Systemic Anatomy (EXAM 1)
1/294
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
295 Terms
What is a joint?
Where two bones are jointed via connective tissue
What is the function of joints?
Holds bones together for movement / flexability
What are synovial joints?
Moveable joint separated by an articular cavity
What is a solid joint?
No cavity, just connective tissue
What are the 3 structural classifications of joints?
- Fibrous
- Cartilaginous
- Synovial
What are the 3 functional classifications of joints?
- Synarthrosis
- Amphiarthrosis
- Diathrosis
What is the fibrous structural classification?
- No synovial cavity
- Lots of collagen
- Dense irregular connective tissue
What is the cartilaginous structural classification?
- No synovial cavity
- Hyaline cartilage
- Fibrocartilage
What is the synovial structural classification?
- Cavity present
- Dense irregular connective tissue
What is the synarthrosis functional classification?
Immovable
What is the amphiarthrosis functional classification?
Slightly moveable
What is the diarthrosis functional classification?
- Freely moveable
- Variety of shapes
- All synovial
Describe sutures.
- Thin layer of dense connective tissue
- Only present in skull
What is the functional and structure type for sutures?
Functional: Synarthrosis
Structural: Fibrous
What is synostosis?
Fusion of two bones
Describe syndesmoses.
- Band or ligaments
- Greater distance between articulating surfaces
- Ex: Interosseus membrane, ACL, PCL
What is the functional and structure type for syndesmoses?
Functional: Amphiarthrosis
Structural: Fibrous
Describe synchondrosis joints.
- Hyaline cartilage
- Ex: 1st sternocostal joint, growth plate
What is the functional and structure type for synchondrosis?
Functional: Synarthrosis
Structural: Cartilaginous (hyaline)
Describe symphyses joints.
- Always at body midline
- Fibrocartilage
What is the functional and structure type for symphyses?
Functional: Amphiarthrosis
Structural: Cartilaginous (fibrocartilage)
What are 3 characteristics of synovial joints?
1. Hyaline cartilage
2. Joint capsule
3. Structures inside the capsule
What is the functional and structure type for synovial joints?
Functional: Diarthrotic
Structural: Synovial
What are 3 features of synovial joints?
1. Articular capsule
2. Synovial fluid
3. Accessory ligaments
What are 2 extracapsular features of synovial joints?
- Bursa
- Tendon sheaths
What is the outer fibrous layer of a synovial joint?
- Extension of periosteum
- Dense, regular connective tissue
- Provides strength and helps with movement
What is the inner fibrous layer of a synovial joint?
- Areolar connective tissue
- Elastic fibers
- Secretes synovial fluid
What is the structure of ligaments?
Bundle of dense, regular connective tissues that resists strains in one direction
What do ligaments do in synovial joints?
Hold bones close together
What secretes synovial fluid?
Synovial membrane
What does synovial fluid consists of?
- Hyaluronic acid
- Interstitial fluid
What are 4 functions of synovial fluid?
- Lubrication
- Shock absorption
- Supplies nutrients
- Removes waste
What are the 2 types of accessory ligaments?
- Extracapsular
- Intracapsular
What are articular discs "Menisci"?
- Fibrocartilage pads between articular surfaces of bones
- Binds to the fibrous membrane
- Divides the synovial cavity into two spaces
Where is the labra found?
Ball and socket joints
What is the labra?
Fibrocartilage lip extending from joint socket
What is the purpose of the labra?
Deepens the joint socket to increase area of contact
What is the function of a bursa sac?
Similar structures to synovial joints that alleviate pressure by cushioning joint movement
What are tendon sheaths?
"Tube-like" bursa that wraps around tendons that experience friction
What is the function of tendon sheaths?
Reduce joint friction as joints move back and forth
What are the 6 shapes of synovial joints?
- Plane (planar)
- Hinge (ginglymus)
- Pivot (trochoid)
- Condylar (ellipsoidal)
- Saddle (sellar)
- Ball and Socket (spheroid)
What are the 3 types of synovial joint movements?
- Uniaxial (one plane)
- Biaxial (two planes)
- Multiaxial (three planes)
What are the 4 main types of synovial joints?
- Gliding
- Angular
- Rotation
- Special movement
What types of bones are involved in gliding movement?
Flat bones
Gliding synovial joints have no alteration to _____________ between bones.
Angle
What do angular synovial joints cause?
Increase or decrease in angle between bones
What 5 types of movement do angular joints do?
- Flexion / hyperflexion
- Extension / hyperextension
- Lateral flexion
- Abduction and Adduction
- Circumduction
What does flexion / extension do?
- Flexion: decrease in angle
- Extension: increase in angle
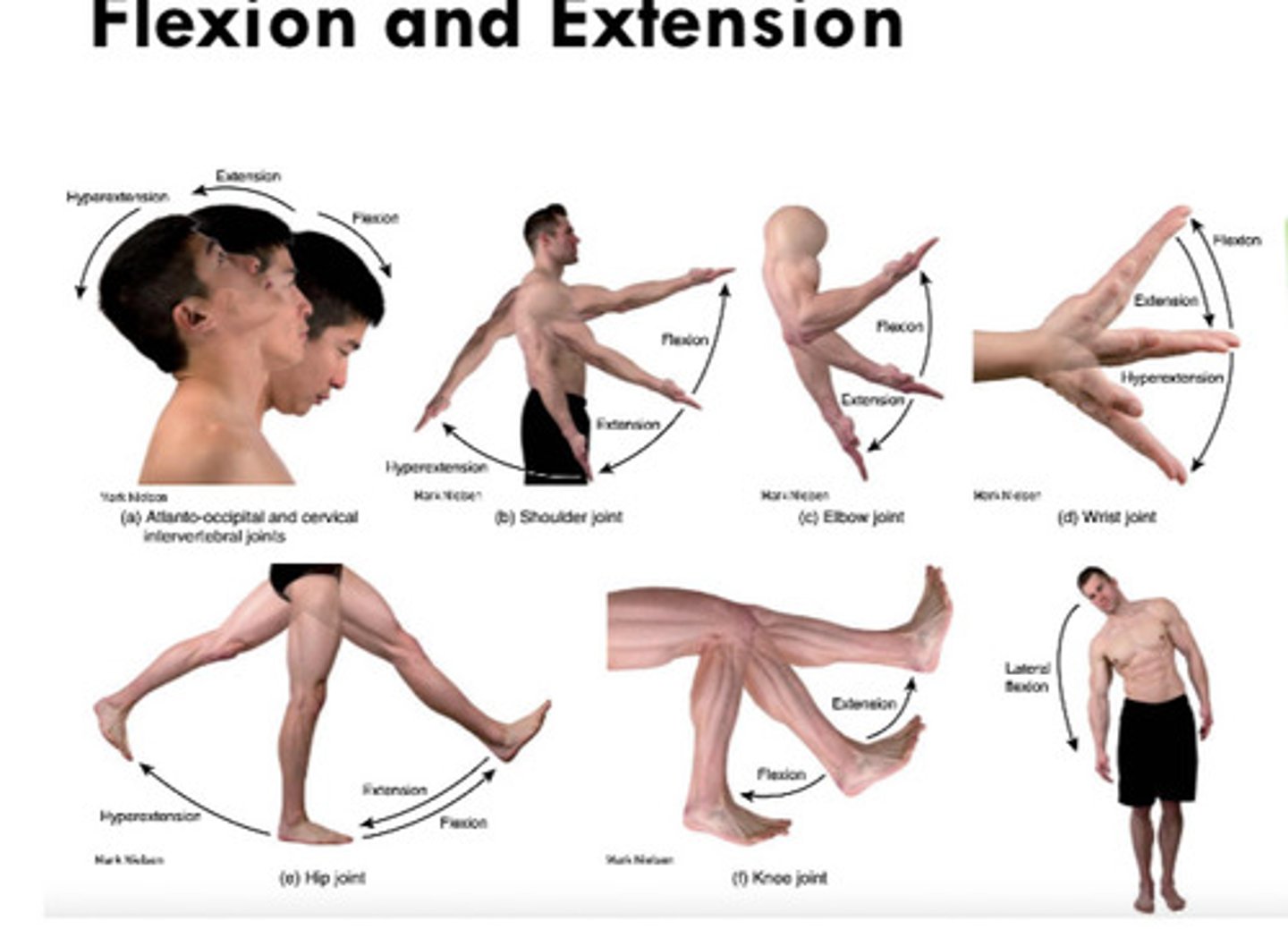
What is hyperflexion / hyperextension?
Movement beyond normal range of motion
What is adduction / ulnar deviation?
Movement toward the midline
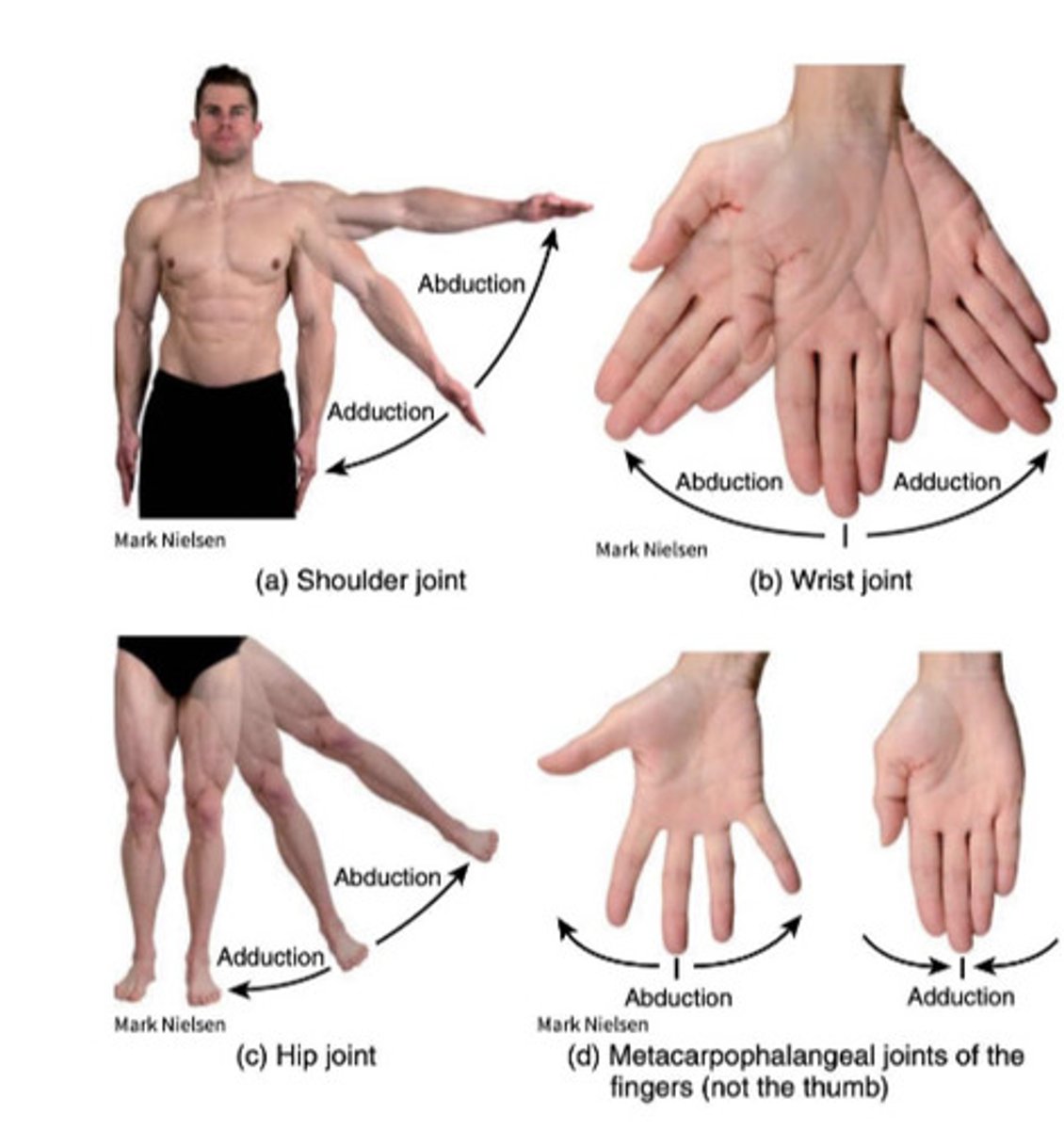
What is abduction / Radial deviation?
Away from midline
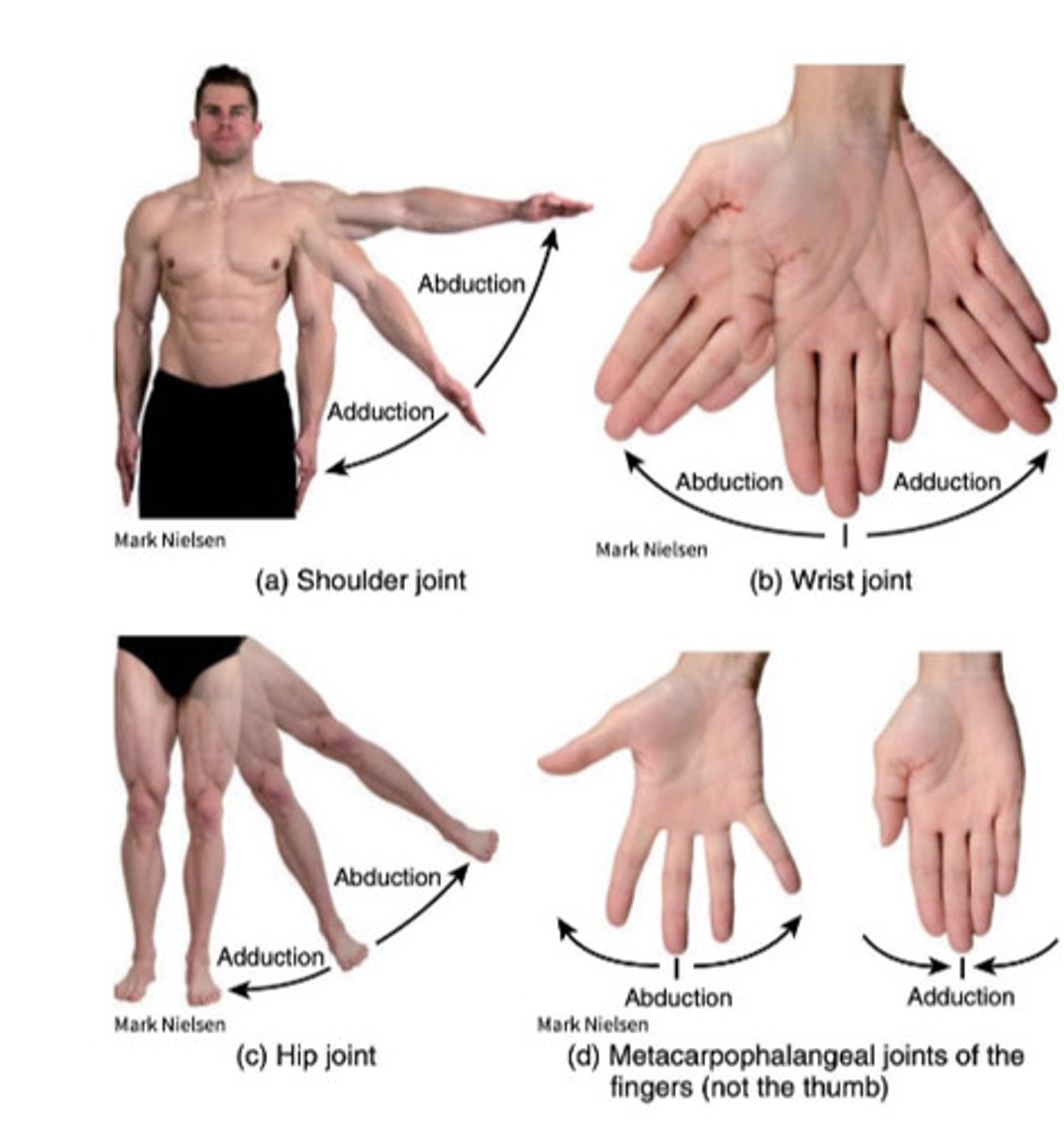
What is the midline of the fingers?
Middle of middle finger
What is the midline of the toes
Line at the second toe
What is rotation?
Bone moving around its own axis
What is medial rotation?
Arm moving to midline
What is lateral rotation?
Arm moving away from midline
What is circumduction?
Combination of movements that move the distal part of body in a circle
What are 6 special movements of the body?
- Elevation / depression
- Protraction / retraction
- Inversion / eversion
- Dorsiflexion / plantar flexion
- Supination / pronation
- Opposition
What is elevation in joint movement?
Superior movement
What is depression in joint movement?
Inferior movement
What is protraction in joint movement?
Anterior movement
What is retraction in joint movement?
Draw back to anatomical position
What is inversion in joint movement?
Turn sole of foot inward
What is eversion in joint movement?
Turn sole of foot outward
What is dorsiflexion in joint movement?
Superior movement of foot
What is plantar flexion in joint movement?
Inferior movement of foot
What is supination in joint movement?
Anatomical position of hand "palm up"
What is pronation in joint movement?
Palms posterior or down
What is opposition in joint movement?
The movement of the thumb across the palm to touch the tips of other fingers.
What are characteristics of plane (planar) joints?
- Flat articular surface
- Back and forth, Side to side or rotation movement
- Multiaxial joints
What are examples of plane (planar) joints?
- Intercarpal
- Sternocostal
- Z-joints
What are characteristics of hinge (ginglymus) joints?
- Convex surface
- Angular motion
- Uniaxial
What are examples of hinge (ginglymus) joints?
- Knee
- Elbow
- Interphalangeal
What are characteristics of pivot (trichoid) joints?
- Rounded
- Uniaxial
What are examples of pivot (trichoid) joints?
- Median Atlanto-axial
- Proximal and distal radio-ulnar
What are characteristics of condyloid (ellipsoid) joints?
- Convex, oval shape
- Biaxial
What are examples of condyloid (ellipsoid) joints?
- Atlanto-occipital
- Radiocarpal
- Metacarpophalangeal
What are characteristics of saddle (sellar) joints?
- Saddle shaped
- Biaxial
What are examples of saddle (sellar) joints?
1st Carpometacarpal joint
Sternoclavicular joints
What are characteristics of ball-and-socket (spheroid) joints?
- Ball like surface to cup like depression
- Multiaxial
What are examples of ball-and-socket (spheroid) joints?
- Glenohumeral
- Acetabulofemoral
What are 5 functions of the muscular system?
1. Stabilizes body position
2. Produce movements
3. Regulates organ volume
4. Moves substanses within body
5. Produces heat
What are the 3 types of muscles? How are they controlled?
- Skeletal
- Smooth
- Cardiac
Nervous system
What is fascia?
Connective tissues that line the body wall and limbs
What are the 4 functions of fascia?
- Allows free movement of muscles
- Carriers nerves and vessels
- Fills space between muscles
- Compartmentalizes muscles
What is the epimysium?
Outer layer of muscle that is continuous with the tendon
What is the perimysium?
Forms bundles called fascicles deep to epimysium
What is the endomysium?
Surrounds individuals muscle fibers
What is the origin of muscles?
Stationary attachment, typically medial or proximal
What is the insertion for muscles?
Mobile attachment, typically lateral or distal
What is the body/belly of muscle?
Flesh portion between tendons
What is muscle action?
Main movement when the muscle contracts
What do longer muscle fibers mean?
Greater range of motion
What do larger muscle fiber cross section mean?
More power
What are the 5 muscle fascicle arrangements?
1. Parallel
2. Fusiform
3. Circular
4. Triangular
5. Pennate
What are parallel muscle fascicles? Give an example.
Fascicles that run parallel to longitudinal axis of muscle
- Sternohyoid muscle
What are fusiform muscle fascicles? Give an example.
Fascicle that are nearly parallel but taper to form a larger belly
What are circular muscle fascicles? Give an example.
Fascicles in circular arrangements than enclose an opening
- Orbicularis oculi
What are triangular muscle fascicles? Give an example.
Fascicles that spread over a broad area but converge at a thick central tendon
- Pec major
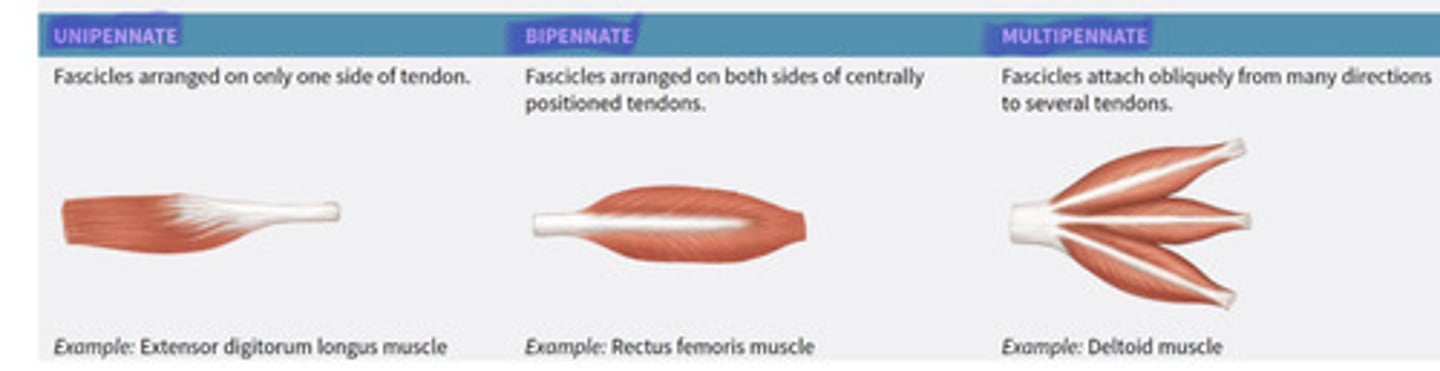
What are pennate muscle fascicles and their 3 types?
Short fascicles whose tendons extend most of muscle
- Unipennate
- Bipennate
- Multipennate