The rate and extent of chemical change
1/26
Earn XP
Description and Tags
C6 - Specification
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
27 Terms
calculating rates of reactions
rate of a chemical reaction can be found by measuring the quantity of a reactant used / quantity of product formed over time :
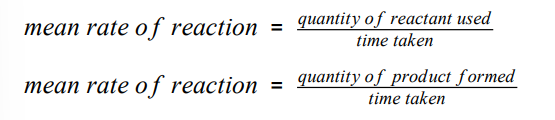
quantity of a reactant / product can be measured by -
mass in grams
volume in cm³
units of rate of reaction
g/s or cm³/s
quantity of reactants
units for rate of reaction
moles
mol/s
factors that affect the rates of chemical reactions -
concentrations of reactants in solution
the pressure of reacting gases
surface area of solid reactants
temperature
presence of catalysts
required practical activity 11 : changes in concentration affects the rates of reactions by a method involving measuring the volume of a gas produced and a method involving a change in colour or turbidity
Measure 50 cm3 of Na2S2O3 solution into the conical flask
Place the white paper with cross marked on it underneath the conical flask
Measure 10 cm3 of dilute HCl into a measuring cylinder
Add the hydrochloric acid into the flask and immediately start the stopwatch
Look down at the cross and stop the timing when the cross can no longer be seen
Solid sulfur is formed which precipitates in solution, turning cloudy:
Na2S2O3 + 2HCl → 2NaCl + S + SO2 + H2O
Record the time, in seconds, in the results table
Repeat steps 1 - 6 using the different concentrations of sodium thiosulfate solution described in the table
collision theory - how various factors affect rates of reactions.
chemical reactions can occur only when reacting particles collide with each other and with sufficient energy.
activation energy
the minimum amount of energy that particles must have to react.
__________, _________ and _________ increases the frequency of collisions and so increases the rate of reaction.
increasing the concentration of reactants in solution
the pressure of reacting gases
the surface area of solid reactants
increasing the temperature -
increases the frequency of collisions and makes the collisions more energetic, and so increases the rate of reaction.
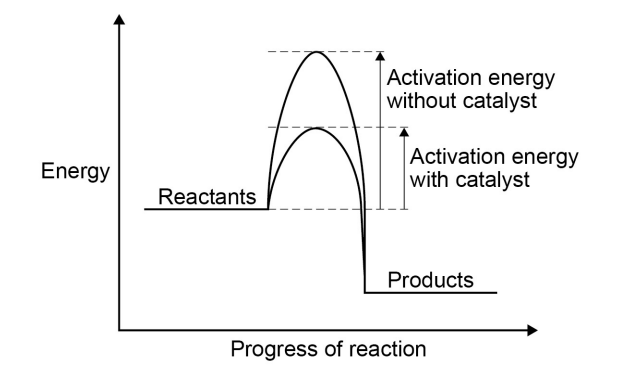
catalysts
change the rate of chemical reactions but are not used up during the reaction
___________ acts as catalysts in biological systems
enzymes
a reaction profile for a catalysed reaction
reversible reactions
the products of the reaction can react to produce the original reactants
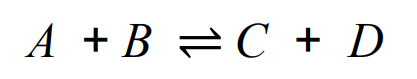
direction of reversible reaction can be changed by -
for example -
changing the conditions

if a reversible reaction is exothermic in one direction -
it is endothermic in the opposite direction.
copper sulphate reactions -
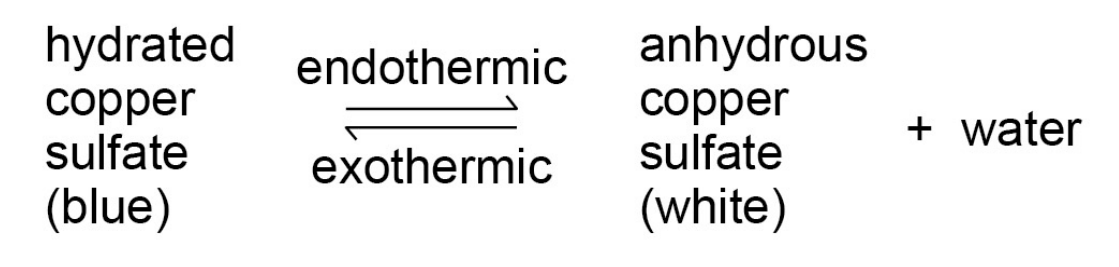
equilibrium is reached when -
a reversible reaction occurs in apparatus which prevents the escape of reactants and products, and the forward and backward reactions occur at exactly the same rate.
relative amounts of all the _________ and __________ at equilibrium depend on the conditions of the reaction.
reactants , products
if a system is at equilibrium, and a change is made to any of the conditions -
the system responds to counteract the change
le chateliers principle -
the effects of changing conditions on a system at equilibrium can be predicted
if the concentration of one of the reactants or products is changed -
the system is no longer at equilibrium and the concentrations of all the substances will change until equilibrium is reached again.
if the concentration of a reactant is increased -
more products will be formed until equilibrium is reached again.
if the concentration of a reaction is decreased -
more reactants will react until equilibrium is reached again.
if the temperature of a system at equilibrium is increased -
the relative amount of products at equilibrium increases for an endothermic reaction.
the relative amount of products at equilibrium decreases for an exothermic reaction.
if the temperature of a system at equilibrium is decreased -
the relative amount of products at equilibrium decreases for an endothermic reaction.
the relative amount of products at equilibrium increases for an exothermic reaction.
for gaseous reactions at equilibrium -
an increase in pressure causes the equilibrium position to -
a decrease in pressure causes the equilibrium position to -
shift towards the side with the smaller number of molecules as shown by the symbol equation for the reaction.
shift towards the side with the larger number of molecules as shown by the symbol equation for the reaction.