Chapter 5 - Data Modeling
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
20 Terms
Structure Model
Describe data and information structures inherent in business process
Create the blueprint for development of relational databases to support collection, aggregation, and communication of process information
Structure Model - Purpose
Describe entities or things in domain of interest (ex: customers or orders)
Describe relationships among these things (ex: customers make orders)
Specify how many instances of one entity can be related to another (ex: customers can place multiple orders)
Identify attributes/characteristics of entities and relationships (ex: customer name, address, phone number, etc.)
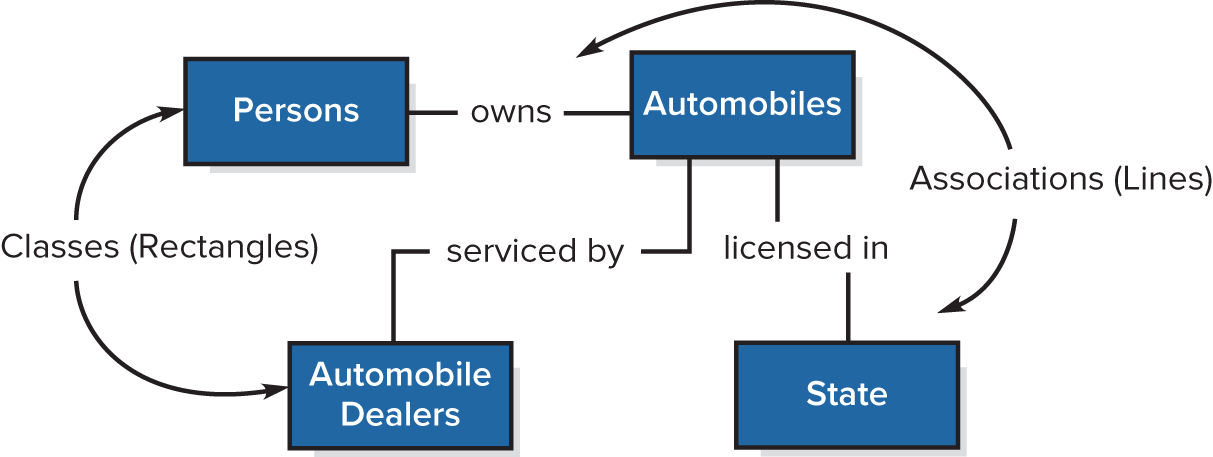
UML Class Diagram Building Blocks
Classes
Association
Multiplicites
UML Class Diagram - Classes
Separately identifiable collections of things about which the organizations wants to collect and store information
Can represent organization resources (ex: machines, buildings, cash, investments)
Can represent people (ex: customers or employees)
Can represent events (ex: sales, purchases, cash receipts)
Can represent conceptual structures (ex: accounts, product categories)
UML Class Diagram - Associations
Depict business relationships between two classes
Sometimes have verb phrases to further clarify relationships
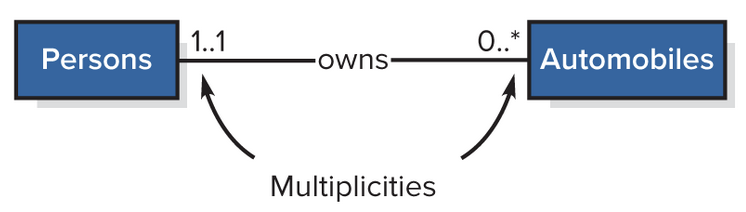
UML Class Diagram - Multiplicities
Minimum and maximum amount of times classes can be associated with each other
Attributes
Columns in a table
Data elements that describe the characteristics of instances in a class
Ex: entity is customers, attributes are customer ID, name, address, etc.
Primary Key
One or multiple attributes that uniquely identify each instant in a class/row
NEVER null
Foreign Keys
Allows tables to be linked to eachother
Shows associations between tables
Other UML Relationship Notation
Generalization
Aggregation
Composition
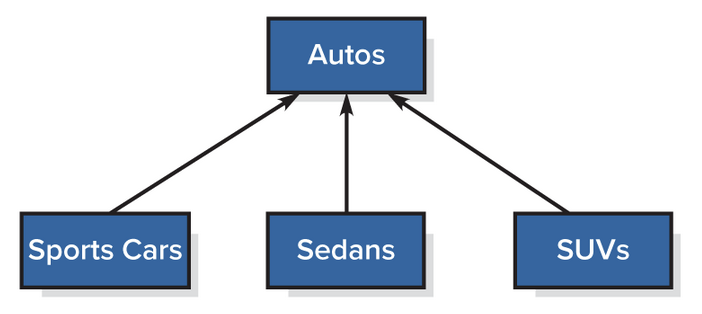
Other UML Relationship Notation - Generalization
Allows for grouping of things that have common characteristics
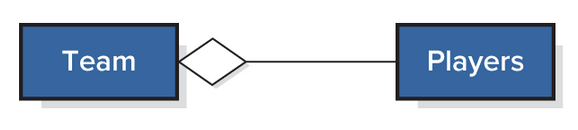
Other UML Relationship Notation - Aggregation
Describe classes that are connected but can exist outside of each other
Ex: Players and Teams, players are on a team but can exist without each other
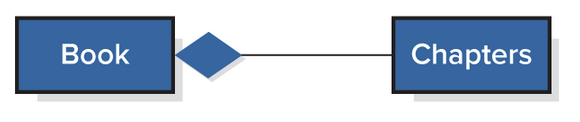
Other UML Relationship Notation - Composition
Describe classes that are connected but cannot exist outside of each other
Ex: Books and chapters, chapter cannot exist separately from books
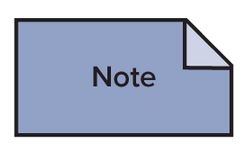
Other Notations: Notes
Allows modeler to add explanations or describe constraints
Can be attached to class with dash lined
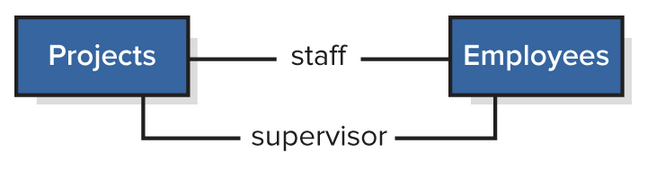
Other Notations: Role Designation
Helps when association depends on specific role that object in class has
Ex: The association between employees and project depend on type of employee
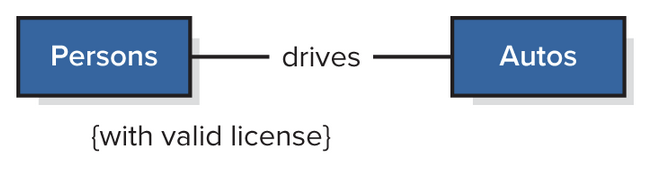
Other Notations: Constraints
Modeled w/ notes or placed near the constrained end of an association
Many-to-Many Associations
0..* and 0..*
0..* and 1..*
1..* and 0..*
1..* and 1..*
Implementing a Database from a Class Diagram
Map classes to tables
Map classes attributes to assign PK
Map associations to FK
Create new tables for many-to-many relationships
Implement relationship among table following diagram
Decision Categories
Eligibility/Approval
Validation
Calculation
Risk
Fraud
Opportunity
Assignment
Targeting
Types of Business Rules
Obligatory: what SHOULD happen
Prohibited: what should NOT happen
Allowed: What is allowed under certain conditions