Orgo CH11 In-Class Notes--Carboxylic Acids and Derivatives: Nucleophilic Acyl Substitution Reactions
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
41 Terms
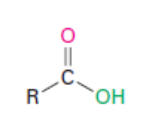
Carboxylic acid
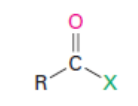
Acid halide
(X = Cl, Br)
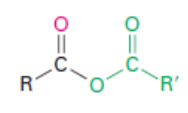
Acid anhydride
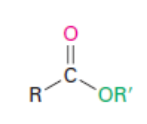
Ester
Amide
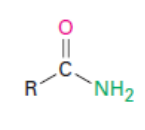
Thioester
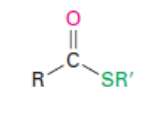
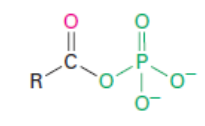
Acyl phosphate
Nitrile
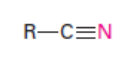
Naming Carboxylic Acids and Derivatives
Carboxylic acids (RCO2H): replace the “e” with “oic acid” ending for alkane, -carboxylic acid ending for cycloalkane.
Carboxylic acids (RCO2H) have priority over aldehydes, ketone, and alcohols
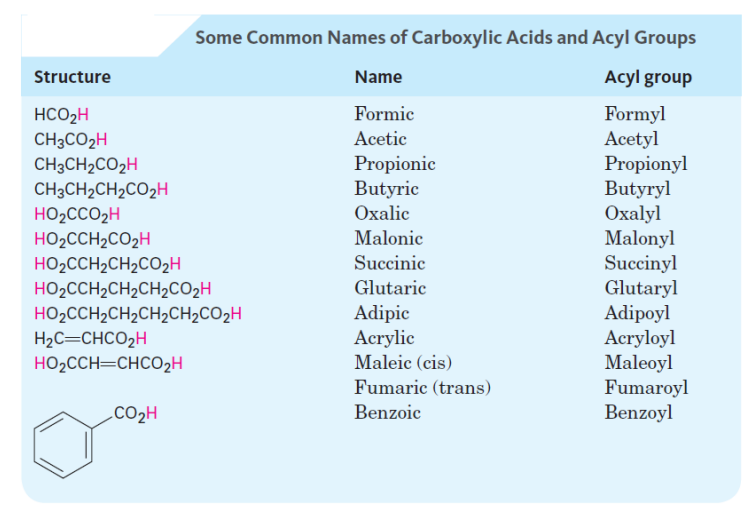
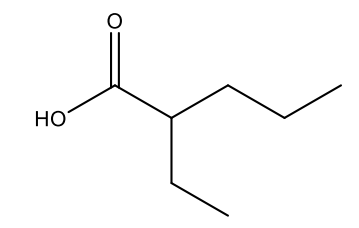
What is the IUPAC name of the following structure?
2-ethylpentanoic acid
Properties of Carboxylic Acids
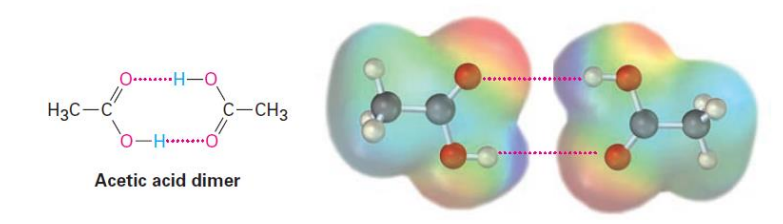
Carboxylic acids have strong IMFs
Most exist as a dimer
Higher boiling points than alkane and alcohol counterparts
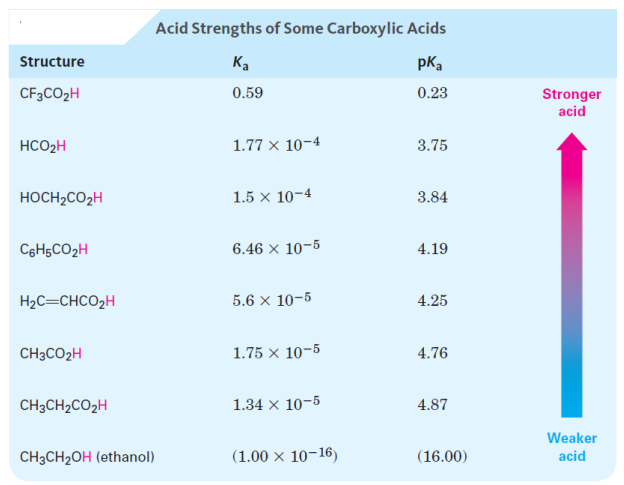
Acidity of Carboxylic Acids
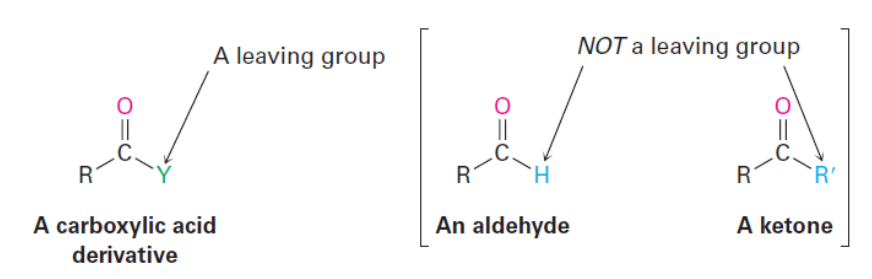
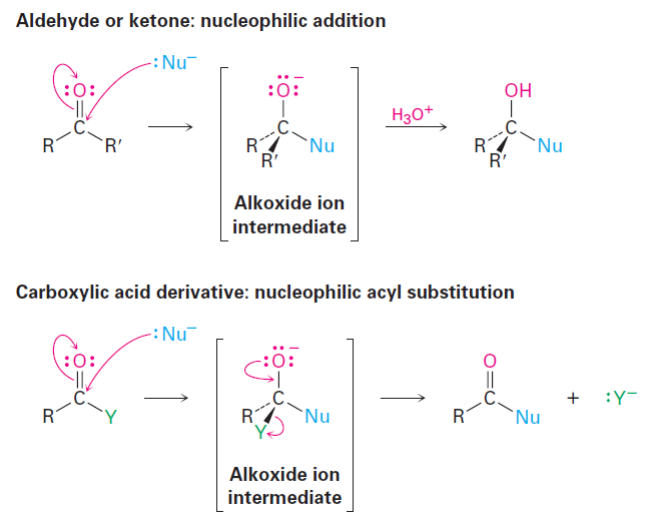
Nucleophilic Acyl Substitution Reactions
Nucleophilic reactions with aldehydes and ketones led to addition reactions.
Other carboxylic acid derivatives can undergo nucleophilic acyl substitution reactions.
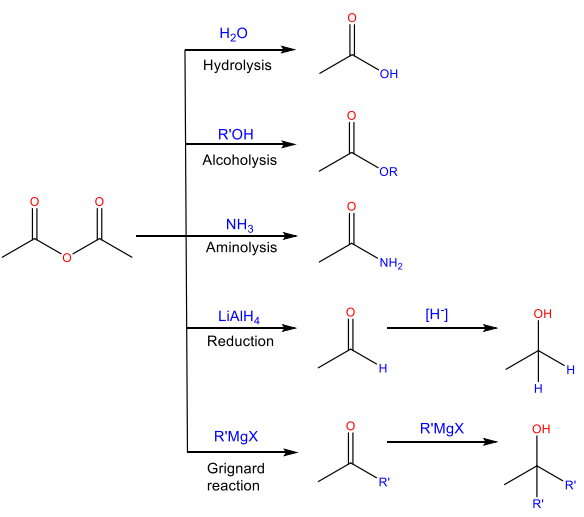
Nucleophilic Acyl Substitution Reactions
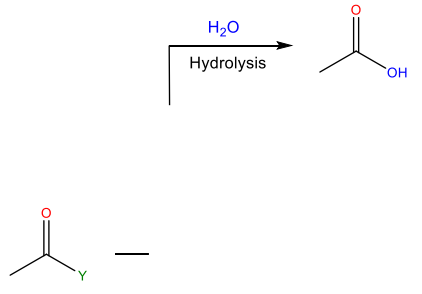
Hydrolysis
Reaction with water to yield carboxylic acid
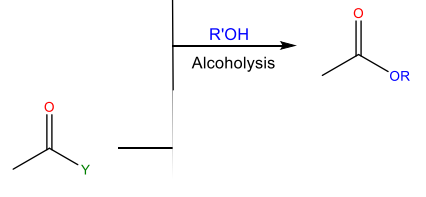
Alcoholysis
Reaction with an alcohol to form an ester
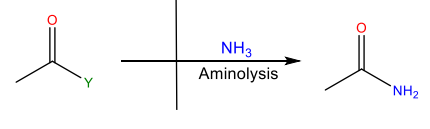
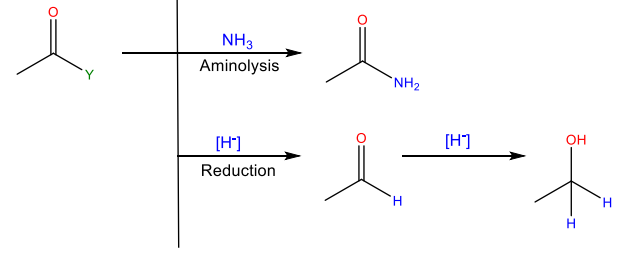
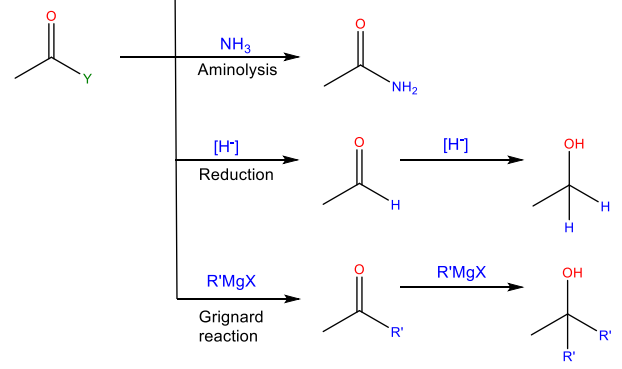
Aminolysis
Reaction with ammonia or an amine to yield an amide
Reduction
Reaction with a hydride reducing agent to yield an alcohol
Grignard reaction
Reaction with an organomagnesium reagent to yield and alcohol
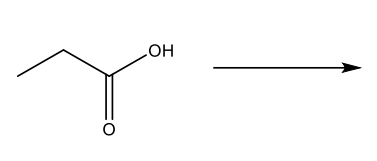
Conversions of carboxylic acids into acid chlorides.
Reaction arrow with SOCl2 (thionyl chloride) and pyridine, making acyl chloride
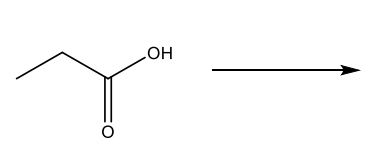
Conversions of carboxylic acids into esters
Reaction arrow with an alcohol (like ethanol) and an acid (H2O+) to make an ester
Reduction of carboxylic acids into alcohols.
Process of reacting carboxylic acids with reducing agents like LiAlH4 or NaBH4 or ether and an acid (H3O+) to yield alcohols.

acid chloride

1 ) LiAlH4, 2) H3O+
Which reagents would be best to use in the following reaction?
Thionyl chloride and a base
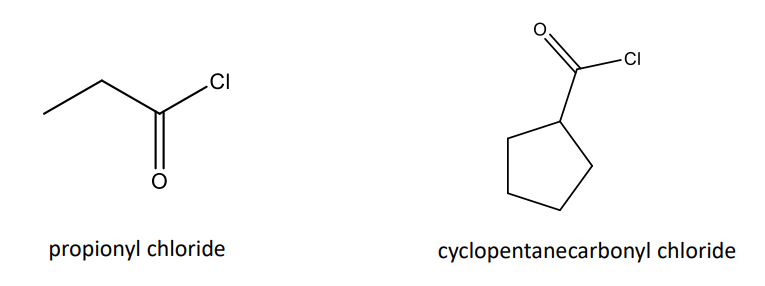
Naming Acid Halides
Acid Halides (RCOX): name of acyl group, followed by halide. If on an alkyl ring, gets –carbonyl halide name.
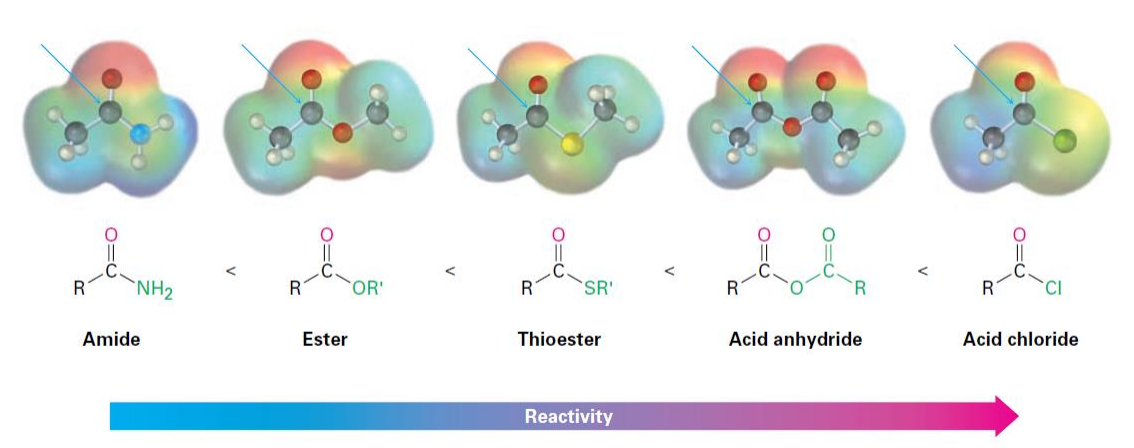
Nucleophilic Acyl Substitution Reactions
A class of reactions in which a nucleophile attacks an acyl compound, leading to the substitution of one group for another, typically involving carboxylic acids and their derivatives.
Acid Halides and Their Reactions
• Acid halides are among the most reactive of the carboxylic acid derivatives.
• They can undergo:
• Hydrolysis
• Alcoholysis
• Aminolysis
• Reduction
• Grignard Reactions

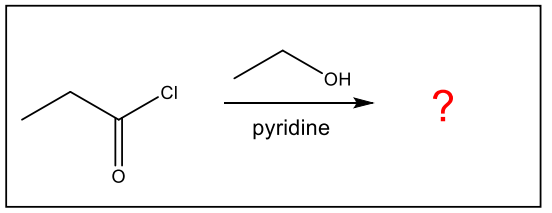
What is the major organic product of the following reaction?
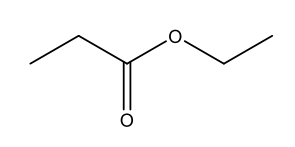
Naming Acid Anhydrides
Acid Anhydrides (RCO2COR’): named like carboxylic acids, except replace “acid” with “anhydride”
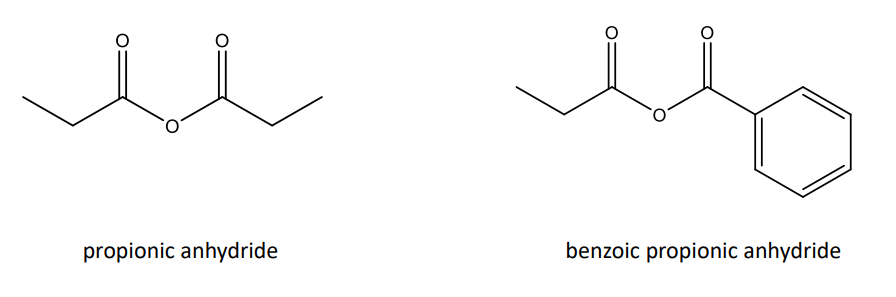
Acid Anhydrides and Their Reactions
• Acid anhydrides are similar to acid chlorides.
• They can undergo: • Hydrolysis • Alcoholysis • Aminolysis • Reduction • Grignard Reactions
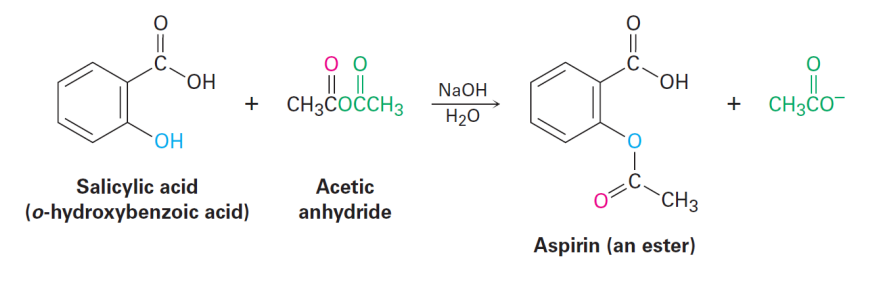
Synthesis of Pain Killers
Naming Esters
Esters (RCO2R’): give the name of alkyl group, then the carboxyl portion as “oate”
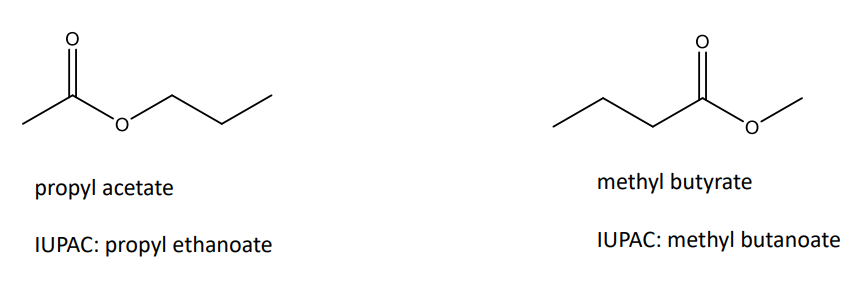
Properties of Esters
Many esters are pleasant-smelling liquids
Ester linkage is present in animal fats and may biologically important molecules
Synthesis of Esters
Esters are usually prepared from acid or acid chlorides.
Esters and their Reactions
Esters undergo similar reactions to acid chlorides and acid anhydrides, however, are less reactive.
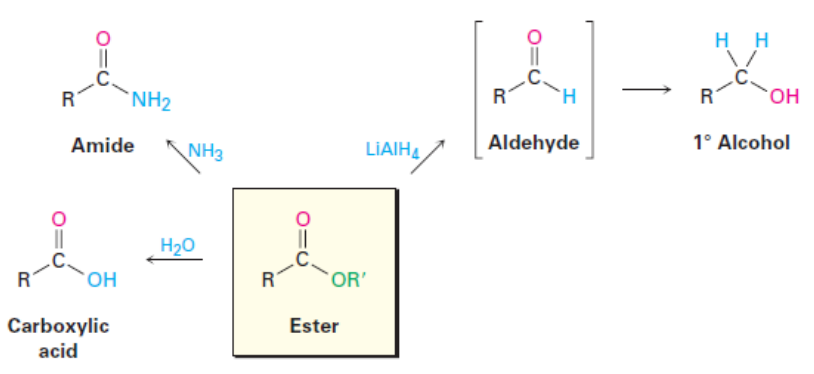
Examples: Esters and their Reactions
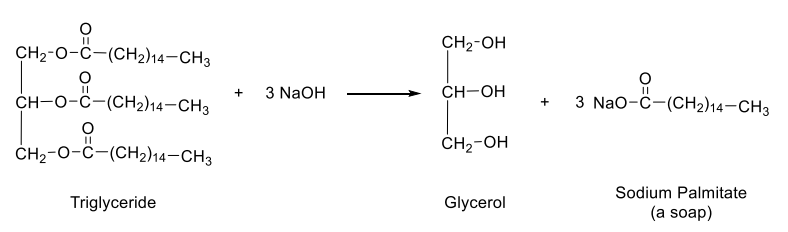
Hydrolysis of Esters: Saponification
This reaction is an important process for making soap
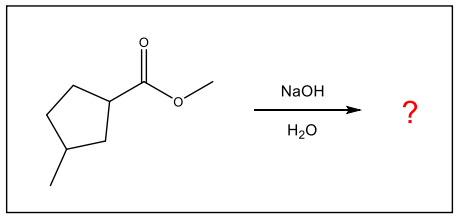
What is the major organic product of the following reaction?
Naming Amides
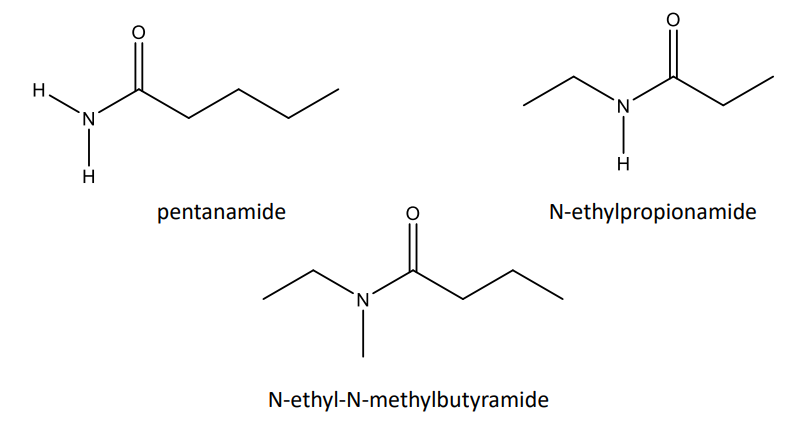
Amides (RCONH2 ): -amide ending, carboxamide if bonded to alkyl ring. If the nitrogen is substituted, use “N-” as the locant number
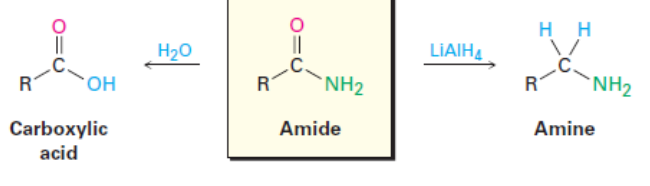
Amides and Their Reactions
Amides are prepared by reaction of an acid chloride with an amine.
Amides are much less reactive than acid chlorides, acid anhydries, and esters.
Amides undergo hydrolysis to form carboxylic acids and reductions to form amines.
Hydrolysis Amide: Antibiotics
Penicillin contains a cyclic amide called a Lactam. The lactam deactivate an enzyme, transpeptidase, required for the biosynthesis of the bacterial cell walls