Ch 12 Tissues and Cells of the Nervous system
1/144
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
145 Terms
Nervous system
-Employs electrical and chemical means to send messages from cell to cell
-Foundation of our conscious experience, personality, and behavior
-Vary complex
Neurobiology
-Combines the behavioral and life sciences
Endocrine system
-Communicates by means of chemical messengers (hormones) secreted into the blood
Receive information
-Sense organs receive information about changes in the body and external environment, and transmit coded messages to the brain and spinal cord (CNS)
Processes information
-CNS processes this information, relates it to past experiences, and determines appropriate response
Sending out commands
-CNS issues commands to muscles and gland cells to carry out such a response
Central Nervous System
-CNS
-Brain and spinal cord enclosed by cranium and vertebral column
Peripheral Nervous System
-PNS
-All nervous system except the brain and spinal cord; composed of nerves and ganglia
-Contains sensory and motor divisions each with somatic and visceral subdivisions
Nerve
-A bundle of nerve fibers (axons) wrapped in fibrous connective tissue that
Ganglion
-Knot-like swelling in a nerve where neuron cell bodies are concentrated
Sensory division
-Afferent
-Carriers signals from receptors to CNS
Somatic sensory division
-Carrier signals from receptors in the skin, muscles, bones, and joints
Visceral sensory division
-Carriers signals from the viscera (heart, lungs, stomach, and urinary bladder)
Motor division
-Efferent
-Carriers signals from CNS to effectors (Glands and muscles that carry out the body's response)
Somatic motor division
-Carrier signals to skeletal muscles
-Output produces voluntary muscular contraction as well as somatic reflexes (involuntary muscle contractions
Visceral motor division
-Autonomic nervous system
-Carries signals to glands, cardiac and smooth muscle
-Its involuntary responses are visceral reflexes
Sympathetic dividion
-Tends to arouse body for action
-Accelerating heartbeat and respiration, while inhibition digestive and urinary systems
-Fight or flight
Parasympathetic division
-Tends to have calming effect
-Slows heart rate and breathing
-Stimulates digestive and urinary system
-Rest and digest
Excitability
-Irritability
-Respond to environmental changes in stimuli
Conductivity
-Respond to stimuli by producing electrical signals that are quickly conducted to other cells at distant locations
Secretion
-When an electrical signal reaches the end of nerve fiber, the cell secretes a chemical neurotransmitter that influences the next cell
Sensory neruons
-Afferent
-Detect stimuli and transmit information about them toward the CNS
Interneuron location
-Lie entirely within CNS connecting motor and sensory pathways
-About 90% of all neurons
Interneuron function
-Receive signals from many neurons and carry out integrative functions
-Make decisions on responses
Motor neuron
-Efferent
-Sends signals out to muscles and gland cells (the effectors)
Neurosoma
-Control center of neuron
-Soma or Cell body of neuron
-Has single, centrally located nucleus with large nucleolus
Cytoplasm of neuron
-Contains mitochondria, lysosomes, Golgi complex, inclusions, extensive rough ER and cytoskeleton
-Dense mesh of microtubules and neurofibrils that compartmentalize rough ER into dark-staining chromatophilic substance (Nissl bodies)
Cytoplasm Inclusions of neuron
-Glycogen, lipid droplets, melanin, and lipofuscin pigment
-No centrioles, no mitosis
Dendrites
-Branches that come off the neurosoma
-Primary sight for receiving signals from other neurons
-More dendrites means it can receive more information
-Precise pathways for the reception and processing of information
Axon
-Nerve fiber
-Originates from a mound on the neurosoma called axon hillock
-Cylindrical, relatively unbranched for most of its length
-One axon per neuron
Axon collaterals
-Branches of axon
-Branch extensively on distal end
-Specialized for rapid conduction of signals to distant points
Axoplasm
-Cytoplasm of axon
Axolemma
-Plasma membrane of axon
Terminal arborization
-Extensive complex of branches
-Distal end of axon
Axon terminal
-Little swelling that forms a junction (synapse) with the next cell
-Contains synaptic vesicles full of neurotransmitters
-many vesicles are docked on plasma membrane ready to release neurotransmitter
-A reserve pool of synaptic vesicles is located further away from membrane
Unipolar neruon
-Single process leading away from neurosoma
-Sensory cells from skin and organs to spinal cord
Anaxonic neuron
-Many dendrites but no axon
-Retina, brain, and adrenal gland
Multipolar neuron
-One axon and multiple dendrites
-Most common neurons in CNS
Bipolar neurons
-One axon and one dendrite
-Olfactory cells, retina, inner ear
Axonal transport
-Two-way passage of proteins, organelles, and other material along with axon
-Microtubules guide materials along axon
-Motor proteins carry materials "on their backs" while they "crawl" along microtubules
Anterograde transport
-Toward the terminal
-Movement down the axon away from neurosoma
Retrograde transport
-Away from the terminal
-Movement up the axon toward the neurosoma
Axonal transport function
-Many proteins made in neurosoma must be transported to axon and axon terminal
-To repair axolemma, serve as gated ion channels, enzymes or neurotransmitters
Kinesin
-Motor proteins in anterograde transport
Dynein
-Motor proteins in retrograde transport
Fast axonal transport
-rate of 20 to 400 mm/day
-Anterograde
-Retrograde
Fast anterograde transport
-Organelles enzymes, synaptic vesicles, and small molecules
Fast retrograde transport
-For recycled materials and pathogens - rabies, herpes simplex, tetanus, polio viruses
-Delay between infection and symptoms is time needed for transport up the axon
Slow axonal transport
-0.5 to 10 mm/day
-Always retrograde
-Damaged nerve fibers regenerate at a speed governed by slow axonal transport
Slow axonal transport function
-Always anterograde
-Moves enzymes, cytoskeletal components, and new axoplasm down the axon during repair and regeneration of damaged axons
-Speed of nerve fiber regeneration
Neuroglia
-Out # neurons 10 to 1
-Neuron protection
-Binds neurons to create nervous framework
-Covers "dead ends"
-Prevents neurons from touching each other
-Gives precise conduction pathways
Oligodendrocytes
-Glia in CNS
-Form myelin sheaths in CNS that speed signal conduction
-Arm-like processes wrap around nerve fibers
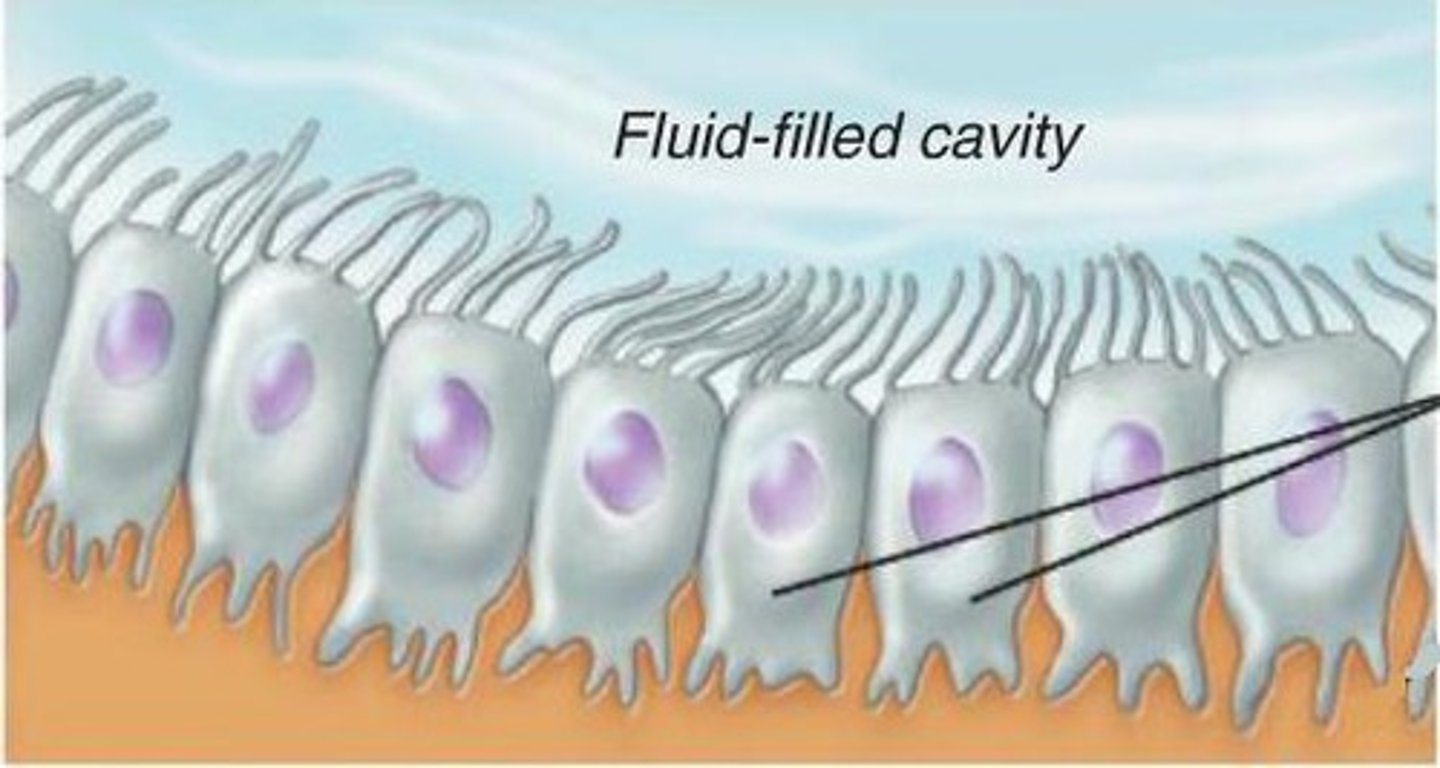
Ependymal cells
-Glia of CNS
-Line internal cavities of the brain
-Secrete and circulate cerebrospinal fluid (CSF)
-Cuboidal epithelium with cilia on apical surface
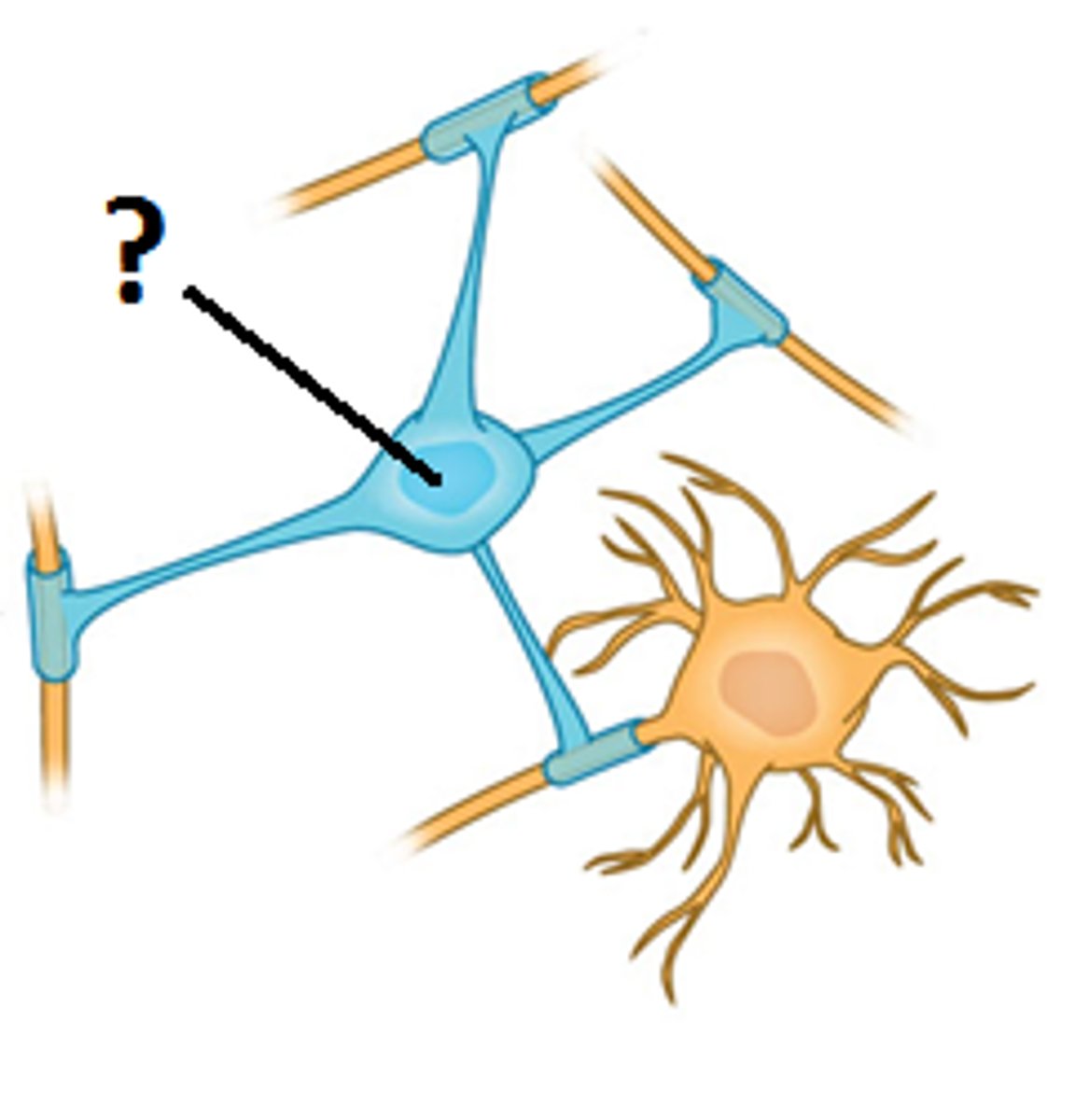
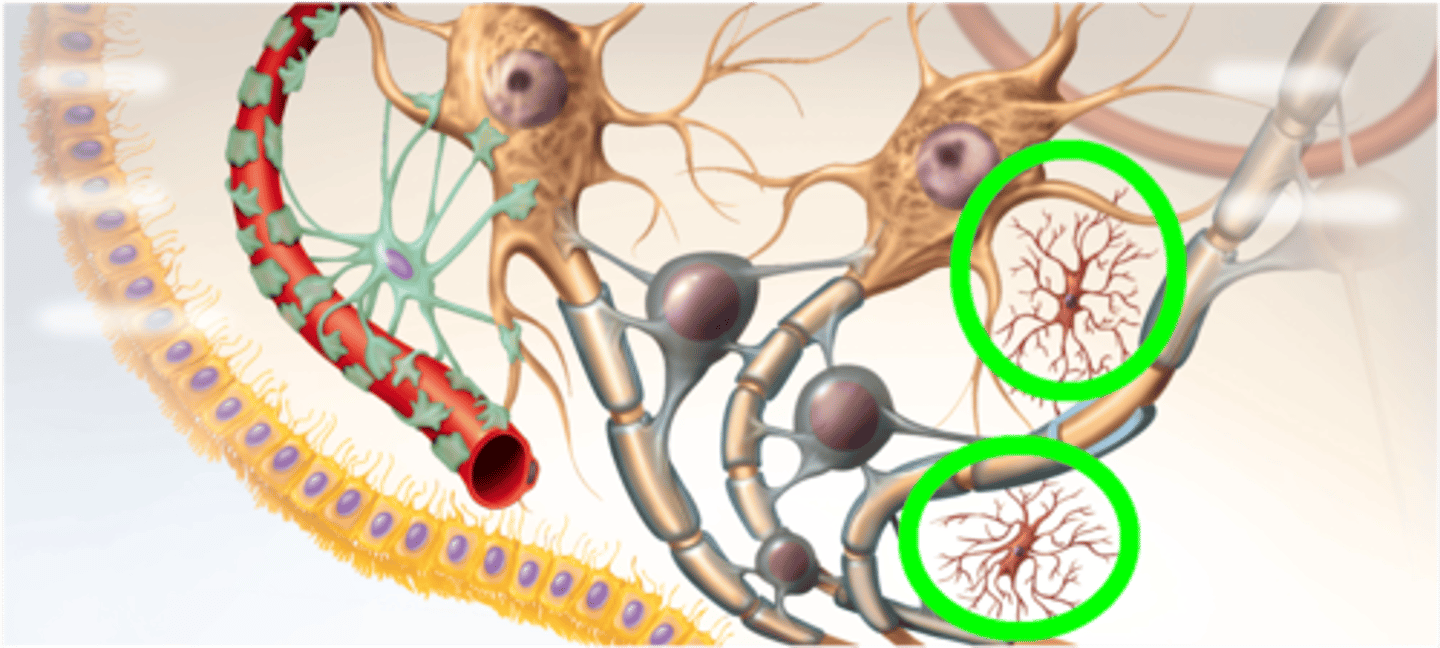
Microglia
-Wander through CNS looking for debris and damage
-Develop from WBC and become concentrated in areas of damage
Astrocytes
-Most abundant Glial cell in CNS
-Covering brain surface and most nonsynaptic regions of neurons in the gray matter
Astrocyte function
-Form supportive framework
-Forms extensions that surround capillaries to form the Blood Brain Barrier
-Monitor neuron activity and regulate blood flow based on metabolic need
-Convert glucose to lactate and supply this to neurons
-Regulate chemical composition of tissue fluid by absorbing excess NT and ions
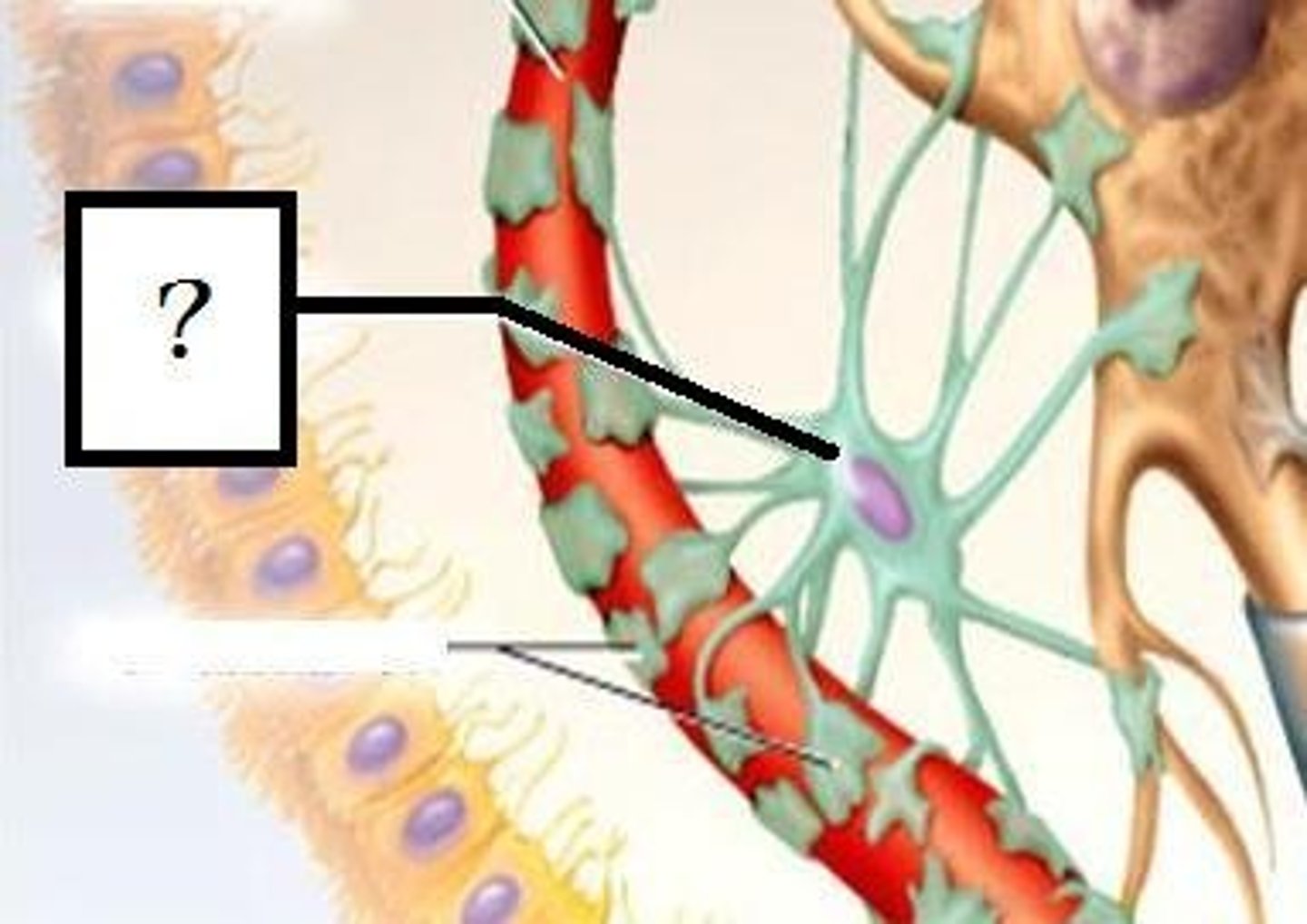
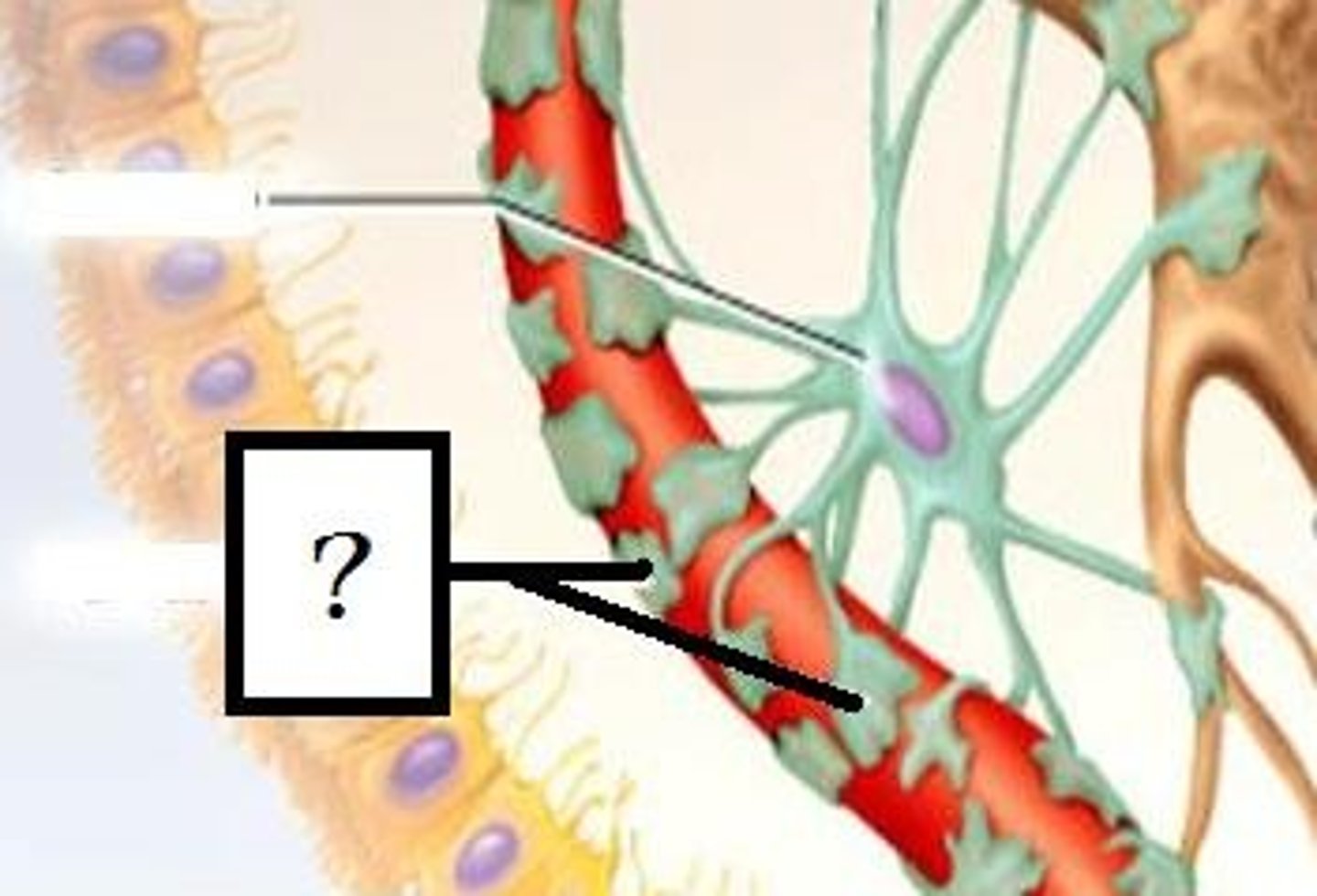
Perivascular feet
-Extensions of astrocytes
Schwann cells
-Envelop nerve fibers in PNS (>100 layers)
-Wind repeatedly around a nerve fiber
-Produce a myelin sheath similar to the ones produced by oligodendrocytes in CNS
-Assist in regeneration of damaged fibers
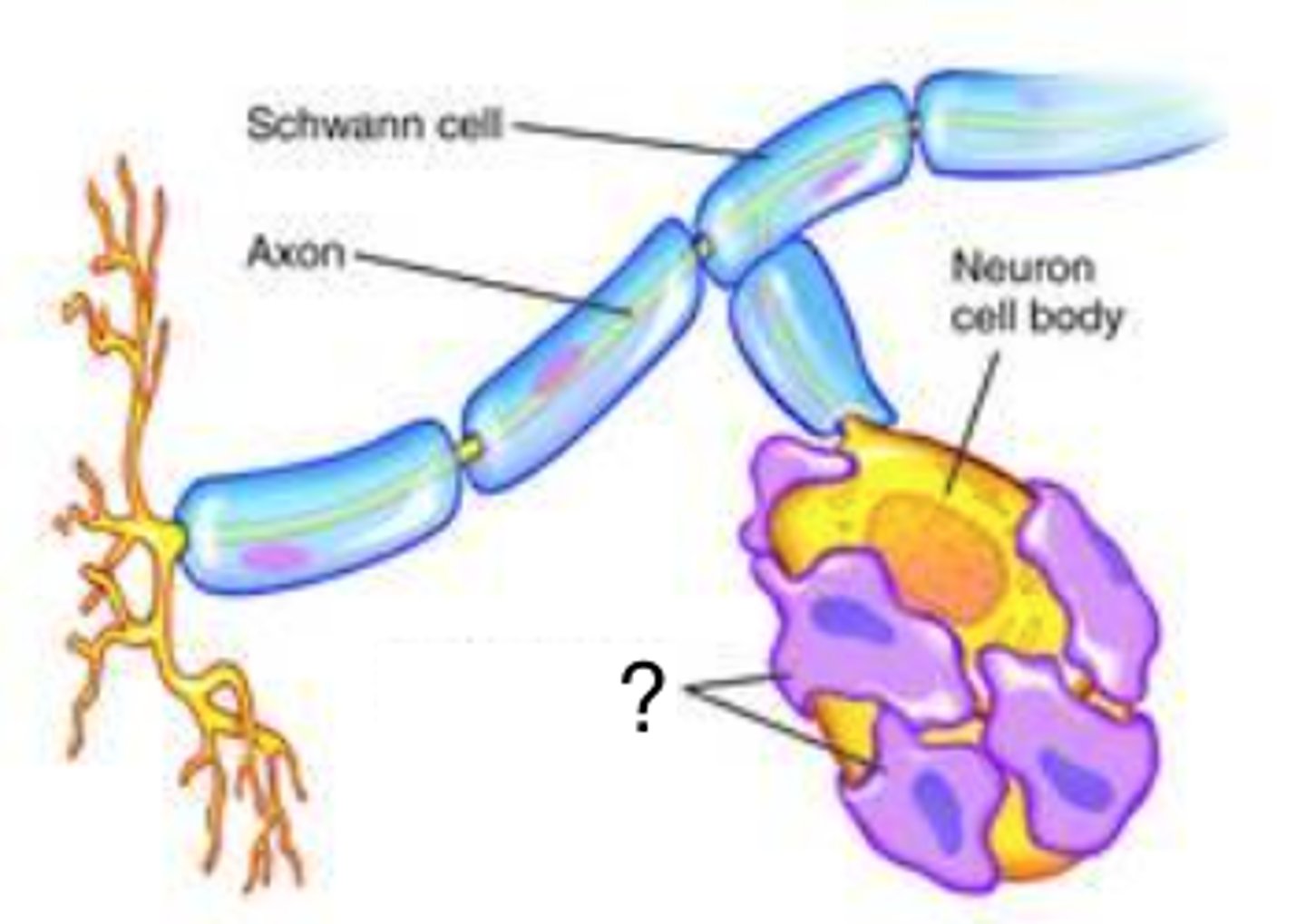
Satellite cells
-Surround the neruosomas in ganglia of the PNS
-Provide electrical insulation around the neurosoma
-Regulate the chemical environment of the neurons
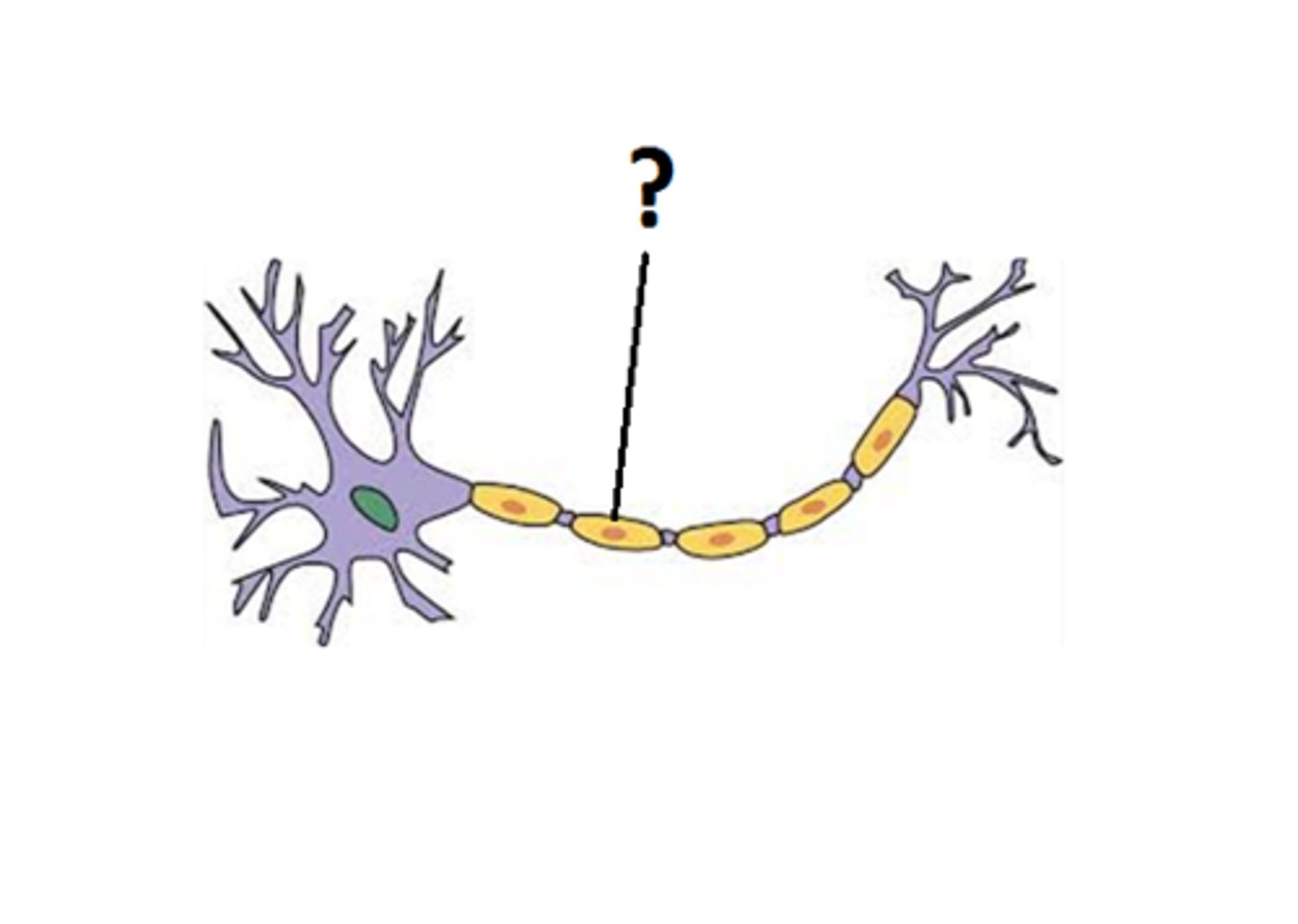
Myelin sheath
-Insulation around a nerve fiber
-Oligodendrocytes in CNS
-Schwann cells in PSN
-Consists of the plasma membrane of glial cells
-20% protein 80% lipid
Myelination
-Production of the myeline sheath
-Begins at 14 weeks of fetal development
-Proceeds rapidly during infancy
-Completed in late adolescence
-Dietary fat is important to CNS development
Neurolemma
-Thick, outermost coil of myelin sheath
-Contains nucleus and most of its cytoplasm
-Surrounded by basal lamina
Endoneurium
-Thin layer of fibrous connective tissue that surrounds neurolemma and basal lamina
Oligodendrocyte function
-Anchors to multiple nerve fibers
-Cannot migrate around
-Must push new layers of myelin underneath old ones
-Nerve fibers in CNS have no neurolemma or endoneurium
Nodes of ranvier
-Gaps between segments of myelin
-Contain many voltage-gated ion channels, while myelin-covered internodes contain few
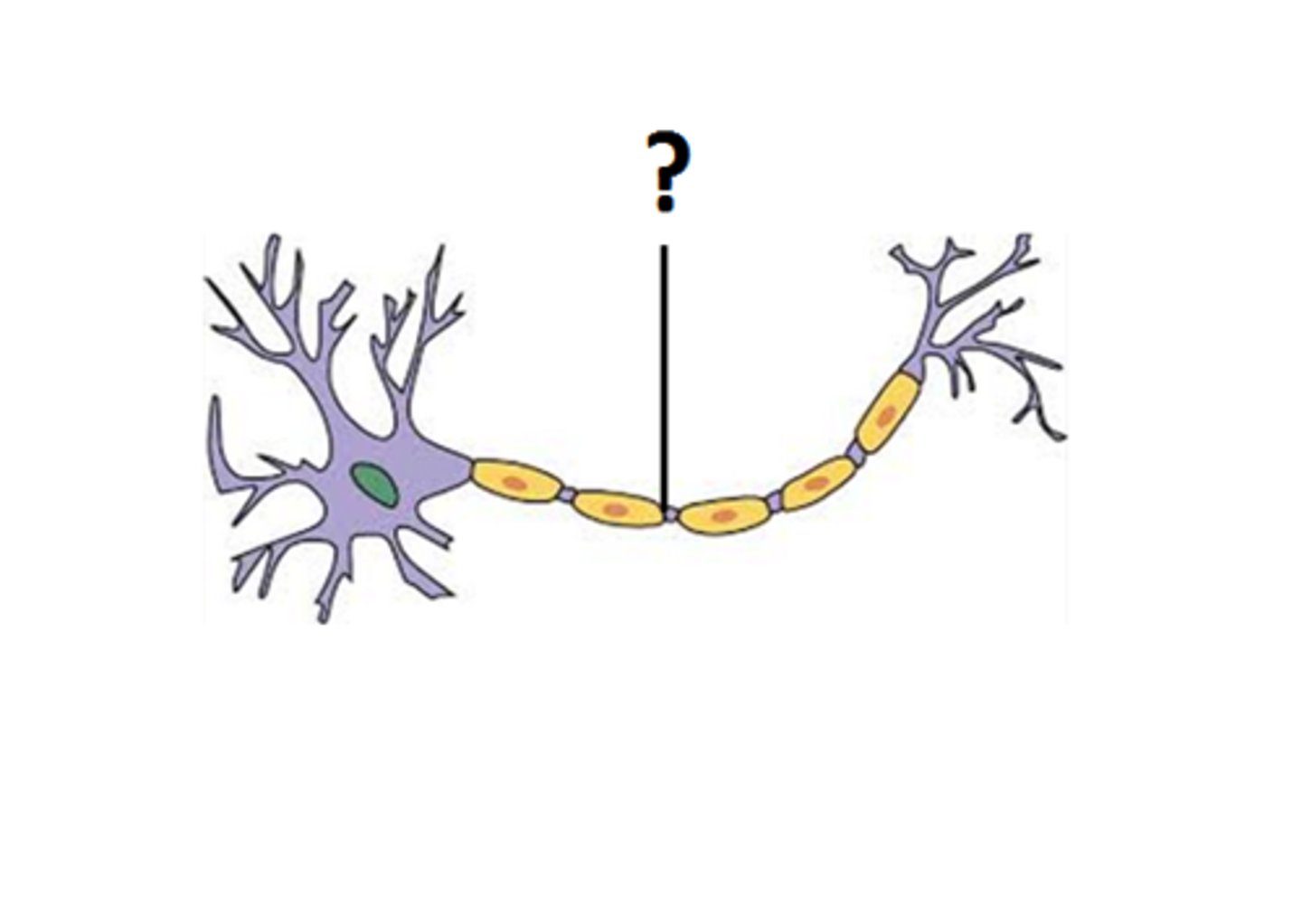
Internodes
-Myelin-covered segments from one gap to the next
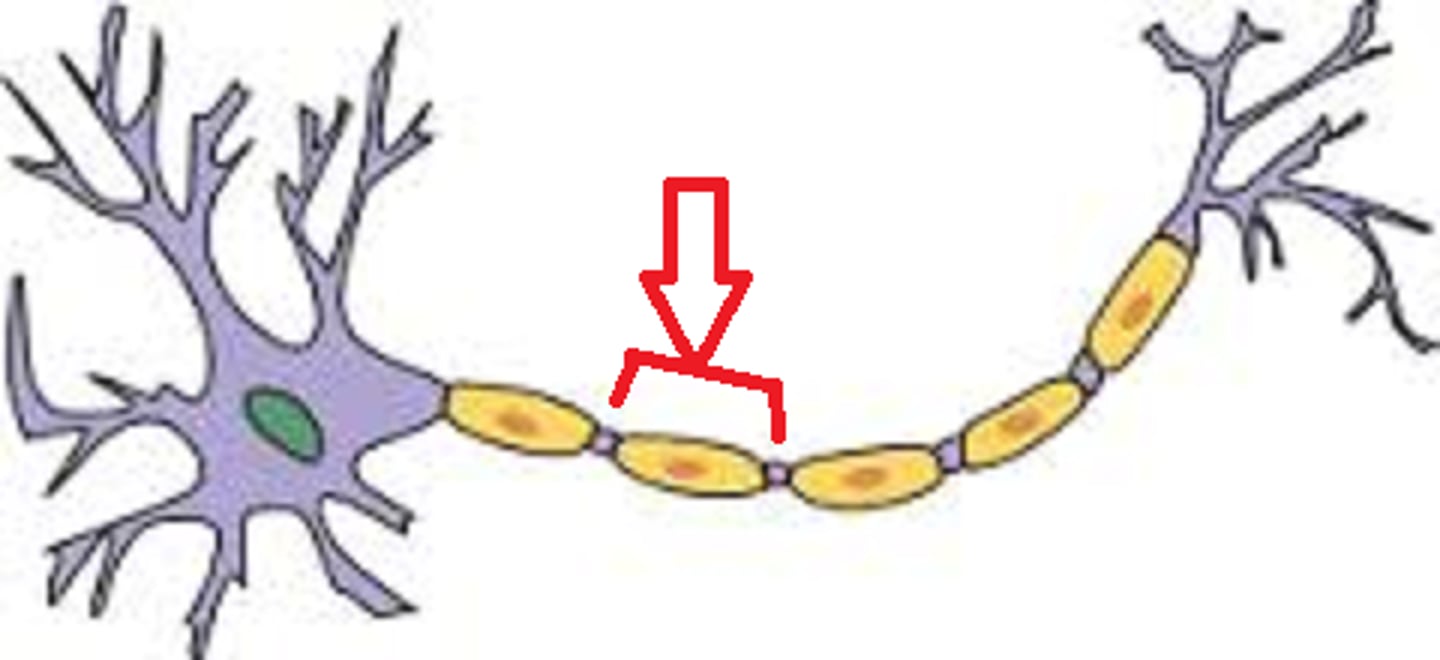
Initial segement
-Short section of nerve fiber between the axon hillock and the first glial cell
Trigger zone
-The axon hillock and the initial segment
-Play an important role in initiating a nerve signal
-350 to 500 gates per um^2
-If excitatory local potential reaches trigger zone and is still strong enough, it can open these gates and generate an AP
Unmyelinated nerve fibers
-Many CNS and PNS fibers are unmyelinated
-In PNS Schwann cells hold 1-12 small nerve fivers in surface grooves
-Membrane folds once around each fiber
Diameter of fiber
-Larger fibers have more surface are and conduct signals more rapidly
Presence of myelin
-Myelin speeds up signal conduction by minimizing leakage of Na+ out of the cell and further separation the inner positive ions from attraction of negative ions outside of cell
-Signal strength does start to fade in the internode
Small unmyelinated fibers
-0.5 to 2.0 m/s
Small myelinated fibers
-3 to 15.0 m/s
Large myelinated fibers
-up to 120m/s
Slow signals
-Gastrointestinal tract speed is less of an issue
Fast signals
-Skeletal muscle speed improves balance and coordinated body movements
Regeneration criteria
-If neurosoma is intact
-At least some neurilemma remains
Step one of regeneration
-Fiber distal to the injury cannot survive and degenerates
-Macrophages clean up tissue debris at point of injury and beyond
Step two of regeneration
-Neurosoma swells, ER breaks up, and nucleus moves off center
-Due to loss of nerve growth factors from neuron's target cell
Step three of regeneration
-Axon stum sprouts multiple growth processes as severed distal end continues to degenerate
Step four of regeneration
-Schwann cells, basal lamina and neurilemma form regeneration tube
-Enables neuron to regrow to original destination and reestablish synaptic contact
Step five of regeneration
-Once contact is reestablished with original target, neurosoma shrinks and returns to its original appearance
-Nucleus returns to normal shape
-Atrophied muscle fibers regrow
Regeneration speed
-Not fast, perfect, or always possible
-Process could take 2 years
-Some nerve fibers connect with the wrong muscle fibers; some die
-Regeneration can not occur in the CNS
Nerve growth factor
-NGF
-protein secreted by gland, muscle, or glial cells and picked up by the axon terminal of neurons
-Prevents apoptosis in growing neurons
-Enables growing neurons to make contact with their targets
Electrophysiology
-Study of cellular mechanisms for producing electrical potentials and currents
-Basis for neural communication and muscles contraction
Electrical potential
-A difference in concentration of charged particles between one point and another
-Living cells are polarized and have RMP (neuron - (-)70mV
-Cells have more negative particles inside of membrane that outside
Electrical current
-A flow of charged particles from one point to another
-Movement of Na+ or K+ through channels
-gated channels opened or closed by various stimuli
-Enables cells to turn electrical currents on and off
Resting membrane potential
-RMP
-Exists because of unequal electrolyte distribution between ECF and ICF
RMP results from ...
-Ions diffuse down their concentration gradient though the membrane
-Plasma membrane is selectively permeable and allows some ion to pass easier that others
-Electrical attraction of cations and anions to each other
Potassium
-K+ has the greatest influence on RMP
-Plasma membrane is more permeable to K+ than any other ion
-Leaks out until electrical charge of cytoplasmic anions attracts it back in and equilibrium is reached
-K+ is about 40x as concentrated in ICF as in ECF
Cytoplasmic anions
-Cannot escape due to size or charge
-Phosphates, sulfates, small organic acids, proteins, ATP, and RNA
Sodium
-Membrane is not vary permeable to Na+
-RMP is slightly influenced by Na+
-12x as concentrated in ECF as in ICF
-Some Na+ leaks into cell, diffusing down its concentration and electrical gradients
-Na+ leakage makes RMP slightly less negative than it would be if RMP were determined solely by K+
Sodium-potassium Pump
-Moves 3 Na+ out for every 2 K+ it brings in
-Works constantly to compensate for Na+ and K+ leakage and requires a great deal of ATP (one per exchange)
-70% of the energy requirement of the nervous system
Sodium-potassium function
-Necessitates glucose and oxygen be supplied to the nervous tissue (energy needed to create RMP)
-The exchange contributes about -3 mV to the cell's RMP of -70mV
Local potentials
-Changes in membrane potential of a neuron occurring at and nearby the part of the cell that is stimulated
-Different neurons can be stimulated by chemicals, light, heat, or mechanical disturbance
Stimulant binds to neuron receptor
-Opens Na+ gates and allows Na+ to enter cell
-Positive Ion entering causes Depolarization
-Na+ entry results in a current that travels toward the cell's trigger zone
Graded local potentials
-Vary in magnitude with stimulus strength
-Stronger stimuli open more Na+ gates
Decremental
-Get weaker the farther they spread from the point of stimulation
-Voltage shift caused by Na+ inflow diminishes with distance
Reversible
-If stimulation ceases, the cell quickly returns to its normal resting potential
Excitatory or inhibitory
-Some neurotransmitters make the membrane potential more negative - hyperpolarize it - so it becomes less likely to produce an AP