ESS chap.2 Ecosystems and ecology
1/43
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
44 Terms
Species
a group of organisms that interbreed and are capable of producing fertile descendants
Population
a group of organisms of the same species living in the same area at the same time, and which are capable of interbreeding
Habitat
the environment in which a species normally lives
Niche
set of biotic and abiotic conditions/resources to which an organism responds
specific to a species
2 types:
fundamental niche: where and how an organism could live
realised niche: where and how an organism does live
Abiotic and biotic factors
Abiotic: non-living factor that influences an organism/ecosystem (temperature, sunlight, pH)
Biotic: living part of an ecosystem that influences an organism/ecosystem
Population interactions
- Competition:
intraspecific (same species)
-> affect the carrying capacity (max number of a species for a given environment)
interspecific (different species)
-Parasitism:
the parasite benefits from the host
-Diseases
-Mutualism: symbiosis
-Predation:
lower the carrying capacity of both prey and predator
-Herbivory
more plants=higher carrying capacity
=biotic factors
J- population curve
- shows exponential growth
1. initially slow growth
2. become increasingly rapid
- no limiting factors
- after peak value -> population crash (caused by abiotic factors)
Biosphere
part of the Earth inhabited by organisms
Ecosystem
community + physical environment with which it interacts
Community
a group of populations living and interacting with each other in a common habitat (biotic component)
Respiration
the conversion of organic matter into carbon dioxide and water in all living organisms, releasing energy.
can be aerobic (requires oxygen) or anaerobic (no oxygen)
glucose + oxygen -> energy + water + carbon dioxide
C6H12O6 + 6CO2 -> Energy + 6H2O + 6CO2
Photosynthesis
the process by which green plants make their own glucose from water and carbon dioxide using energy from sunlight.
happens in the chloroplasts
carbon dioxide + water -> glucose + oxygen
6CO2 + 6H2O -> C6H12O6 + 6O2
Food chains/webs
to model feeding relationships
chain (linear), web (complex)
composed by trophic levels (position an organism occupies in a food chain)
producer, primary consumer (herbivore), secondary consumer (carnivore), tertiary consumer (top carnivore)
Pyramids of numbers
number of organisms (producers and consumers) coexisting in an ecosystem
pros
quick overview
compare numbers in different seasons
cons
no account taken of size of organisms
Pyramids of biomass
shows the biological mass at each trophic level
pros
takes into account the size of organisms
cons
have to kill organisms
seasonal variation
some animals have bone or shell (affects weight)
Pyramids of productivity
the flow of energy through trophic levels
always show a decrease in the energy
pros
shows energy over time (rates of production)
compare ecosystems easily
never an inverted pyramid
cons
collecting data is difficult (bc over time)
many species feed at more than one trophic level, which affects results
Bioaccumulation/biomagnification
increase in toxins within an organism
increases in toxins along a food chain
Energy transfer/transformation
-solar energy -> chemical energy (biomass) -> transferred between trophic levels -> leaves as heat energy
- ecological efficiency: % energy transferred from one trophic level to the next (only 10%)
-new biomass/energy supplied * 100
Gross vs Net productivity
the total gain in energy or biomass per unit area per unit time (through photosynthesis or absorption)
A gain in energy or biomass per unit area per unit time after respiratory losses
Primary vs Secondary productivity
Gain by producers in energy or biomass per unit area per unit time
Biomass gained by consumers through feeding and absorption measured in units of mass or energy per unit area per unit time
Gross vs Net Primary Productivity
Total gain on energy or biomass per unit area per unit time by photosynthesis in green plants
Gain by producers in energy or biomass per unit area per unit time after respiratory losses
Gross vs Net Secondary Productivity
Total gain by consumers in energy or biomass per unit area per unit time through absorption
Gain by consumers in energy or biomass per unit area per unit time remaining after respiratory losses
Max sustainable yield
the highest rate of harvesting that does not lead to a reduction in the original natural capital - net productivity
Producers (autotrophs)
make their own food (glucose) and convert inorganic molecules into organic ones (plants, algae)
photoautotrophs: sunlight energy -> chemical energy
chemoautotrophs: chemical energy -> glucose
Consumers (heterotrophs)
obtain energy, minerals, and nutrients by eating other organisms
Decomposers
Organisms that break down the dead remains of other organisms
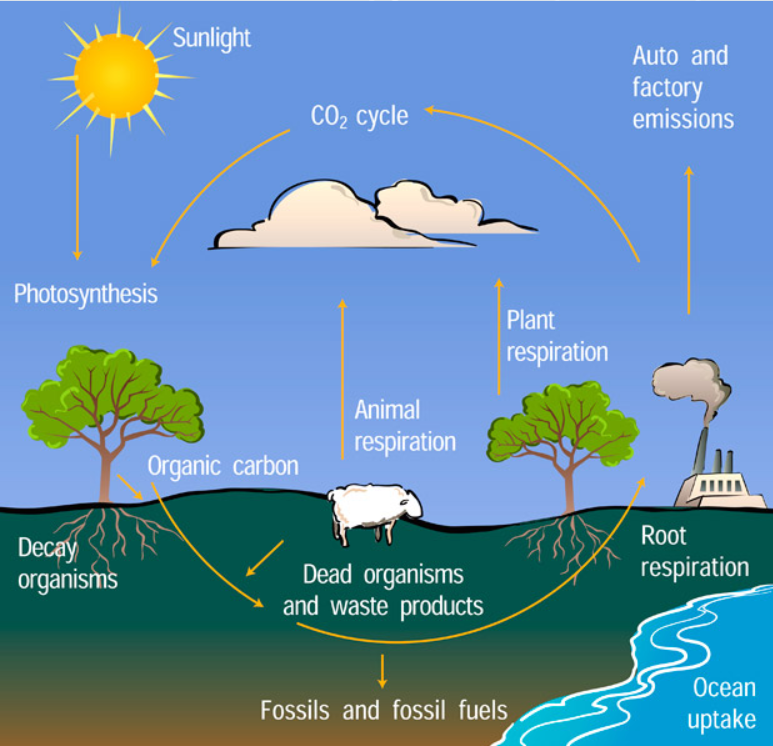
Carbon cycle
The organic circulation of carbon from the atmosphere into organisms and back again
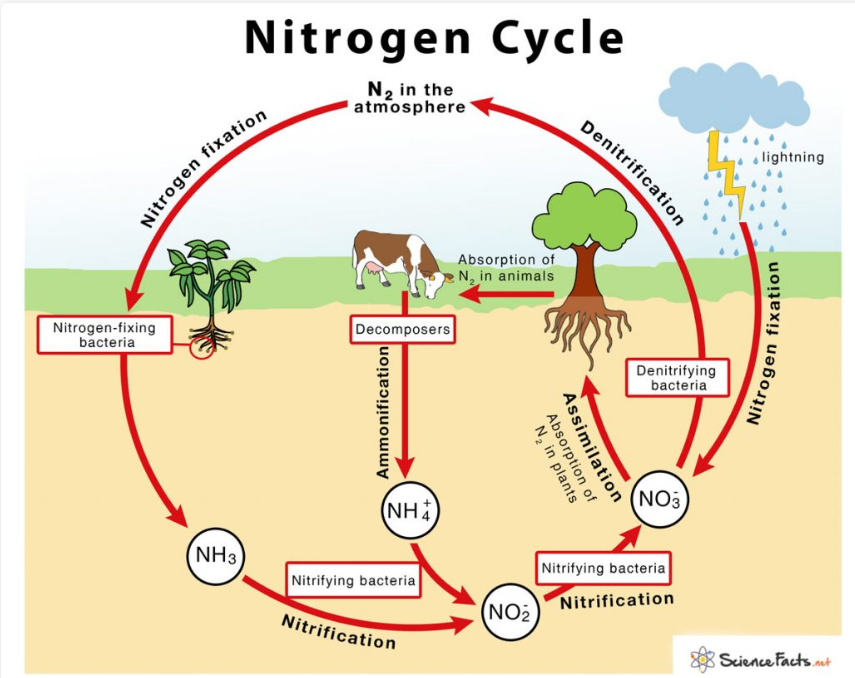
Nitrogen cycle
nitrogen - nucleic acid and protein
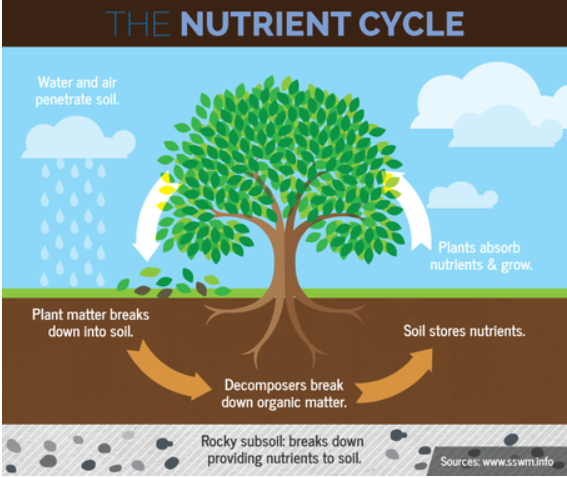
Gersmehl’s nutrient model: input and output of nutrients
main gas of the atmosphere and fertilizer
Energy flows
one direction - energy loss between trophic levels
ex: food webs, food chains, pyramids
Matter cycles
Impacts of human activity on the carbon cycle (urbanization, deforestation, agriculture, fossil fuel use)
Impacts of human activity on the nitrogen cycle (agriculture, deforestation, fossil fuel use, human population growth)
S-population curve
- establishment of a population
1. lag phase: low population numbers
2.exponential growth phase: limiting factors are not restricting the growth
3.transitional phase: limiting factors start to restrict the growth
4. plateau phase: achieved carrying capacity - changes can cause increase or decrease
Succession
how an ecosystem changes over time - natural, gradual changes
primary: begins in a place without any soil (sides of volcanoes, landslides) + starts with the arrival of pioneer species (do not need soil to survive)
secondary: begins in a place that already has soil and was once the home of living organisms (forest after a fire)
Tundra (biome)
a collection of ecosystems sharing similar climatic conditions
located above the Arctic Circle (Arctic Tundra) or at high altitude on moungtains (Alpine Tundra) - coldest biome - low precipitations - low biodiversity (low-growing plants and limited animals such as polar bears) - limited productivity (frozen soil)
Tricellular model of atmospheric circulation
Describes the three cells - Hadley, Ferrel, and Polar - that drive global wind patterns and weather systems.
Zonation
changement of an ecosystem over a distance
Climax communitites
more or less stable community of organisms that is in equilibrium with natural environmental conditions (climate) - happens at the end of ecological succession
more productive, complex food webs, negative feedback mechanisms
K-strategists
Species that concentrate their reproductive investment in a small number of offspring, thus increasing their survival rate and adapting them for living in long-term climax communities (s-curve)
example : elephants, people, sequoia trees
r-strategists
species that tend to spread their reproductive investment among a large number of offspring so that they are well adapted to colonise new habitats rapridly and make opportunistic use of short-lived resources (j-curve)
example : mice, rabbits, bacterias
Temperate forest (biome)
temperatures and light intensity vary with the seasons
sufficient rainfalls
seasonal (lose their leaves in winter) and evergreen (thick leaves or needles) trees
often dominated by one species
rich shrub layers due to high sunlight amounts (not do dense trees)
High NPP
Tropical rainforest (biome)
high rainfall, sunlight, and temperature
consistent light and temperature: no seasons
complex structure with =/ layers : emergent trees + low layers
only 1% of sunlight reaches the floor so nutrient-poor soil because of the dense canopy
most productivity in the canopy
very high NPP
Desert (biome)
low rainfall, high sunlight, very hot temperatures in the daytime and cold at night
low vegetation, no tall trees
many plants and animals adapted to desert conditions like cactus
soil: low water-holding capacity + easy erosion with the wind (low fertility)
low NPP
Temperate grassland (biome)
flat areas dominated by grasses and non-woody plants (no trees)
clear skies, low rainfall, threat of drought
grasses die in winter but roots survive
mat of decomposed vegetation that is rich in nutrients
animals such as kangaroos, antelopes, or coyotes
examples: north american prairies, pampas in Argentina
not so very high NPP
Aquatics (biome)
largest of all the world’s biomes
water absorbs some light and limits photosynthesis (no ps in deep oceans)
freshwater may freeze in temperate or polar winters
NPP and biodiversity: high in tropical coral reefs, very low in deep oceans, and moderate in freshwater
Nutrient cycle