module 3
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
Overweight and obesity are defined as …. or excessive fat accumulation that may impair health
For adults, the World Health Organization (WHO) defines overweight and obesity as follows:
Overweight is a BMI greater than or equal to ..; and
Obesity is a BMI greater than or equal to ..
abnormal 25 30
Causes
High energy input high food intake
Low energy output
low …. activity
hypo………
genetics
Underlying Factors
Genetics
….. influences
Social
determinants… activity
Physiological
physical thyroidism Emotional physiological
Raised BMI is a major risk factor for noncommunicable diseases such as:
•….. diseases (mainly heart disease and stroke)
•Diabetes
•…. disorders (especially osteoarthritis – a highly disabling degenerative disease of the joints)
•Some … (including endometrial, breast, ovarian, prostate, liver, gallbladder, kidney, and colon)
Cardiovascular Musculoskeletal cancers
Childhood …. is associated with a higher chance of obesity, premature death and disability in adulthood. But in addition to increased future risks, obese children experience …. difficulties, increased risk of fractures, hypertension, early markers of ….. disease, insulin resistance and psychological effects.
obesity breathing cardiovascular
An estimated 1/2 of those suffering from diabetes are not aware of their condition! (t or f)
t

polyuria polydypsia polyphagia
Complications:
Neuropathy (…. system)
Retinopathy (…. sight)
Nephropathy (kidney)
Can lead to amputation and …. disease
nervous eye heart
3 major risk factors for CVD:
1.Elevated Blood …
2.S……
3.Hyper……
Cholesterol smoking hypertension
Injury / Damage in the lining of arteries
Build Up of Plaque
(made up of …, ……. and …….)
Narrowing of arteries : …..
fat calcium cholesterol Atherosclerosis
Cardiovascular Disease Recommendations
For adults, the Acceptable Macronutrient Distribution Range (AMDR) for fat is 20-35% of total calories
Dietary cholesterol does not seem to play a major role in blood cholesterol which is rather affected by:
-….. activity
-body ….
-intake of saturated and … fat
-heredity, age, and sex.
→→ no recommendation set for cholesterol intake (lack of adequate evidence)
physical weight trans
•Hypertension (HTN) = Chronic elevation in … pressure
•Occurs in 1 out of every 3 adults
•Approximately 30% of adults are unaware of their hypertension (asymptomatic; silent).
Risk Factors:
•Genetic predisposition
•Obesity
•Age
•Smoking
•Lack of physical activity
•Salt sensitivity
•Alcohol
•Diet – low in fruits, vegetables, nuts, potassium, calcium; high in fat
•Medications: cortisone and other steroids; estrogens; non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs
blood
If untreated, chronic high blood pressure may lead to:
•….. artery disease,
•…. failure
•…. failure
•Myocardial Infarction, stroke
•… problems (retinopathy)
Coronary cardiac Kidney vision
DASH Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension
•Decrease ….
•Inclusion of …., vegetables, and whole grains
•Limit fat and …. fat
•Increase calcium, potassium, fiber
•Limit ….
•Monitor caffeine intake
Some medications taken if unable to control, while still making lifestyle modifications
sodium fruits saturated alcohol
Cancer causes
•Genetics
•…./increased body fat
•Sedentary lifestyle
•Inadequate … and vegetable intake
•Intake of ….
•Excessive intake of … and cured meat
•Viruses
•Occupational/ environmental exposure to ….
•….. exposure
•…. or tobacco use, passive exposure to tobacco
•Repetitive tissue injury (e.g. chronic reflux)
Obesity fruit alcohol red carcinogens Radiation Smoking
Methods of food preservation
Food preservation can enhance carcinogens
}N-nitrosocompounds (NOC) known as ….:
◦Formed in smoked, salted and pickled foods cured with nitrates and nitrites.
◦Give hot dogs and luncheon meats their pink color.
◦Also found in vegetables and drinking water.
}Acrylamide:
◦Byproduct formed during frying, roasting and baking at very high temperatures.
◦May be a carcinogen.
nitrosamines
•Undernutrition makes children in particular much more vulnerable to … and death.
disease

D coffee tea folate folic fruits vegetables soy
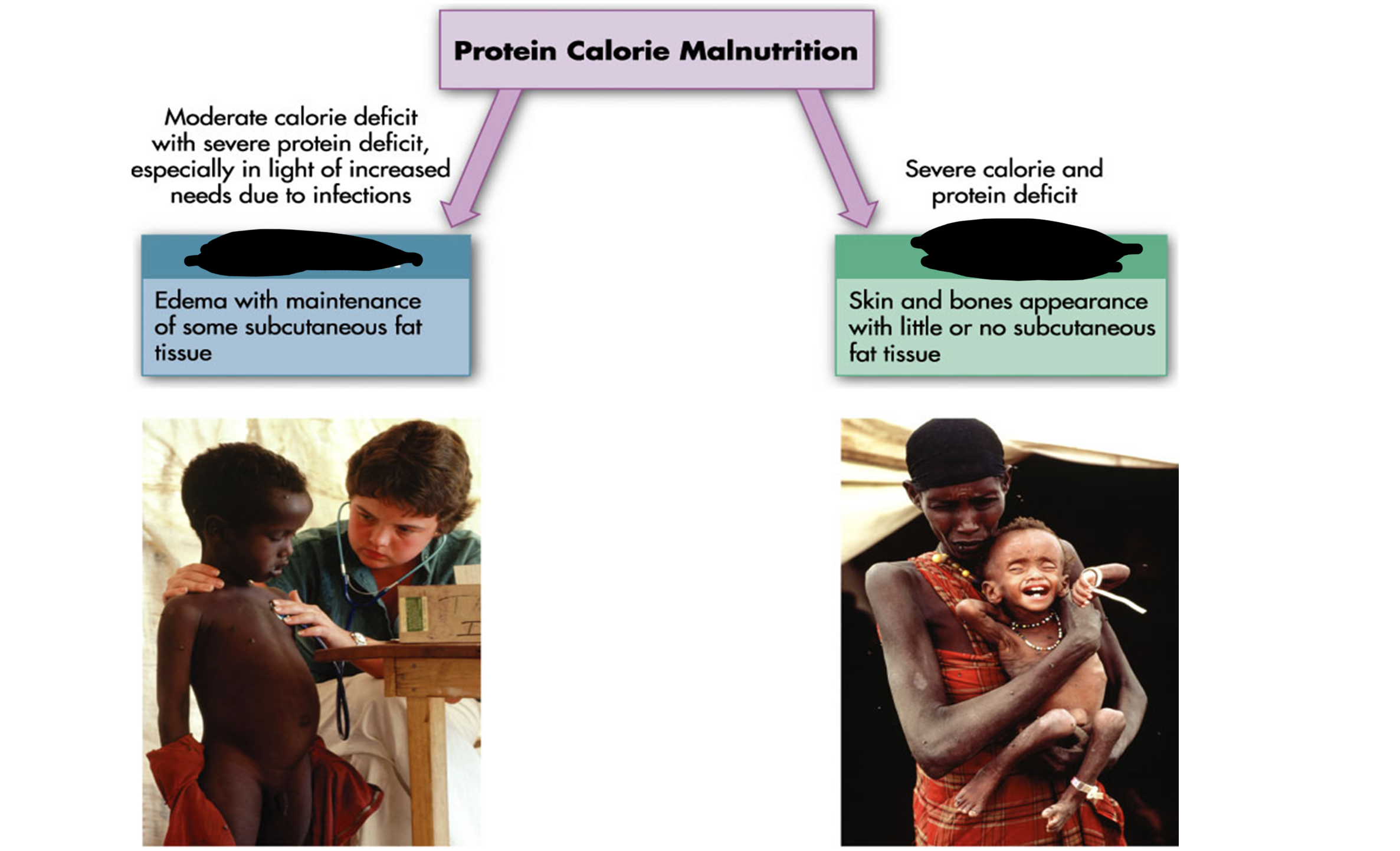
kwashiorkor marasmus
•Micronutrients enable the body to produce …, …, and other substances that are essential for proper growth and development.
•
•Micronutrient deficiencies can cause several serious health issues.
•
•…, … and vitamin . are the most important in global public health terms; their deficiency represents a major threat to the health and development of populations worldwide, particularly children and pregnant women in low-income countries.
•
enzymes hormones iron iodine A
•A lack of iron, folate and vitamins B12 and A can lead to ….
•
•Anemia is a condition in which there is a reduced number of red blood cells or … concentration, causing fatigue, weakness, shortage of breath and dizziness.
•
•This can further lead to difficulties in functioning in …, … and community engagement.
•
•An estimated 42% of children under 5 years of age and 40% of pregnant women worldwide are anemic.
•
anemia hemoglobin work education
IRON DEFICIENCY IS MOST COMMON AT TIMES IN LIFE WHERE IRON NEEDS INCREASE, LIKE
menstruation pregnancy early childhood
•Severe iodine deficiency can lead to …. damage and during pregnancy can cause a number of issues including stillbirth, spontaneous … and congenital anomalies.
•
•Less severe iodine deficiency may still cause …. impairment that reduces intellectual capacity.
•
•The preferred strategy for the control of iodine deficiency remains universal salt iodization, which requires that all food-grade salt used in household and food processing be fortified with iodine. UNICEF estimates that 66% of households globally have access to iodized salt.
brain abortion mental
•
•Vitamin A deficiency is the leading cause of preventable …. in children and increases the risk of disease and death from severe infections
•
•Vitamin A deficiency may also occur in women during the last trimester of pregnancy in high-risk areas.
•
•….. is the best way to protect babies from vitamin A deficiency and, in areas where vitamin A deficiency is a public health problem, vitamin A supplementation is recommended in infants and children 6-59 months of age.
blindness breastfeeding
•The World Food Programme’s (WFP) supports governments to ensure that all school-aged children have access to school meals and are … and ready to learn
•
•School-meal Programme also act as an incentive for families to enroll their children in school and keep them there relieving parents from having to budget for lunches
•
•They also help reduce early … for young girls.
Thus, school meals empower girls
healthy marriages
•SNAP is administered in the US by USDA's Food and Nutrition Service (FNS)
•SNAP provides … benefits for purchasing food & helps low-income families, seniors, the disabled, and others
•Eligibility and benefits depend on … size, … & other factors
•Benefits can be used for most foods prepared at home but cannot be spent on tobacco, alcohol, nonfood items, or hot/prepared foods, except in certain cases
•SNAP served 42.1 million participants per month in Fiscal Year 2023 on average, at an annual Federal cost of $112.8 billion
electronic household income
•…. … has long been an essential food security crop in Sub-Saharan Africa (SSA).
•
•Orange-fleshed varieties: high in beta-carotene, a precursor to vitamin _
•Mozambique's approach to promoting orange-fleshed sweet potato has been an effort involving:
•Research
•Farmer support
•Nutritional education
•Market development
sweet potato A
• WHO provides practical implementation guidance through global resources such as ACTIVE, a package of effective interventions on physical activity
•It outlines four policy action areas, which directly reflect the four objectives of the Global Action Plan endorsed by the World Health Assembly (May 2018) & identifies the key policies within each action area:
-
-
-
-
active people
active societies
active environments
active systems
WHO monitors country's progress in adopting policies and other measures to achieve healthy diets
-Country scorecards have been developed for:
1…. … … (TFA)
2.S…..
3.S…..
-Progress towards eliminating trans-fat and reducing the intake of sodium and sugars is assessed against the mandatory and/or voluntary approaches that countries apply
trans fatty acids sodium sugar
SDG3 Good Health and Wellbeing
Dietary behavior is tightly related to …
Need for ….. and …. EVERY DAY
Many dietary guidelines: emphasize the need for all the different food groups, moderation in certain items, and the importance of a healthy …
All forms of malnutrition (undernutrition, overnutrition and nutrient imbalances) are associated with significant health problems
Deficiencies can impair growth and be fatal
Infants, children and pregnant women are the most at-risk
health macronutrients micronutrients weight
The United Nations (UN) General Assembly proclaimed 2016–2025 the United Nations Decade of Action on Nutrition, which calls for policy action across 6 key areas:
1.Creating sustainable, resilient food … for healthy diets;
2.Providing social protection and nutrition-related … for all;
3.Aligning health systems to nutrition needs, and providing universal coverage of essential nutrition interventions;
4.Ensuring that trade and investment policies improve nutrition;
5.Building safe and supportive environments for nutrition at all ages;
6.Strengthening and promoting nutrition governance and accountability, everywhere.
systems education
1- Good Health and ….. (SDG 3)
2- Zero …. (SDG 2)
3- Responsible Production and … (SDG 12)
4- Pulling Everything together
wellbeing hunger consumption