CH322 - Semiconductors & Insulators
1/6
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
7 Terms
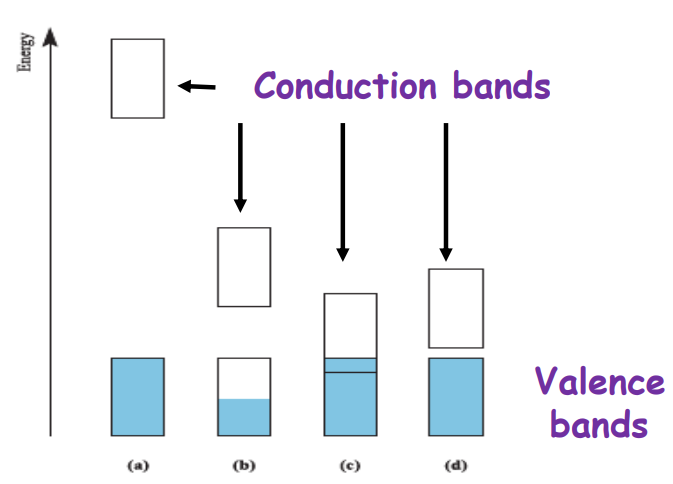
Describe the differences between an insulator and a semiconductor and metals
Insulators have a large band gap, so electrons can't easily move to the conduction band, making them poor conductors.
Semiconductors have a smaller band gap, allowing some electron movement, so they conduct better than insulators but worse than metals.
Metals are excellent conductors because their valence and conduction bands overlap, letting electrons move freely.
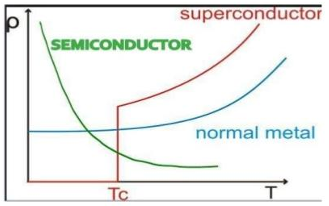
Explain the variation in resistivity with temperature for a semiconductor.
In semiconductors, resistivity generally decreases as temperature increases. This is because elevated temperatures lead to more free charge carriers in the semiconductor, increasing conductivity and thus lowering resistance.
P-type semiconductor
Electrical conductivity arises from thermal population of an acceptor level which leaves vacancies in the lower band.
N-type semiconductor
A donor level is close in energy to the conduction band
representation of the band levels (valence and conduction bands) for an insulator and for a p-type and n-type semiconductor
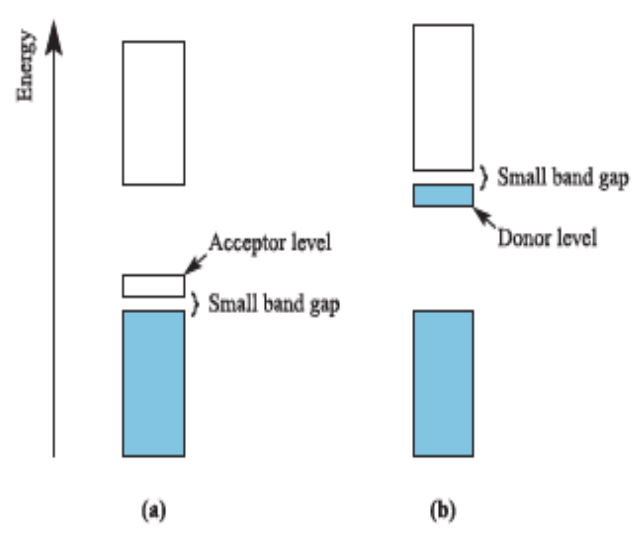
Band levels
The relative energies of occupied and empty bands in (a) an insulator, (b) a metal in which the lower band is only partially occupied, (c) a metal in which the occupied and empty bands overlap, and (d) a semiconductor.
Draw in one diagram (conductivity vs temperature) the behaviour of a metal (conductor), of a semiconductor and of a superconductor.