Biology - Exam revision
1/75
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
76 Terms
What is the Cell Theory?
All living things are made up of cells.
Every cell comes from a pre-existing cell.
What are the differences between plant and Animal cells?
Animal cells have centrosomes and lysosomes and plant cells do not.
Plant cells have a cell wall and a chloroplast and animal cells do not.
What are the similarities between plant and Animal cells?
Both Eukariotic cells.
Both have a cell membrane, nucleus, mitochondria, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi bodies, ribosomes, and cytoplasm.
 What is the Cytoplasm?
What is the Cytoplasm?
A jelly like substance which occupies a large part of animal cells and a small part in plant cells.
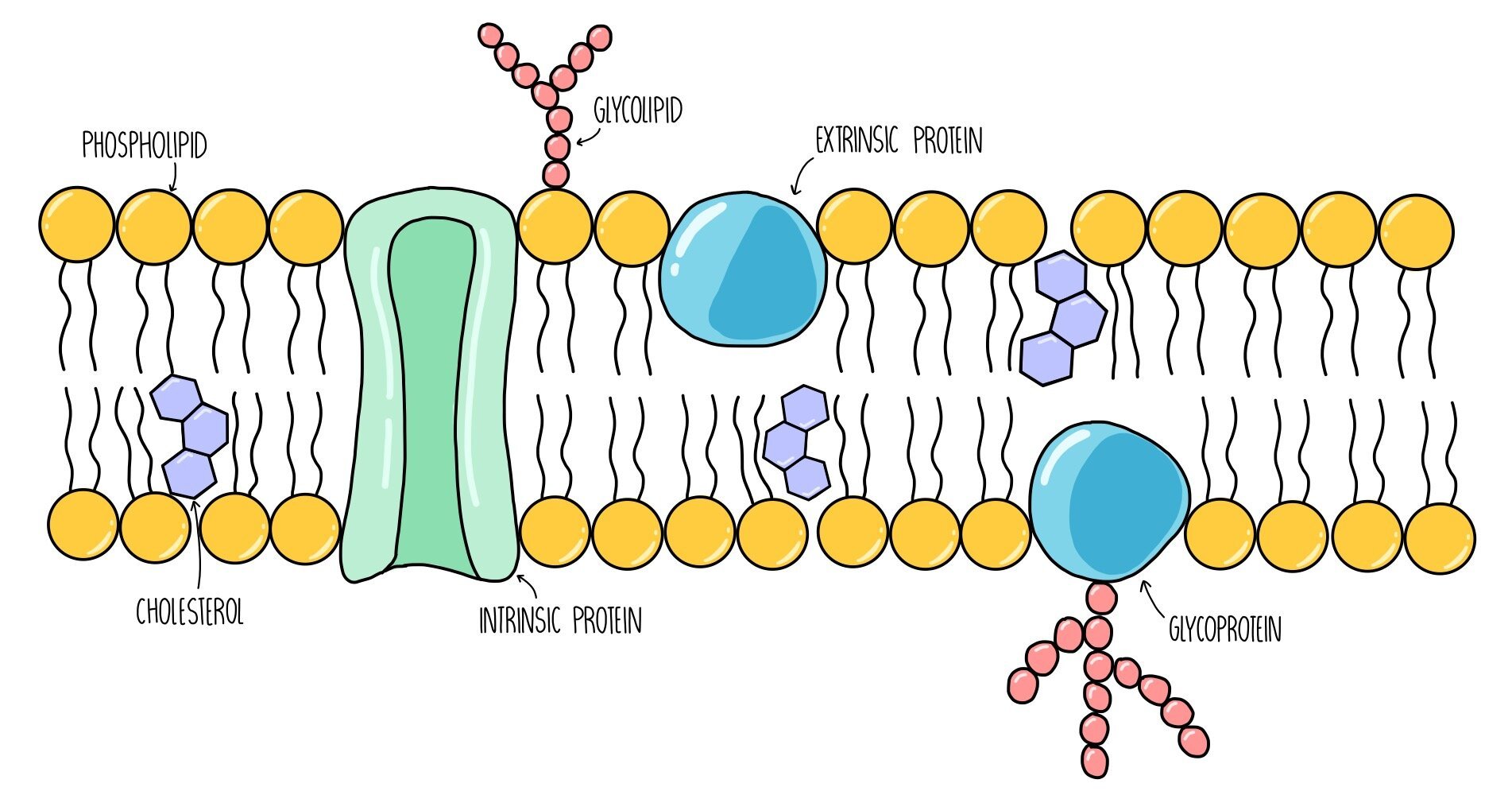 What is the cell membrane?
What is the cell membrane?
The cell membrane is made up of two layers of fat molecules called a lipid bilayer.
Protein molecules are present between the two layers.
The proteins allow substances to enter and exit the cell.
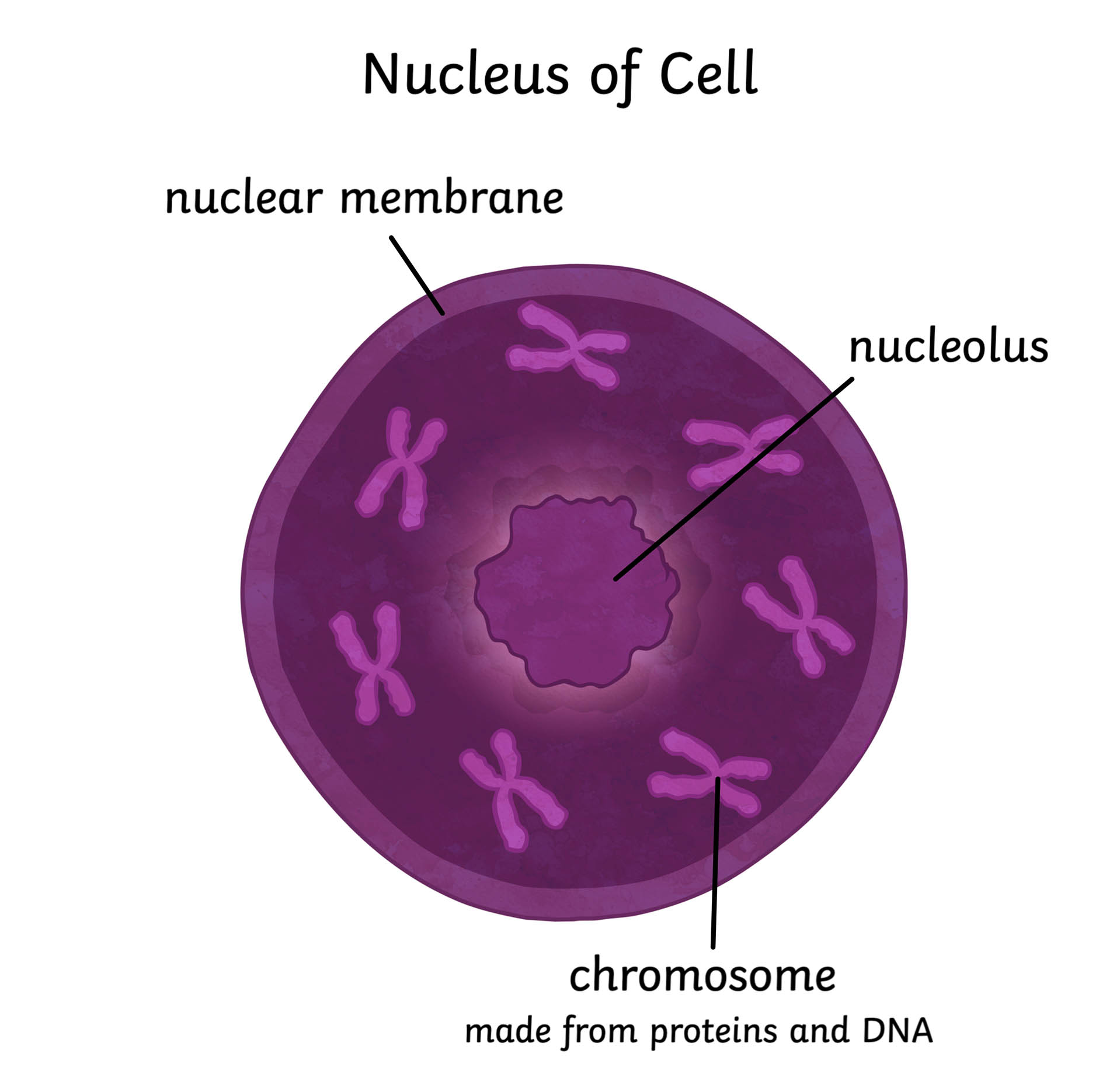 What is the nucleus?
What is the nucleus?
Only found in Eukaryotic cells.
The largest and most prominent feature of the cell.
Usually located in the centre of animal cells and towards the cell wall in plant cells.
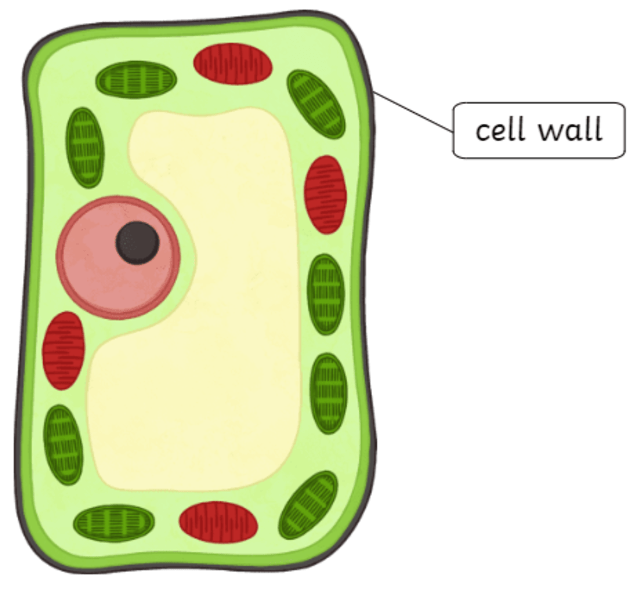 What is a cell wall?
What is a cell wall?
The cell wall is only found in plant cells.
Made up of a tough, rigid, cross-linked matrix of substances.
Helps keep the cells structure and shape.
 What is the endoplasmic reticulum?
What is the endoplasmic reticulum?
The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) is a system of membranes in the cytoplasm.
Rough (ER) have ribosomes attached.
The (ER) is important for transportation around the cell.
 What are the Golgi bodies?
What are the Golgi bodies?
The Golgi bodies are stacks of smooth flattened membrane.
They produce proteins and carbohydrates for the cells.
 What is the Vacuole?
What is the Vacuole?
The vacuole is a fluid filled space that is bounded by membrane.
In plant cells it is large and in animal cells it is much smaller.
Their role is to maintain the water-salt balance within the cell.
The fluid is made up of:
Salts (in the form of ions)
simple sugars
Amino acids
 What is the chloroplast?
What is the chloroplast?
The chloroplast is made from a type of placid (particles involved in storage).
The chloroplast is the site of photosynthesis.
Only found in plant cells.
 What are lysosomes?
What are lysosomes?
Lysosomes are small, circular, membrane bound organelles found in the cytoplasm.
They are formed by Golgi bodies.
Contain enzymes which breakdown macromolecules.
 What are ribosomes?
What are ribosomes?
Ribosomes are small circular organelles.
They are the protein factories of the cell and are the site of protein synthesis.
They can be found floating in the cytoplasm.
When Ribosomes attach to the (ER) it forms the rough (ER).
What are eukaryotic cells?
They carry DNA in the nucleus.
Contain membrane bound organelles.
Much larger than prokaryotic cells.
Can be unicellular or multicellular.
What are prokaryotic cells?
Have a cell wall on the outside of the cell membrane.
They carry DNA in the cytoplasm where it is organised in circular chromosomes.
Exists in unicellular or multicellular.
What are Autotrophs?
They create their own energy.
contains chloroplasts.
e.g plant cells.
What are heterotrophs?
Eat other objects for food and energy.
Do not contain chloroplasts.
e.g animal cells.
What is one similarity between Autotrophs and Heterotrophs?
Both require glucose to fuel their cellular respiration, reproduction, and cell growth.
What is the process of photosynthesis?
When autotroph cells produce food and energy from glucose and water.
What is the word question for photosynthesis?
Carbon dioxide + water → Glucose + water
What is the difference between Anerobic respiration and Aerobic respiration?
Both use glucose, however Anerobic respiration does not require oxygen and Aerobic respiration does.
Both also produce energy in the form of ATP.
What is a light microscope?
Can magnify up to 1500x
Light passes through thin tissue
Light is focused through the eye piece and objective sense.
What is an electron microscope?
Can magnify up to 100,000x
beams of electrons pass through a vacuum and then a thin tissue.
Better resolution than light microscopes. It can seperate close objects.
Name modes of active transport into and out of the cell.
Name modes of passive transport into and out of the cell.
Does passive transport require energy?
No, passive transport does not require energy.
It goes with the concentration gradient.
Does active transport require energy?
Yes, active transport does require energy.
It goes against the concentration gradient.
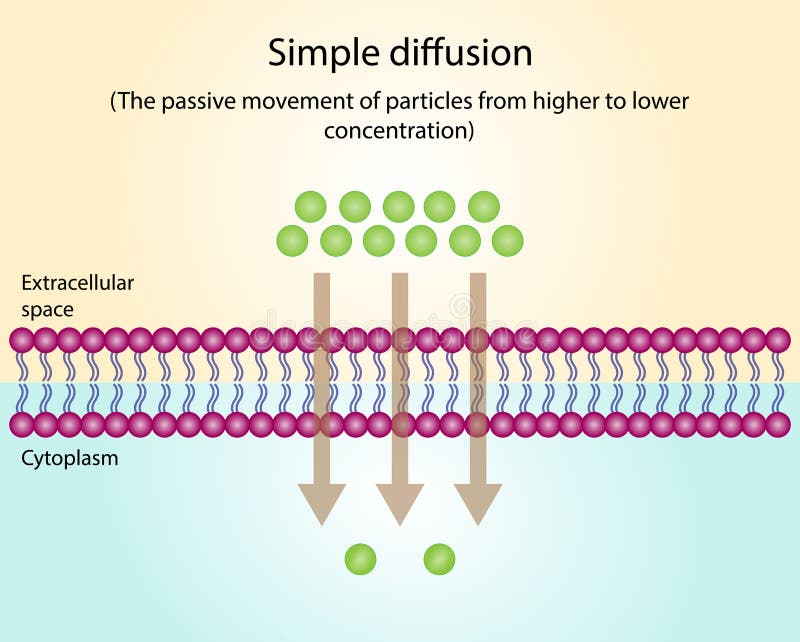 What is diffusion?
What is diffusion?
A form of passive transport.
Does not require energy.
 What is facilitated diffusion?
What is facilitated diffusion?
A form of passive transport.
Does not require energy.
When molecules move higher concentration to concentration and are assisted by a carrier.
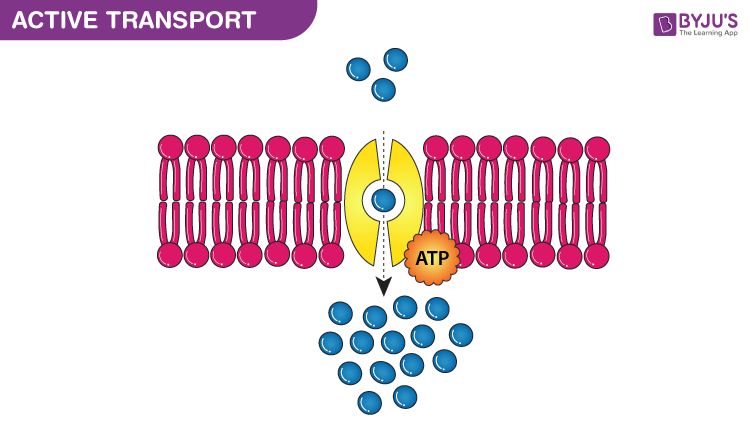 What is Active transport?
What is Active transport?
When molecules move through the cellular membrane using cellular energy.
What is Hypertonic?
When any external solution has a higher concentration level of solute and lower water concentration.
This is when water leaves the cell.
What is an example of Hypotonic?
When a solution contains a lower amount of solute in comparison to the solute concentration inside the membrane.
What is Isotonic?
When a solution has the same level of solute concentration as the cell membrane/inside the cell.
Hypertonic
When a plant cell is placed into a solution of 30% and inside was a concentration of 10%.
Would it be Hypertonic, Hypotonic, or Isotonic?
Hypotonic
When a plant cell is placed into a solution of 2% salt and had a concentration of 10%.
Would it be Hypertonic, Hypotonic, or Isotonic?
What is Binary Fission?
Binary fission is a form of reproduction which occurs in 20 minutes however, the conditions must be favourable.
It is a result of an organism duplicating itself.
e.g bacteria
What is Mitosis?
The reproduction cycle of cells that do not use binary fission to reproduce.
What is Interphase?
When
- DNA forms as a chromatin
- DNA replication
- Cell grows through interphase
What is Preparation?
The first step in prophase
When
- DNA condenses to form chromosomes
- Nucleus dissolves
What is Metaphase?
The “Middle” phase
When
- Chromosomes align in the middle (equator)
- Spindle fibres start to for and attach
What is Anaphase?
The “Away” phase
When
- The cell elongates
- Spindle fibres start to pull the sister chromatids apart at the centrome.
What is Telophase?
The “Two” phase
When
- Cytoplasm dissolves
- Nucleus reforms
What is cytokinesis?
The final phase
When
- End of Mitosis
- 2 genetically identical daughter cells are formed
What is an example of beneficial microorganisms?
Bacteria is an important part of the digestion and immune system.
e.g gut bacteria which helps break foods down in the gut.
What percentage of microorganisms are harmful to humans?
less than 1%.
What are the different types of microorganisms?
Bacteria, Fungi, Protists, Parasites, and Viruses.
What are the ideal conditions for bacterial growth?
Nutrients, Numeral pH, Water, Temperature, Oxygen, and Energy.
What is bacteria?
- Unicellular
- Prokaryote
- Heterophobic
Reproduces through binary fission.
Genetically identical.
e.g E. coli & Salmonella
What is Fungi?
- Unicellular (yeast)
- Multicellular (mould)
- Eukaryote with a nucleus & cell wall
- Heterophobic
Reproduces by releasing spores which grow into a new organism.
e.g mushrooms & athletes foot
What are Protists?
- Unicellular
- Eukaryote with a nucleus & cell wall
- Large and diverse group
- Heterophobic & Autotrophic
Reproduces asexually through binary fission.
Genetically identical.
e.g algae
What are Parasites?
- Unicellular
- Eukaryote with a nucleus & cell wall
- Heterophobic
Reproduces asexually through binary fission.
e.g ringworm
What are viruses?
- Non-cellular
- Contains acids such as DNA & RNA
- Requires a host cell to live
- Kills the host cell
Reproduces inside of the host cell
e.g HIV & COVID-19
Infectious diseases
are diseases or illnesses that can be transmitted from one organism to another.
Types are
- Viruses, bacteria, & parasites
e.g Common cold, influenza, & chicken pox
Non-infectious diseases
are diseases which can not be transmitted from one organism to another.
Caused by genetics, aging, anatomical difference, and the environment you live in.
e.g Arthritis, diabetes, cancer & dementia
Direct contact
Touching or being touched by a infected person can transmit pathogenic organisms from one person to the other.
This includes hand shaking and STDs
Vectors
Carriers of disease and it carries diseases from one infected organism to a non-infected organism and infects them.
e.g mosquitos
Some methods of disease control are
- Hand sanitation
- keeping personal hygiene
- Vaccines
- Medicines
What are the physical barriers of the human body?
The first line of defence include:
The skin - outer barrier of protection
Alimentary canal - Stomach acid
What is the body’s second line of defence?
The Innate immune system has natural killer cells, which are special white blood cells.
other symptoms include: inflammation, and a rise in body temperature.
What is the body’s third line of defence?
The adaptive immune system releases a specialised attack on antigens and uses antibodies to produce proteins to create a response to a specific antigen.
Also uses T & B lymphocytes and Memory cells.
What are T & B Lymphocytes?
T - remain inactive in the blood until they come into contact with a pathogen.
B - also live in the blood and are activated by antigens.
What are memory cells?
Memory cells can remain in the body for a long time and they carry receptors that can recognise specific antigens.
Vaccination definition
a safe simple way of protecting people against harmful diseases.
How do vaccines work?
A small amount of pathogen is injected into a person’s body to help the body build immunity and create memory cells.
What is the independent variable?
The variable that is manipulated.
What is the dependent variable?
The variable that is measured as a result of the independent variable (IV) being manipulated.
What is a constant?
The factors that do not change.
What is the aim?
The statement which explains what the experiment is attempting to achieve.
What is the hypothesis?
a proposed explanation made on the basis of limited evidence.
How is the average calculated?
By adding all the numbers given together and dividing them by the amount of numbers given.
e.g if there was 5 numbers given, you would add them ups and divide them by 5.
What is a random error?
An error which occurs due to chance and only affects one sample.
e.g human error.
What is a systematic error?
An error which happens because of mechanical reasons and affects all data samples.
e.g technology malfunction.
What are the different influences on a SHE task?
Social, ethical, economical, & cultural.
What are limitations?
Examples include inaccurate measurements, or calibration errors.
What is heterotroph?
An organism which eats another organism for their food and/or energy source.
What is an Autotroph?
An organism which generates its own food and energy.
e.g plant cells through photosynthesis.