HS 200 Test 2 Bryce Lane
1/102
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
103 Terms
What determines which ornamental category that a plant fits under(i.e. tree, shrub, vine, ground cover)?
Appearance
Tree
exposed trunk with canopy
Shrub
Multistemmed with branches
Vine
grows upward
Ground cover
grows along the ground. Becomes a vine when it grows upright.
Evergreen
Leaves fall off every 3 to 5 years
Deciduous
Leaves fall off ever year
Tropical
will not tolerate below 32F
(ex: bananas, tomatoes)
Subtropical
tolerates short periods of freezing
(ex:citrus)
Temperate
tolerates long periods of freezing and below
(ex: apples, maples, hollies)
"FFFD" in Raleigh
April 15th(tax day)
"LFFD" in Raleigh
October 31st(halloween)
Annual
1 year growing season, killed by frost
Unless brought inside
Fast to grow and quick to flower
Biennial
Completes life cycle in 2 years
1st year= vegetative growth
2nd year=reproductive growth
(ex:carrots, foxglove)
Perennial
Plants that live for more than 3 years
(ex: oak=woody perennial, asparagus=herbaceous perennial)
Tender Perennial
May need protection on particularly cold days
Raleigh on the USDA Plant Hardiness Map
Zone 7A and 7B
Volunteers
Die but "set seed" that "overwinter" and come up the next year
Biome
Community of flora and fauna determined by rainfall, temperature, wind and soil.
(ex:forrest, tundra, rainforrest, desert)
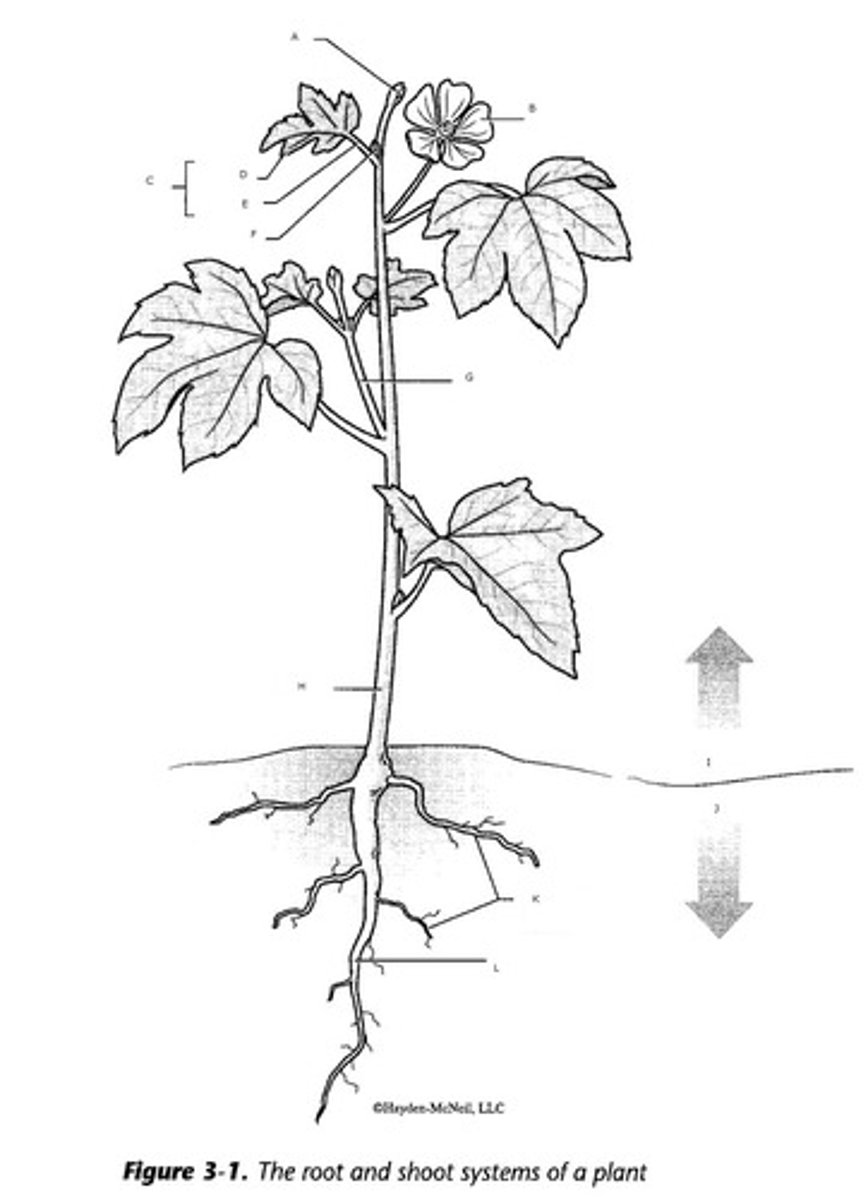
6 plant parts
3 Vegetative
Roots
Stems
Leaves
3 Reproductive
Flowers
Fruits
Seeds
3 Vegetative plant parts
Roots, Stems and Leaves
3 Reproductive plant parts
Flowers, Fruits and Seeds
4 Root Functions
Absorption, Anchorage, Transportation, Storage
3 types of roots
Primary, Secondary, Adventitious
Primary root
Stems from seed
Secondary root
Stems from primary and other secondary roots
Adventitious root
Stems from abnormal places such as leaves and stems
Tap Root
grows straight down
large, swollen primary root
Are all tap roots primary?
Yes!
Are all primary roots tap roots?
No!
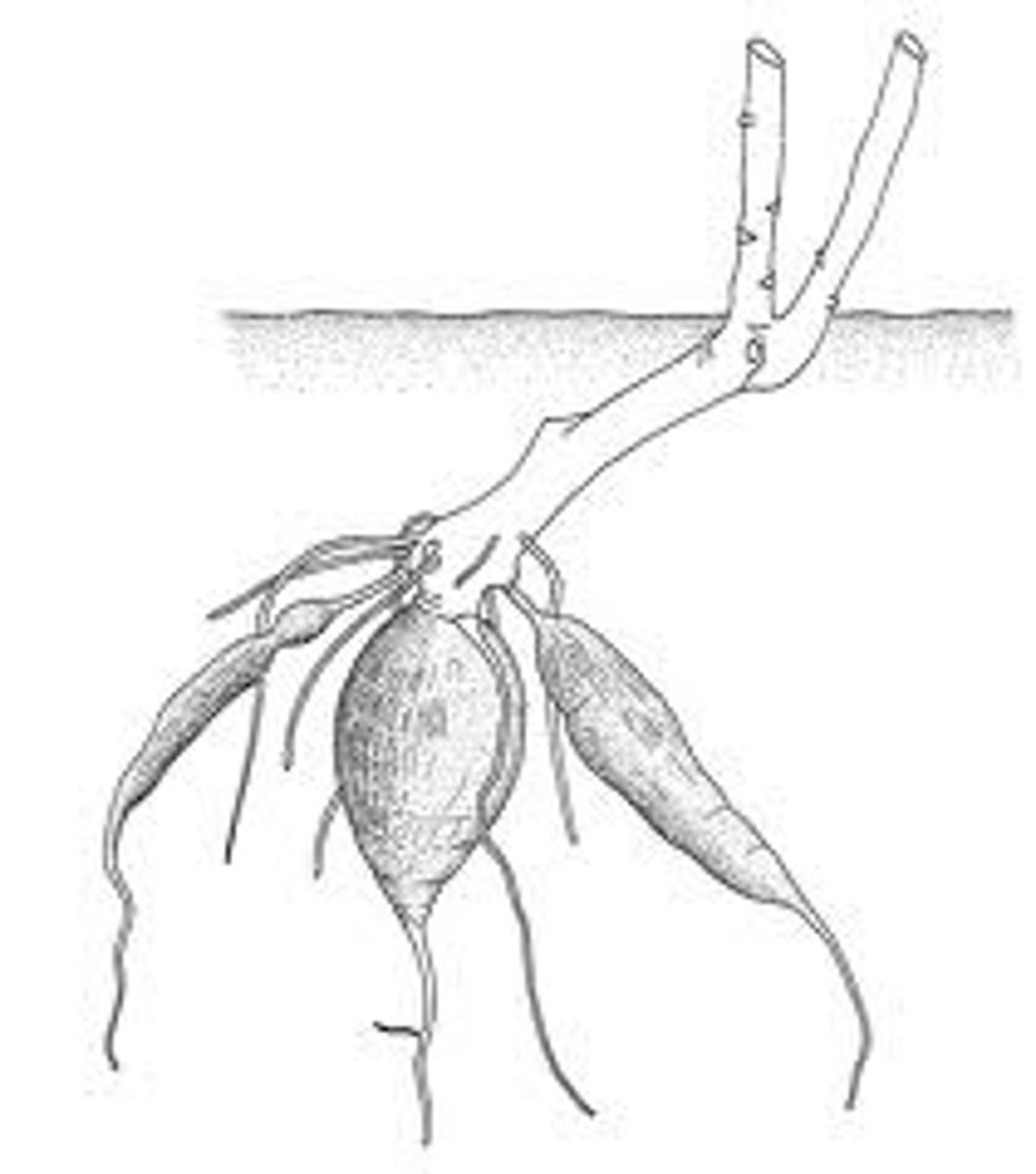
Tuberous Root
large, swollen secondary root
(ex: Sweet potato)
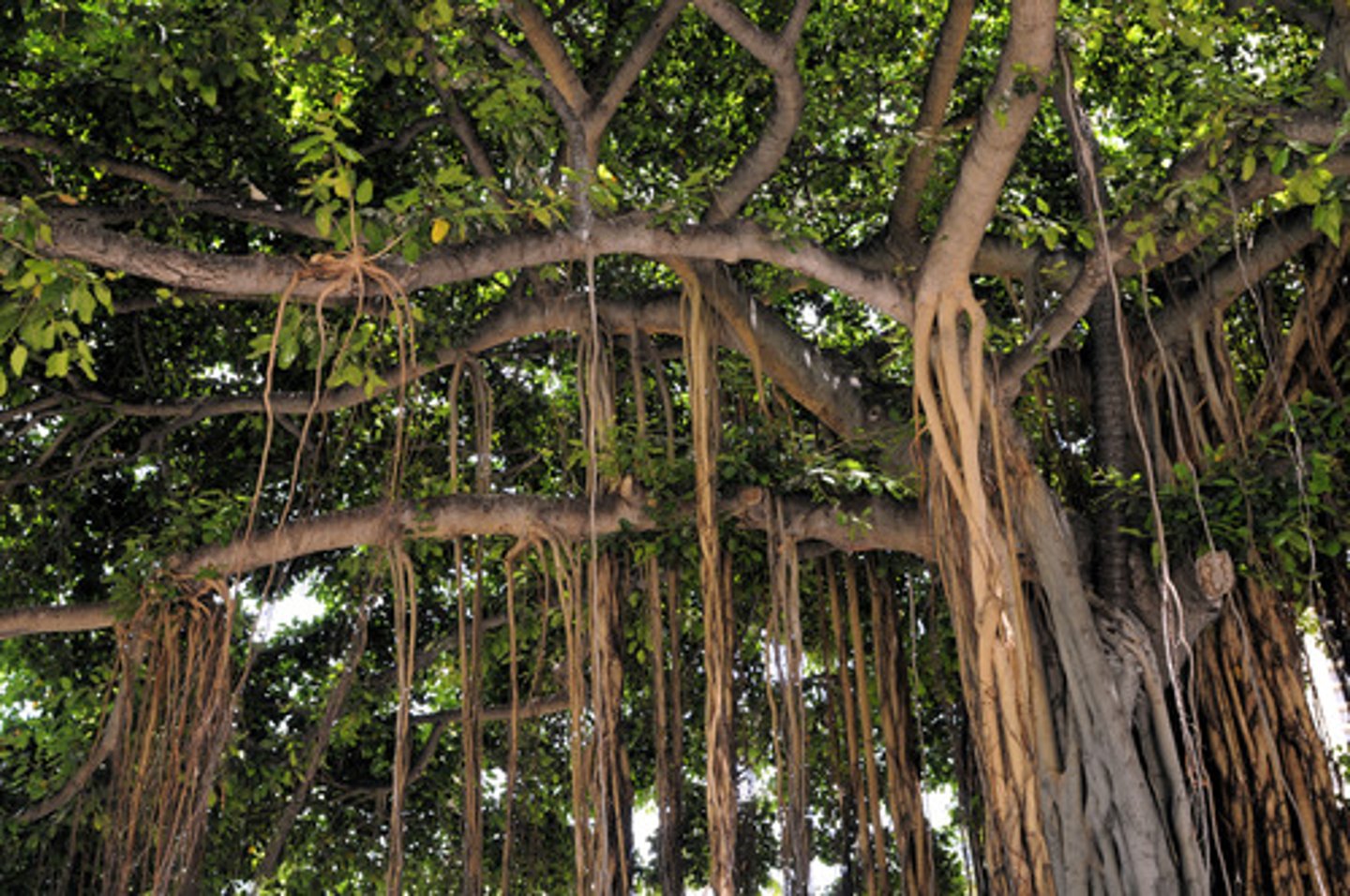
Aerial Roots
roots that grow above ground
(ex: Orchid)

Epiphitic
Plants that grow on other plants
Symbiotic
2 organisms that depend on eachother to live
4 Functions of stems
Storage, Transportation, Support, Food Production
Prostrate stem
Stems that run along the ground
(ex: iris, bamboo)
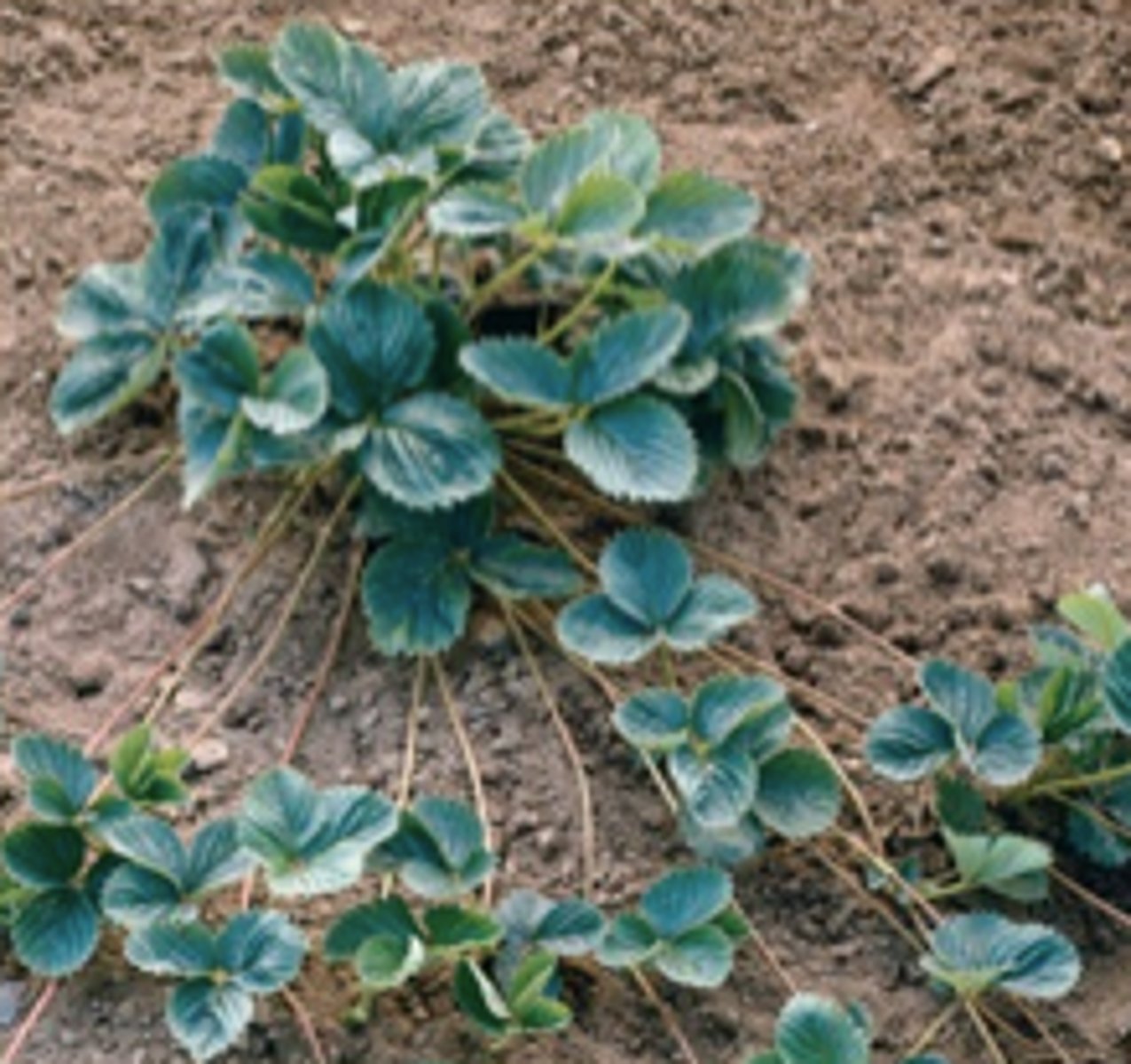

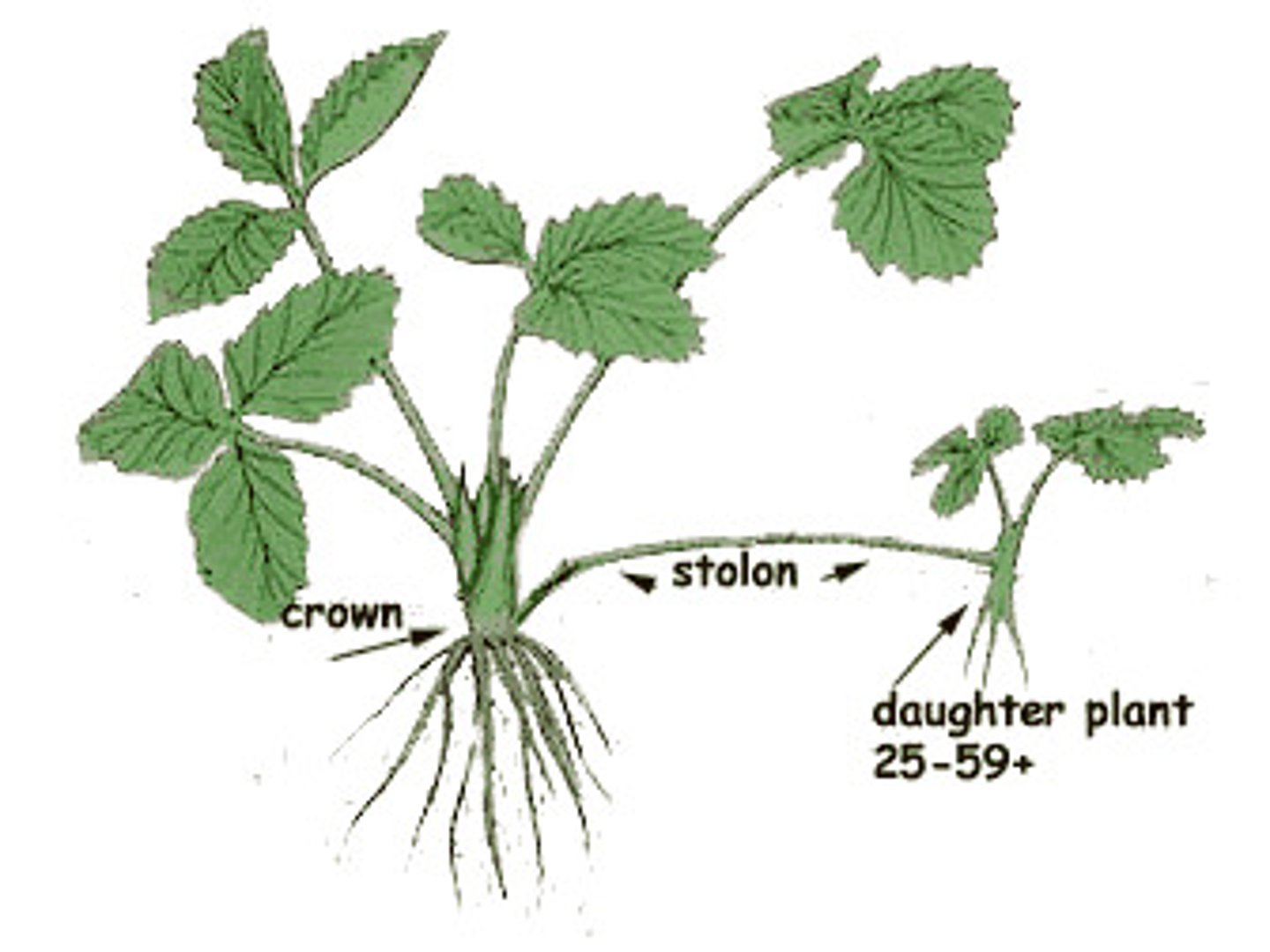
Stolon stem
A prostrate stem that runs along the ground and produces a plantlet tip
(ex: strawberries, spiderplants)
Rhizome
Prostrate stem that runs below ground and produces plantlet at tip
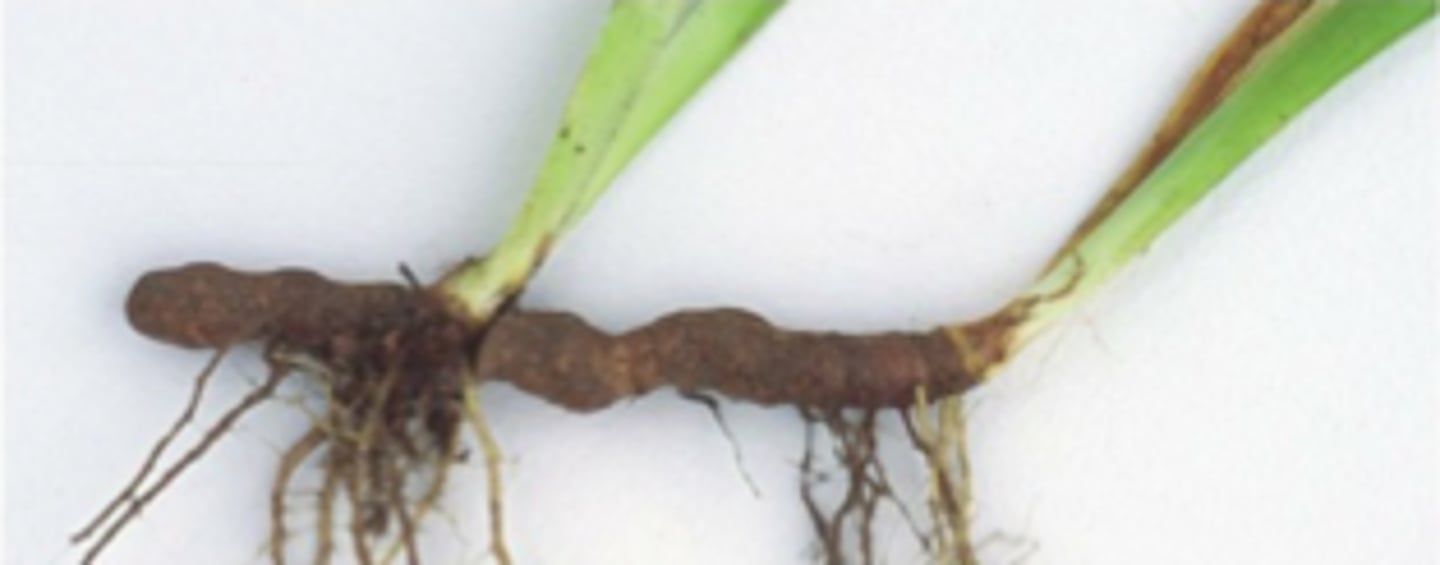

Crowns
Area where stem meets the ground
(ex: african iris, asparagus)
Tuber
Large swollen underground stem
(ex irish potato)
How do we distinguish between roots and stems?
Stems have nodes and internodes
Node
Place where leaves come out
Internode
Place between where leaves come out
Budbreak
When the bud breaks and the stem starts to grow
Sweet Potato
-is a root that has an organized system of eyes
-the eyes are nodes
What is the difference between an Irish Potato and a Sweet Potato?
An Irish Potato is a large, swollen underground STEM.
A sweet potato is a ROOT
2 Functions of Leaves
1) Food Production - Primary food producing organ
2) Storage - nutrition and water
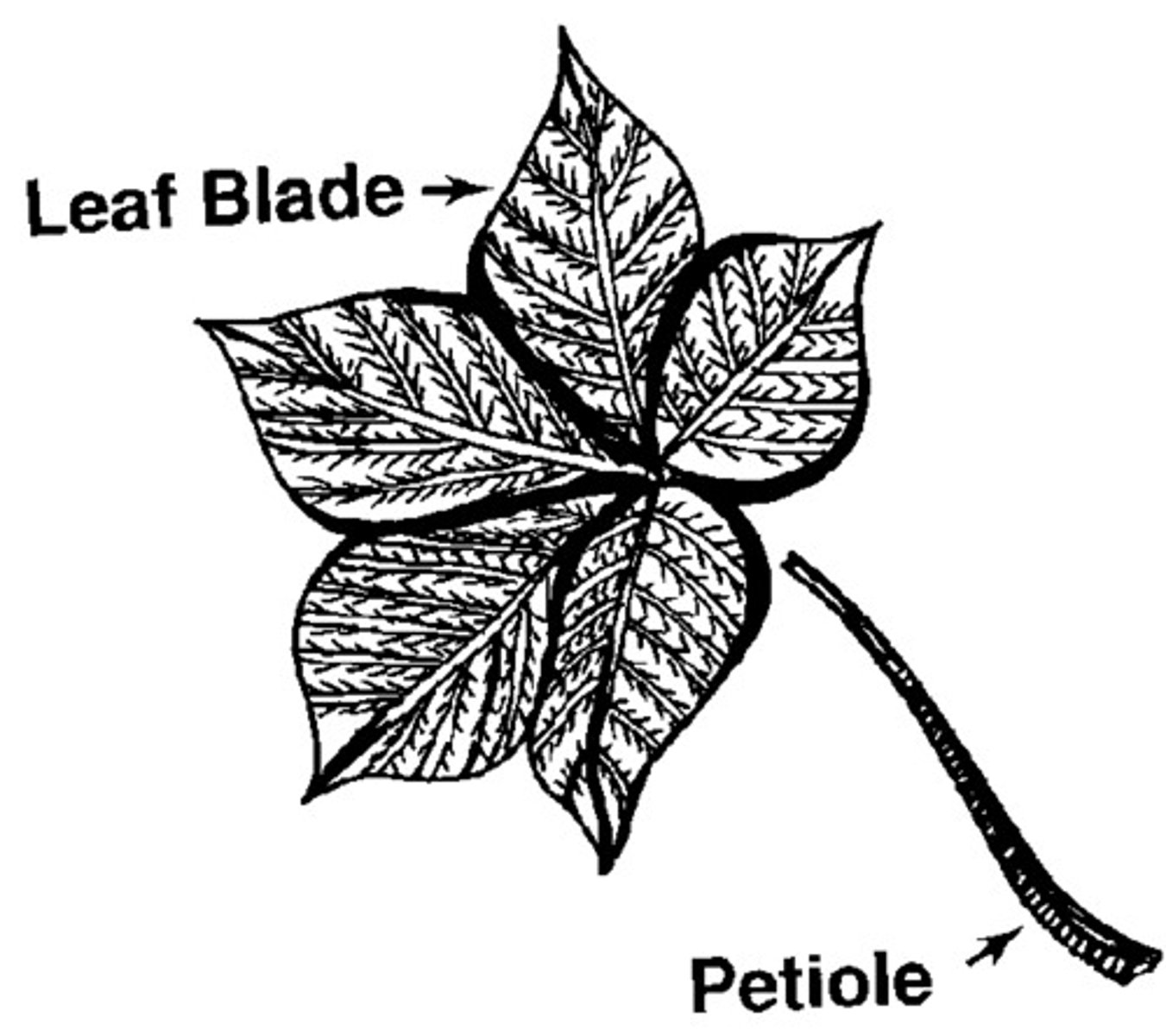
Simple leaf
one blade, plus petiole
Petiole
attaches at the node
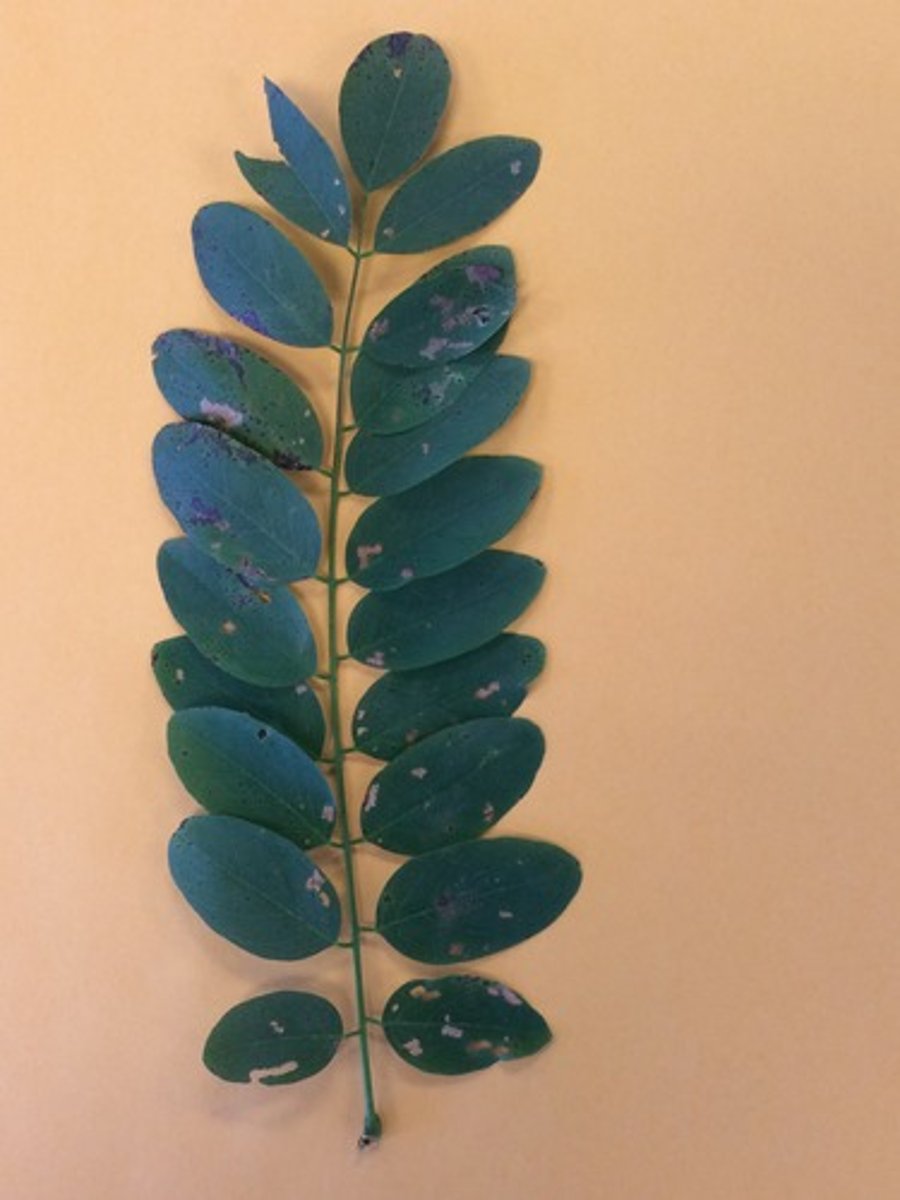
Pinnately Compound Leaf
-start at the tip of the leaf and look for a bud
-"leaflets" are what make up the compound leaf

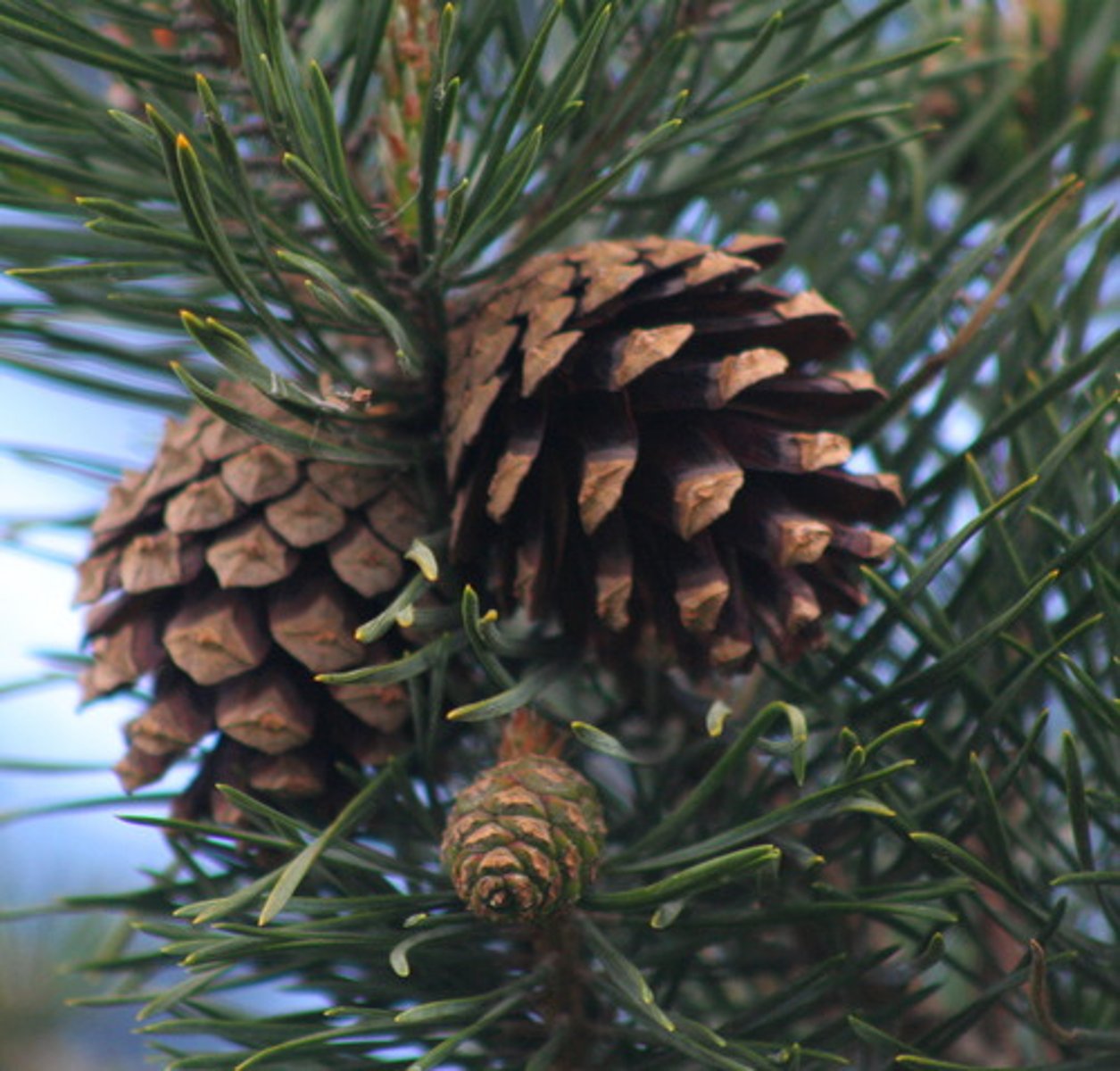
Gymnospermes
Can't use terms "simple" or "compound"
Means naked seeds
(ex: conifers, ginko)

4 things necessary for plant growth
Water, Nutrition, Sugar, and Chemical Energy(the sun)
Dry Weight
stuff that the plant is made of
96% sun-sugar
4% soil
Full sun
6+ hours of sunlight
Photosynthesis
gives sugar for building blocks and energy for plant growth
5 Plant Growth Processes
1)Absorption
2)Translocation
3)Photosynthesis
4)Transpiration
5)Respiration
Absorption
passive- movement with no energy, osmosis
It is the diffusion of water across semi-permeable membrane
Fertilizer burn
dehydration on the border of leaves because of high salt level in soil("dessication" injury)
Leaching
water taking nutrients through the soil into the groundwater
What do you do if you over-fertilize?
Treat with copious amounts of water
What are the negatives of over-fertilizing?
Pollution of ground water
Carrier Molecule Theory
Nutrient specific molecules are responsible for nutrient uptake(not sure which parts are responsible)
Energy must be expended
"Active Transport"
Translocation
Movement of materials in the plant from one area to another
Happens in the tube(traecheaphyta)
Xylem, Phloem, Vascular Tissue, Veins
Photosynthesis
Most important process on earth
2 ingredients - H2O and CO2
Makes oxygen and glucose
Energy Source? Light
2 products- Glucose and Oxygen
What are the 2 ingredients of Photosynthesis?
H2O and CO2
Today and 100 years ago
Oxygen-same
CO2- greater
Photosynthetic area- Greater(for every 1 tree cut down, 3 are planted)
Chlorophyll Molecule
-Relies on nitrogen and magnesium
-has a short life
Equation 6CO2+6H2O=C6H12O6+6O2
What are the 2 Products of Photosynthesis?
Glucose and Oxygen
Chlorophyll
Light sensitive
Production stimulated by light
High intensities destroy chlorophyll
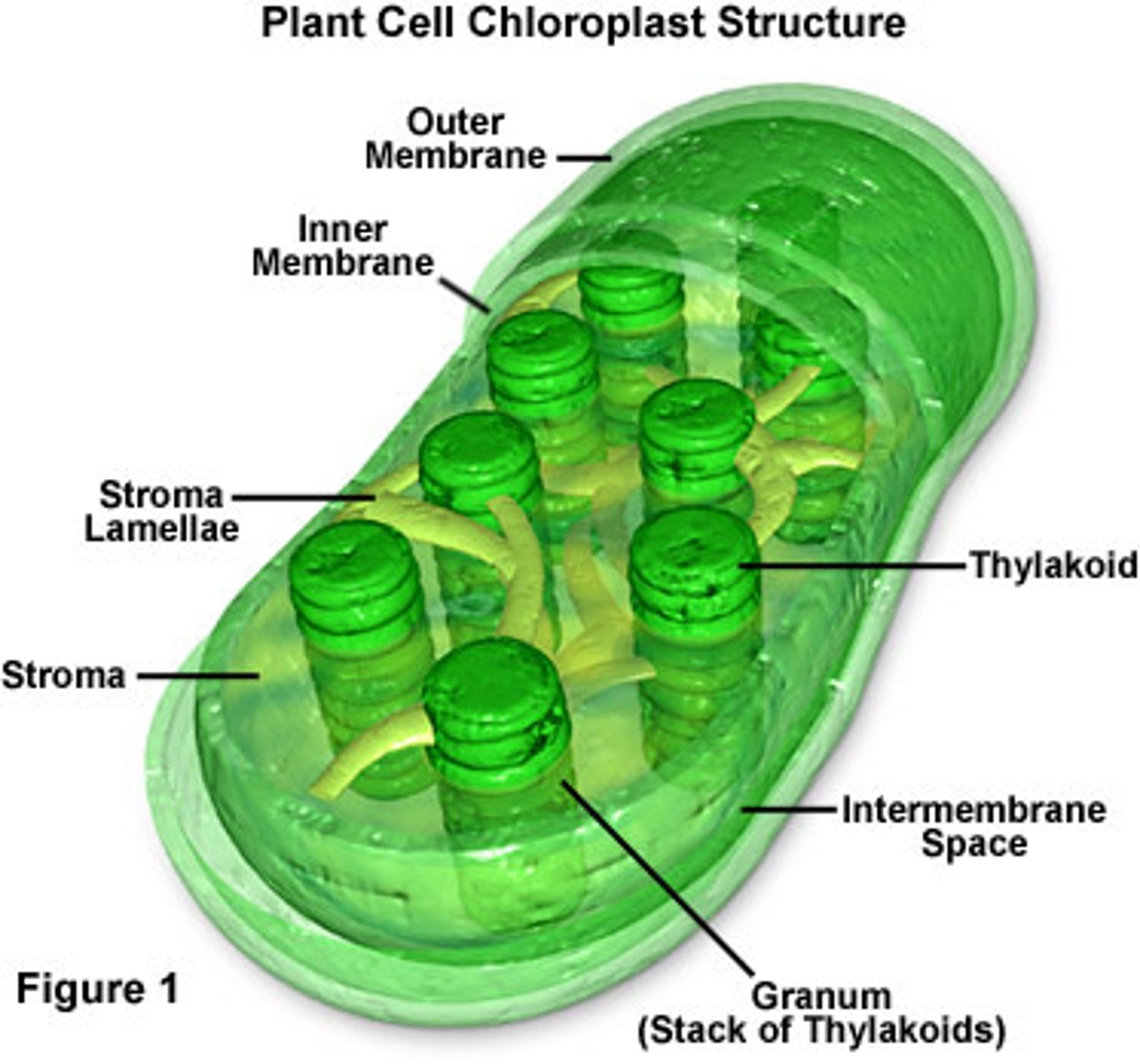
Chlorophyll is inside of the chloroplast
Chlorosis
yellowing due to lack of chlorophyll
Etiolation
grown in dark, no chlorophyll
What do we know about photosynthesis?
-turns sunlight into energy
-photons
-happens in the leaves
-Chlorophyll and chloroplast
-Physical Reaction:Reversible
-Chemical Reaction: Irreversible
Unlimited light intensity
Desert
Very low intensity
Floor of the rainforest
What changes a plants appearance?
light intensity
What color leaves require slightly higher light intensity?
Varigated, yellow and burgundy
-less green, less chlorophyll
Transpiration
-(absorption, osmosis)
-Process where water is absorbed by the roots, translocated through the plant and evaporated through the leaves.
-Cohesion- water sticking to water
-Adhesion- Water to something else
What percentage of the water absorbed by the plant is used for photosynthesis?
Between 1 and 2%
99% is lost in transpiration
As photosynthesis increases, transpiration increases as well(positive correlation)
Why so much transpiration?
Transportation system for nutrients and water
Turgidity-full of water-not for cooling
What are the factors that affect the rate of transpiration?
Relative humidity, Temperature, Air movement
Stomate / Stomata
-organelle of transpiration
-backs of leaves
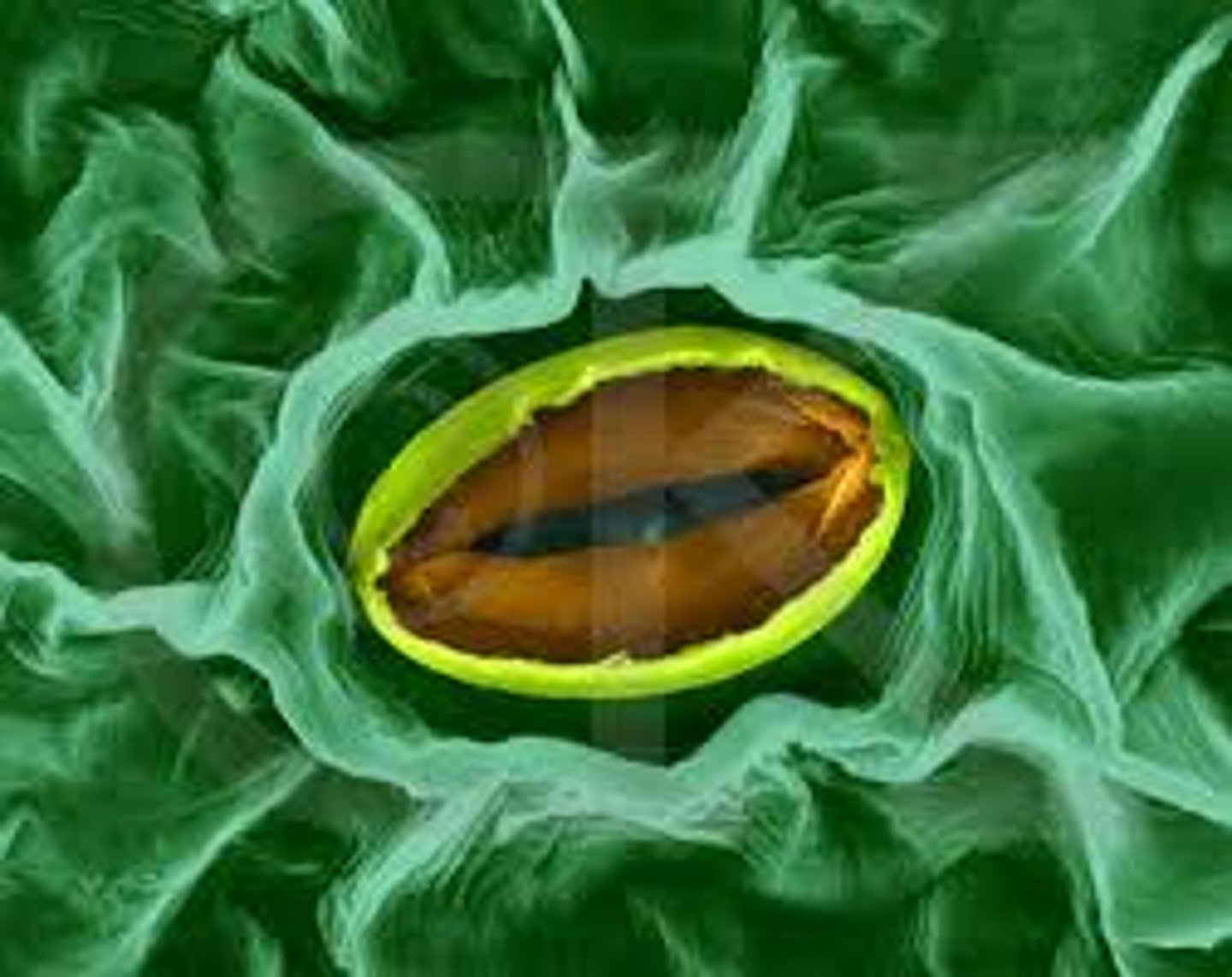
How many stomata per square centimeter?
10's of thousands per square centimeter on the back of an apple leaf(39,000)
Plants defficient in potassium have
yellow, crispy leaves
What does potassium deficiency cause stomata to do?
open when they're supposed to be closed and close when they're supposed to be open
What happens to the sugars?
Building blocks, storage, chemical synthesis, burned for energy
What effects respiration?
Temperature
-it's the only influencing factor
What effects transpiration?
Humidity, air movement, temperature
Fertilizer
NPK - Nitrogen, Phospherous, Potassium
Respiration
Some of the sugars made are burned yielding chemical energy(ATP)
Light Energy->Physical Energy->Chemical Energy
E (ATP)
the energy the plant needs to build something like a leaf
Often the greatest limitation with plant growth
Light availability
Flush
when plants put out vegetative growth
Default growth of plant not producing enough sugar
Vegetative growth
Schuleman (Dendrochronologist forrestry)
4000 years old
Bristle cone pines
limestone soil of the Sierra Nevada mountains
Oldest 5067 years old
Venus Fly trap
Dioneae Muscipula
Native to E NC and NE SC
Need nitrogen and phosphorous poor environments
2 terminal lobes, hinged at the midrib
Tricomes- trapping structure of tiny hairs
Stays closed for 12 hours
2 main reasons why plants fail?
1) don't understand their light needs
2) don't understand their soil
What is soil?
Soil= Stuff+Space
Mineral material- from rock, 10-50 thousand years
Organic Material- anything from living material
Soil organisms- biological component (worms and bacteria)
Space- water and air
Not a living thing- but it does have some living properties
Where does soil come from?
Parent material(rock)
Time
Climate
Topography
Biology
Soil properties
Physical: color, particle size, water
Chemical: nutrient holding ability
Biological: Up to 1 million bacteria, Soil Fungi(mycorrhiza)
What does "healthy" garden soil provide?
Anchorage
Water
Oxygen
Nutrients