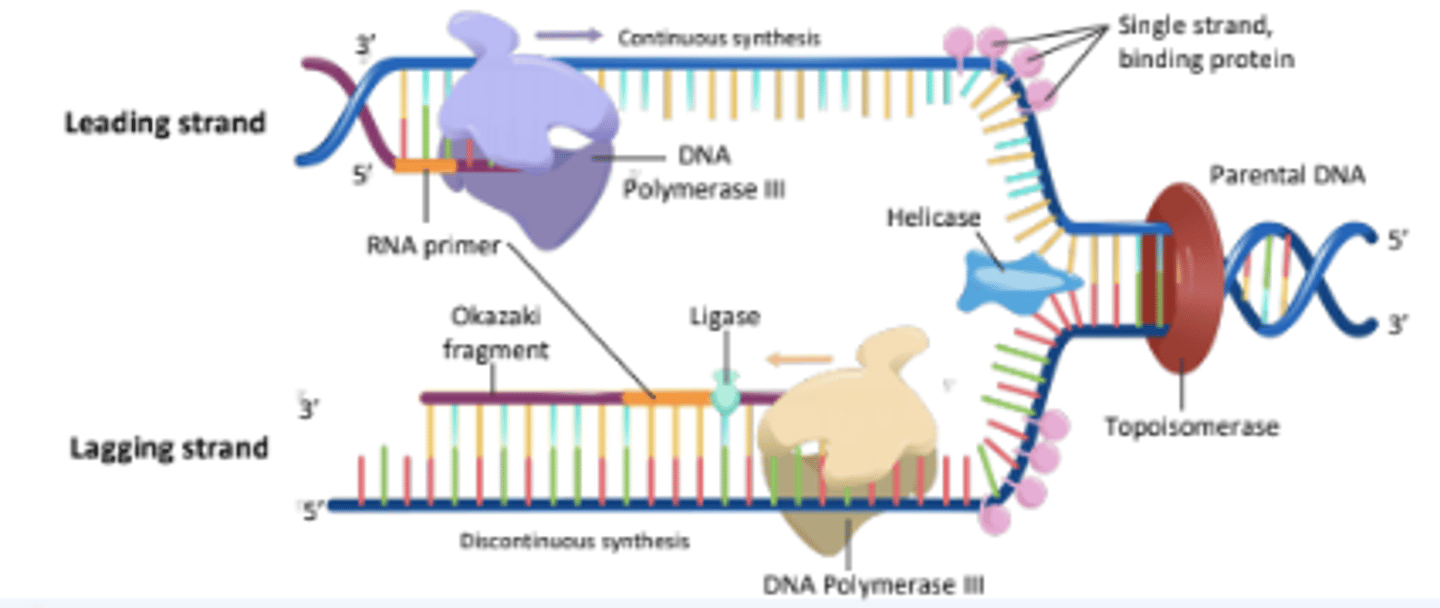
The strand of DNA that is synthesized continuously in the same direction as the replication fork opens.
Leading Strand
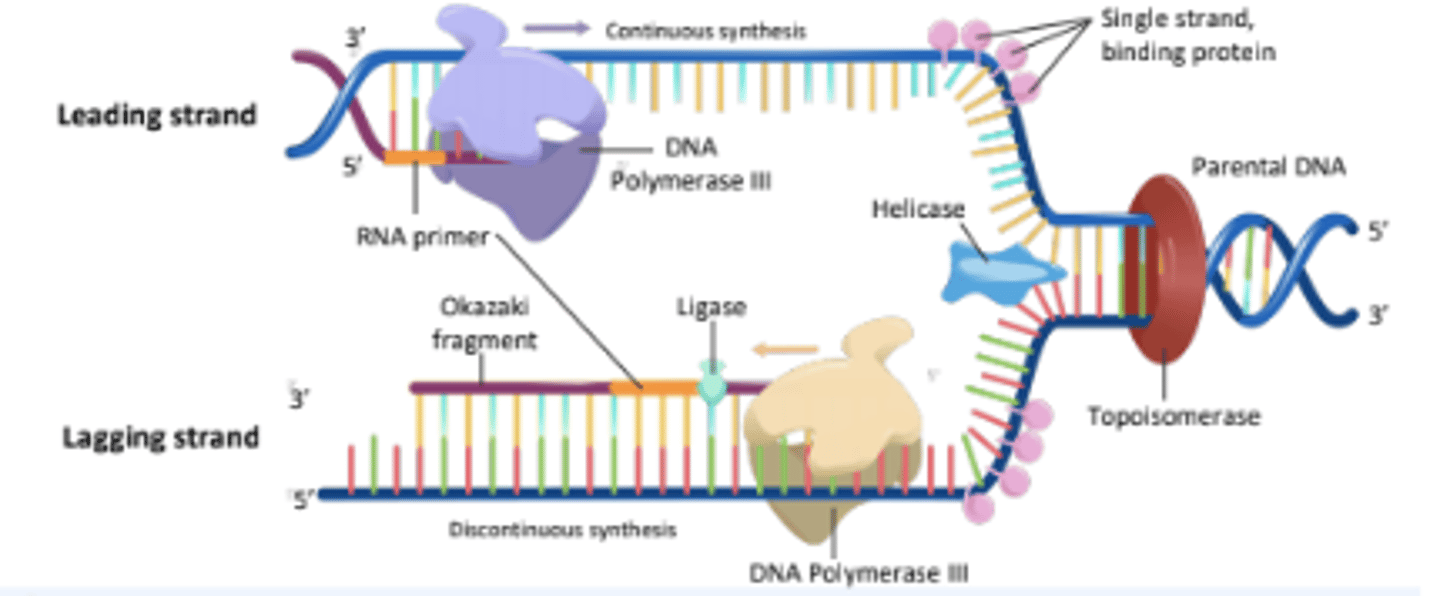
The strand of DNA that is synthesized discontinuously in short segments called Okazaki fragments.
Lagging Strand
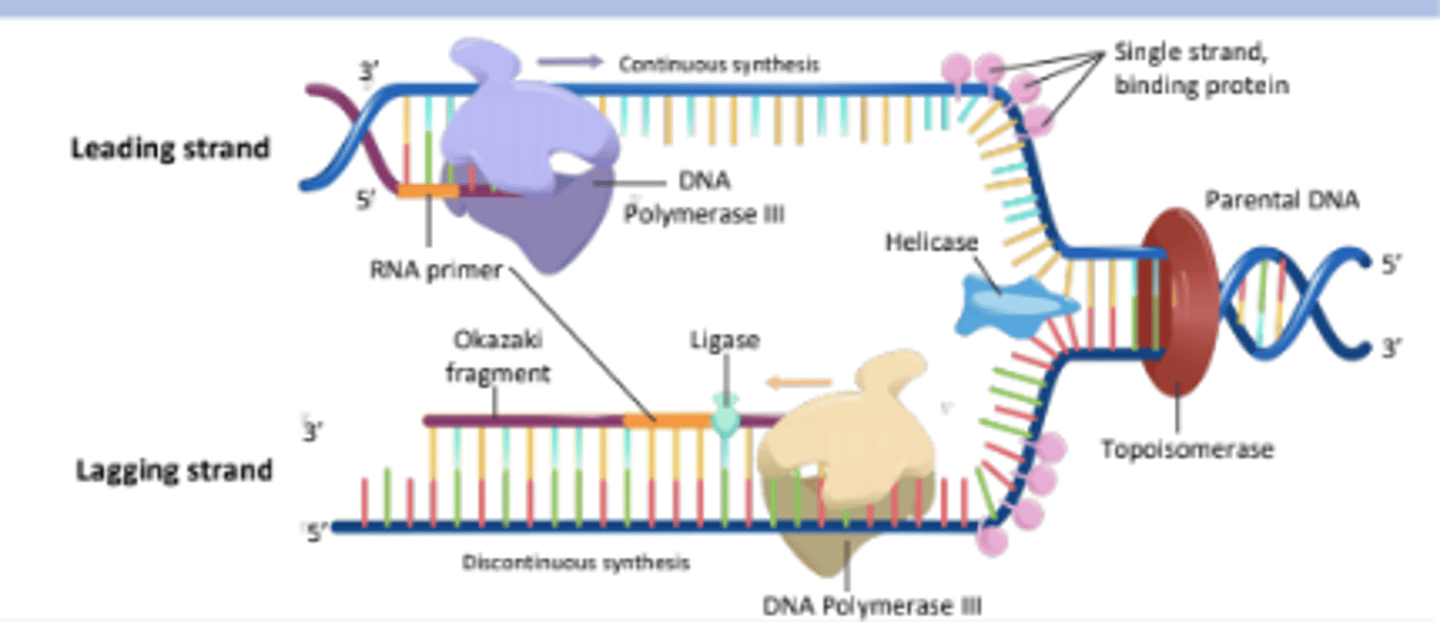
Short stretches of nucleotides synthesized on the lagging strand during DNA replication.
Okazaki Fragments
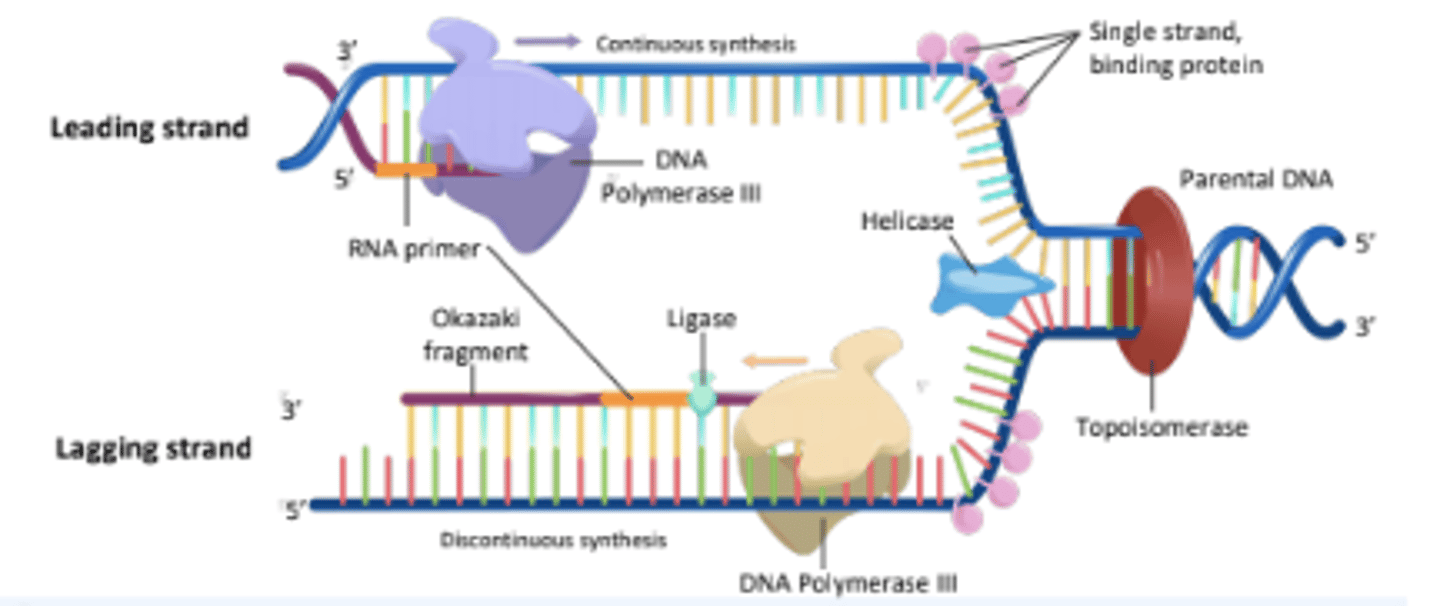
An enzyme that unwinds the DNA double helix, separating the two strands for replication.
Helicase
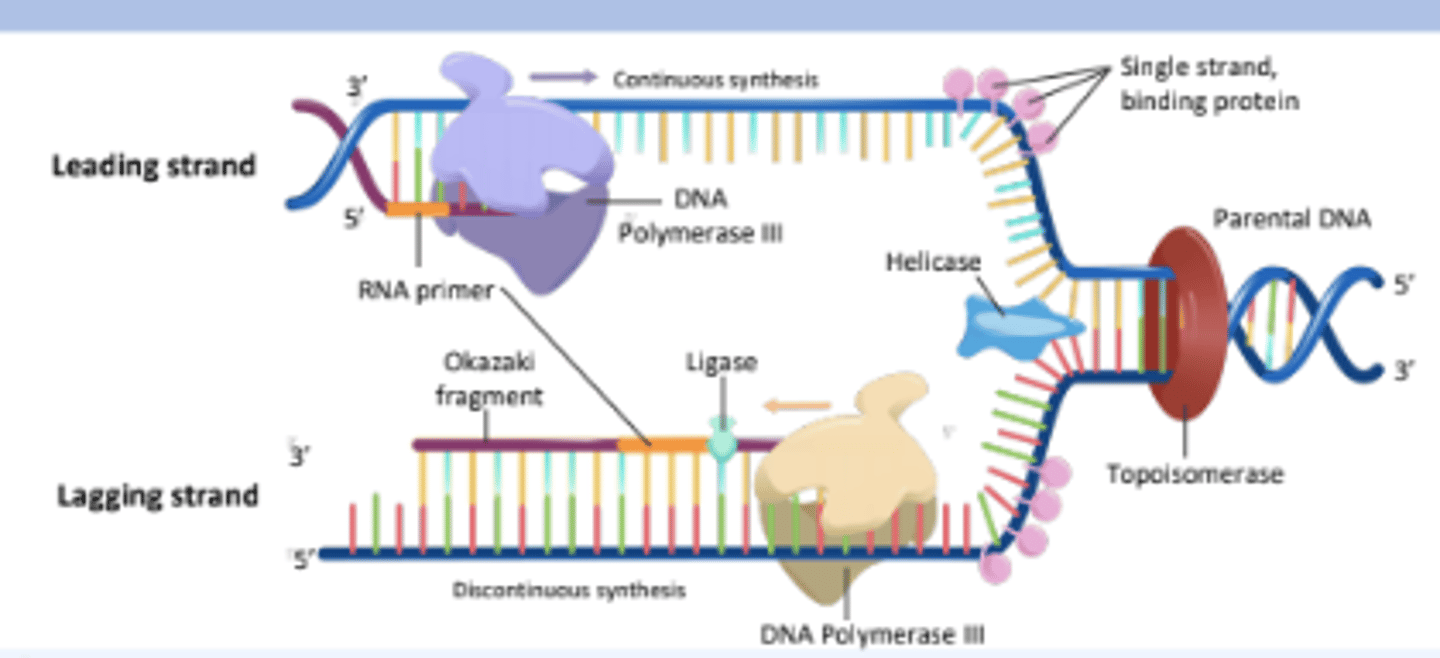
The enzyme responsible for synthesizing new DNA strands by adding nucleotides in the 5' to 3' direction.
DNA Polymerase III
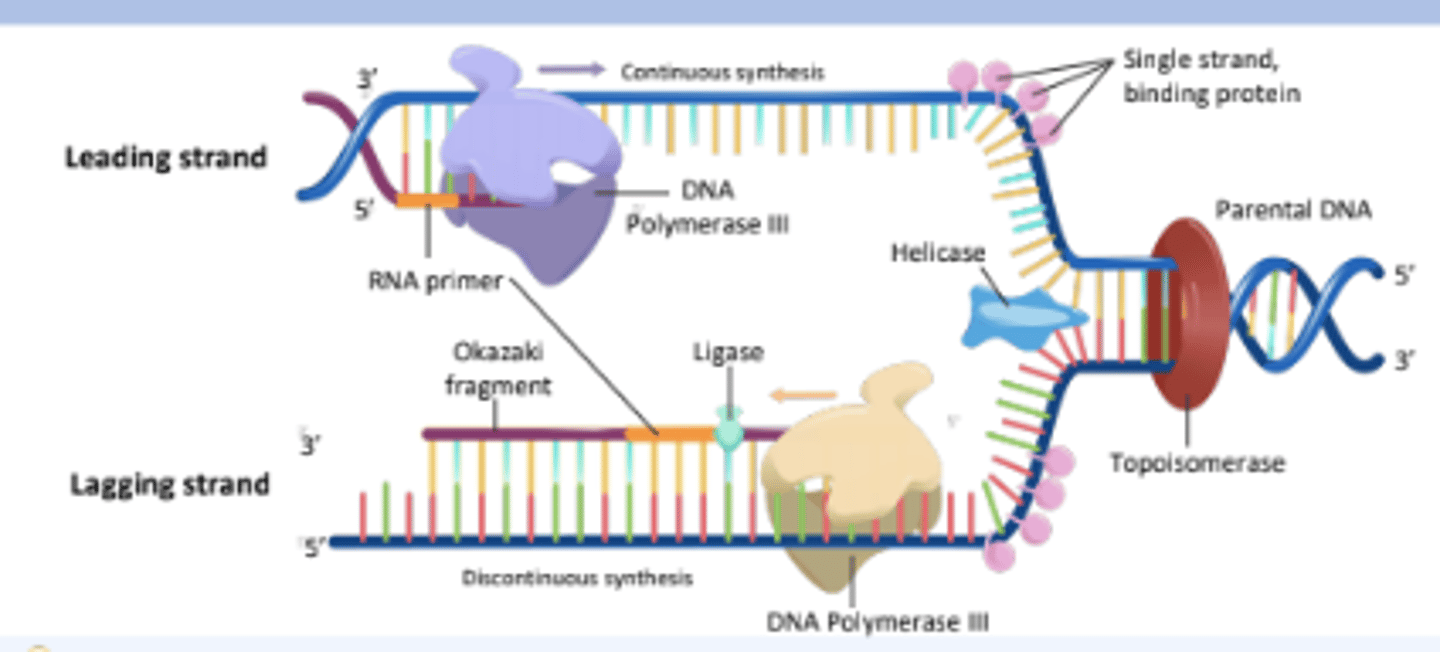
A short segment of RNA that provides a starting point for DNA synthesis.
RNA Primer
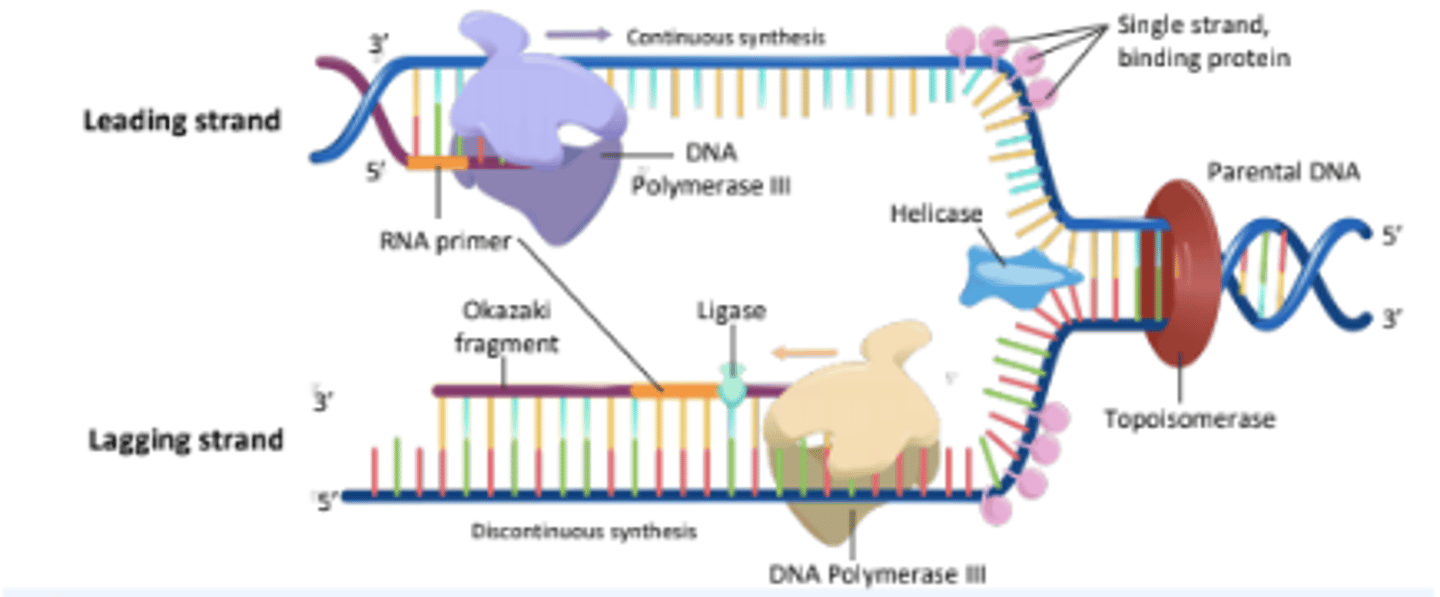
An enzyme that seals gaps between Okazaki fragments on the lagging strand, forming a continuous DNA strand.
Ligase
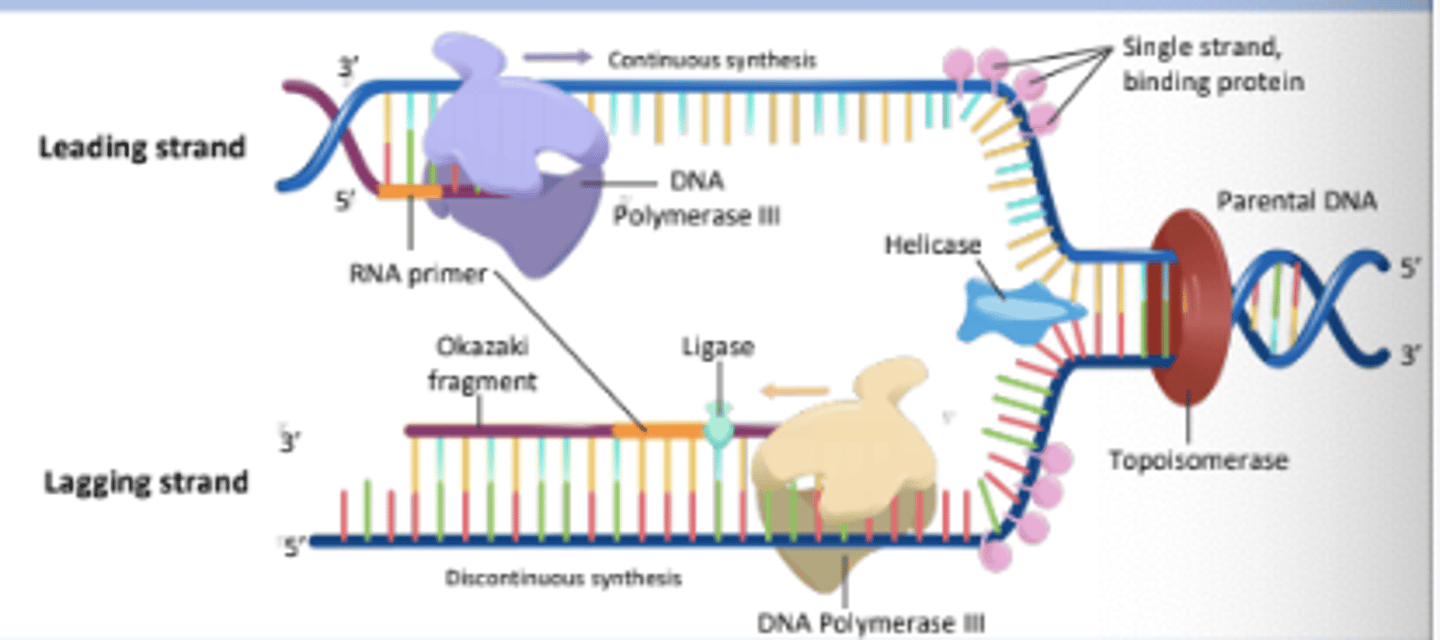
An enzyme that alleviates the torsional strain generated ahead of the replication fork by breaking and rejoining DNA strands.
Topoisomerase
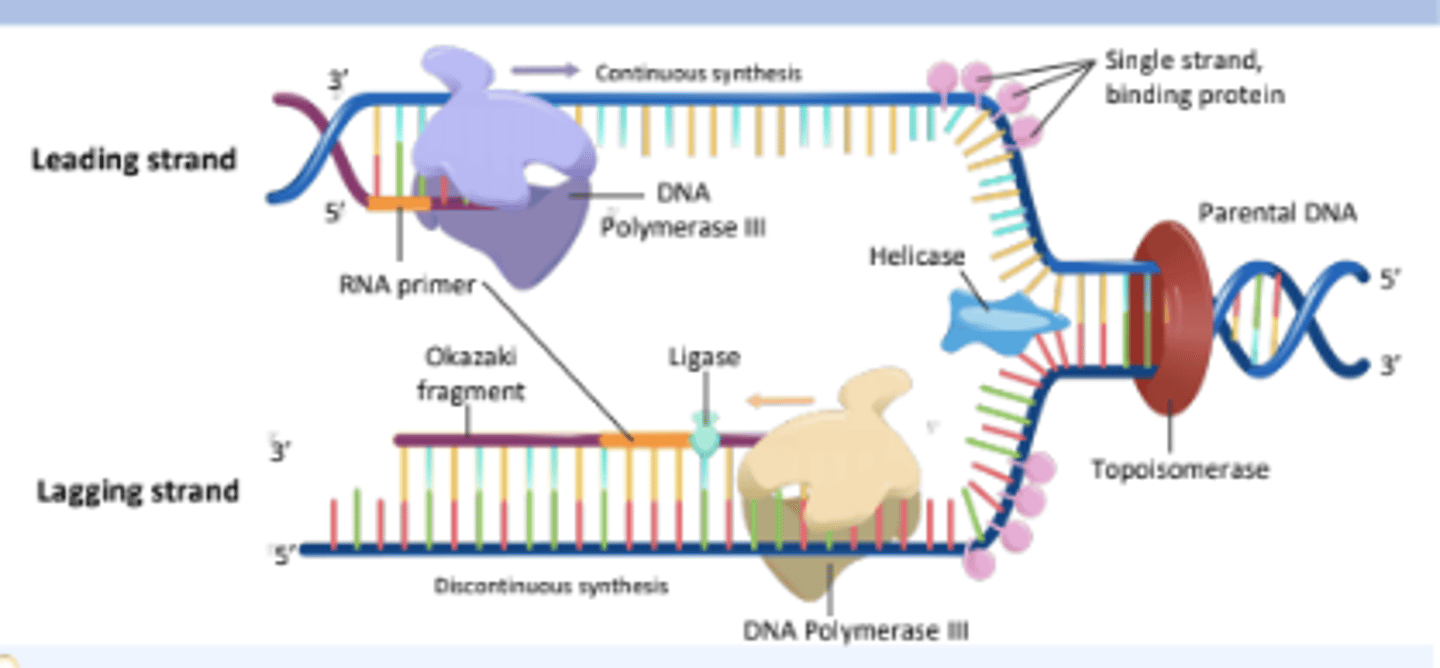
Proteins that bind to single-stranded DNA near the replication fork to prevent the strands from re-annealing.
Single Stranded Binding Proteins
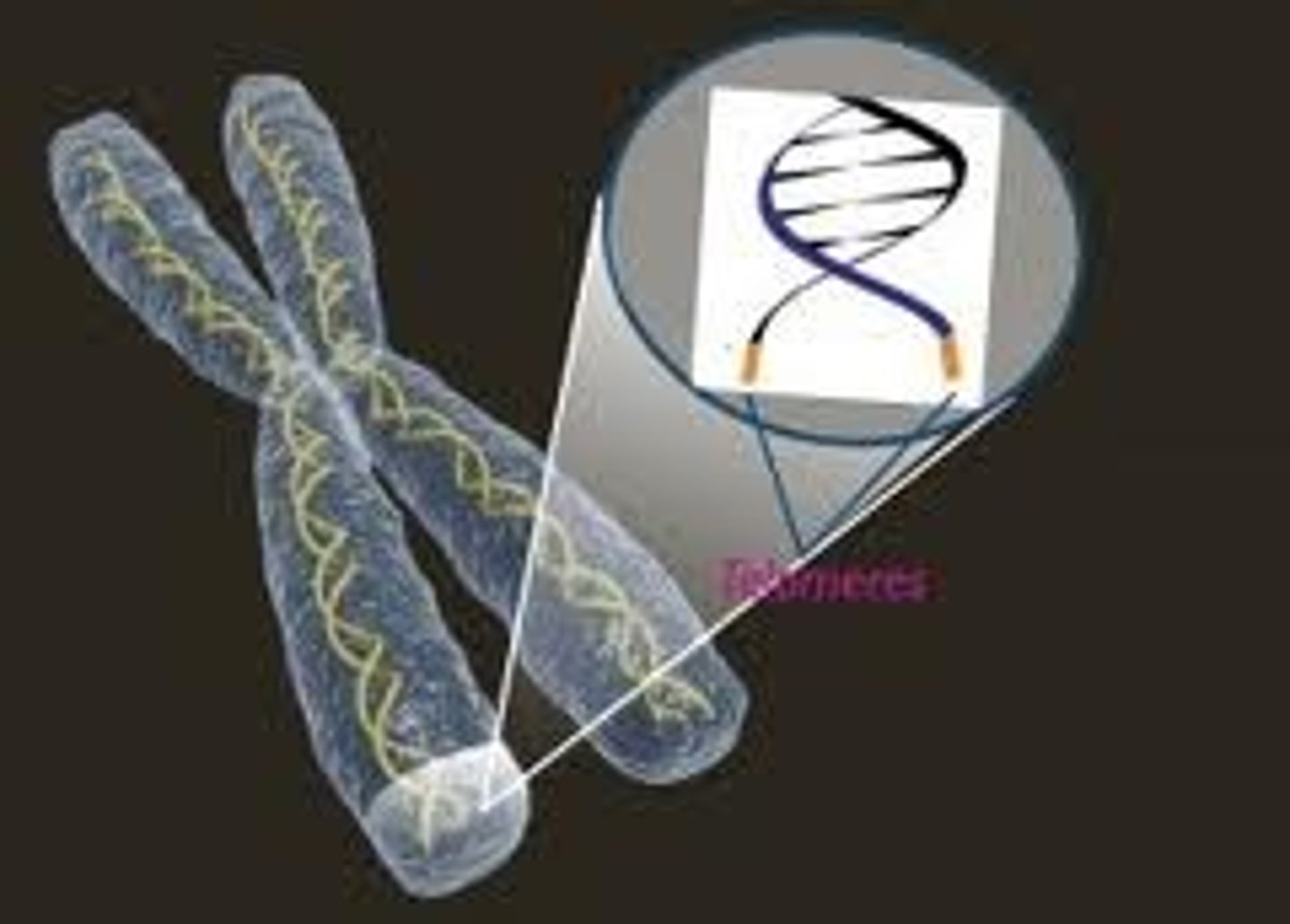
A repetitive nucleotide sequence at the ends of chromosomes that protects them from deterioration.
Telomere
An enzyme that adds telomere sequences to the ends of chromosomes, preventing loss of genetic information during replication.
Telomerase
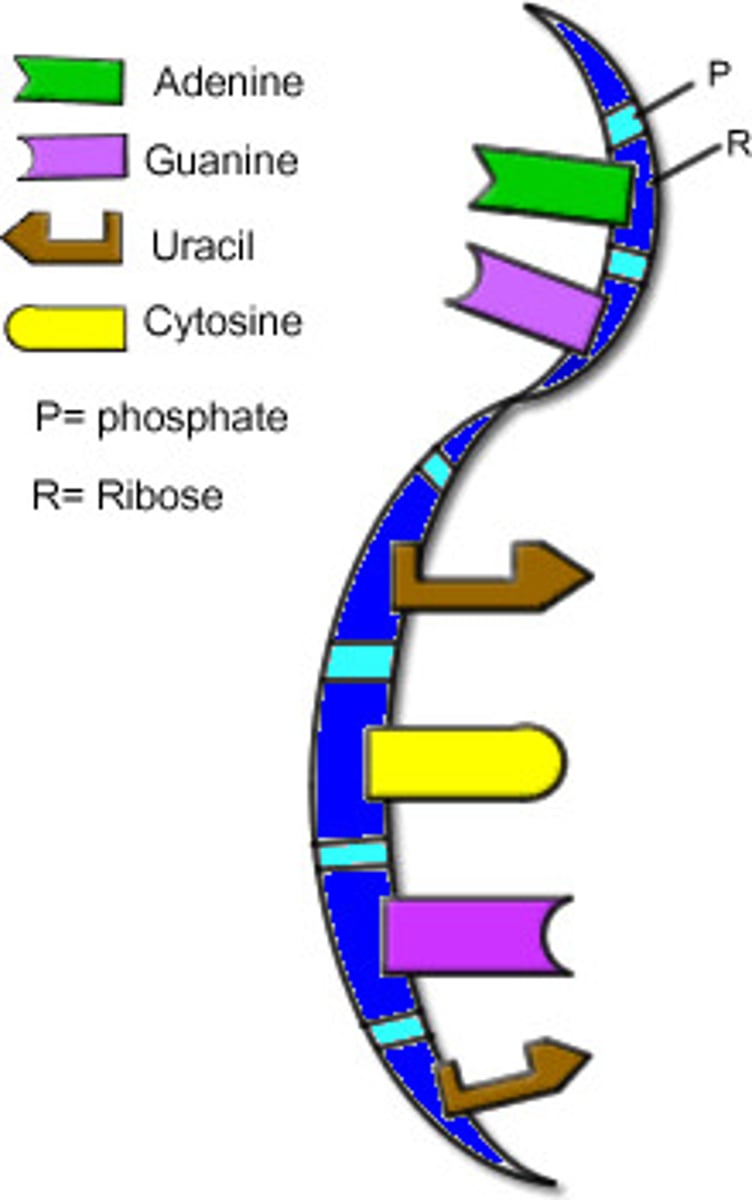
Messenger RNA that carries genetic information from DNA to the ribosome for protein synthesis.
mRNA
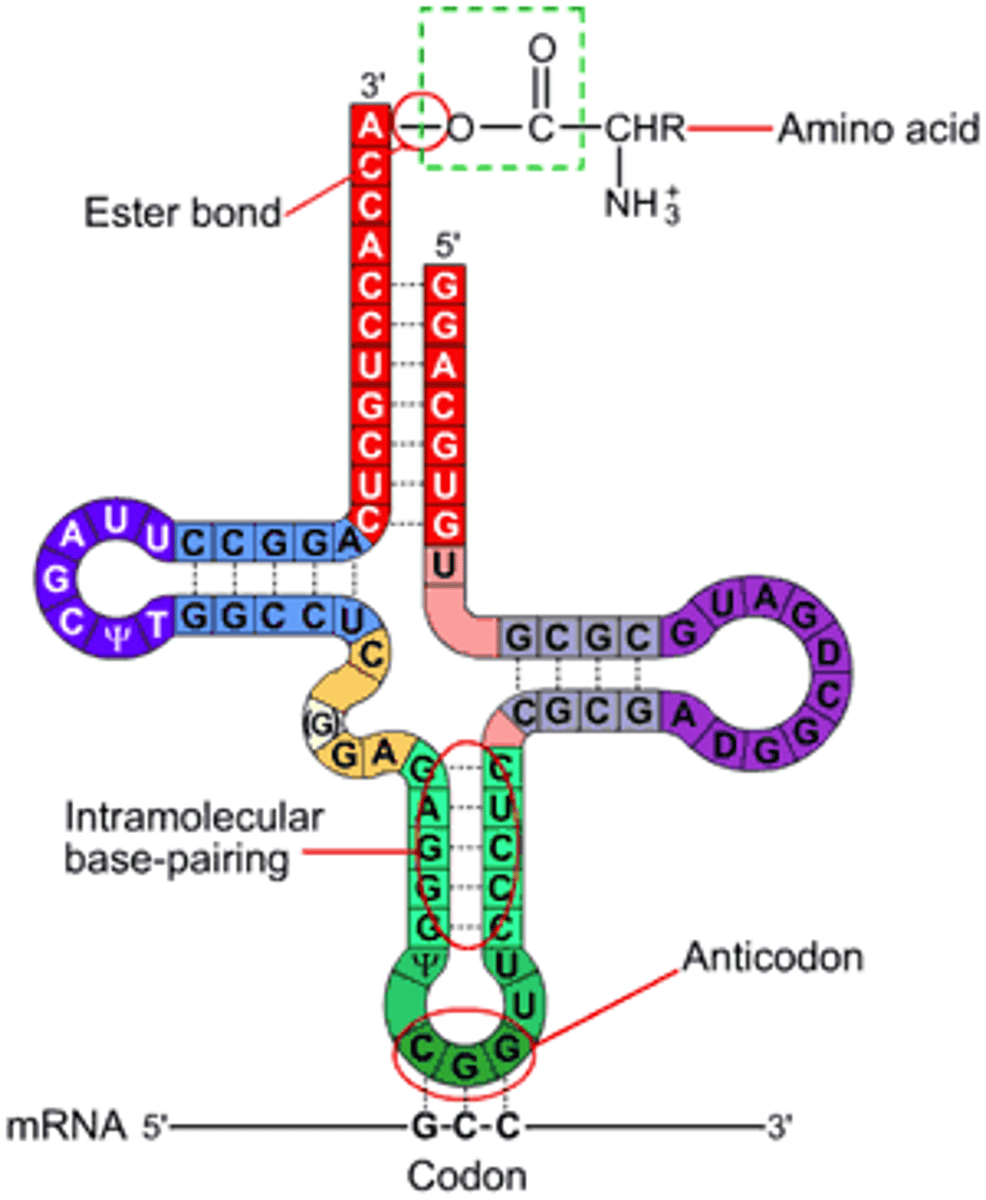
Transfer RNA that transports specific amino acids to the ribosome during protein synthesis.
tRNA
Ribosomal RNA that forms part of the ribosome and is essential for protein synthesis.
rRNA
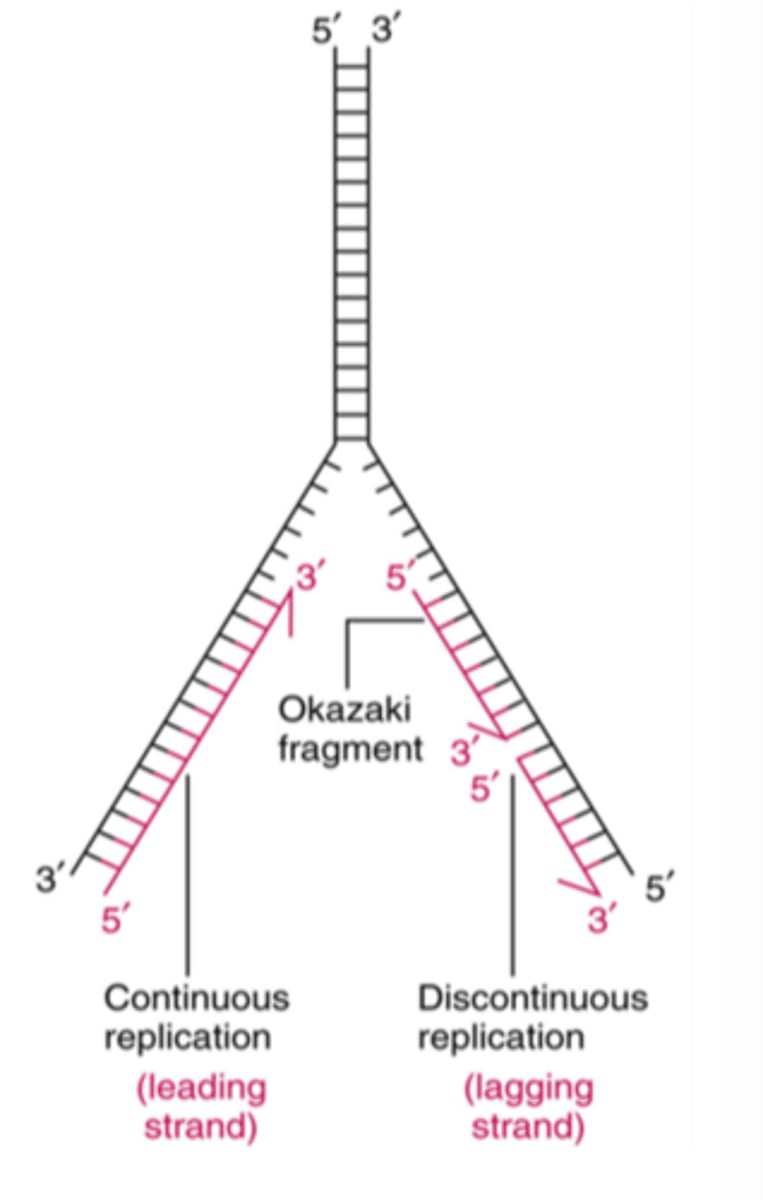
The process by which the lagging strand is synthesized in short fragments rather than continuously.
Discontinuous Synthesis
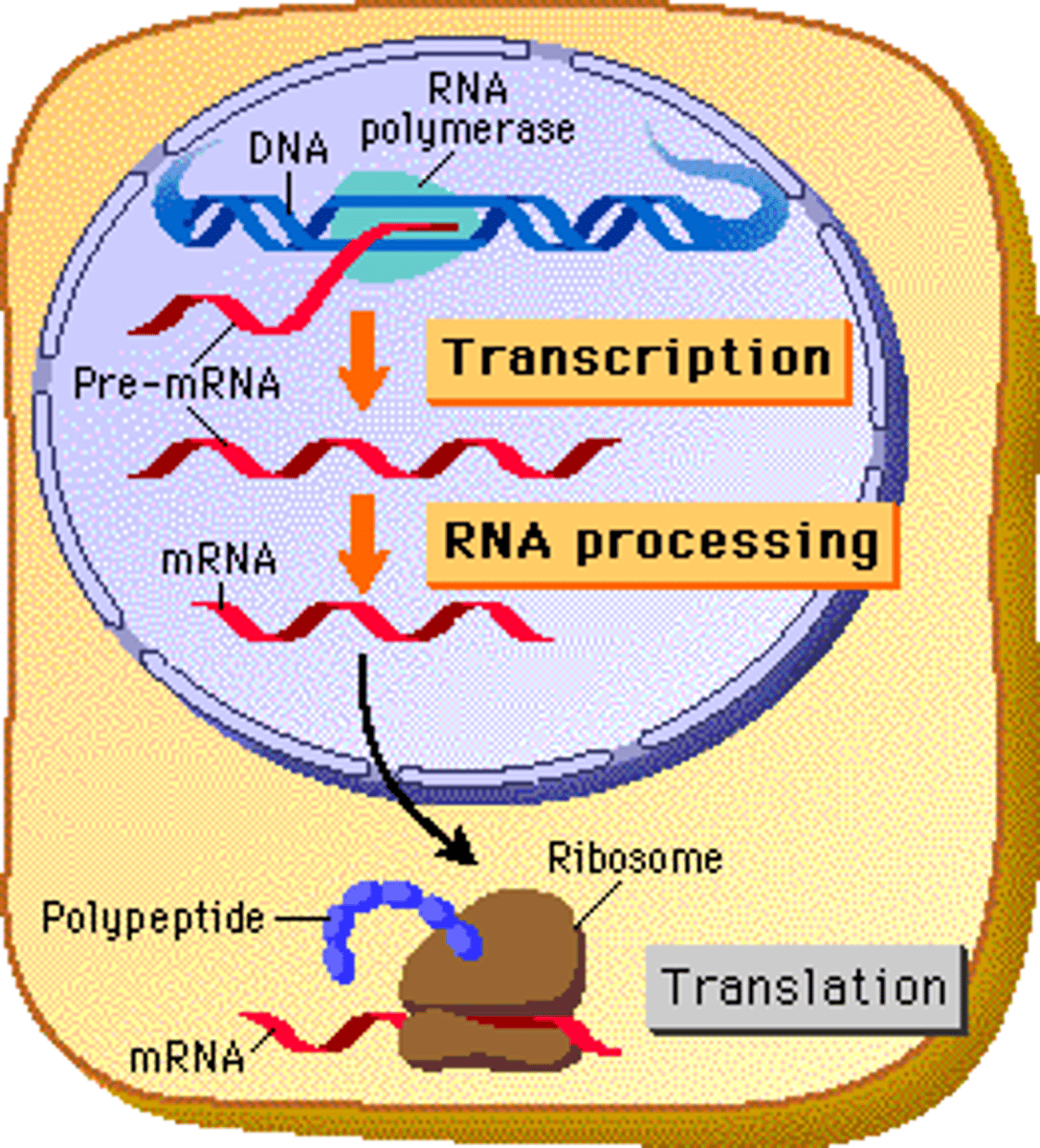
The process of synthesizing RNA from a DNA template, where a specific gene is transcribed.
Transcription
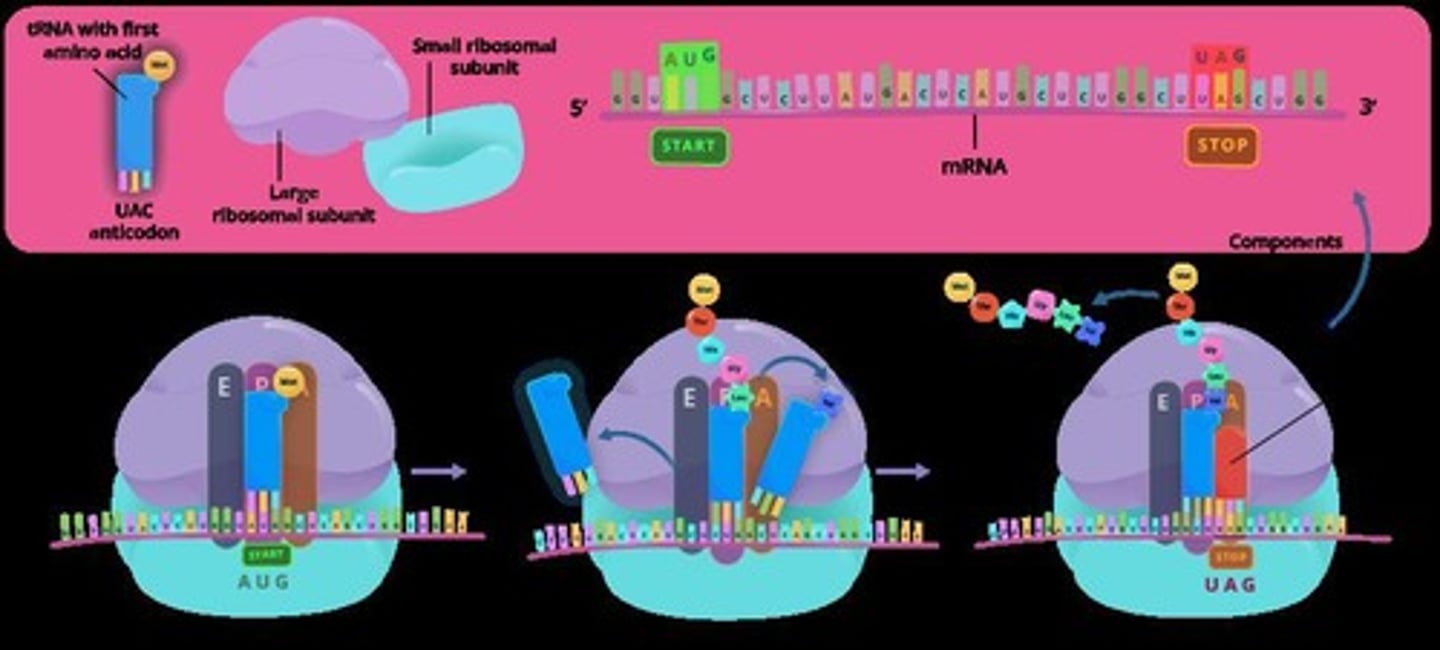
The synthesis of proteins based on the sequence of mRNA nucleotides.
Translation
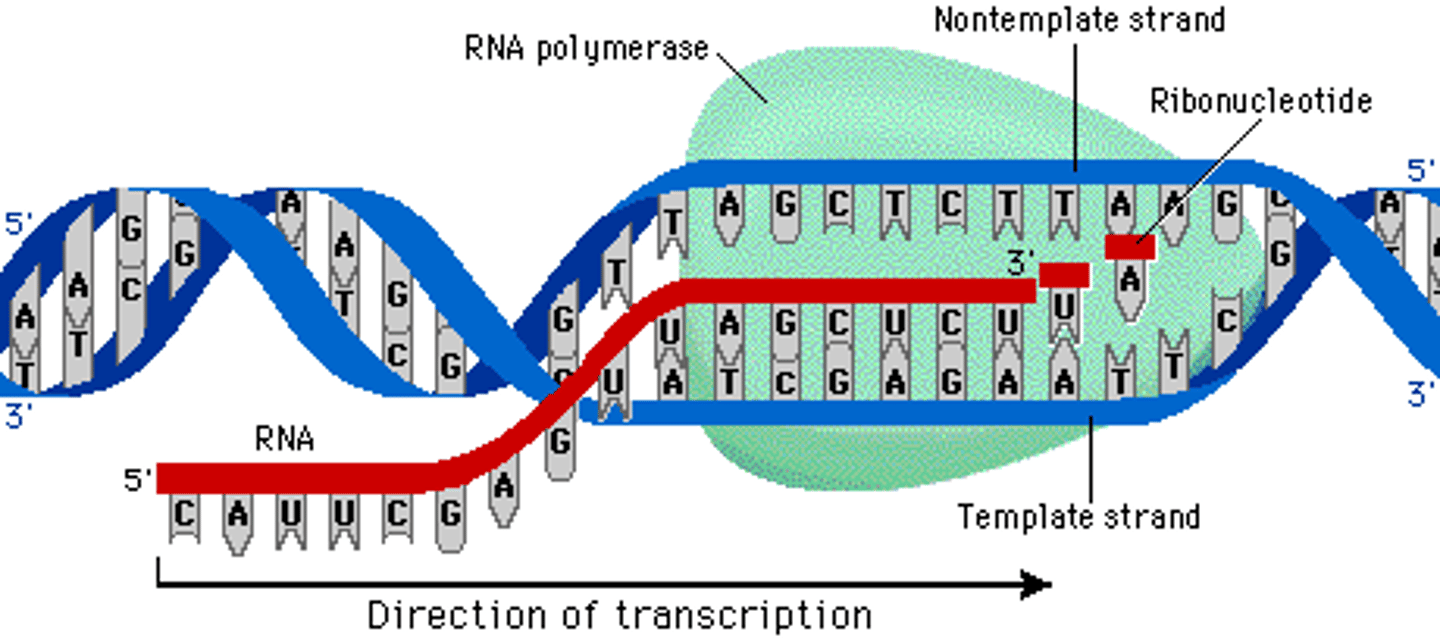
An enzyme that synthesizes RNA by attaching to the promoter region on DNA and unwinding the DNA strands.
RNA Polymerase
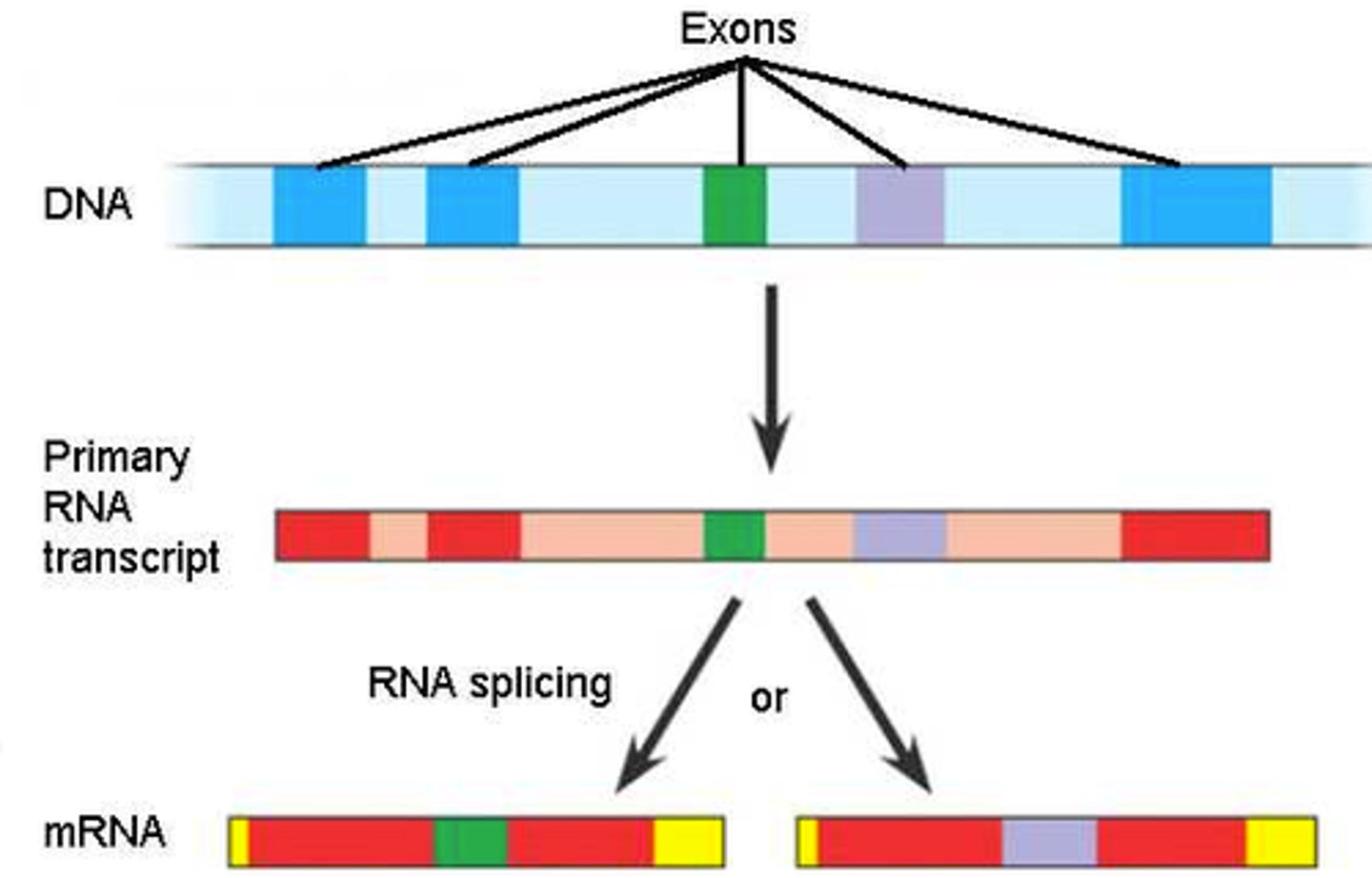
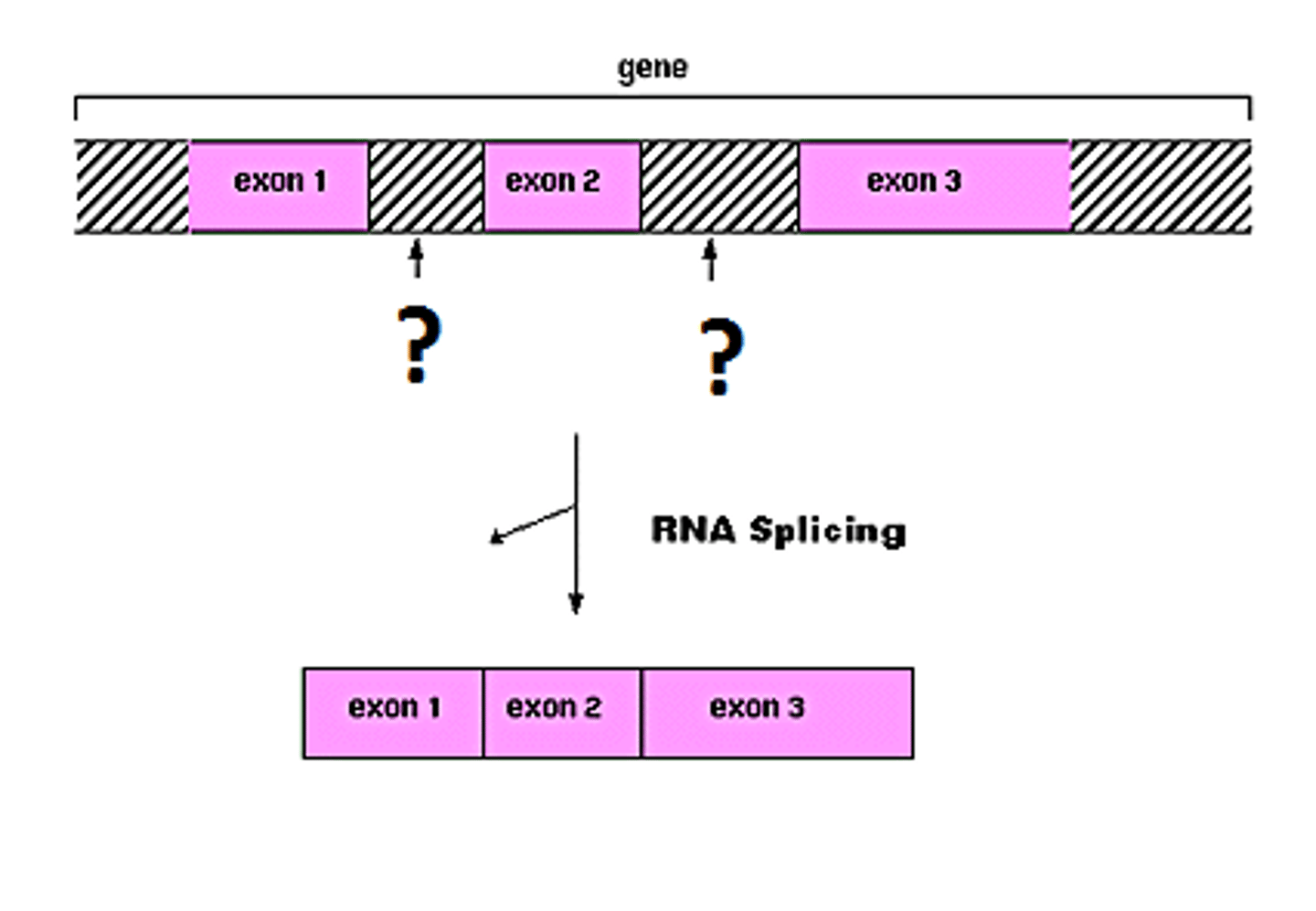
The process of removing non-coding sections of pre-mRNA and reconnecting the remaining coding regions, known as exons.
RNA Splicing
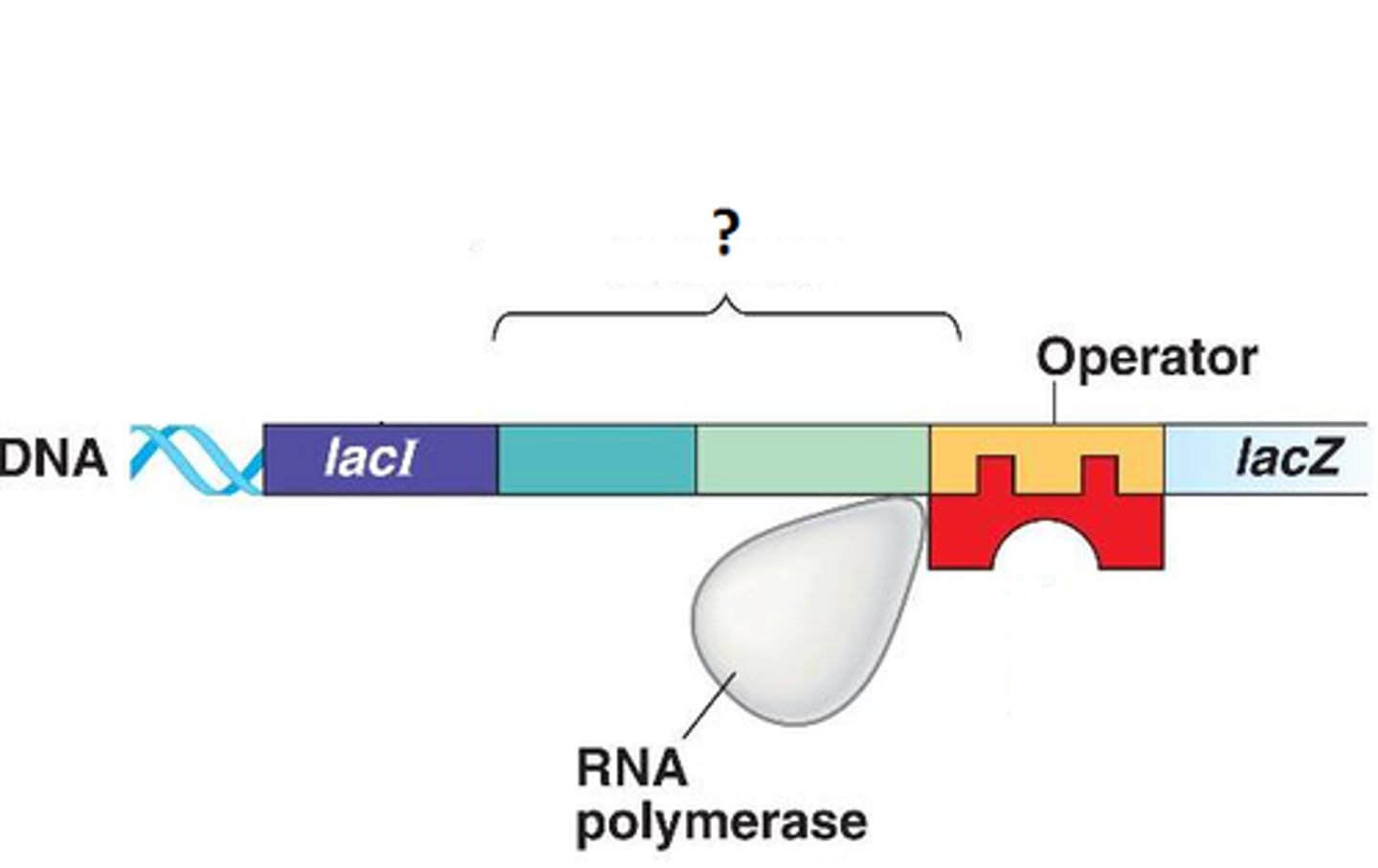
A specific DNA sequence where RNA polymerase attaches to initiate transcription.
Promoter Region
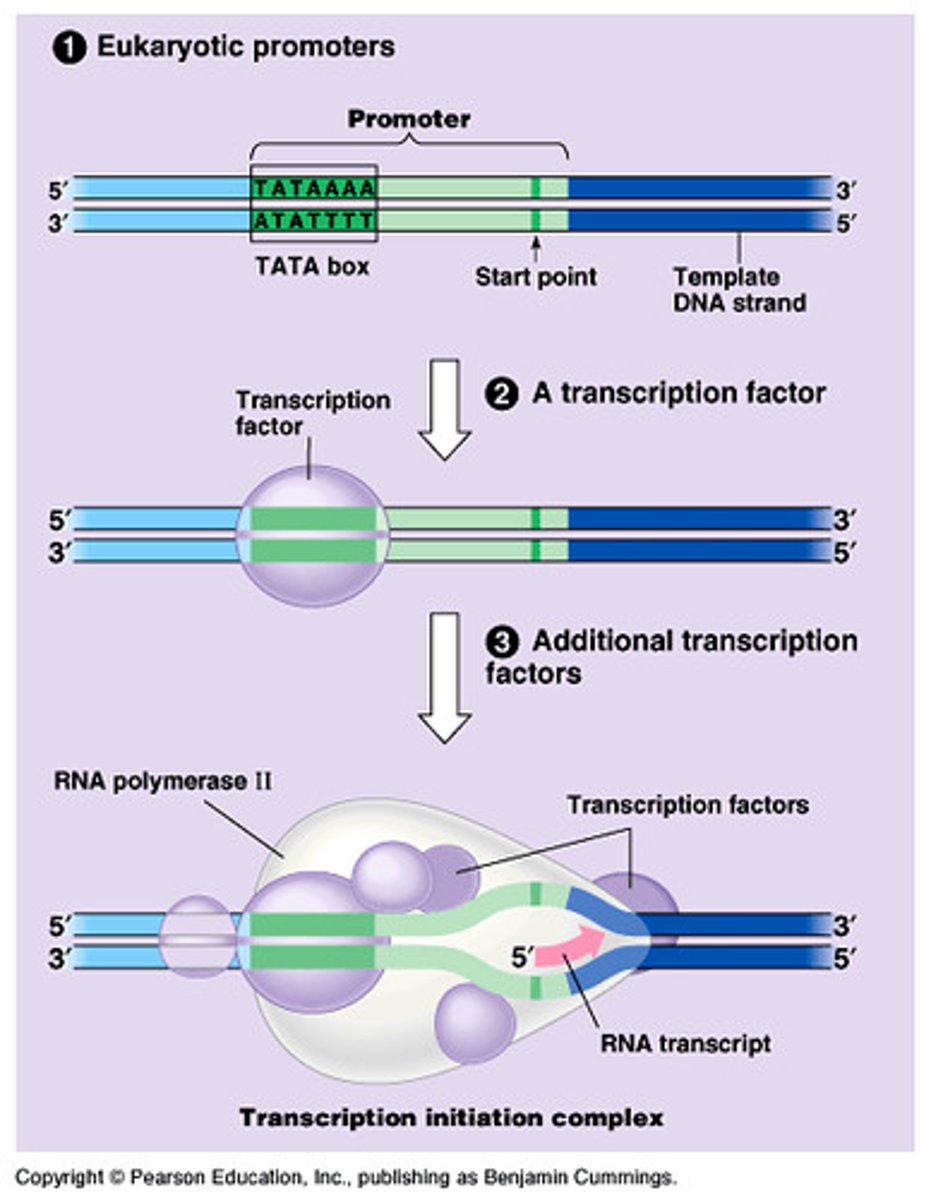
Proteins that bind to promoter and regulatory sequences to control the transcription of specific genes.
Transcription Factors
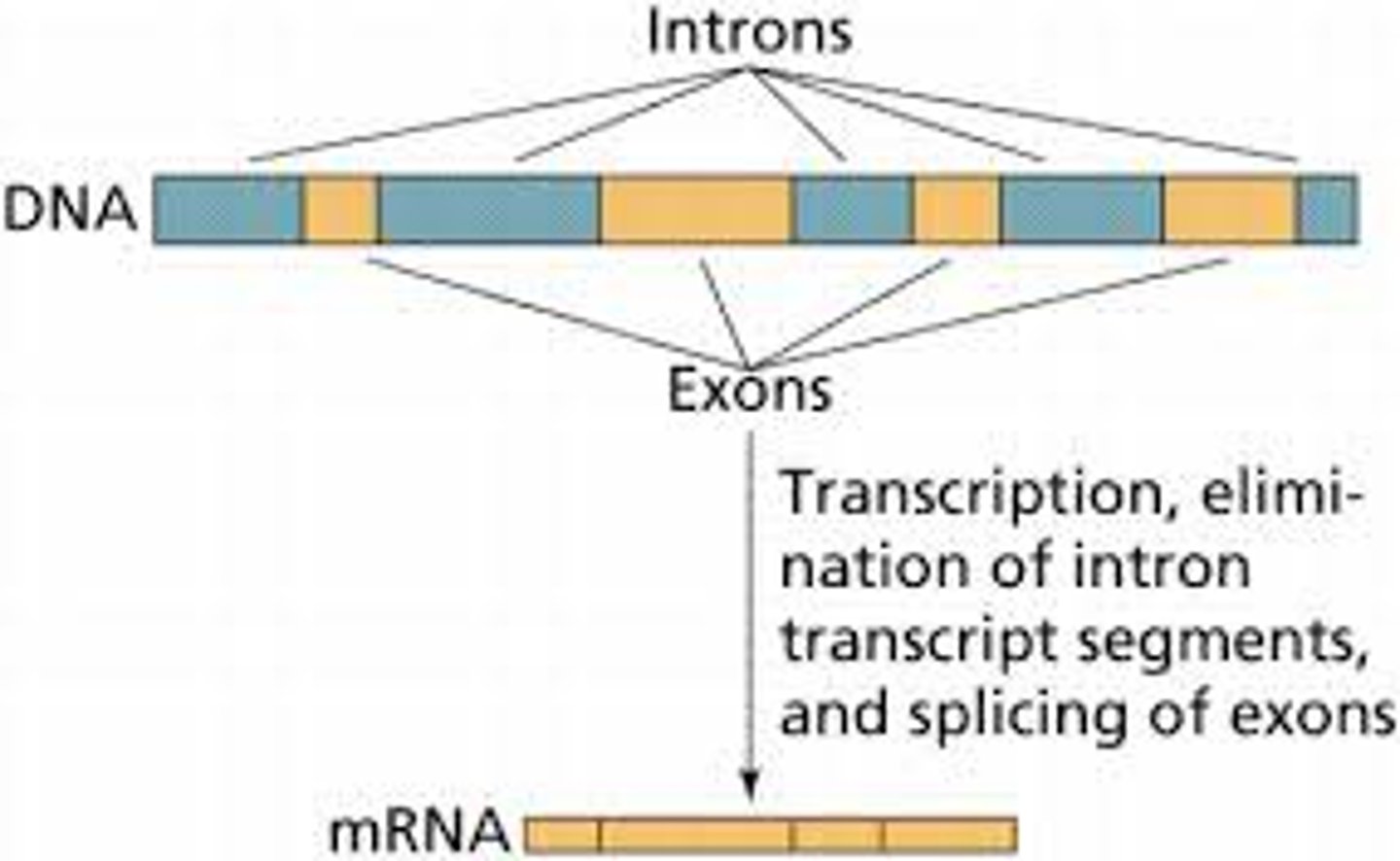
Protein-coding regions of mRNA that are expressed in the final protein product.
Exons
Non-coding regions in mRNA that are removed during RNA splicing.
Introns
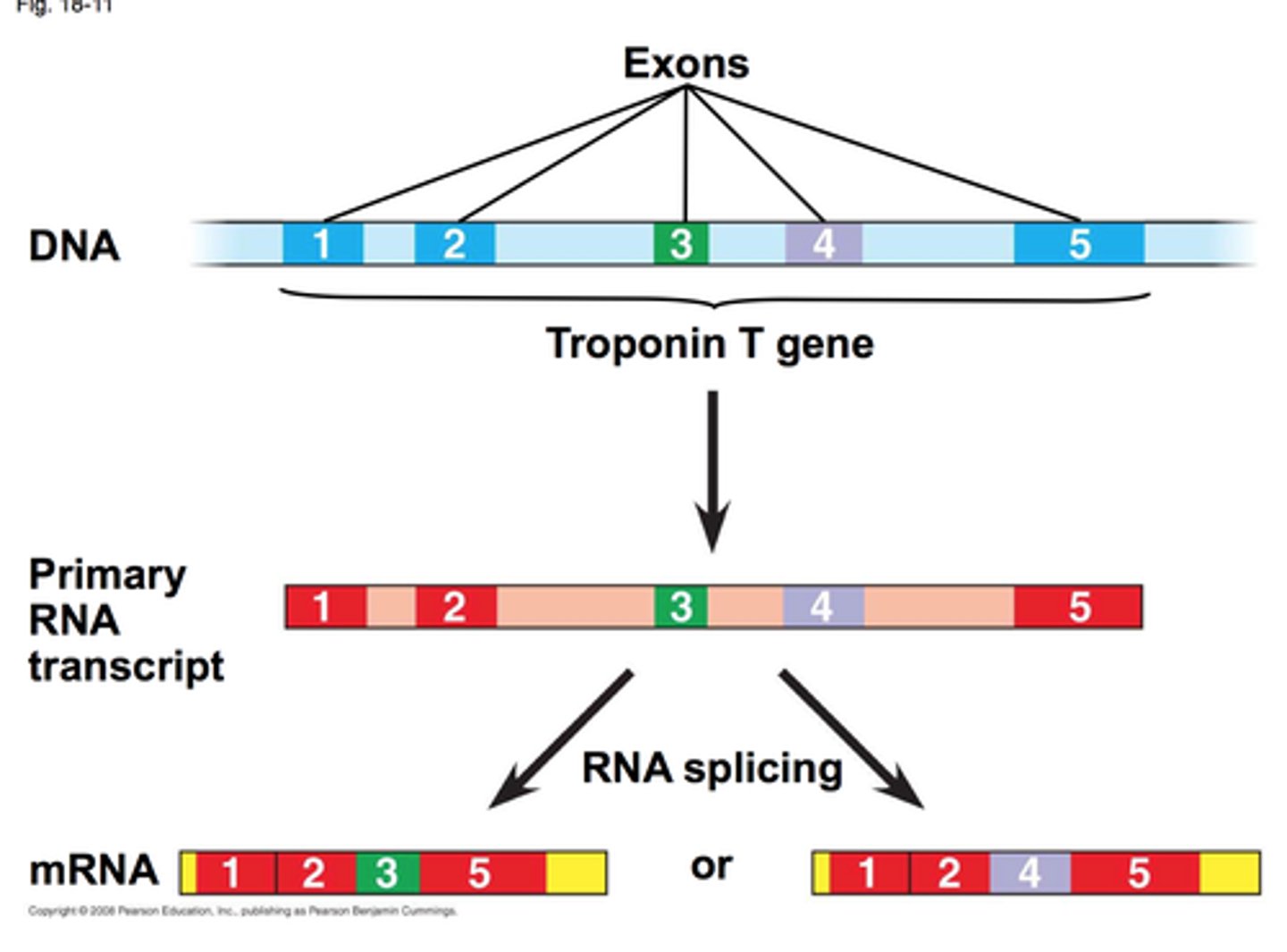
A process that allows for the production of multiple protein types from a single gene by using different combinations of exons.
Alternative Splicing
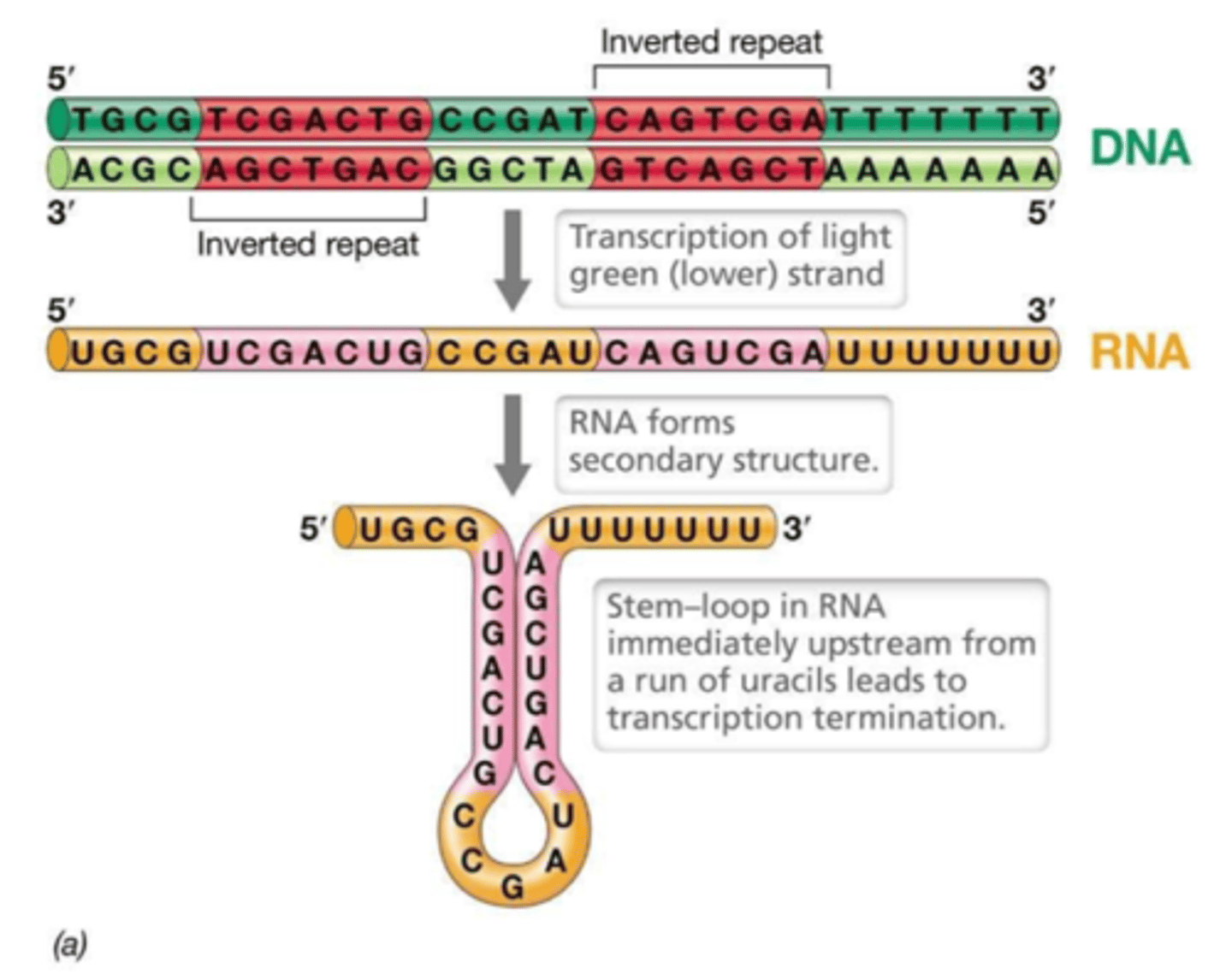
The process where RNA polymerase reaches a specific sequence, detaches from the DNA, and disassembles.
Termination (Transcription)
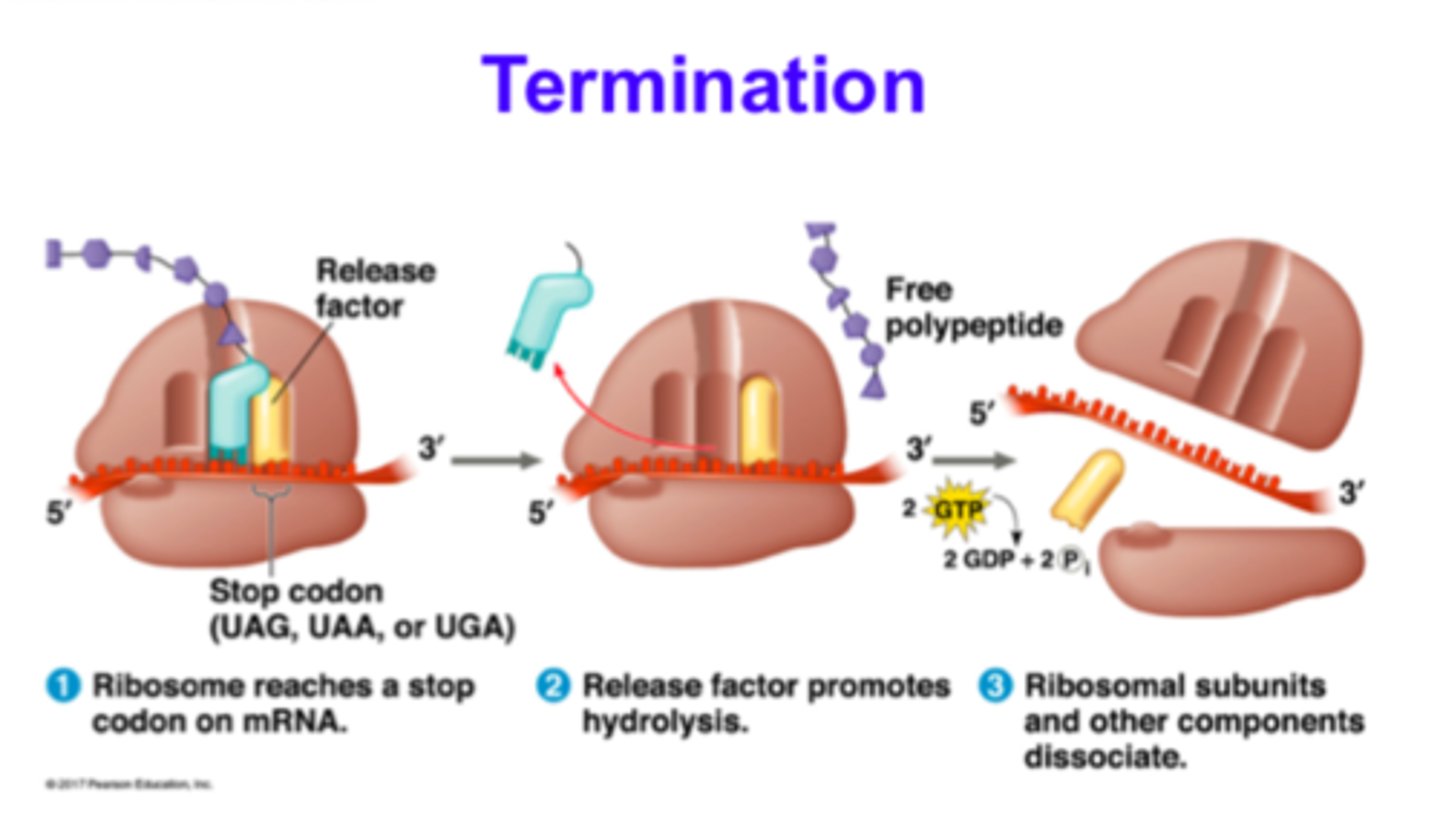
The process where translation ends upon encountering stop codons, leading to the release of the newly synthesized polypeptide.
Termination (Translation)
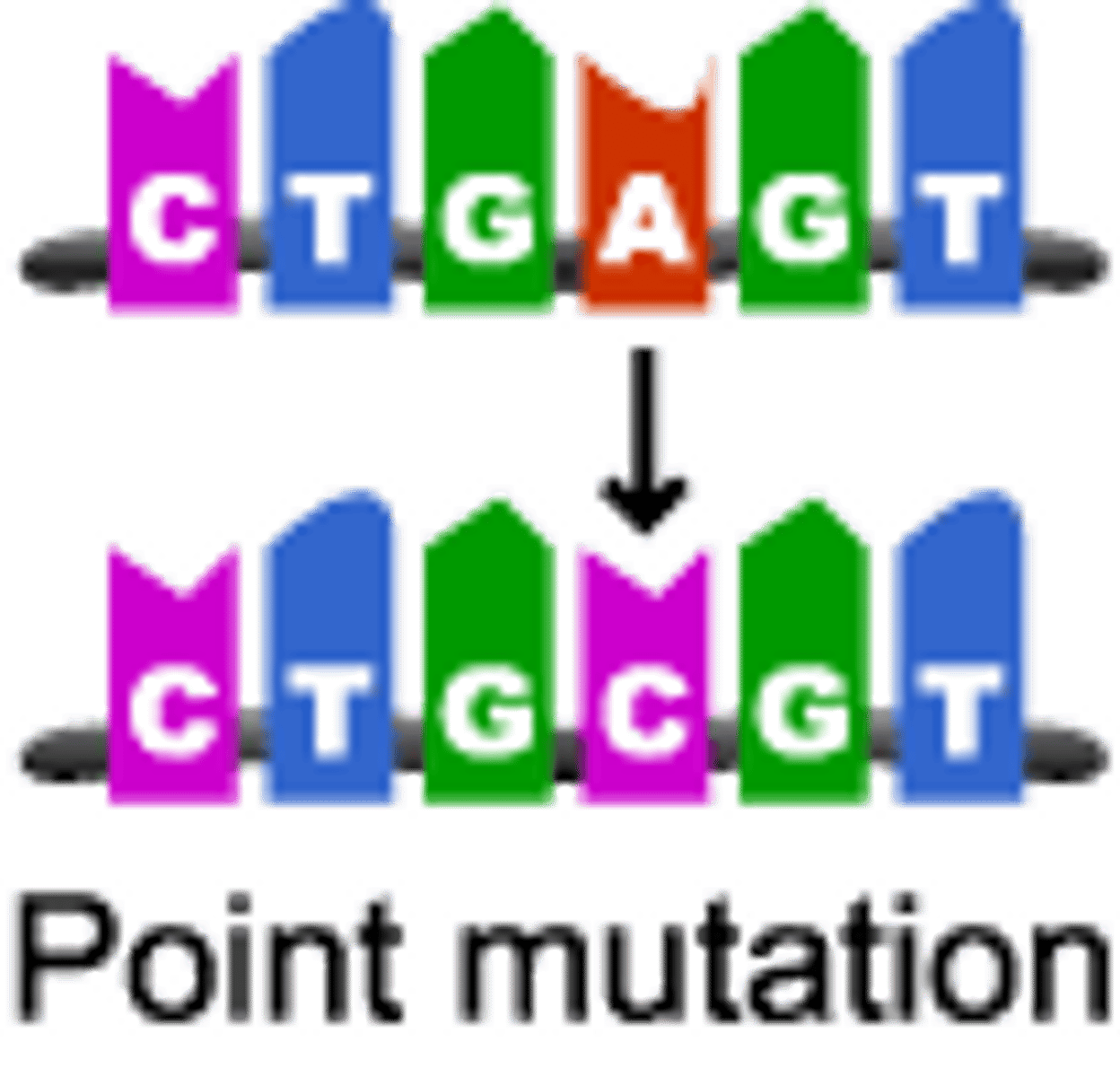
A single nucleotide change in DNA that can result in substitution, insertion, or deletion.
Point Mutation
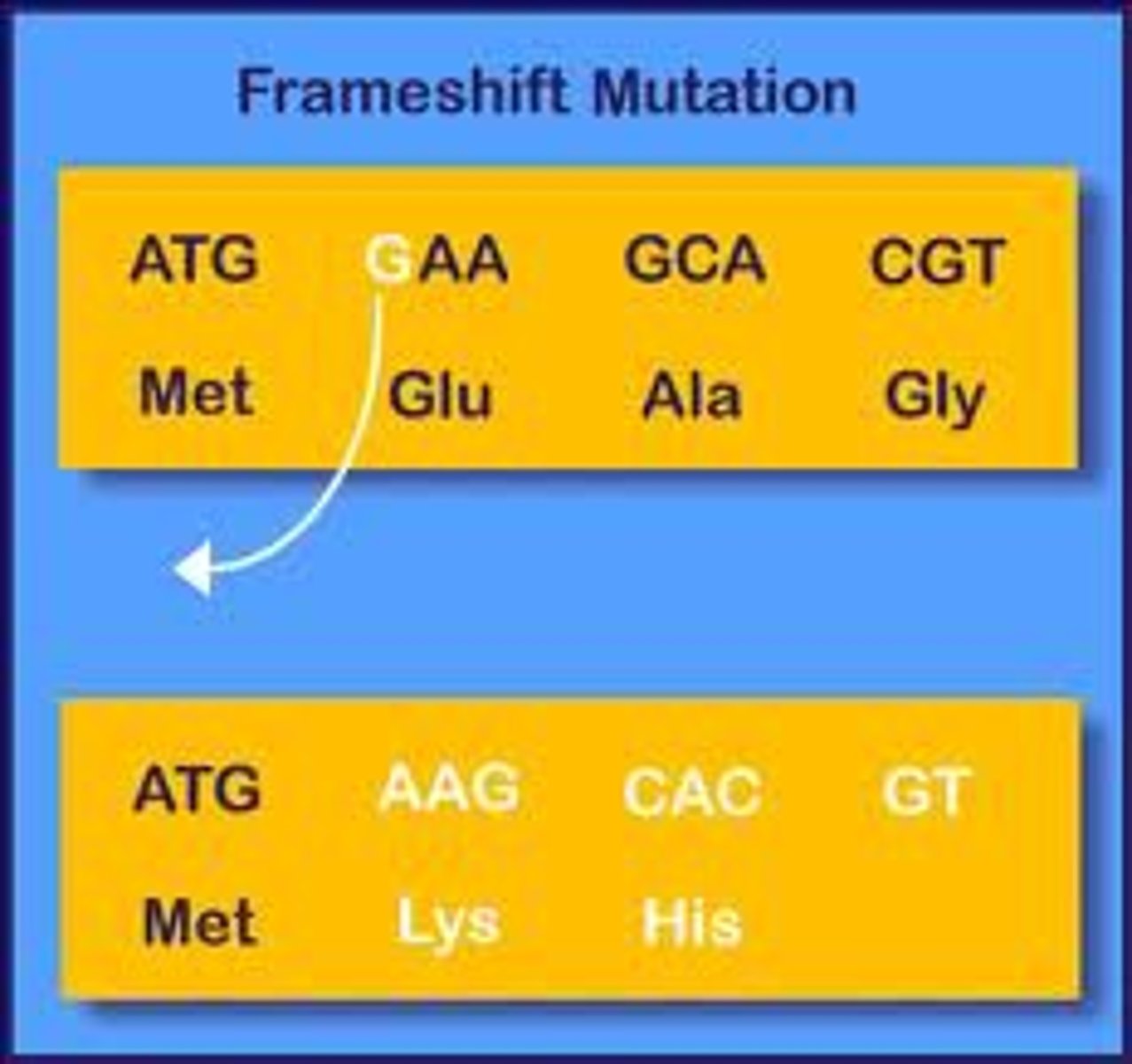
A mutation caused by insertion or deletion of nucleotides that shifts the reading frame of the RNA transcript, altering the resulting protein.
Frameshift Mutation
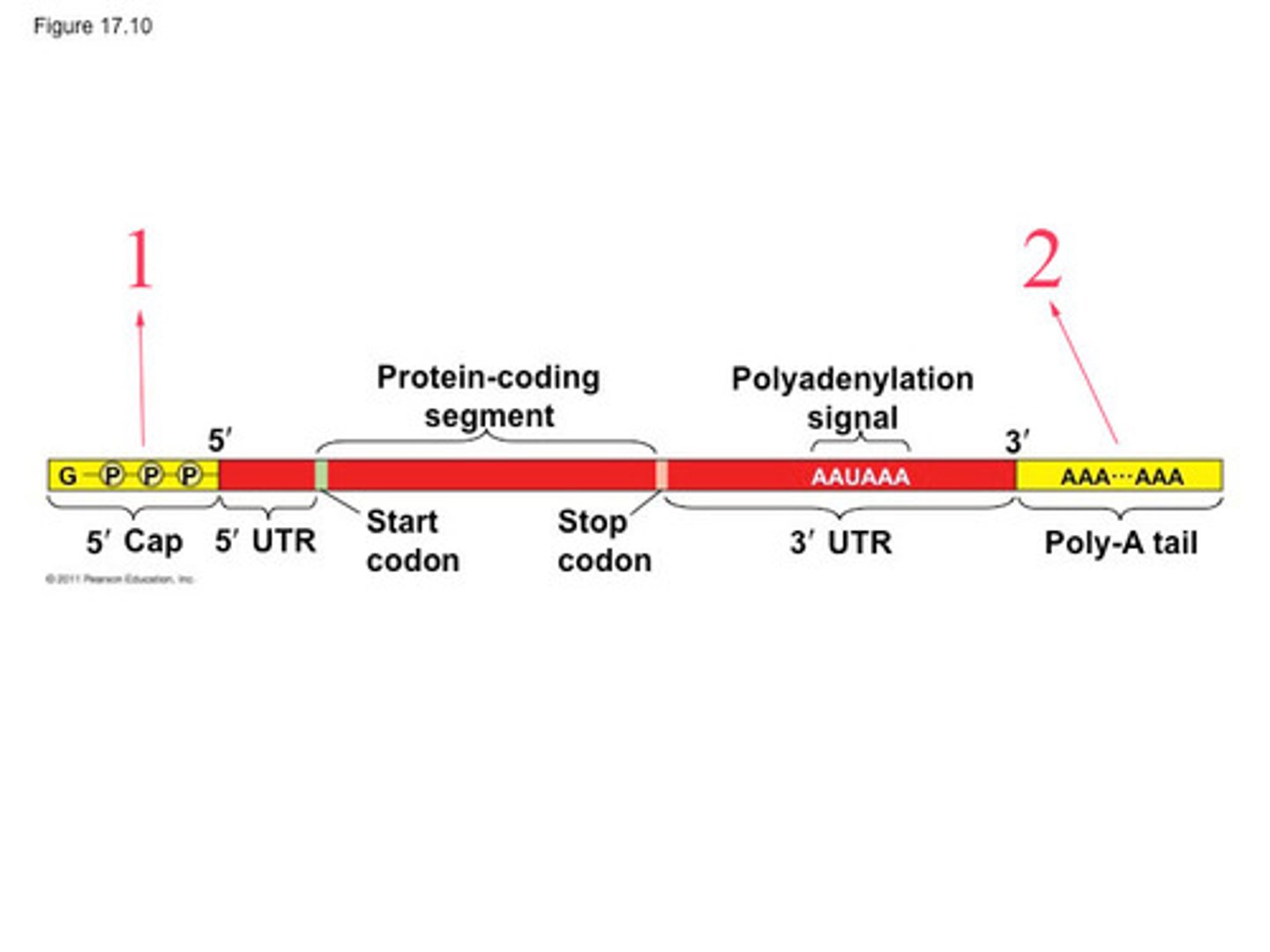
A modified guanine nucleotide added to the 5' end of mRNA for stability and protection from degradation.
5' Cap
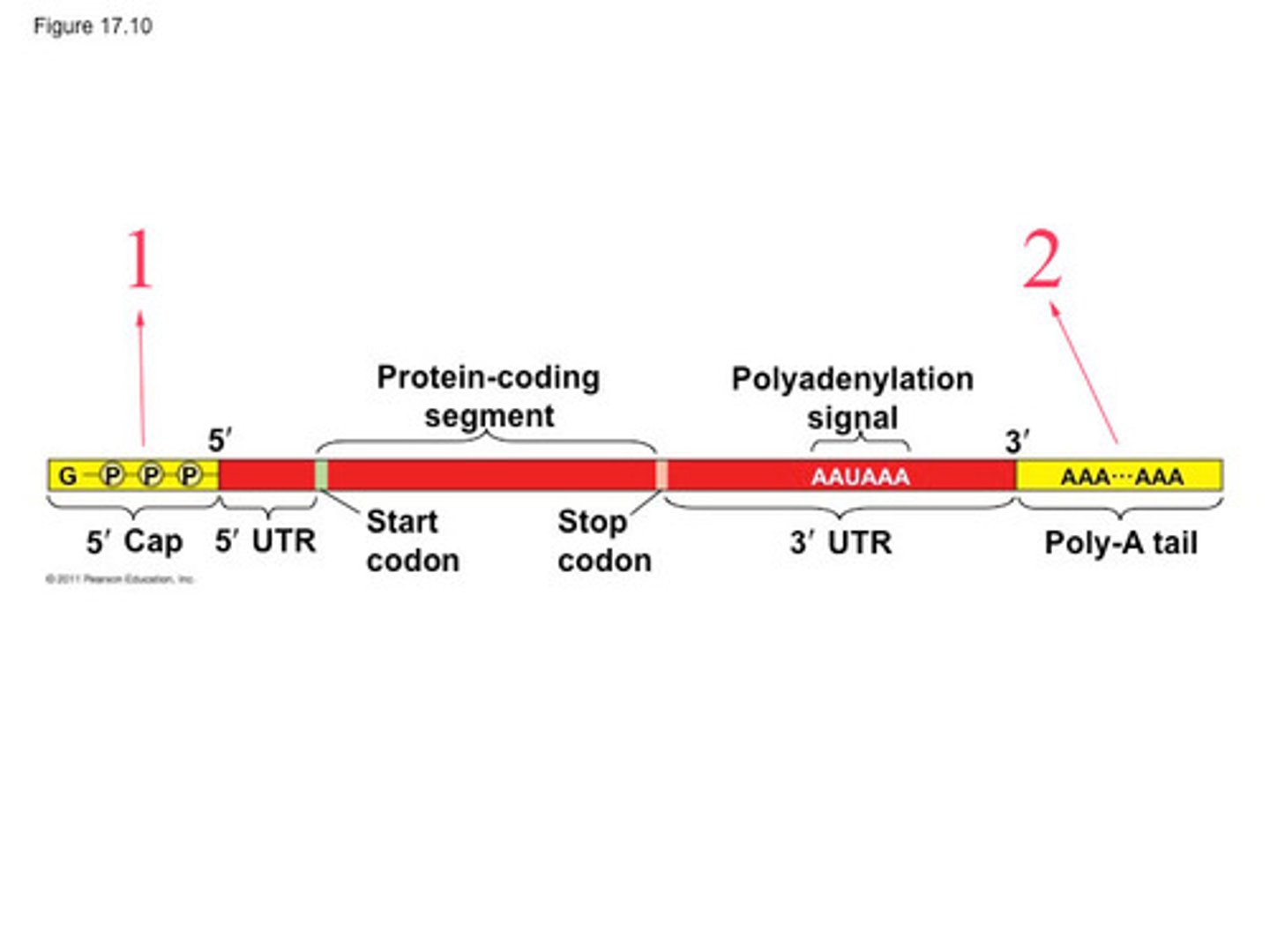
A sequence of adenine nucleotides added to the 3' end of mRNA to enhance stability and facilitate export from the nucleus.
Poly-A Tail
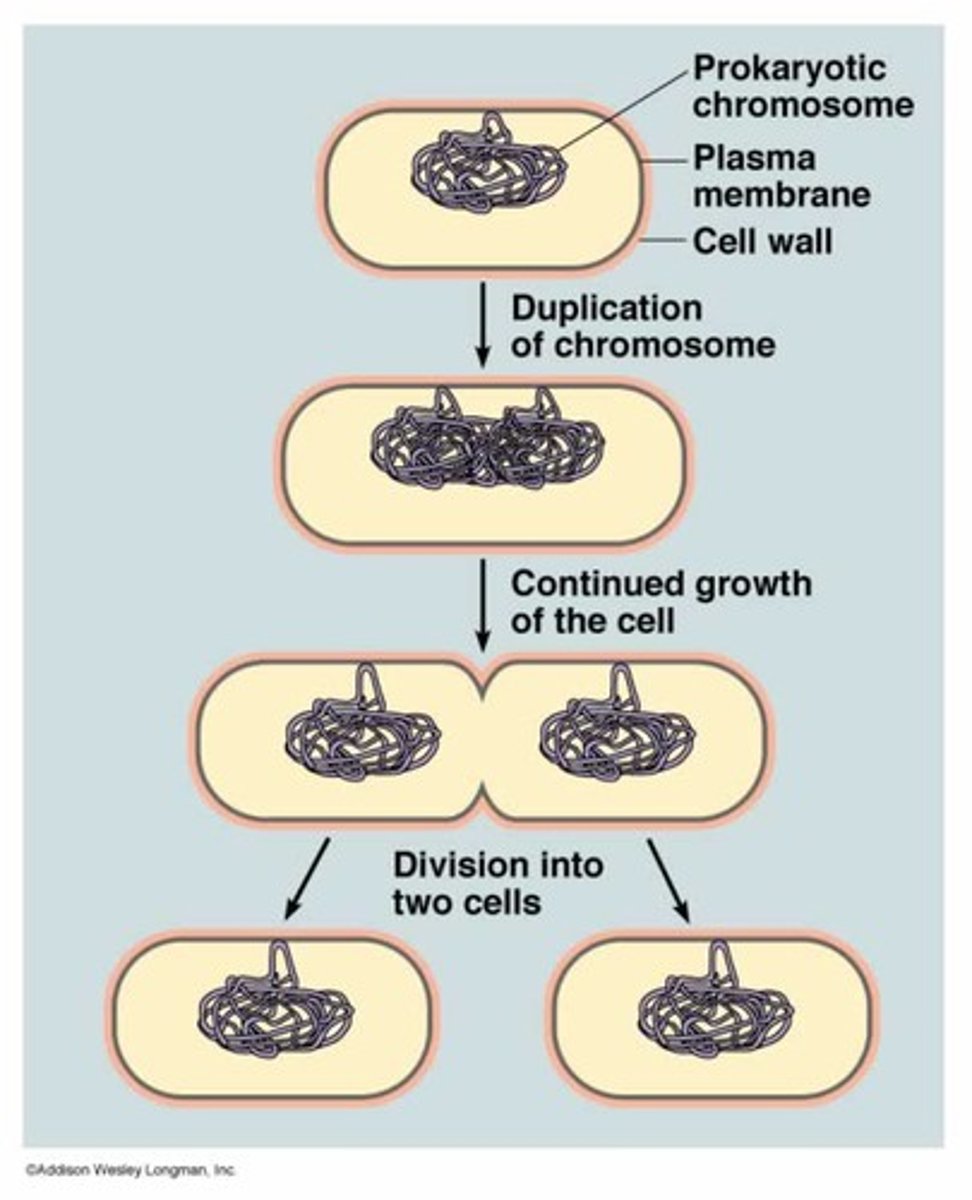
A method of asexual reproduction in bacteria where a single cell divides into two identical daughter cells after duplicating its DNA.
Binary Fission
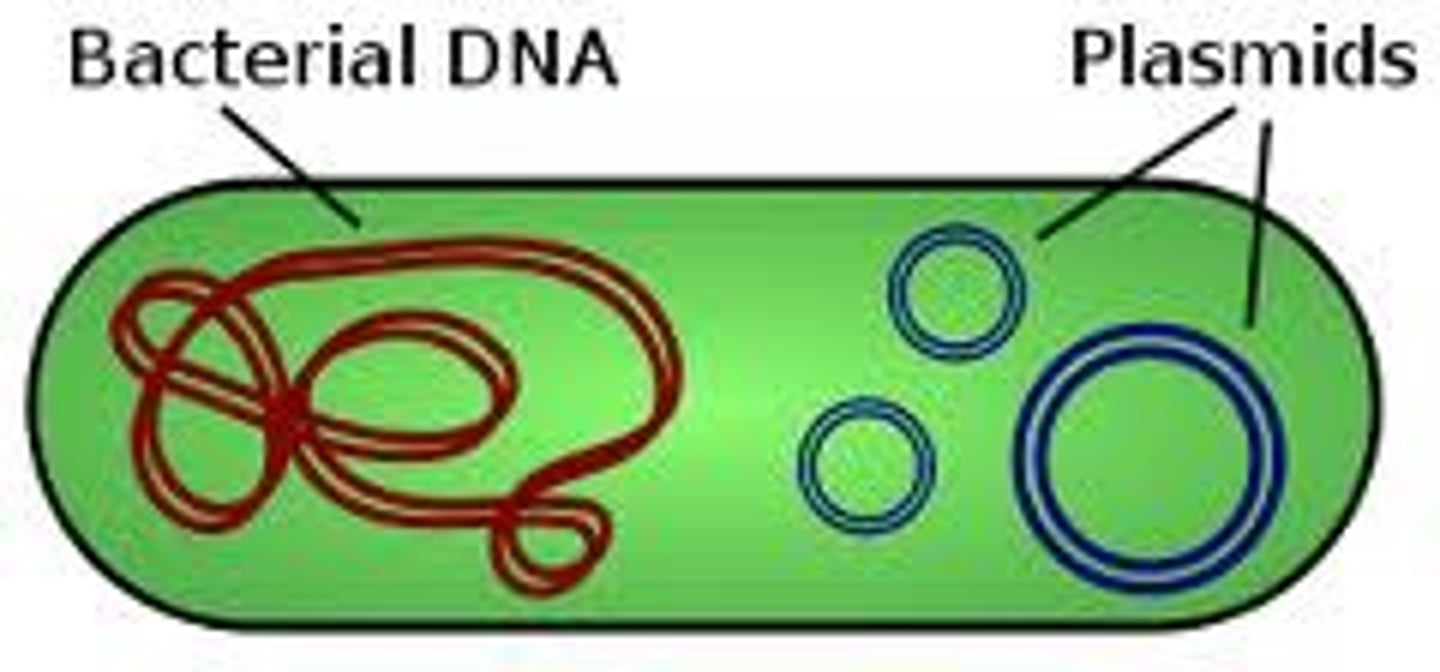
A small, circular double-stranded DNA molecule that is separate from the chromosomal DNA and can carry genes that are beneficial but not essential for survival.
Plasmid
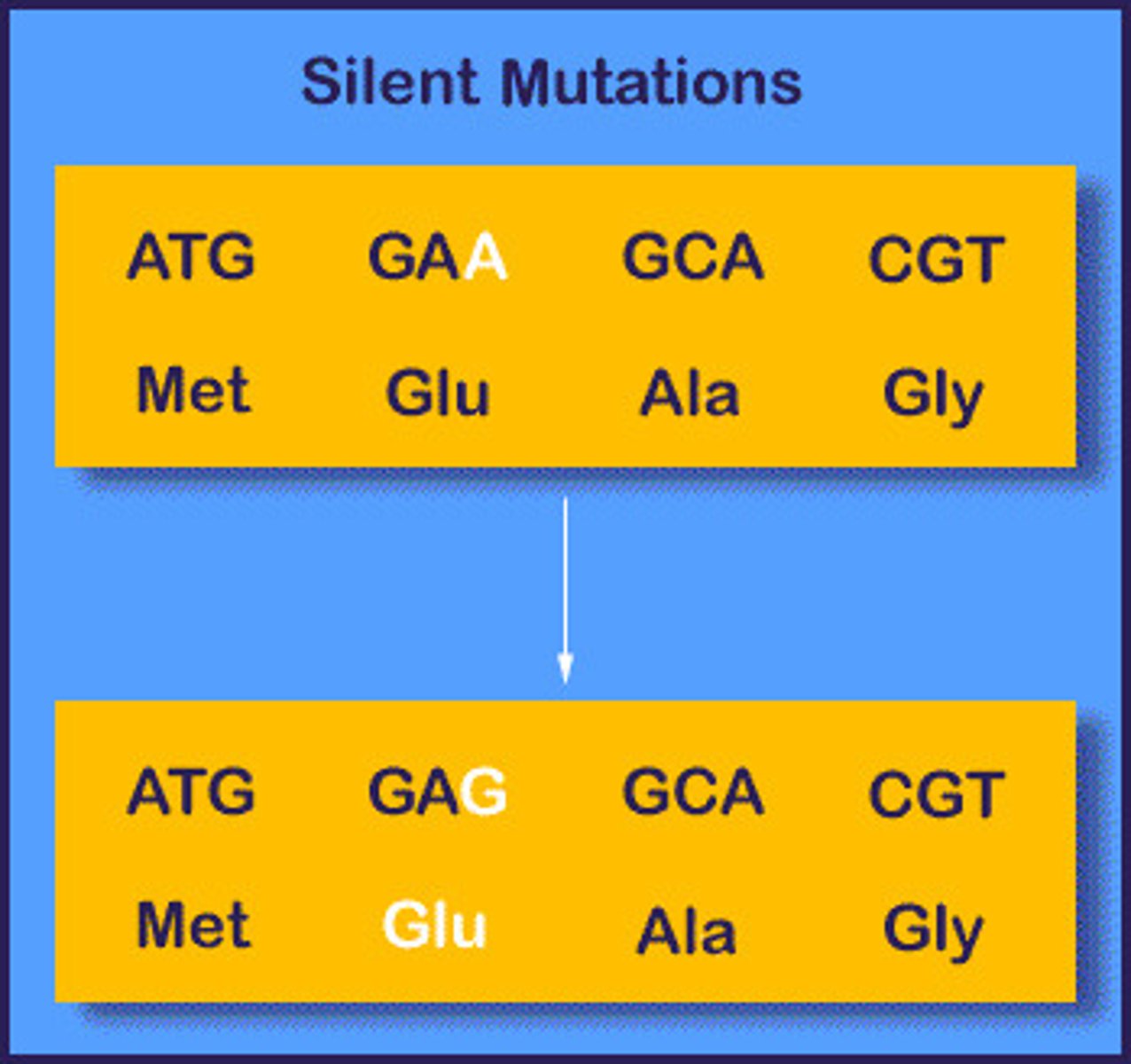
A change in the DNA sequence that does not alter the amino acid sequence of the resulting protein due to the redundancy of the genetic code.
Silent Mutation
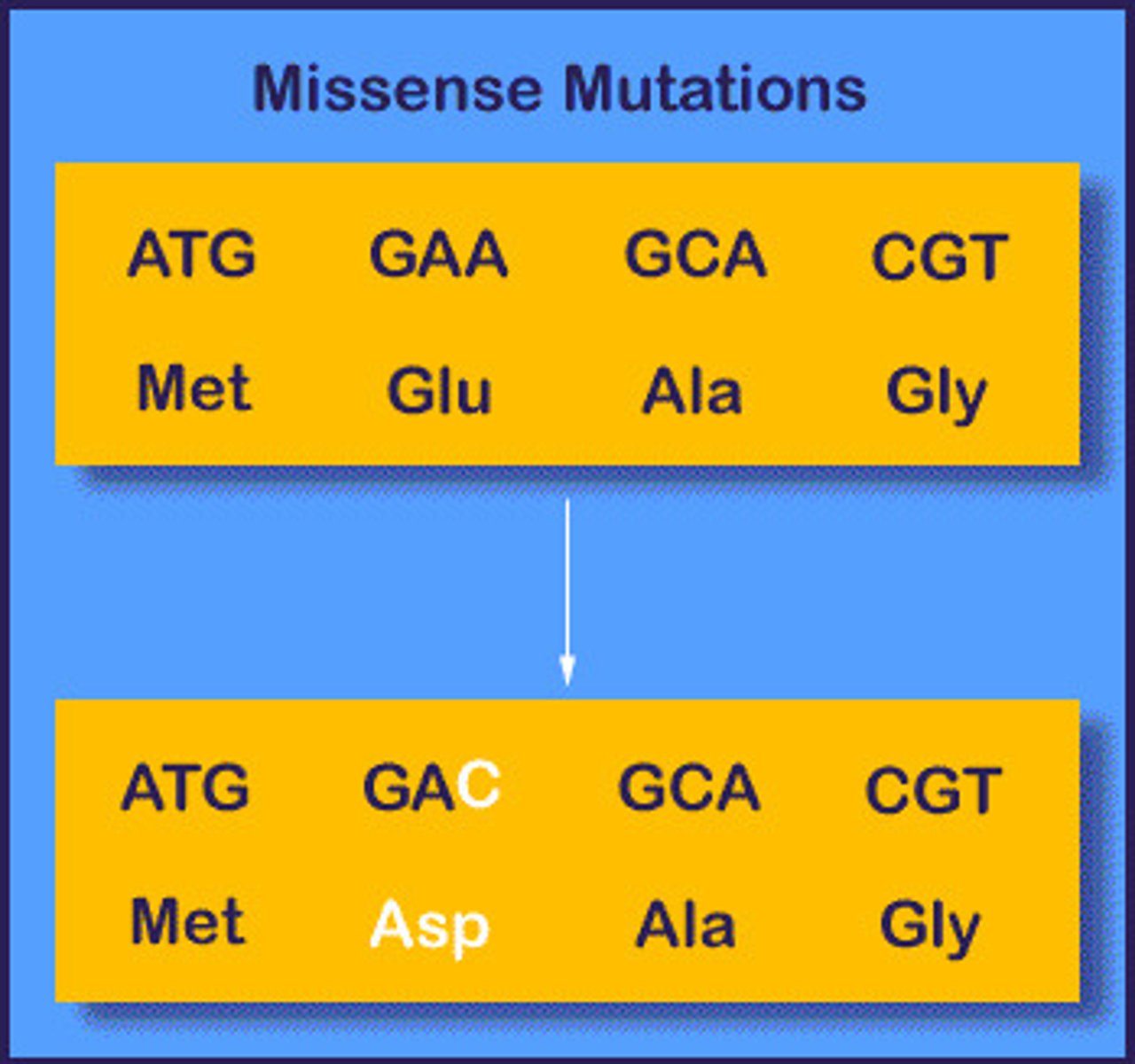
A mutation that results in a codon change that leads to the incorporation of a different amino acid in the protein.
Missense Mutation
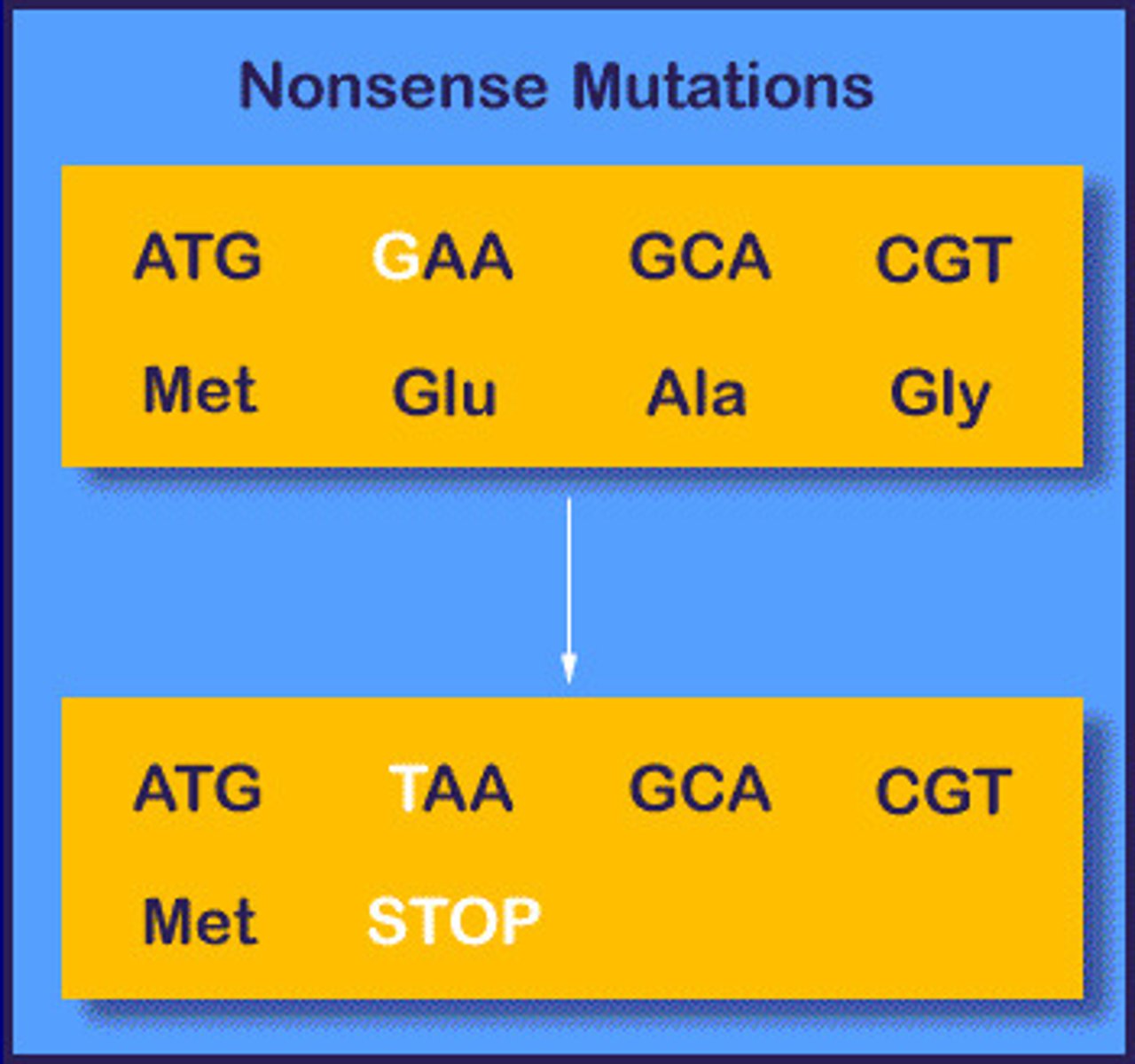
A mutation that converts a codon encoding an amino acid into a stop codon, leading to premature termination of protein synthesis.
Nonsense Mutation
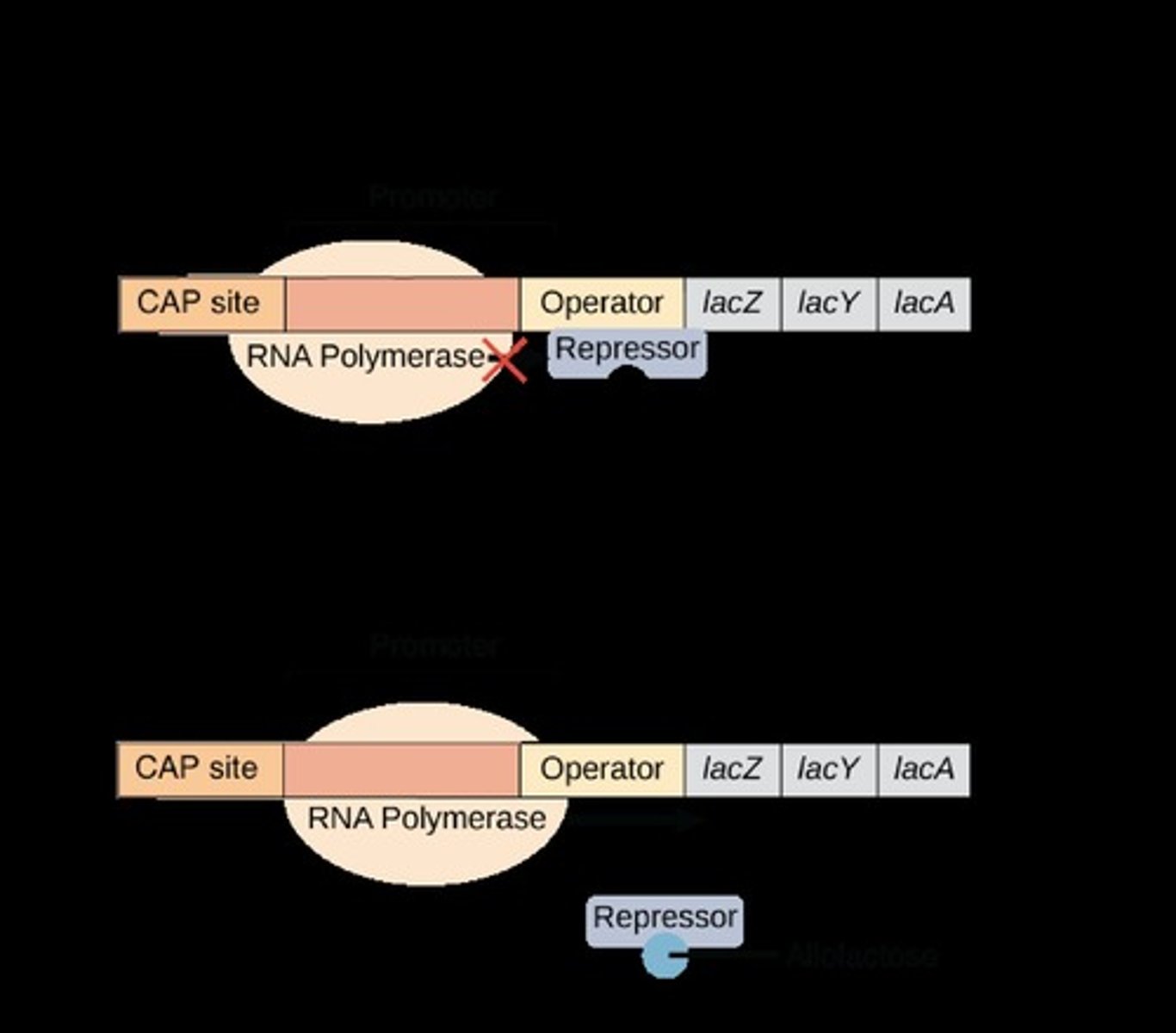
A set of genes in prokaryotic cells that are involved in the metabolism of lactose, which is activated in the presence of lactose.
Lac Operon
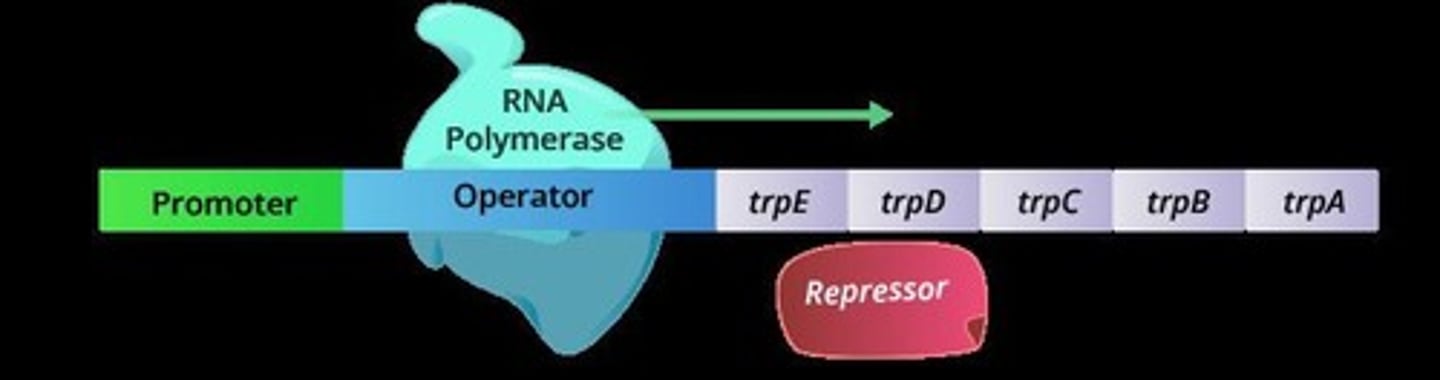
A group of genes in prokaryotic cells required for the synthesis of tryptophan, regulated by the availability of tryptophan.
Trp Operon
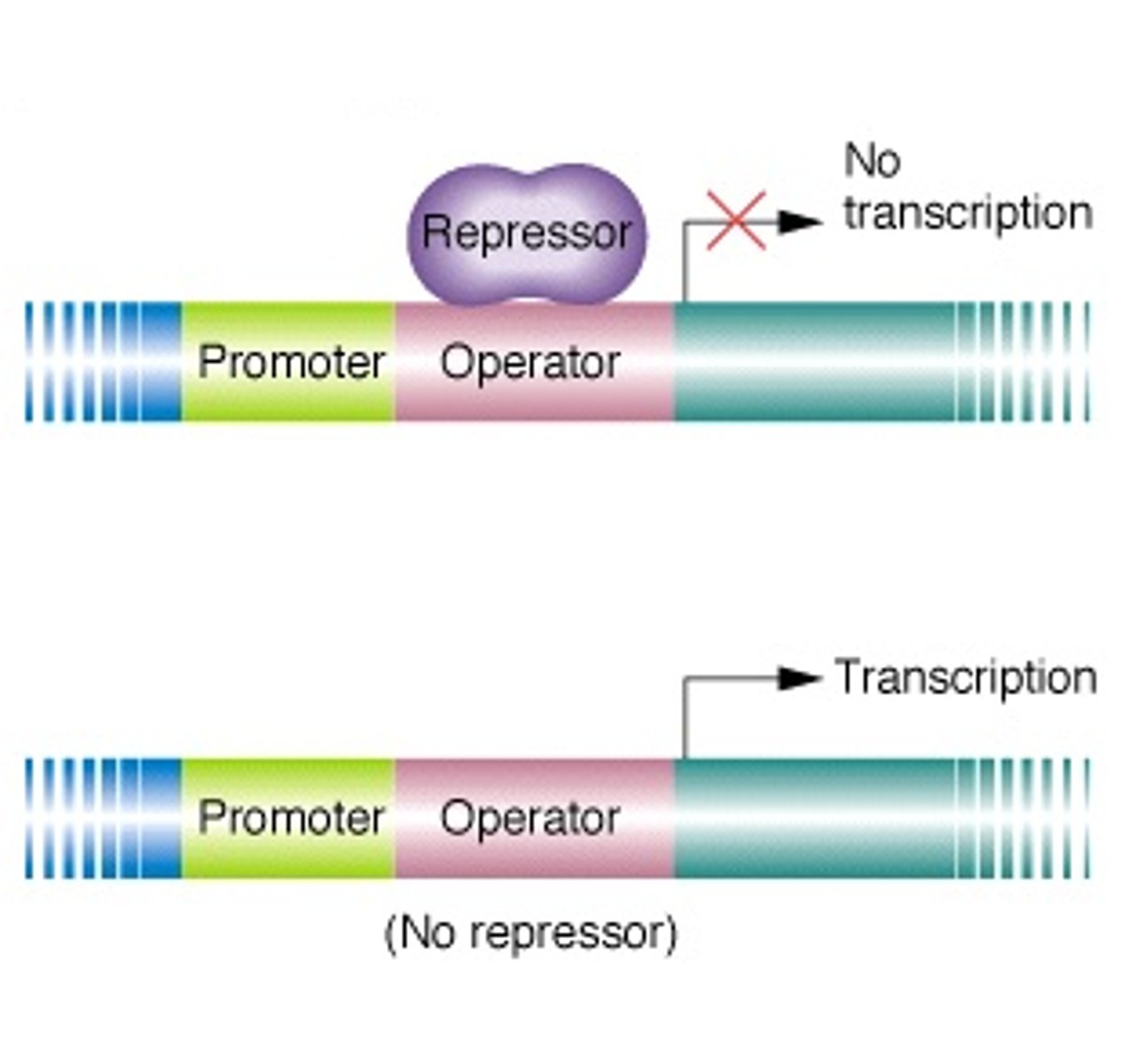
A cluster of genes under the control of a single promoter that are transcribed together, including structural genes and regulatory elements.
Operon
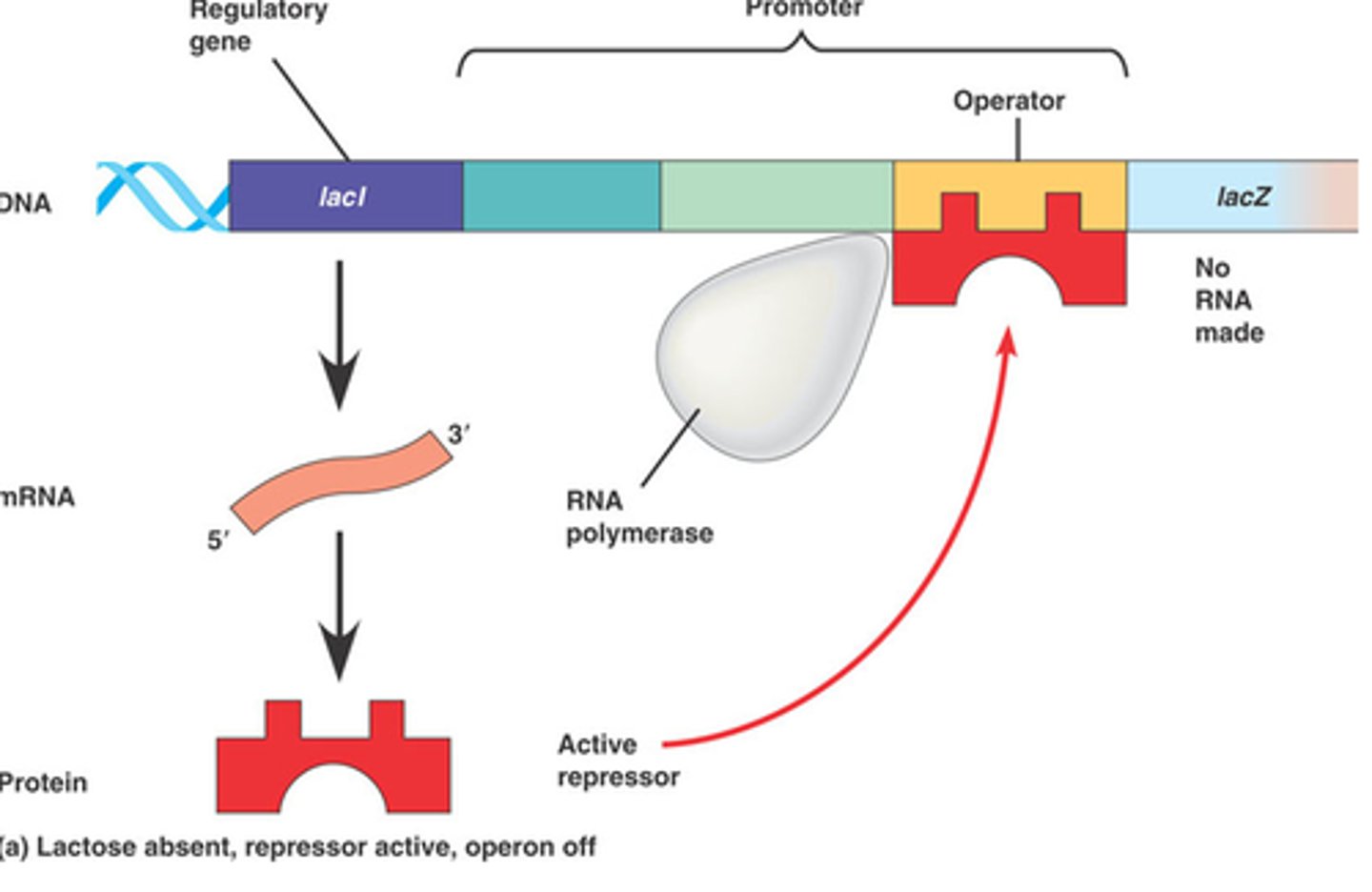
A protein that binds to the operator region of an operon to inhibit transcription of the associated genes.
Repressor
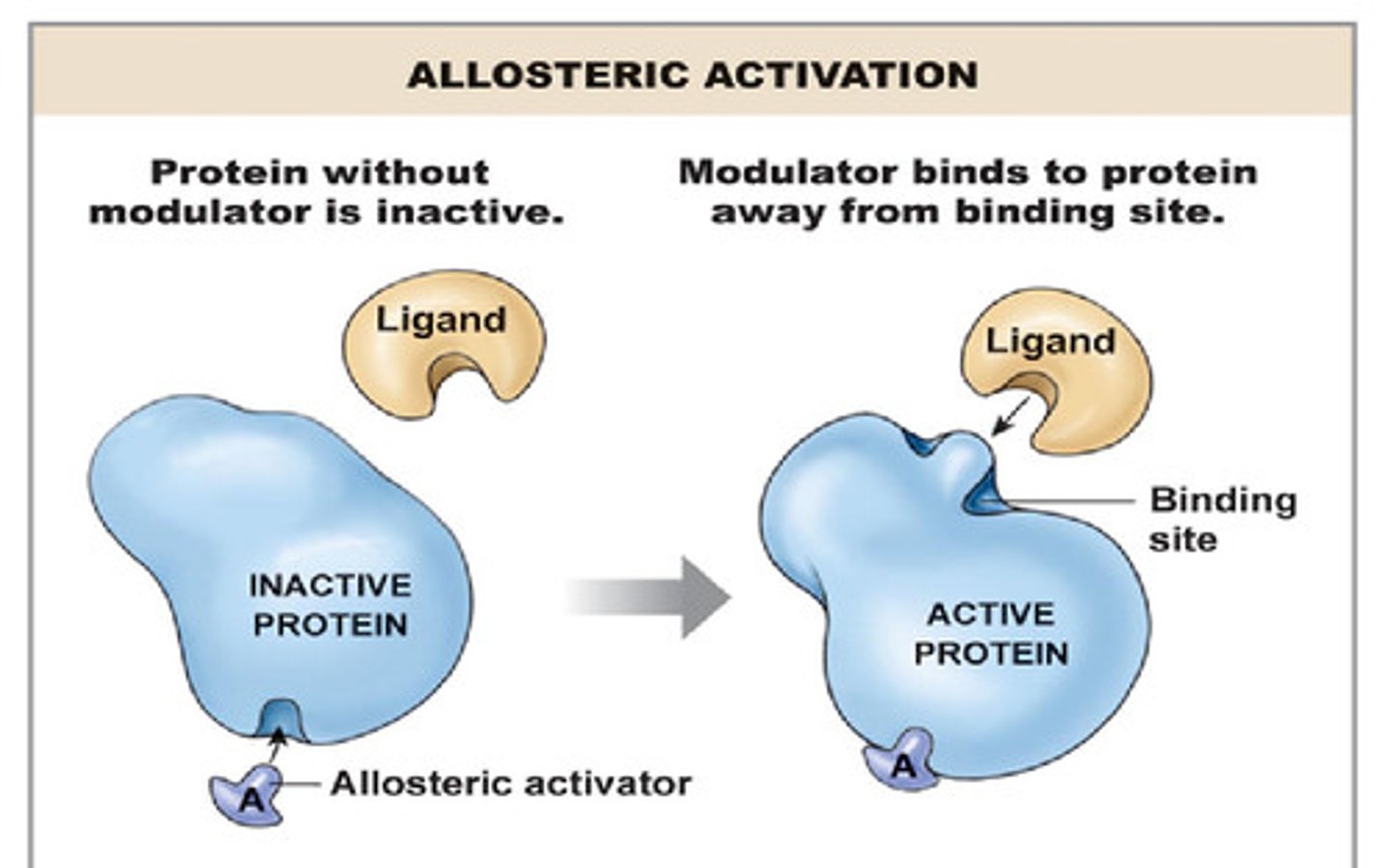
A protein that binds to an operator or promoter region to enhance transcription and facilitate RNA polymerase binding.
Activator
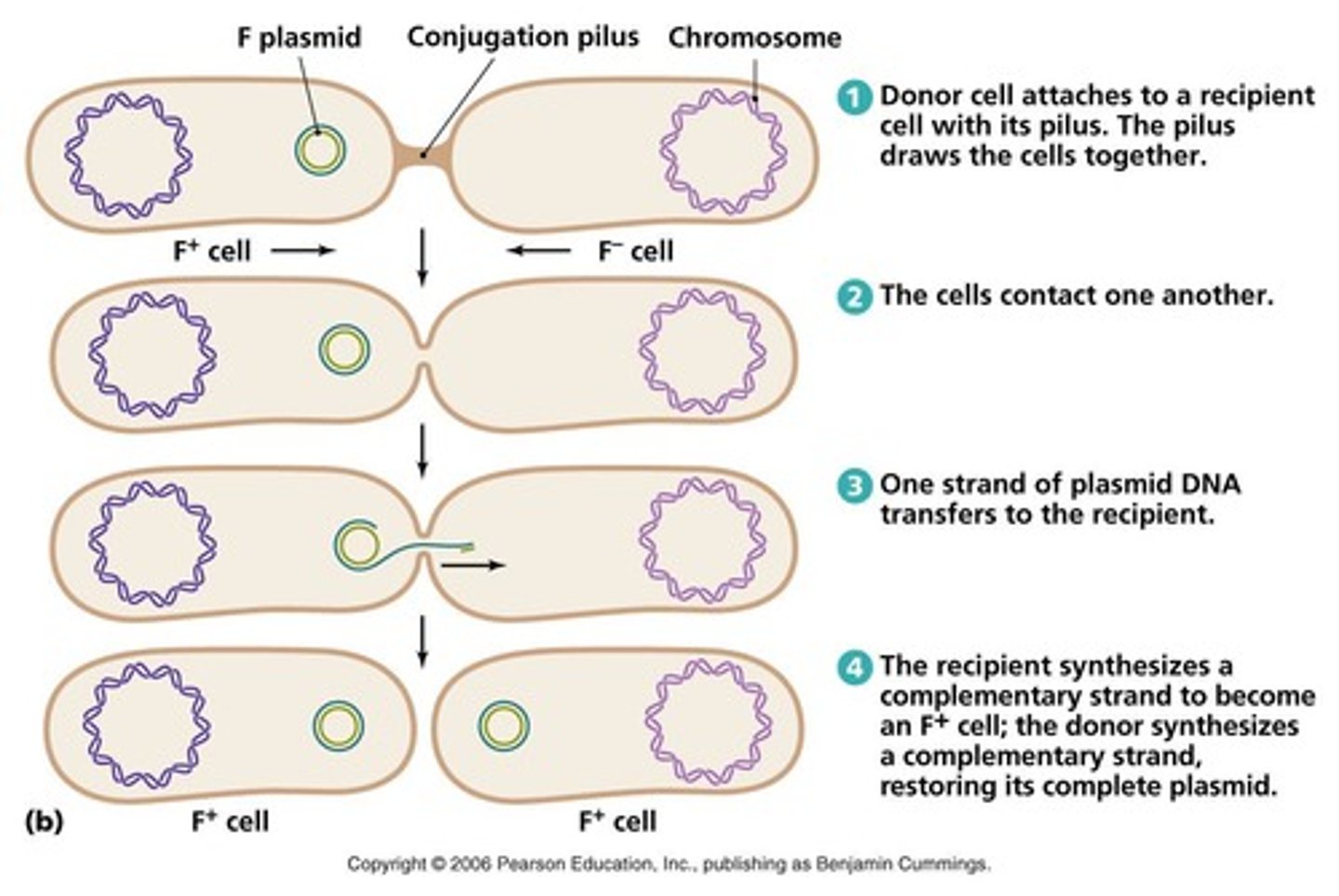
A process of genetic transfer in bacteria where DNA is transferred from one bacterium to another through direct cell-to-cell contact.
Conjugation
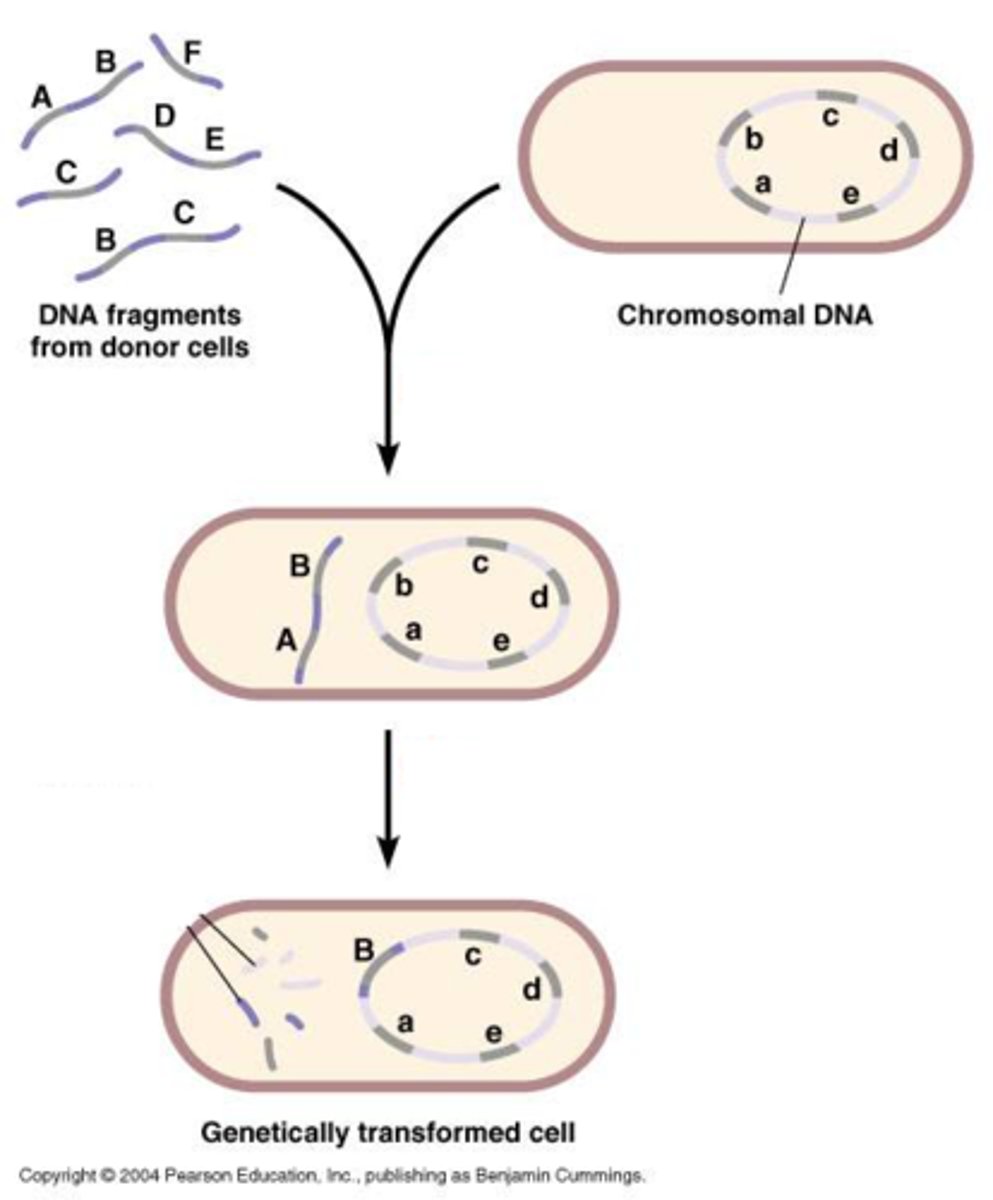
The uptake of free DNA from the environment by a competent bacterium.
Transformation
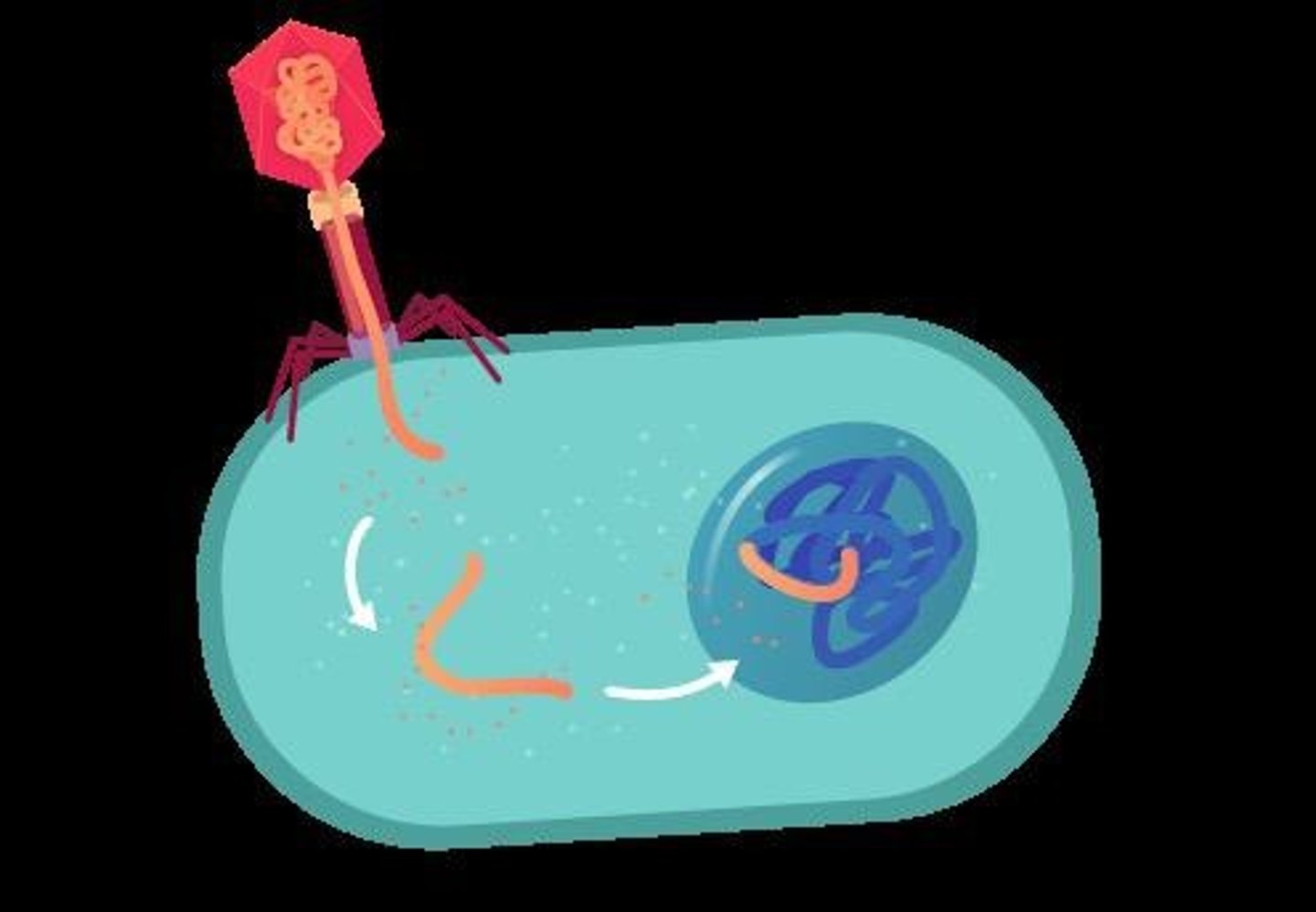
The transfer of genetic material from one bacterium to another via a bacteriophage.
Transduction
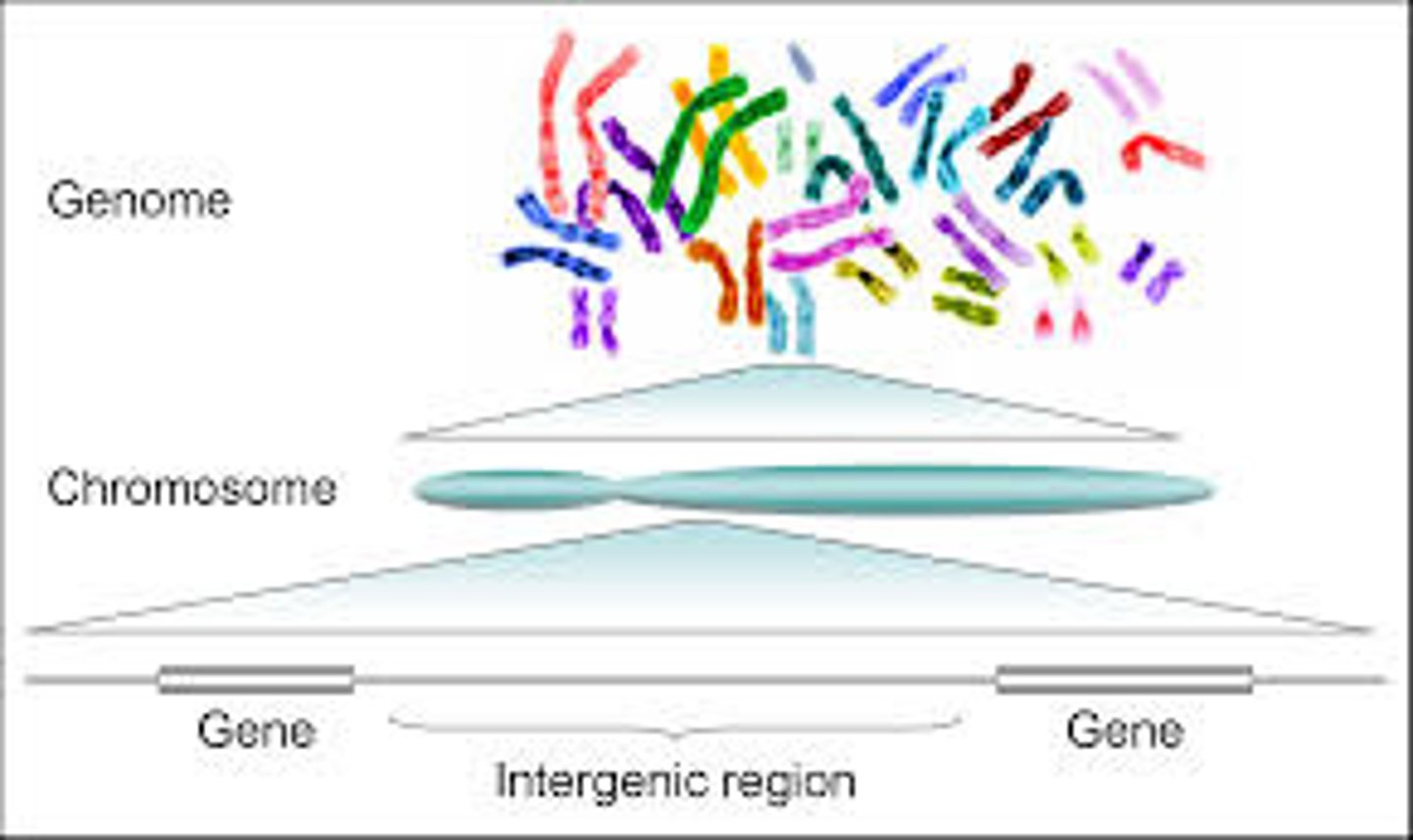
The complete set of genetic material present in an organism, including both coding and non-coding regions.
Genome
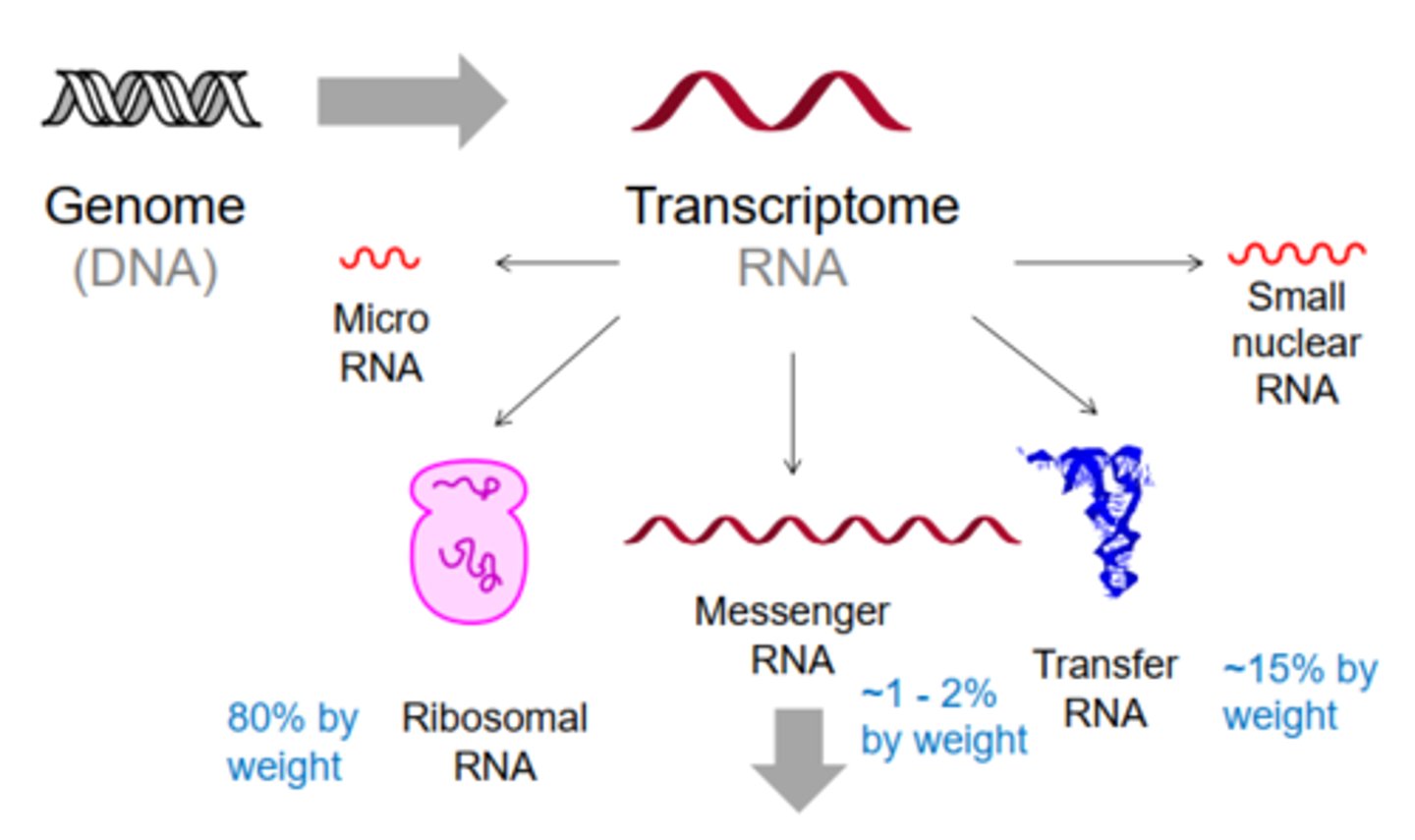
The full range of RNA molecules that are produced in a cell at a given time.
Transcriptome
The entire set of proteins expressed by a genome, cell, tissue, or organism at a certain time.
Proteome
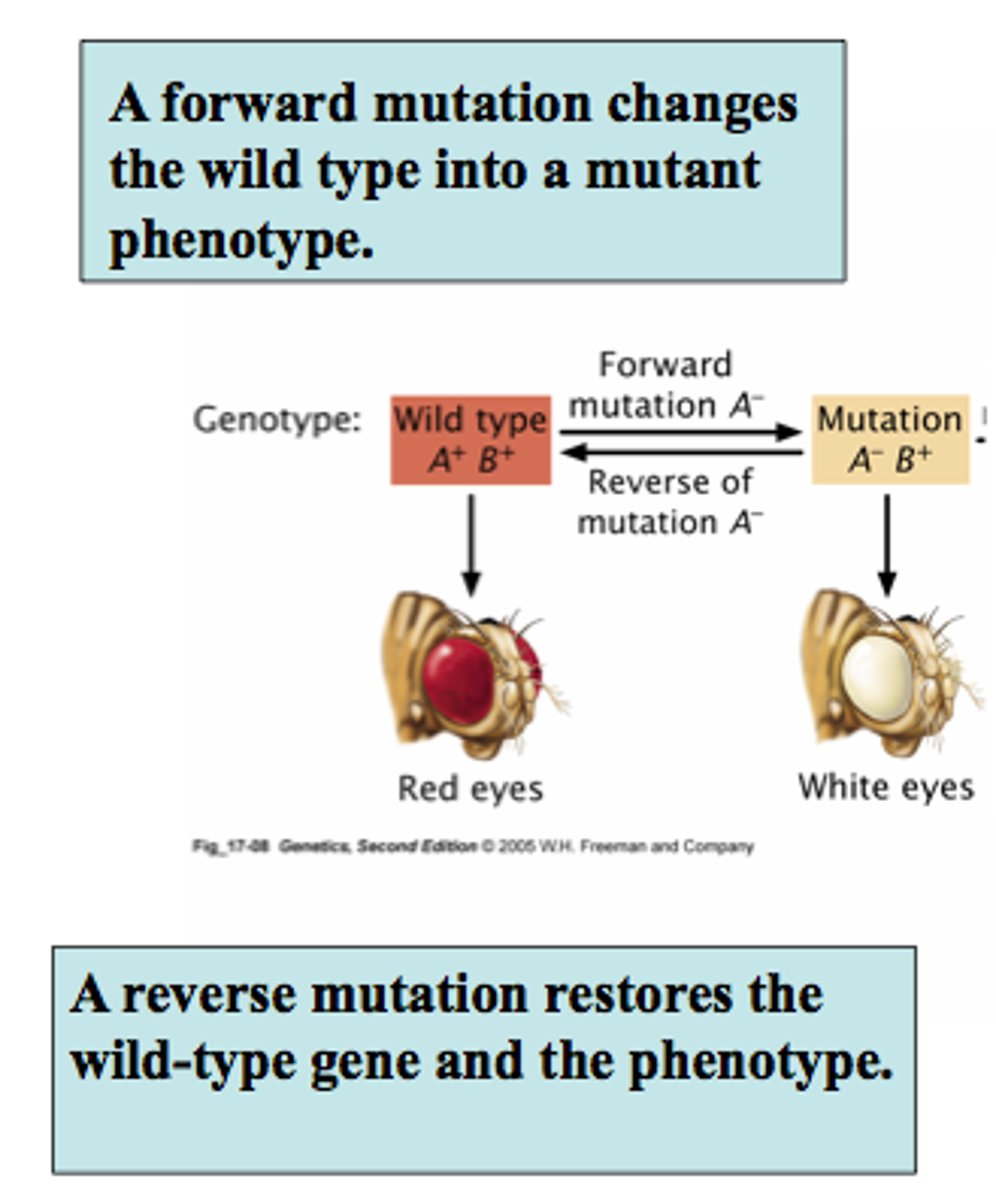
A mutation that changes a wild type allele into a mutant allele.
Forward Mutation
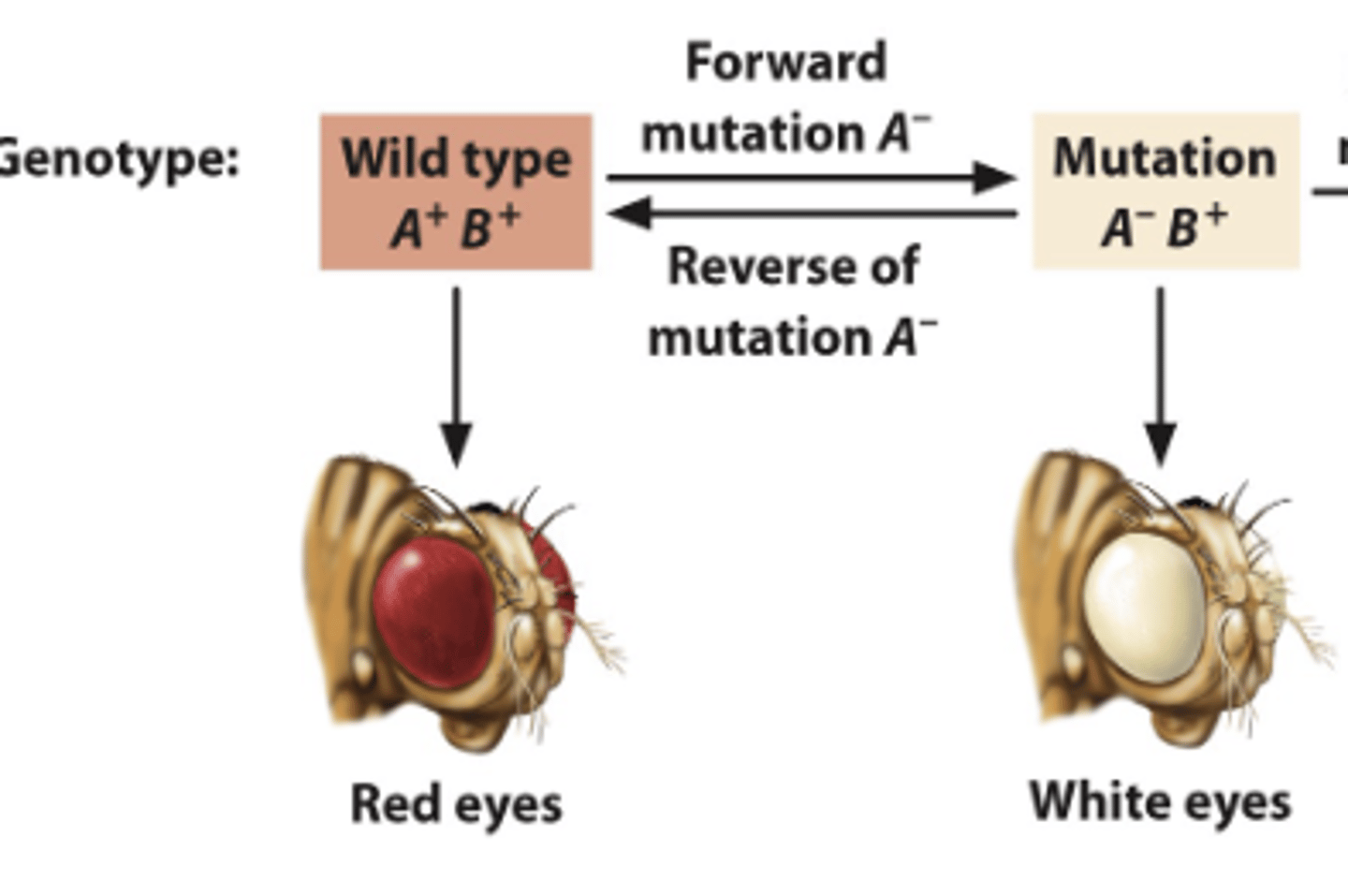
A mutation that reverts a mutant allele back to its original wild type form.
Backward Mutation
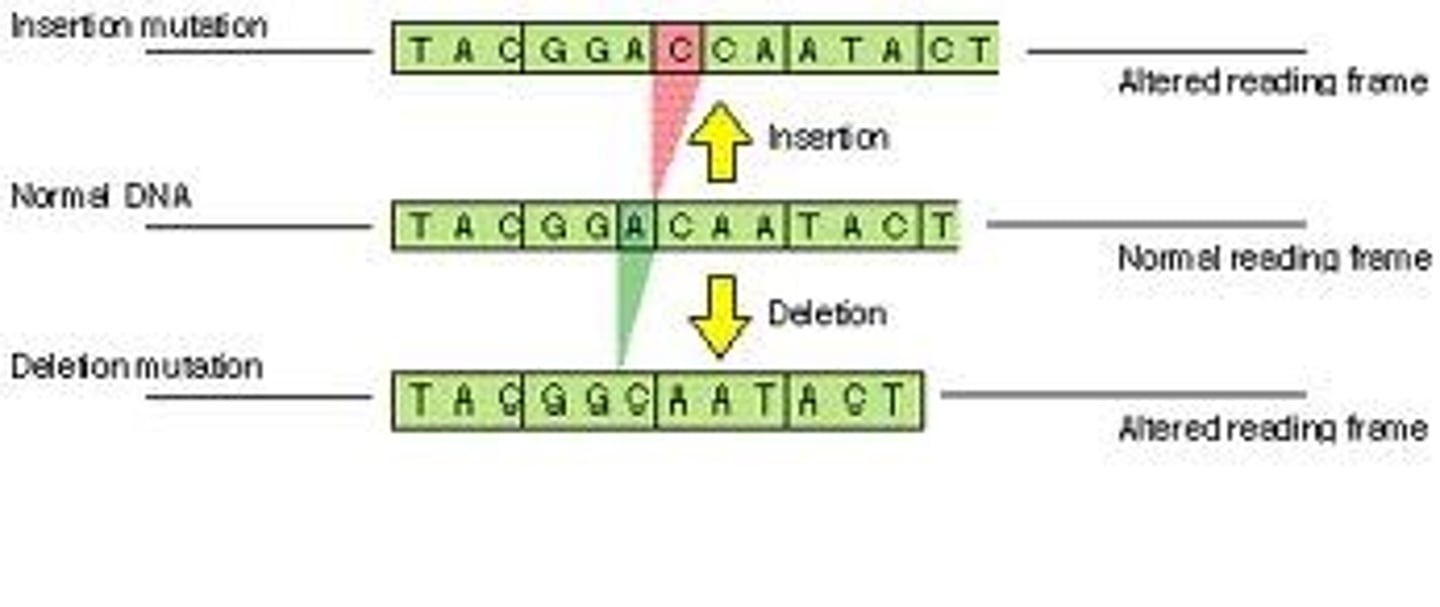
A mutation involving the addition of one or more nucleotide pairs into a DNA sequence, which can cause a frameshift.
Base-Pair Insertion
A mutation involving the removal of one or more nucleotide pairs from a DNA sequence, which can also result in a frameshift.
Base-Pair Deletion
The total number of nucleotides an organism has.
Genome Size
The total number of genes, which are sequences of nucleotides that code for a product.
Gene Number
The ratio of gene number to genome size.
Gene Density
Sequences of DNA that are unrelated to the organism's functional genes, often without correlation to genome size.
Repetitive DNA
DNA sequences that do not code for proteins but play roles in gene regulation and genome structure.
Unique Noncoding DNA
The study of changes in gene expression that do not involve alterations to the underlying DNA sequence.
Epigenetics
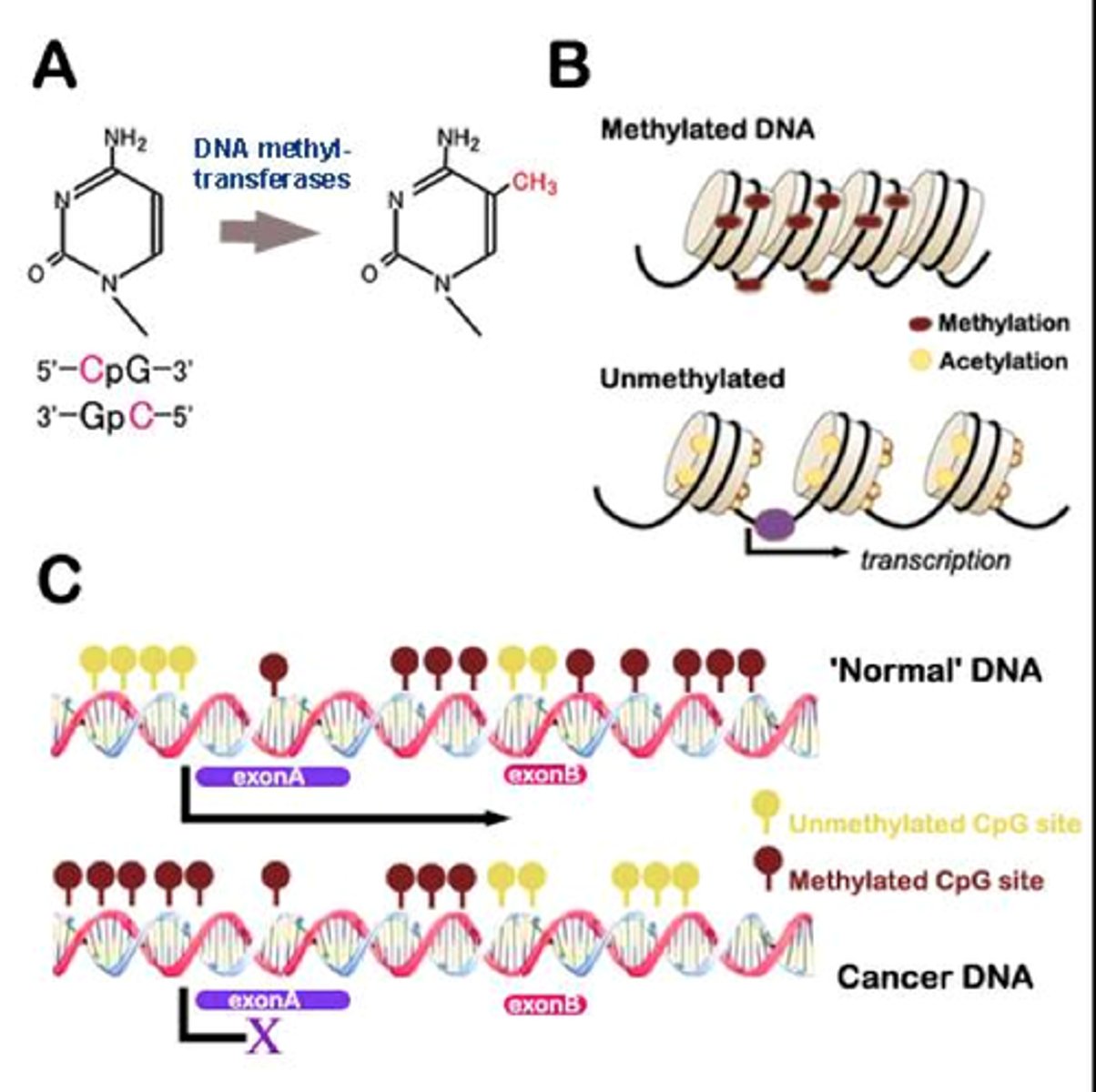
An epigenetic mechanism that involves adding a methyl group to DNA, often leading to gene silencing.
DNA Methylation
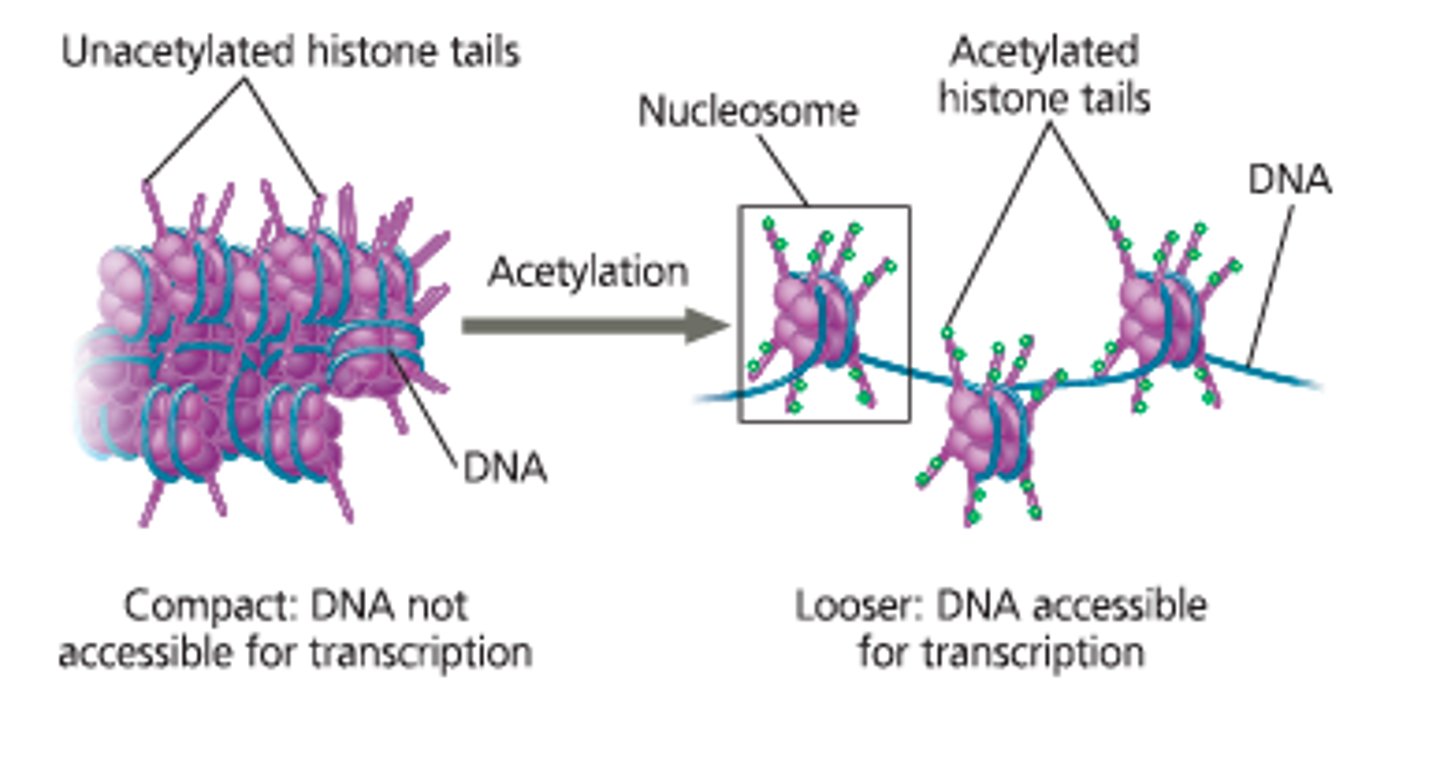
An epigenetic modification that adds acetyl groups to histones, resulting in increased gene expression.
Histone Acetylation
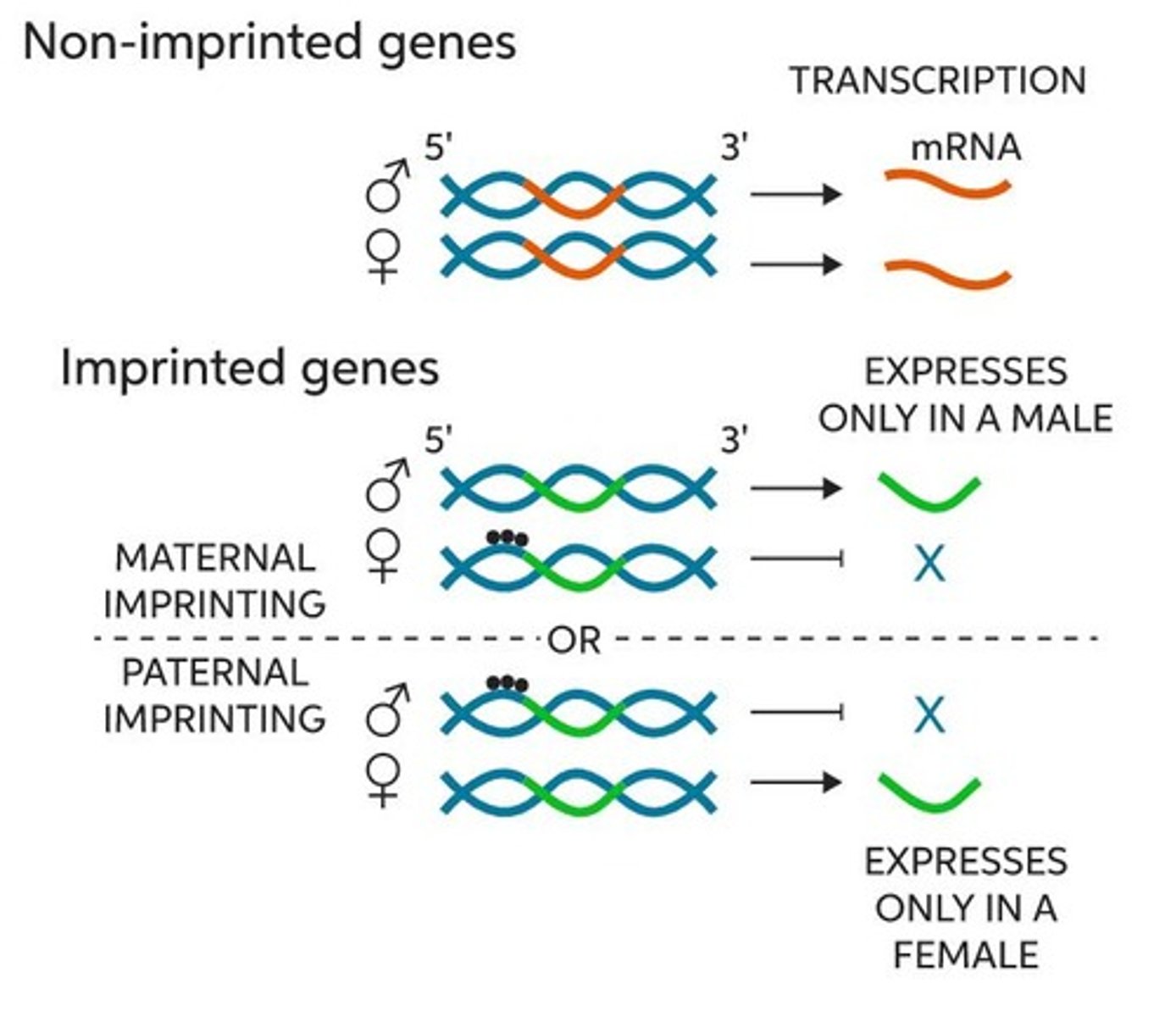
A genetic phenomenon where only one allele of a gene is expressed depending on its parental origin.
Genomic Imprinting
A process where the sex of an organism is determined by the environmental temperature during a critical period of development.
Temperature-Dependent Sex Determination
A genetic disorder caused by the loss of function of genes on the paternal chromosome 15, leading to various health issues.
Prader-Willi Syndrome
A genetic disorder caused by the loss of function of genes on the maternal chromosome 15, resulting in developmental delays and other health problems.
Angelman Syndrome
DNA sequences that can change their position within the genome, potentially disrupting gene function.
Transposable Elements
RNA molecules that are not translated into proteins but have roles in regulating gene expression.
Non-coding RNAs
Female honeybees that develop from larvae fed a special diet, resulting in distinct phenotypic traits compared to worker bees.
Queen Bees