Biology 20 AP: Unit E - Respiratory System
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
40 Terms
Why do we need to breathe?
Need oxygen for cellular respiration (energy for cellular metabolism)
Carbon dioxide is a by product of cellular respiration and is not used (waste)
Take in oxygen and release carbon dioxide to environment
What are the 2 main requirements?
large surface area: maximal oxygen and carbon dioxide exchange
moist environment: dissolves oxygen and carbon dioxide
Stages in respiration
Breathing: inspiration (inhaling) and expiration (exhaling)
External respiration: exchange of gases between air and blood (alveoli and capillaries - both have very thin walls)
Internal respiration: exchange of gases between blood and body tissues
Cellular respiration: energy releasing chemical reactions that take place within the cell
Nostrils
entry point for incoming air
external nasal opening
Nasal passage
warms, moistens, and cleans incoming air
lined with ciliated cells and cells that secrete mucous
Pharynx (throat)
passageway for air into respiratory system & food and water into digestive system
located behind mouth
connects mouth & nasal cavity to the larynx and esophagus
Glottis
allows passage of air to lower respiratory tract
opening from pharynx to the trachea
Larynx
holds the vocal chords (vibrate to make sound)
voice box
made form cartilage
Trachea
passageway for air moving to the bronchi
wind pipe
strengthened by semicircular cartilaginous arches
Lung
principal organ of respiration
deep within the body
protected by bone and muscle of chest cavity
Bronchi
cleans foreign particles out of incoming air
smaller branches off of the trachea
cartilage (“c”) rings to provide support
lined with cilia and mucous-producing cells
Bronchioles
cleans foreign particles out of incoming air
small and fibre tubes that branch off of the bronchi
lined with cilia and mucous-producing cells
end with alveoli
Alveoli
tiny sacs enclosed by a membrane (alveolar wall)
surrounded by a network of capillaries
site of actual gas exchange between blood in capillaries and air in alveoli
blood leaving the lungs has a high oxygen content
Pleural membrane
enables lungs to expand and contract with chest movement
double-layered membrane
outer layer attaches to the inside of the chest wall and inner layer attaches to lung
Diaphragm
contraction contributes to inhalation by increasing volume of thoracic cavity
muscle layer
separates the region of the lungs (thoracic cavity) from the region of the stomach and liver (abdominal cavity in mammals)
controls air pressure
Rib cage
protects the lungs
structure is made of bone and muscle
Rib muscles
intercostal muscles
found between ribs and ventral side of ribs
extend to diaphragm
control air pressure along with diaphragm
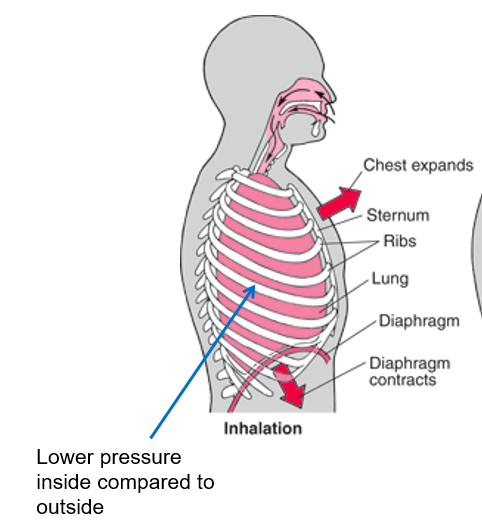
Mechanics of inhalation
external rib muscles and diaphragm contract
rib cage up and outward
diaphragm downward
volume in thoracic cavity INCREASES
air pressure in lungs DECREASES
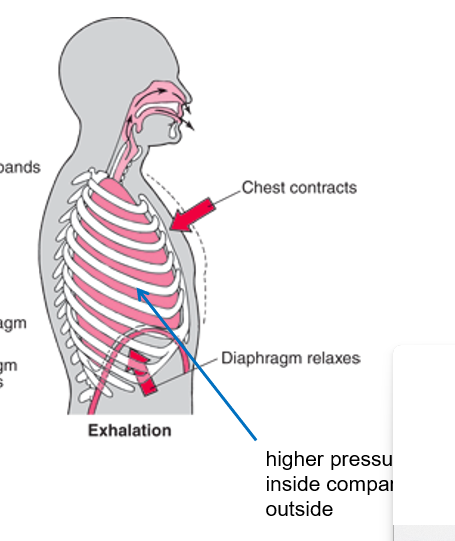
Mechanics of exhalation
diaphragm and rib muscles relax
rib cage down and inward
diaphragm up
volume in thoracic cavity DECREASES
air pressure in lungs INCREASES
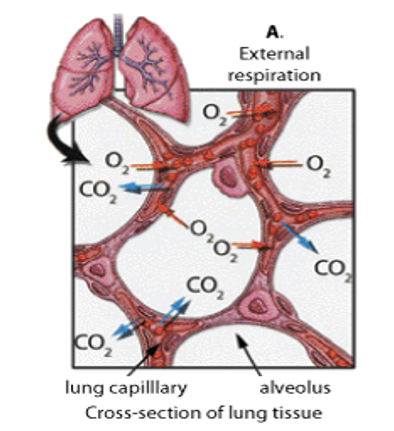
External respiration (in-depth)
between alveoli + capillaries
O2 from air in alveoli enter capillaries
CO2 diffuses out of blood into alveoli
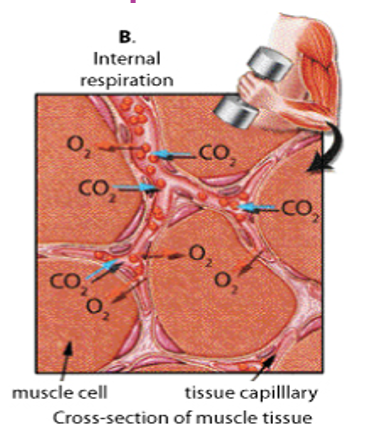
Internal respiration (in-depth)
between capillaries + body tissues
O2 diffuses from blood into O2 poor tissues
CO2 diffuses from tissues into blood
Diffusion (external respiration)
higher concentration of oxygen in air coming in moves to lower concentration in of oxygen in capillaries
Facilitated diffusion (external respiration)
~30% of oxygen is transferred by channel proteins embedded in alveoli cell membranes
with concentration gradient
Oxygen transport
hemoglobin increases oxygen carrying capacity of blood by about 70x
oxygen diffuses into the blood plasma and forms a weak bond with hemoglobin to make oxyhemoglobin
only 1% of O2 molecules dissolve directly in the plasma
Carbon dioxide transport
7% of CO2 is carried in the blood plasma
23% of CO2 is transported by hemoglobin in the form of carbaminohemoglobin
70% combines with plasma water to form carbonic acid
carbonic anhydrase: enzyme that helps the dissociation and reformation of carbonic acid
Breathing
need to breath to keep concentration of CO2 in alveoli low
not breathing = CO2 concentration increases in alveoli
chemoreceptors in brain detect changes in carbon dioxide and oxygen levels
main regulator in air breathers = CO2
Pneumothorax
medical term for lungs collapsing
air collects b/w the pleura membrane due to an injury
pressure outside of the lungs causes them to collapse
physicians insert a tube into the chest to withdraw the air that has entered the pleura (allows the lung to reinflate)
Tonsilitis (upper respiratory)
infection of the tonsils (in pharynx)
viral infection
tonsils may be surgically removed
tonsils help prevent bacteria and other foreign particles from entering the body
Laryngitis (upper respiratory)
inflammation of the larynx (vocal chords cannot vibrate normally)
most common cause: viral infection
allergies and overstraining the voice can also lead to this disorder
Bronchitis (lower respiratory)
bronchi become inflamed and filled with mucus (leads to coughing)
Pneumonia (lower respiratory)
alveoli become inflamed and fill with liquids
lobular or bronchial
interferes with gas exchange
body becomes starved for oxygen
Pleurisy (lower respiratory)
swelling and irritation of the pleura
pleura = membranes that surround the lungs
Emphysema (lower respiratory)
obstructive respiratory disorder
walls of alveoli break down and lose their elasticity
reduces surface area for gas exchange
causes oxygen shortages to the tissues
Cystic fibrosis (lower respiratory)
genetic condition that affects the lungs
abnormal gene that disrupts the function of cells lining the passageway of the lungs (over production of mucus)
Asthma (lower respiratory)
chronic obstructive lung disease that affects bronchi and bronchioles
breathing difficult or impossible because of reduced air flow
Carcinoma (lower respiratory)
uncontrolled and invasive growth of abnormal cells in the lungs
leading cause of cancer deaths for Canadian men and women
Carcinogenic
cancer-causing
Metastasis
spread of cancerous cells from original site to new locations where they can grow and invade new tissues
Path air follows
Nostril → nasal passage → pharynx → epiglottis → glottis → larynx → trachea → bronchi → bronchioles → alveoli → back out again
Path oxygen follows (atmosphere → hemoglobin)
Nostrils → nasal passage → pharynx → epiglottis → glottis → trachea → bronchi → bronchioles → alveoli → capillaries → RBCs → hemoglobin → oxyhemoglobin