Chpt.14: T cell activation
1/54
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
55 Terms
T cells recognize soluble antigens directly in lymph
False. TCRs recognize presented antigens via MHC on APCs
Blood is the only fluid that circulates through the spleen
True
B7 proteins are constitutively expressed on all antigen-presenting cells
False. B7 (CD80/86) is only expressed by activated APCs
The marginal zone in the spleen is enriched with T cells
False. It contains phagocytes and marginal zone B cells
Dendritic cells migrate to the paracortex due to CCR7 expression
True
High endothelial venules (HEVs) allow blood entry into lymph nodes
True
T cells that do not receive signal 2 become anergic
True
IL-2 works in a paracrine fashion to stimulate T cell proliferation
False. IL-2 acts autocrinely on the activated T cell that produces it
The cortex of the lymph node is enriched with B cells
True
The cortex of the lymph node is enriched with B cells
False. CD4+ T cells are helpers, not killers
TH1 cells activate macrophages via CD40L and IFN-γ
True
MHC I is only used to activate CD4+ T cells
False. MHC I activates CD8+ T cells, while MHC II activates CD4+
Naïve T cells can enter lymph nodes through afferent lymphatic vessels
False. They enter via HEVs, not afferent lymphatics
The PALS region of the spleen is rich in B cells
False. It is rich in T cells
TH17 cells stimulate neutrophils via IL-17
True
Only professional APCs can activate naïve T cells
True
Tregs promote immune activation
False. They suppress immune responses
CD8+ T cells rely on IL-2 from CD4+ T cells for full activation
True
TFH cells migrate to the paracortex to help B cells
False. They migrate to the cortex, where B cells reside
All antigen-presenting cells have afferent and efferent lymphatic vessels
False. This applies to organs, not cells. The spleen, for instance, lacks afferent vessels
Granzyme release by CD8+ T cells leads to intrinsic apoptosis
True
CD28 is expressed only after T cell activation
False. CD28 is constitutively expressed on T cells
Tregs rely on TGF-β for differentiation
True
IL-4 induces B cell isotype switching to IgE
True
The paracortex of lymph nodes is the outermost layer
False. The cortex is outer; paracortex is deeper
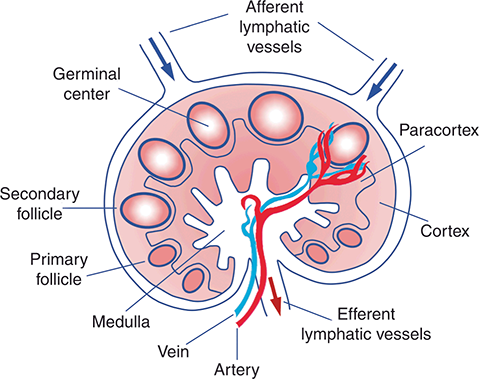
CCR7 guides both dendritic cells and T cells to the paracortex
True
IL-21 is secreted by TH1 cells to activate macrophages
False. IL-21 is secreted by TFH cells to help B cells
Fas ligand on Tc cells delivers an extrinsic apoptosis signal
True
CXCL13 attracts T cells to the paracortex
False. CXCL13 attracts B cells to the cortex
IL-6 is an early cytokine that promotes TFH differentiation
True
The __________ region of the lymph node contains most of the B cells
Cortex
The receptor CCR7 is attracted to __________ and __________
CCL19, CCL21
Signal 1 in T cell activation is the binding of __________ to __________
TCR, antigen-MHC
Signal 2 in T cell activation is the interaction between CD28 and _________
B7
TFH cells secrete __________ and __________ to help B cells
IL-4, IL-21
Tregs are induced by the cytokine __________
TGF-β
The cytokine __________ is critical for TH17 function and neutrophil recruitment
IL-17
CD8+ T cells recognize antigens presented on __________ molecules
MHC I
Activated TH1 cells stimulate macrophages using CD40L and __________
IFN-γ
The __________ sheath in the spleen contains T cells
Periarteriolar lymphocyte (PALS)
The __________ receptor on B cells binds CXCL13 to localize them in the cortex
CXCR5
__________ are professional APCs that bridge innate and adaptive immunity
Dendritic cells
_________ chemokine is important for B cell localization in lymph nodes
CXCL13
The CD4+ T cell subset that helps clear intracellular pathogens is _________
TH1
Tc cells induce apoptosis by secreting perforin and _________
Granzymes
Which of the following is NOT a professional antigen-presenting cell?
A. Macrophage
B. Dendritic cell
C. B cell
D. Neutrophil
D. Neutrophil – Neutrophils are not APCs
Which region of the spleen is most enriched with B cells?
A. Red pulp
B. Marginal zone
C. PALS
D. Paracortex
B. Marginal zone – It has marginal zone B cells
What chemokine draws T cells into the paracortex of lymph nodes?
A. CXCL13
B. CCL2
C. CCL19
D. IL-2
C. CCL19 – Along with CCL21, it attracts CCR7+ cells
Which subset of CD4+ T cells is responsible for activating macrophages?
A. TH2
B. TH17
C. TH1
D. TFH
C. TH1 – TH1 cells help macrophages fight intracellular pathogens
Which of the following cytokines promotes differentiation into Tregs?
A. IL-12
B. IL-6
C. IL-4
D. TGF-β
D. TGF-β – Required for Treg induction.
What is the function of IL-2 in T cell activation?
A. Recruits neutrophils
B. Kills infected cells
C. Promotes T cell proliferation
D. Activates dendritic cells
C. It’s an autocrine growth factor
Which structure in the lymph node is rich in B cells?
A. Paracortex
B. Medullary sinus
C. Cortex
D. HEV
C. Cortex – The follicular zone contains B cells
Which CD4+ subset helps activate B cells via IL-21?
A. TH1
B. TH2
C. TH17
D. TFH
D. TFH
Which interaction prevents T cell anergy during activation?
A. TCR-MHC
B. CD40-CD40L
C. CD28-B7
D. IL-4–IL-5
C. CD28-B7 – Signal 2 is needed to prevent anergy
What do CD8+ T cells recognize on infected cells?
A. IgG
B. MHC II
C. Complement
D. MHC I with antigen
D. MHC I with antigen